Exogenous C2 Ceramide Suppresses Matrix Metalloproteinase Gene Expression by Inhibiting ROS Production and MAPK Signaling Pathways in PMA-Stimulated Human Astroglioma Cells
Abstract
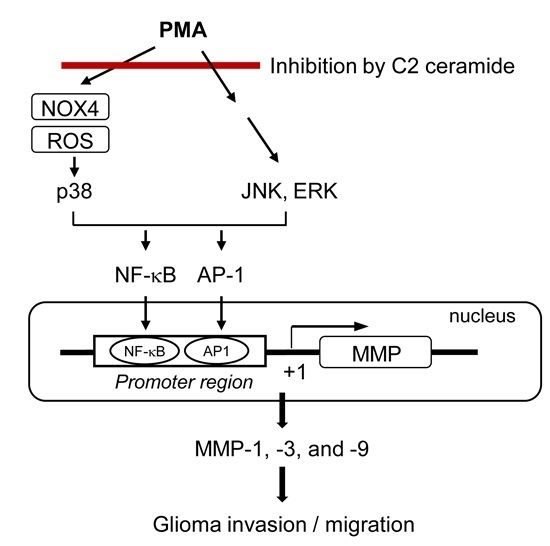
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. C2 Ceramide Suppresses the mRNA Levels and Promoter Activities of MMP-1, -3, and -9 in U87MG Glioma Cells
2.2. C2 Ceramide Inhibits the Protein Expressions of MMP-1, -3, and -9 in U87MG Glioma Cells
2.3. C2 Ceramide Inhibits the in Vitro Invasion and Migration of U87MG Glioma Cells
2.4. C2 Ceramide Inhibits DNA Binding and Promotor Activities of NF-κB and AP-1, Which Are Important Transcription Factors for MMP Gene Expression
2.5. C2 Ceramide Suppresses Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Phosphorylation and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production in PMA-Treated U87MG Glioma Cells
2.6. Treatment of ROS Inhibitor Mimicked the Effects of C2 Ceramide on MMP Gene Expression and NF-κB/AP-1 via Inhibition of p38 MAPK
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Transient Transfection Assays
4.3. RT-PCR
4.4. Zymography and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.5. Matrigel Invasion Assay
4.6. Wound Healing Assay
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
4.9. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP | activator protein |
| DCF | dichlorodihydrofluorescein |
| DMEM | Dulbecco/Vogt modified Eagle’s minimal essential medium |
| DPI | diphenylene iodonium |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| ELISA | enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| EMSA | electrophoretic mobility shift assay |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| PMA | phorbol myristate acetate |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
References
- Nagase, H.; Visse, R.; Murphy, G. Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 69, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, V.W.; Krekoski, C.A.; Forsyth, P.A.; Bell, R.; Edwards, D.R. Matrix metalloproteinases and diseases of the CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1998, 21, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Li, M.; Luo, T.; Yin, Y.; Jiang, Y. Matrix metalloproteinases in tumorigenesis: An evolving paradigm. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 3853–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Kurozumi, K.; Date, I. Angiogenesis and invasion in glioma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2011, 28, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, J.S. Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: The role of proteases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Tsai, L.L.; Tsai, J.P.; Hsieh, S.C.; Yang, S.F.; Hsueh, J.T.; Hsieh, Y.H. Licochalcone A inhibits the migration and invasion of human lung cancer cells via inactivation of the Akt signaling pathway with downregulation of MMP-1/-3 expression. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 12139–12149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercapide, J.; Lopez De Cicco, R.; Castresana, J.S.; Klein-Szanto, A.J. Stromelysin-1/matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) expression accounts for invasive properties of human astrocytoma cell line. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, R.; Go, Y.; Kyritisis, A.P.; Uhm, J.; Venkaiah, B.; Mohanam, S.; Gokaslan, Z.L.; Rao, J.S. Elevated levels of Mr 92,000 type IV collagenase during tumor growth in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 251, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saddoughi, S.A.; Ogretmen, B. Diverse functions of ceramide in cancer cell death and proliferation. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 117, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galadari, S.; Rahman, A.; Pallichankandy, S.; Thayyullathil, F. Tumor suppressive functions of ceramide: Evidence and mechanisms. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 689–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dany, M.; Ogretmen, B. Ceramide induced mitophagy and tumor suppression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 2834–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, D.; Lucks, J.; Fuchs, S.; Schiffmann, S.; Schreiber, Y.; Ferreirós, N.; Merkens, J.; Marschalek, R.; Geisslinger, G.; Grösch, S. Long chain ceramides and very long chain ceramides have opposite effects on human breast and colon cancer cell growth. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H. C2-ceramide induces cell death and protective autophagy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 3336–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.S.; Yu, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.M.; Sun, G.; Zhu, J.; Xu, J.; Guo, J.; Fu, L.S. The short chain cell-permeable ceramide (C6) restores cell apoptosis and perifosine sensitivity in cultured glioblastoma cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 5645–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debret, R.; Brassart-Pasco, S.; Lorin, J.; Martoriati, A.; Deshorgue, A.; Maquart, F.X.; Hornebeck, W.; Rahman, I.; Antonicelli, F. Ceramide inhibition of MMP-2 expression and human cancer bronchial cell invasiveness involve decreased histone acetylation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Hyun, J.W.; Min, S.W.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.S. Glycitein inhibits glioma cell invasion through down-regulation of MMP-3 and MMP-9 gene expression. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 15, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Joh, T.H. Matrix metalloproteinases, new insights into the understanding of neurodegenerative disorders. