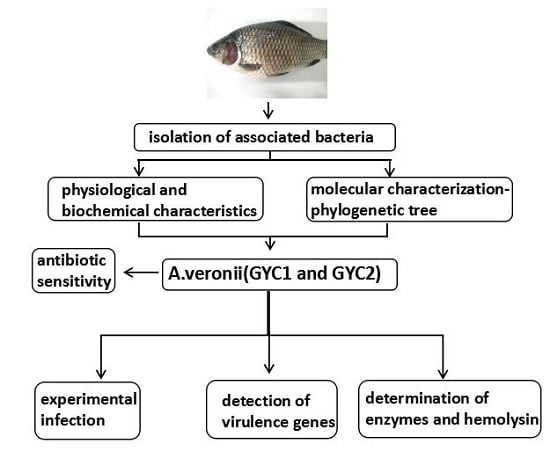
Characterization of Virulence Properties of Aeromonas veronii Isolated from Diseased Gibel Carp (Carassius gibelio)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Diseased Fish and Gross Examination
2.2. Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics
2.3. Molecular Characterization
2.4. Experimental Infection
2.5. Determination of Extracellular Enzymes and Hemolysin Activities
2.6. Detection of Virulence Genes
2.7. Antibiotic Sensitivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Diseased Fish and Gross Examination
4.2. Isolation of the Associated Bacteria
4.3. Identification of the Isolates
4.3.1. Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics
4.3.2. Molecular Characterization
4.3.3. Nucleotide Accession Numbers
4.4. Evaluation the Virulence of Isolates
4.4.1. Experimental Infection
4.4.2. Determination of Extracellular Enzymes and Hemolysin Activities
4.4.3. Detection of Virulence Genes
4.5. Antibiotic Sensitivity
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wahli, T.; Burr, S.E.; Pugovkin, D.; Mueller, O.; Frey, J. Aeromonas Sobria, a causative agent of disease in farmed perch, Perca Fluviatilis L. J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, S.; Philip, R.; Singh, I.S. Characterization and virulence potential of phenotypically diverse Aeromonas veronii isolates recovered from moribund freshwater ornamental fishes of Kerala, India. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2013, 103, 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. The genus Aeromonas: Taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, A.C.; Williams, D.; Faucher, J.; Horneman, A.J.; Gogarten, P.; Graf, J. Complex evolutionary history of the Aeromonas veronii group revealed by host interaction and DNA sequence data. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Navarro, C.P.; Kuhn, I.; Huys, G.; Swings, J.; Mollby, R. Identification and characterization of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria associated with epizootic ulcerative syndrome in fish in Bangladesh. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2002, 68, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.M.; Mittge, E.; Kuhlman, J.; Baden, K.N.; Cheesman, S.E. Distinct signals from the microbiota promote different aspects of zebrafish gut differentiation. Dev. Biol. 2006, 297, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, J.; Kikuchi, Y.; Rio, R.V. Leeches and their microbiota: Naturally simple symbiosis models. Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M. Isolation of pathogenic bacteria from the skin ulcerous symptomatic gourami (Colisa lalia) through 16S rDNA analysis. Univ. J. Zool. Rajshahi Univ. 2008, 27, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Yang, H.; Li, T.; Luo, L.; Gao, J. Isolation and identification of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii isolated from infected Siberian sturgeon (Acipenser baerii). J. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Von Gravenitz, A. The role of Aeromonas in diarrhea: A review. Infection 2007, 35, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ni, X.D.; Liu, Y.J.; Lu, C.P. Detection of three virulence genes alt, ahp and aerA in Aeromonas hydrophila and their relationship with actual virulence to zebrafish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 110, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.W.; You, M.J.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, C.S.; Kwon, J.K.; Shin, G.W. Molecular characterization of Aeromonas species isolated from farmed eels (Anguilla Japonica). Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, L.A.; Ellis, A.E.; Nieto, T.P. Purification and characterization of an extracellular metalloprotease, serine protease and haemolysin of Aeromonas hydrophila strain B32: All are lethal for fish. Microb. Pathog. 1992, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaco´n, M.R.; Figueras, M.J.; Castro-Escarpulli, G.; Soler, L.; Guarro, J. Distribution of virulence genes in clinical and environmental isolates of Aeromonas spp. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2003, 84, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, K.; Rodgers, M. Distribution of six virulence factors in Aeromonas species isolated from U.S. drinking water utilities: A PCR identification. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera-Arreola, M.G.; Hernández-Rodríguez, C.; Zúñiga, G.; Figueras, M.J.; Castro-Escarpulli, G. Aeromonas hydrophila clinical and environmental ecotypes as revealed by genetic diversity and virulence genes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 242, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, D.J.; Krieg, N.R.; Staley, J.T. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 546–551. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.J.; Qin, G.M.; Bing, X.W.; Yan, B.L.; Liang, L.G. Molecular and phenotypic characterization of Vibrio aestuarianus, a pathogen of the cultured tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis Gunther. J. Fish. Dis. 2011, 34, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun-Ja, H.; Tatsuo, T.; Hidehiro, K.; Ikuo, H.; Takashi, A. Pathogenic potential of a collagenase gene from Aeromonas veronii. Can. J. Microbiol. 2008, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Marel, M.; Schroers, V.; Neuhaus, H.; Steinhagen, D. Chemotaxis towards, adhesion to, and growth in carp gut mucus of two Aeromonas hydrophila strains with different pathogenicity for common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yánez, M.A.; Catalán, V.; Apráiz, D.; Figueras, M.J.; Martínez-Murcia, A.J. Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Aeromonas based on gyrB gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, A.; Mano, N.; Takano, H.; Beppu, T.; Ueda, K.; Hirose, K. OmpA is an adhesion factor of Aeromonas veronii, an optimistic pathogen that habituates in carp intestinal tract. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105, 1441–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.S.; Zhao, N.; Amer, S.; Qian, M.M.; Lv, M.X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Su, X.; Cao, J.; He, H.X.; Zhao, B.H. Protective efficacy of PLGA microspheres loaded with divalent DNA vaccine encoding the ompA gene of Aeromonas veronii and the hly gene of Aeromonas hydrophila in mice. Vaccine 2013, 31, 5754–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavin, R.; Rabaan, A.A.; Merino, S.; Tomas, J.M.; Gryllos, I.; Shaw, J.G. Lateral flagella of Aeromonas species are essential for epithelial cell adherence and biofilm formation. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 43, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirov, S.M.; Castrisios, M.; Shaw, J.G. Aeromonas flagella (polar and lateral) are enterocyte adhesins that contribute to biofilm formation on surfaces. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawaz, M.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, A.A.; Sung, K.; Tran, Q.; Kerdahi, K.; Steele, R. Detection and characterization of virulence genes and integrons in Aeromonas veronii isolated from catfish. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Cantas, L.; Shah, S.Q.; Cavaco, L.M.; Manaia, C.M.; Walsh, F.; Popowska, M.; Garelick, H.; Bürgmann, H.; Sørum, H. A brief multidisciplinary review on antimicrobial resistance in medicine and its linkage to the global environmental microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kemper, N. Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polz, M.F.; Cavanaugh, C.M. Bias is template to product ratios in multitemplate PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbial. 1998, 64, 3724–3730. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, S.; Harayama, S. PCR amplification and direct sequencing of gyrB genes with universal primers and their application to the detection and taxonomic analysis of Pseudomonas putida strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.S.; Fang, H. Human and Animal Pathogenic Bacteriology; Hebei Science and Technology Press: Shijiazhuan, China, 2003; pp. 1550–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. Comparative Study between Biological Characteristics of the Different Animal Species Aeromonas veronii and Four Virulence Genes. Master’s Thesis, Agricultural University, Jilin, China, April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, S.; Gavin, R.; Vilches, S.; Shaw, J.G.; Tomas, J.M. A colonization factor (production of lateral flagella) of mesophilic Aeromonas spp. is inactive in Aeromonas salmonicida strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Lu, C.P.; Yao, H.C. Cloning, sequence analysis and detection of an extracellular temperaturelabile protease encoding gene (eprJ) from Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Fish Sci. China 2006, 6, 924–927. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.Y.F.; Heuzenroeder, M.W.; Flower, R.L.P. Inactivation of two haemolytic toxin genes in Aeromonas hydrophila attenuates virulence in a suckling mouse model. Microbiology UK 1998, 144, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igbinosa, I.H.; Chigor, V.N.; Igbinosa, E.O.; Obi, L.C.; Okoh, A.I. Antibiogram, adhesive characteristics, and incidence of class 1 integron in Aeromonas species isolated from two South African rivers. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Items | Isolates | A. veronii | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GYC1 | GYC2 | ||
| Arabitol | − | − | − |
| Mannose | + | + | + |
| Maltose | + | + | + |
| H2S production | − | − | − |
| Tartrate utilization | − | − | − |
| V–P test | + | + | + |
| Xylose | − | − | − |
| Mannitol | + | + | + |
| Sucrose | + | + | + |
| Galactosidase | + | + | [+] |
| Aesculin | + | + | + |
| Dulcitol | − | − | − |
| Lactose | − | − | − |
| Inositol | − | − | − |
| Mushroom sugar | + | + | + |
| Nitrate reduction | + | + | + |
| Acetate | − | − | [+] |
| α-methyl-d-glucoside | − | − | [+] |
| Galactose | + | + | + |
| Sorbitol | − | − | − |
| O–F test | F | F | F |
| Erythrite | − | − | − |
| l-Rhamnose | − | − | − |
| Isolates | Caseinase | Esterase | Amylase | Lecithinase | Hemolysin | Gelatinase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GYC1 | + | + | + | + | β-hemolysis | − |
| GYC2 | + | + | + | + | β-hemolysis | − |
| Groups | Chemicals | Disc Content (μg) | Mean Inhibition Zone Diameter (mm) | Sensitivity a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GYC1 | GYC2 | GYC1 | GYC2 | |||
| Penicillins | Oxacillin | 1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | R | R |
| Piperacillin | 100 | 26.0 | 0.0 | S | R | |
| Penicillin G | 10 | 15.0 | 0.0 | R | R | |
| Ampicillin | 10 | 13.0 | 0.0 | I | R | |
| Cephalosporins | Cephradine | 30 | 25.0 | 24.0 | S | S |
| Cefoperazone | 75 | 26.0 | 22.0 | S | S | |
| Cefalotin | 30 | 20.0 | 0.0 | S | R | |
| Cefotaxime | 30 | 27.0 | 25.0 | S | S | |
| Cefuroxime | 30 | 25.0 | 24.0 | S | S | |
| Cefoxitin | 30 | 20.0 | 20.0 | S | S | |
| Cefepime | 30 | 26.0 | 25.0 | S | S | |
