All-Trans Retinoic Acid Modulates DNA Damage Response and the Expression of the VEGF-A and MKI67 Genes in ARPE-19 Cells Subjected to Oxidative Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. All-Trans Retinoic Acid (ATRA) Increases the Level of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress-Induced DNA Damage
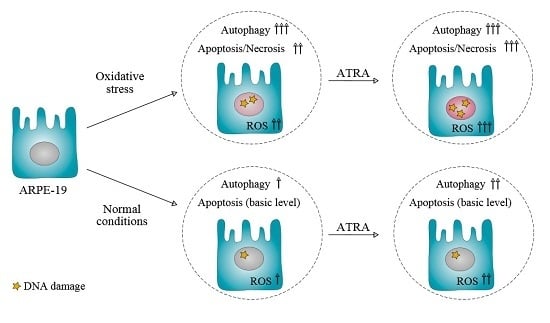
2.2. ATRA Potentiates Cell Death Induced by Oxidative Stress
2.3. ATRA Does Not Change DNA Repair
2.4. ATRA Induces Autophagy in Normal Conditions and Does Not Influence this Process in Oxidative Stress
2.5. ATRA Does Not Influence Cell Cycle Regulation in Oxidative Stress
2.6. ATRA Increases the Expression of VEGF-A and MKI67
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell lines, Viability, and Treatment
4.2. Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species
4.3. DNA Damage—The Comet Assay
4.4. DNA Damage—Phosphorylation of H2AX and ATM
4.5. DNA Repair
4.6. Cell Death
4.7. Autophagy
4.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.9. Gene Expression
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATRA | All-trans retinoic acid |
| AMD | Age-related macular degeneration |
| DSB | DNA double-strand break |
| DCF | Dichlorofluorescein |
| DDR | DNA damage response |
| FACS | Fluorescence activated cell sorting |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| RPE | Retinal pigment epithelium |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SSB | DNA single-strand break |
| tBH | Tert-butyl hydroperoxide |
References
- Ambati, J.; Atkinson, J.P.; Gelfand, B.D. Immunology of age-related macular degeneration. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambati, J.; Anand, A.; Fernandez, S.; Sakurai, E.; Lynn, B.C.; Kuziel, W.A.; Rollins, B.J.; Ambati, B.K. An animal model of age-related macular degeneration in senescent Ccl-2- or Ccr-2-deficient mice. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.Y.; Cringle, S.J. Oxygen distribution and consumption within the retina in vascularised and avascular retinas and in animal models of retinal disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2001, 20, 175–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, P.N.; Sheibani, N.; Albert, D.M. Retinal light toxicity. Eye (London) 2011, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.J.; Morgan, J.I.; Merigan, W.H.; Sliney, D.H.; Sparrow, J.R.; Williams, D.R. The susceptibility of the retina to photochemical damage from visible light. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2012, 31, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, M.V.; Liles, M.R.; Newsome, D.A. Evaluation of oxidative processes in human pigment epithelial cells associated with retinal outer segment phagocytosis. Exp. Cell Res. 1994, 214, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, K.; Szaflik, J.P.; Zaras, M.; Sklodowska, A.; Janik-Papis, K.; Poplawski, T.R.; Blasiak, J.; Szaflik, J. DNA damage/repair and polymorphism of the hOGG1 gene in lymphocytes of AMD patients. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 827562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, P.S.; Ahmed, F.; Liu, A.; Allman, S.; Sheng, X.; Sharifzadeh, M.; Ermakov, I.; Gellermann, W. Macular pigment imaging in AREDS2 participants: An ancillary study of AREDS2 subjects enrolled at the Moran Eye Center. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 6178–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, Z.; Ucgun, N.I.; Yildirim, F. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2011, 66, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szaflik, J.P.; Janik-Papis, K.; Synowiec, E.; Ksiazek, D.; Zaras, M.; Wozniak, K.; Szaflik, J.; Blasiak, J. DNA damage and repair in age-related macular degeneration. Mutat. Res. 2009, 669, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunaief, J.L.; Dentchev, T.; Ying, G.S.; Milam, A.H. The role of apoptosis in age-related macular degeneration. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiser, P.; Golczak, M.; Palczewski, K. Chemistry of the retinoid (visual) cycle. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 194–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, R.A.; Yuan, Q.; Hu, J.; Peng, J.H.; Lloyd, M.; Nusinowitz, S.; Bok, D.; Travis, G.H. Accelerated accumulation of lipofuscin pigments in the RPE of a mouse model for ABCA4-mediated retinal dystrophies following vitamin a supplementation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3821–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, P.; Kong, J.; Kim, S.R.; Sparrow, J.R.; Allikmets, R.; Rando, R.R. Small molecule RPE65 antagonists limit the visual cycle and prevent lipofuscin formation. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, N.L.; Lichter, J.B.; Vogel, R.; Han, Y.; Bui, T.V.; Singerman, L.J. Investigation of oral fenretinide for treatment of geographic atrophy in age-related macular degeneration. Retina 2013, 33, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.S.; Park, S.H.; Jang, K.L. All-trans retinoic acid induces cellular senescence by up-regulating levels of p16 and p21 via promoter hypomethylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 412, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, N.D.; Sun, Y.; Price, B.D. Activation of the kinase activity of ATM by retinoic acid is required for CREB-dependent differentiation of neuroblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16577–16584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrass, P.; Rendl, M.; Mildner, M.; Gruber, F.; Lengauer, B.; Ballaun, C.; Eckhart, L.; Tschachler, E. Retinoic acid increases the expression of p53 and proapoptotic caspases and sensitizes keratinocytes to apoptosis: A possible explanation for tumor preventive action of retinoids. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6542–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Kao, Y.H.; Hu, D.N.; Tsai, L.Y.; Wu, W.C. All-trans retinoic acid remodels extracellular matrix and suppresses laminin-enhanced contractility of cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 88, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, J.W.; Dowgiert, R.K.; Buzney, S.M. Factors modulating the effect of retinoids on cultured retinal pigment epithelial cell proliferation. Curr. Eye Res. 1992, 11, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, H.; Mishima, H.K.; Yamashita, U. Effects of retinoic acid and TGF-β in the proliferation and melanin synthesis in chick retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. Curr. Eye Res. 1998, 17, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacDonald, I.M.; Peters, C.; Chen, M.H. Effect of retinoic acid on wound healing of laser burns to porcine retinal pigment epithelium. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 31, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.C.; Hu, D.N.; Mehta, S.; Chang, Y.C. Effects of retinoic acid on retinal pigment epithelium from excised membranes from proliferative vitreoretinopathy. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 21, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, M.G.; Fujiki, K.; Murayama, K.; Suzuki, M.T.; Shindo, N.; Hotta, Y.; Iwata, F.; Fujimura, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Cho, F.; et al. Studies on the mechanism of early onset macular degeneration in cynomolgus monkeys. II. Suppression of metallothionein synthesis in the retina in oxidative stress. Exp. Eye Res. 1996, 62, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watabe, H.; Soma, Y.; Ito, M.; Kawa, Y.; Mizoguchi, M. All-trans retinoic acid induces differentiation and apoptosis of murine melanocyte precursors with induction of the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Satyamoorthy, K.; Herlyn, M.; Rosdahl, I. All-trans retinoic acid (atRA) differentially induces apoptosis in matched primary and metastatic melanoma cells—A speculation on damage effect of atRA via mitochondrial dysfunction and cell cycle redistribution. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alakhras, R.S.; Stephanou, G.; Demopoulos, N.A.; Grintzalis, K.; Georgiou, C.D.; Nikolaropoulos, S.S. DNA fragmentation induced by all-trans retinoic acid and its steroidal analogue EA-4 in C2C12 mouse and HL-60 human leukemic cells in vitro. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanus, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, S. Induction of necrotic cell death by oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajawat, Y.; Hilioti, Z.; Bossis, I. Retinoic acid induces autophagosome maturation through redistribution of the cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 2165–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfali, N.; O’Donovan, T.R.; Nyhan, M.J.; Britschgi, A.; Tschan, M.P.; Cahill, M.R.; Mongan, N.P.; Gudas, L.J.; McKenna, S.L. Induction of autophagy is a key component of all-trans-retinoic acid-induced differentiation in leukemia cells and a potential target for pharmacologic modulation. Exp. Hematol. 2015, 43, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, L.; Kang, R.; Yang, M.