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2012, 20, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Curcumin is a potent broad spectrum inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in human astroglioma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 337, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.K.; Melendez, J.A. Mitochondrial redox control of matrix metalloproteinases. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 37, 768–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatrowski, T.P.; Nathan, C.F. Production of large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumour cells. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Yang, L.Y.; Shen, S.C.; Chen, Y.C. IGF-I plus E2 induces proliferation via activation of ROS-dependent ERKs and JNKs in human breast carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 212, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.S. The signaling mechanism of ROS in tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, M. Reactive oxygen species in tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2008, 266, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkhiri, A.; Richards, C.; Whaley, M.; McQueen, S.A.; Orr, F.W. Incresed expression of activated matrix metalloproteinase-2 by human endothelial cells after subethal H2O2 exposure. Lab. Investig. 1997, 77, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.K.; Subbaram, S.; Connor, K.M.; Dasgupta, J.; Ha, X.F.; Meng, T.C.; Tonks, N.K.; Melendez, J.A. Redox-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression is regulated by JNK through Ets and AP-1 promoter motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 14100–14110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, Z.; Hu, X. Inhibiting cancer metastasis via targeting NADPH oxidase 4. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushio-Fukai, M. Localizing NADPH oxidase-derived ROS. Sci. STKE 2006, 349, re8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambeth, J.D. NOX enzymes and the biology of reactive oxygen. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babior, B.M. NADPH oxidase: An update. Blood 1999, 93, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Cao, Z.; Xu, Z.; van Meir, E.G.; Lambeth, J.D. Homologs of gp91phox: Cloning and tissue expression of Nox3, Nox4, and Nox5. Gene 2001, 269, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shono, T.; Yokoyama, N.; Uesaka, T.; Kuroda, J.; Takeya, R.; Yamasaki, T.; Amano, T.; Mizoguchi, M.; Suzuki, S.O.; Niiro, H.; et al. Enhanced expression of NADPH oxidase Nox4 in human gliomas and its roles in cell proliferation and survival. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Shyu, W.C.; Chiang, C.Y.; Kuo, J.W.; Shen, W.C.; Liu, R.S. NADPH oxidase subunit 4-mediated reactive oxygen species contribute to cycling hypoxia-promoted tumor progression in glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Chang, H.T.; Shen, W.C.; Shyu, W.C.; Liu, R.S. Imaging the impact of Nox4 in cycling hypoxia-mediated U87 glioblastoma invasion and infiltration. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2012, 14, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.H.; Woo, M.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, W.K.; Hyun, J.W.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.S. Ginseng saponin metabolite suppresses phorbol ester-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression through inhibition of activator protein-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in human astroglioma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, M.S.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Hyun, J.W.; Ko, K.H.; Kim, W.K.; Kim, H.S. Curcumin suppresses phorbol ester-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9expression by inhibiting the PKC to MAPK signaling pathways in human astroglioma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Le, T.K.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.S. Protopanaxatriol ginsenoside Rh1 inhibits the expression of matrix metalloproteinases and the in vitro invasion/migration of human astroglioma cells. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Gene | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer (5′→3′) | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| MMP-1 | ATATCGGGGCTTTGATGTACC | AGCTGTAGATGTCCTTGGGGT | 408 bp |
| MMP-2 | GAAGTATGGGAACGCCGATGG | TTGTCGCGGTCGTAGTCCTCA | 311 bp |
| MMP-3 | GATATAAATGGCATTCAGTCCCTC | TCCTTGCTAGTAACTTCATATGCG | 287 bp |
| MMP-9 | ATGT ACCCTATGTACCGCTTCACT | CAGAGAAGAAGAAAAGCTTCTTGG | 496 bp |
| GAPDH | GGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTGGCCG | GGTTCACACCCATCACAAACATGG | 395 bp |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, J.-S.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Moon, B.-I.; Kim, H.-S. Exogenous C2 Ceramide Suppresses Matrix Metalloproteinase Gene Expression by Inhibiting ROS Production and MAPK Signaling Pathways in PMA-Stimulated Human Astroglioma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040477
Jung J-S, Ahn Y-H, Moon B-I, Kim H-S. Exogenous C2 Ceramide Suppresses Matrix Metalloproteinase Gene Expression by Inhibiting ROS Production and MAPK Signaling Pathways in PMA-Stimulated Human Astroglioma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(4):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040477
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Ji-Sun, Young-Ho Ahn, Byung-In Moon, and Hee-Sun Kim. 2016. "Exogenous C2 Ceramide Suppresses Matrix Metalloproteinase Gene Expression by Inhibiting ROS Production and MAPK Signaling Pathways in PMA-Stimulated Human Astroglioma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040477
APA StyleJung, J.-S., Ahn, Y.-H., Moon, B.-I., & Kim, H.-S. (2016). Exogenous C2 Ceramide Suppresses Matrix Metalloproteinase Gene Expression by Inhibiting ROS Production and MAPK Signaling Pathways in PMA-Stimulated Human Astroglioma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040477