| Cefazolin | 30 | 14.0 | 14.0 | R | R | |
| Macrolides | Midecamycin | 30 | 16.0 | 14.0 | I | I |
| Clarithromycin | 15 | 25.0 | 20.0 | S | S | |
| Erythromycin | 15 | 27.0 | 20.0 | S | I | |
| Quinolones | Levofloxacin | 5 | 0.0 | 11.0 | R | R |
| Ofloxacin | 5 | 9.0 | 10.0 | R | R | |
| Ciprofloxacin | 5 | 9.0 | 0.0 | R | R | |
| Norfloxacin | 10 | 0.0 | 10.0 | R | R | |
| Aminoglycosides | Gentamycin | 10 | 19.0 | 16.0 | S | S |
| Tobramycin | 10 | 18.0 | 20.0 | S | S | |
| Streptomycin | 10 | 22.0 | 15.0 | S | S | |
| Streptomycin | 30 | 20.0 | 18.0 | S | S | |
| Amikacin | 30 | 19.0 | 16.5 | S | I | |
| Spectinomycin | 100 | 27.0 | 0.0 | S | R | |
| Lincomycins | Clindamycin | 2 | 15.0 | 12.5 | I | R |
| Amphenicols | Chloramphenicol | 30 | 22.0 | 22.0 | S | S |
| Polymyxin | Polymyxin B | 300 | 14.0 | 0.0 | S | R |
| Nitrofuran | Macrodantin | 300 | 18.0 | 16.0 | S | I |
| Aztreonam | Aztreonam | 30 | 26.0 | 10.0 | S | R |
| Glycopeptides | Vancomycin | 30 | 11.0 | 10.0 | R | R |
| Target Gene | Product Size (bp) | PCR Primers Sequence (5′-3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| ompAI | 1026 | F: GACGATATCATGATGAAAATGGCTCTT | Wang Hui [32] |
| R: GCGAAGCTTTTACTTCTGAACTTCTTG | |||
| ompAII | 1001 | F: GCTGAATTCATGAAACTCAAAATGGCTC | Wang Hui [32] |
| R: GCGAAGCTTTTACTGTTGTACTTGC | |||
| lafA | 550 | F: GGTCTGCGCATCCAACTC | Merino et al. [33] |
| R: GCTCCAGACGGTTGATG | |||
| act | 232 | F: AGAAGGTGACCACCACCAAGAACA | Mohamed et al. [26] |
| R: AACTGACATCGGCCTTGAACTC | |||
| aer | 431 | F: CCTATGGCCTGAGCGAGAAG | Mohamed et al. [26] |
| R: CCAGTTCCAGTCCCACCACT | |||
| fla | 608 | F: TCCAACCGTYTGACCTC | Mohamed et al. [26] |
| R: GMYTGGTTGCGRATGGT | |||
| gcaT | 237 | F: CTCCTGGAATCCCAAGTATCAG | Mohamed et al. [26] |
| R: GGCAGGTTGAACAGCAGTATCT | |||
| acg | 761 | F: AACAAGCACCCGTTAAGCCAC | Han et al. [19] |
| R: ACGTAGTCGAGCCCCTTGAGG | |||
| eprCAI | 387 | F: GCTCGACGCCCAGCTCACC | Ren et al. [34] |
| R: GGCTCACCGCATTGGATTCG | |||
| ela | 513 | F: ACACGGTCAAGGAGATCAAC | Sen and Rodgers [15] |
| R: CGCTGGTGTTGGCCAGCAGG | |||
| hly | 597 | F: GGCCGGTGGCCCGAAGATACGGG | Wong et al. [35] |
| R: GGCGGCGCCGGACGAGACGGG | |||
| ahp | 911 | F: ATTGGATCCCTGCCTA | Li et al. [11] |
| R: GCTAAGCTTGCATCCG | |||
| lip | 382 | F: ATCTTCTCCGACTGGTTCGG | Sen and Rodgers [15] |
| R: CCGTGCCAGGACTGGGTCTT | |||
| ast | 331 | F: TCTCCATGCTTCCCTTCCACT | Mohamed et al. [26] |
| R: GTGTAGGGATTGAAGAAGCCG | |||
| alt | 442 | F: TGACCCAGTCCTGGCACGGC | Yang and Fang [31] |
| R: GGTGATCGATCACCACCAGC | |||
| exu | 323 | F: AGACATG CACAACCTCTTCC | Yang and Fang [31] |
| R: GATTGGTATTGCCTTGCAAG |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Wen, Y.; Lin, L. Characterization of Virulence Properties of Aeromonas veronii Isolated from Diseased Gibel Carp (Carassius gibelio). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040496
Sun J, Zhang X, Gao X, Jiang Q, Wen Y, Lin L. Characterization of Virulence Properties of Aeromonas veronii Isolated from Diseased Gibel Carp (Carassius gibelio). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(4):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040496
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jingjing, Xiaojun Zhang, Xiaojian Gao, Qun Jiang, Yi Wen, and Li Lin. 2016. "Characterization of Virulence Properties of Aeromonas veronii Isolated from Diseased Gibel Carp (Carassius gibelio)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040496
APA StyleSun, J., Zhang, X., Gao, X., Jiang, Q., Wen, Y., & Lin, L. (2016). Characterization of Virulence Properties of Aeromonas veronii Isolated from Diseased Gibel Carp (Carassius gibelio). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040496