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xie, M.; Yin, X.; Livesey, K.M.; et al. Autophagy regulates myeloid cell differentiation by p62/SQSTM1-mediated degradation of PML-RARα oncoprotein. Autophagy 2011, 7, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, F.; Yuan, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q. All-trans retinoic acid upregulates the expression of p53 via axin and inhibits the proliferation of glioma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 2269–2274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.H.; Kwak, J.; Jang, K.L. All-trans retinoic acid induces p53-depenent apoptosis in human hepatocytes by activating p14 expression via promoter hypomethylation. Cancer Lett. 2015, 362, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudas, L.J.; Wagner, J.A. Retinoids regulate stem cell differentiation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonge, P.D.; Andrews, P.W. Retinoic acid directs neuronal differentiation of human pluripotent stem cell lines in a non-cell-autonomous manner. Differentiation 2010, 80, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, K.C.; Aotaki-Keen, A.E.; Putkey, F.R.; Hjelmeland, L.M. Arpe-19, a human retinal pigment epithelial cell line with differentiated properties. Exp. Eye Res. 1996, 62, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.T.; Liang, J.B.; Chou, C.L.; Shyu, R.C.; Lu, D.W. Retinoic acid induces VEGF gene expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells (ARPE-19). J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 21, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweider, N.; Fragoulis, A.; Rosen, C.; Pecks, U.; Rath, W.; Pufe, T.; Wruck, C.J. Interplay between vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2): Implications for preeclampsia. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 42863–42872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Hayes, J.D.; Henderson, C.J.; Wolf, C.R. Identification of retinoic acid as an inhibitor of transcription factor Nrf2 through activation of retinoic acid receptor alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19589–19594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.P.; Kosuge, K.; Yang, M.; Ito, S. NRF2 as a determinant of cellular resistance in retinoic acid cytotoxicity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 1663–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.P.; McCoy, M.T.; Tice, R.R.; Schneider, E.L. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 175, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaude, M.; Eriksson, S.; Nygren, J.; Ahnstrom, G. The comet assay: Mechanisms and technical considerations. Mutat. Res. 1996, 363, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, K.; Blasiak, J. In vitro genotoxicity of lead acetate: Induction of single and double DNA strand breaks and DNA-protein cross-links. Mutat. Res. 2003, 535, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, P.; Kaarniranta, K.; Blasiak, J. Inhibition of DNA methyltransferase or histone deacetylase protects retinal pigment epithelial cells from DNA damage induced by oxidative stress by the stimulation of antioxidant enzymes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 776, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpato, R.; Castagna, S.; Aliotta, R.; Azzara, A.; Ghetti, F.; Filomeni, E.; Giovannini, C.; Pirillo, C.; Testi, S.; Lombardi, S.; et al. Kinetics of nuclear phosphorylation (γ-H2AX) in human lymphocytes treated in vitro with UVB, bleomycin and mitomycin C. Mutagenesis 2013, 28, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tokarz, P.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W.; Kaarniranta, K.; Blasiak, J. All-Trans Retinoic Acid Modulates DNA Damage Response and the Expression of the VEGF-A and MKI67 Genes in ARPE-19 Cells Subjected to Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060898
Tokarz P, Piastowska-Ciesielska AW, Kaarniranta K, Blasiak J. All-Trans Retinoic Acid Modulates DNA Damage Response and the Expression of the VEGF-A and MKI67 Genes in ARPE-19 Cells Subjected to Oxidative Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(6):898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060898
Chicago/Turabian StyleTokarz, Paulina, Agnieszka Wanda Piastowska-Ciesielska, Kai Kaarniranta, and Janusz Blasiak. 2016. "All-Trans Retinoic Acid Modulates DNA Damage Response and the Expression of the VEGF-A and MKI67 Genes in ARPE-19 Cells Subjected to Oxidative Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 6: 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060898
APA StyleTokarz, P., Piastowska-Ciesielska, A. W., Kaarniranta, K., & Blasiak, J. (2016). All-Trans Retinoic Acid Modulates DNA Damage Response and the Expression of the VEGF-A and MKI67 Genes in ARPE-19 Cells Subjected to Oxidative Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(6), 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060898