Stanniocalcin-1 Protects a Mouse Model from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Affecting ROS-Mediated Multiple Signaling Pathways
Abstract
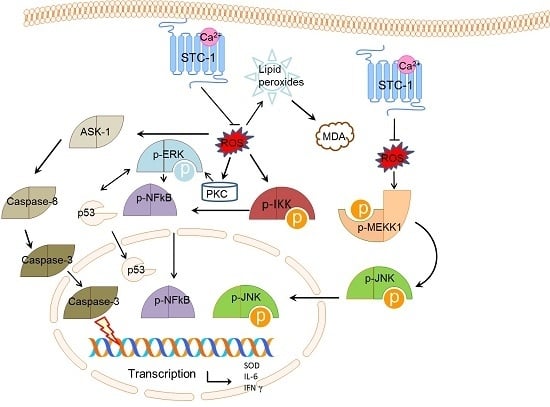
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Evaluation for Renal Dysfunction of RIRI Model
2.2. Increased Expression of STC-1 in the Kidney of Mouse Model
2.3. The Effects of STC-1 on Immunological and Biochemical Parameters
2.4. Intercellular ROS Concentration
2.5. STC-1 Affects the mRNA Levels of ROS-Mediated Molecules
2.6. STC-1 Decreased the Protein Levels of ROS-Mediated Molecules
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Establishment of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Model
4.3. Assessment of Renal Function
4.4. Biodices Index Assay
4.5. Isolation of Renal Progenitor Cells from Renal Cortex of Mouse
4.6. Assay of Intracellular ROS
4.7. Construction of Plasmids
4.8. Construction of STC-1 shRNA
4.9. Groups
4.10. qRT-PCR (Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR)
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASK-1 | apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 |
| STC-1 | stanniocalcin-1 |
| RIRI | renal ischemia-reperfusion injury |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| IFN | interferon |
| p-MEKK-1 | phosphorylated mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| NF | nuclear factor |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| IKK | IkB kinase |
References
- Jakobsson, S.; Graipe, A.; Huber, D.; Bjorklund, F.; Mooe, T. The risk of ischemic stroke after an acute myocardial infarction in patients with decreased renal function. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 37, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Li, T.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Lin, C. Polydatin inhibits mitochondrial dysfunction in the renal tubular epithelial cells of a rat model of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Anesth. Analg. 2015, 121, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benck, U.; Schnuelle, P.; Kruger, B.; Nowak, K.; Riester, T.; Mundt, H.; Lutz, N.; Jung, M.; Birck, R.; Kramer, B.K.; et al. Excellent graft and patient survival after renal transplantation from donors after brain death with acute kidney injury: A case-control study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2015, 47, 2039–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahhabaghai, H.; Heidari, R.; Zeinoddini, A.; Soleyman-Jahi, S.; Golmanesh, L.; Rasoulian, B.; Akbari, H.; Foadoddoni, M.; Esmailidehaj, M. Hyperoxia-induced preconditioning against renal ischemic injury is mediated by reactive oxygen species but not related to heat shock proteins 70 and 32. Surgery 2015, 157, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khader, A.; Yang, W.L.; Kuncewitch, M.; Prince, J.M.; Marambaud, P.; Nicastro, J.; Coppa, G.F.; Wang, P. Novel resveratrol analogues attenuate renal ischemic injury in rats. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 193, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Xing, B.Z.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Weng, X.D.; Qiu, T.; Liu, L. Ischemic postconditioning attenuates inflammation in rats following renal ischemia and reperfusion injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, M. The study of pentoxifylline drug effects on renal apoptosis and Bcl-2 gene expression changes following ischemic reperfusion injury in rat. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Lim, T.; Xu, J.; Tang, H.; Wan, Y.; Zhao, H.; Hossain, M.; Maxwell, P.H.; Maze, M. Xenon preconditioning protects against renal ischemic-reperfusion injury via HIF-1α activation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiko, Y.; Aubin, J.E.; Maeda, N. Stanniocalcin 1 (STC1) protein and mRNA are developmentally regulated during embryonic mouse osteogenesis: The potential of stc1 as an autocrine/paracrine factor for osteoblast development and bone formation. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2002, 50, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Gu, L.; Li, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, D.; Gong, H.; Li, S.; Niu, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Hypoxia-induced overexpression of stanniocalcin-1 is associated with the metastasis of early stage clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, G.J.; DiMattia, G.D.; Prockop, D.J. Stanniocalcin-1 regulates extracellular ATP-induced calcium waves in human epithelial cancer cells by stimulating ATP release from bystander cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellard, J.P.; McCudden, C.R.; Tanega, C.; James, K.A.; Ratkovic, S.; Staples, J.F.; Wagner, G.F. The respiratory effects of stanniocalcin-1 (STC-1) on intact mitochondria and cells: STC-1 uncouples oxidative phosphorylation and its actions are modulated by nucleotide triphosphates. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 264, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh-Hamad, D. Mammalian stanniocalcin-1 activates mitochondrial antioxidant pathways: New paradigms for regulation of macrophages and endothelium. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2010, 298, F248–F254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wehrens, X.H.; Belousova, T.; Abdelrahim, M.; DiMattia, G.; Sheikh-Hamad, D. Human stanniocalcin-1 suppresses angiotensin II-induced superoxide generation in cardiomyocytes through UCP3-mediated anti-oxidant pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36994. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.E.; Wu, C.P.; Wu, S.Y.; Peng, C.K.; Perng, W.C.; Kang, B.H.; Chu, S.J.; Huang, K.L. Stanniocalcin-1 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 71, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, J.S.; Huang, L.; Belousova, T.; Lu, L.; Yang, Y.; Reddel, R.; Chang, A.; Ju, H.; DiMattia, G.; Tong, Q.; et al. Stanniocalcin-1 inhibits renal ischemia/reperfusion injury via an AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Belousova, T.; Chen, M.; DiMattia, G.; Liu, D.; Sheikh-Hamad, D. Overexpression of stanniocalcin-1 inhibits reactive oxygen species and renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durukan Tolvanen, A.; Westberg, J.A.; Serlachius, M.; Chang, A.C.; Reddel, R.R.; Andersson, L.C.; Tatlisumak, T. Stanniocalcin 1 is important for poststroke functionality, but dispensable for ischemic tolerance. Neuroscience 2013, 229, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, C. Role of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK 1)-mediated signaling pathway during ischemic retinal injury. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi 2008, 112, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, A.; Elmadhoun, O.; Peng, C.; Ding, J.Y.; Geng, X.; Guthikonda, M.; Ding, Y. Reduced apoptosis by ethanol and its association with PKC-δ and Akt signaling in ischemic stroke. Aging Dis. 2014, 5, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Liu, L.Z.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, N.L.; Barnett, J.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Agani, F.; Jiang, B.H. Cadmium increases HIF-1 and VEGF expression through ROS, ERK, and AKT signaling pathways and induces malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 125, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filichia, E.; Shen, H.; Zhou, X.; Qi, X.; Jin, K.; Greig, N.; Hoffer, B.; Luo, Y. Forebrain neuronal specific ablation of p53 gene provides protection in a cortical ischemic stroke model. Neuroscience 2015, 295, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, L.; Sung, S.S.; Lobo, P.I.; Brown, M.G.; Gregg, R.K.; Engelhard, V.H.; Okusa, M.D. NKT cell activation mediates neutrophil IFN-γ production and renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5899–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, B.D.; Abell, A.N.; Johnson, G.L. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases in signal integration. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3159–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, S.J.; Tseng, C.H.; Tu, Y.F.; Liao, N.S.; Huang, C.C.; Ho, C.J. TNFR1-JNK signaling is the shared pathway of neuroinflammation and neurovascular damage after LPS-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic injury in the immature brain. J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Atorvastatin attenuates cognitive deficits through Akt1/caspase-3 signaling pathway in ischemic stroke. Brain Res. 2015, 1629, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Hu, C.; Guo, B.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y. Temporal regulation of HIF-1 and NF-κB in hypoxic hepatocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9409–9419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, H.K.; Lee, H.G.; Piao, J.Y.; Zhong, X.; Lee, H.N.; Han, H.J.; Kim, W.; Kim, D.H.; Cha, Y.N.; Na, H.K.; et al. Helicobacter pylori induces Snail expression through ROS-mediated activation of Erk and inactivation of GSK-3β in human gastric cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.N.; Chen, W.; Zheng, X.X. ROS, MAPK/ERK and PKC play distinct roles in EGF-stimulated human corneal cell proliferation and migration. Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-Grand) 2015, 61, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Shi, Q.; Song, X.; Xia, X.; Su, C.; Liu, Z.; Song, E.; Song, Y. Tetrachlorobenzoquinone exhibits neurotoxicity by inducing inflammatory responses through ROS-mediated IKK/IκB/NF-κB signaling. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 41, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleem, S.; Siddiqui, S.; Siddiqui, H.H.; Badruddeen; Hussain, A.; Arshad, M.; Akhtar, J.; Rizvi, A. Eupalitin induces apoptosis in prostate carcinoma cells through ROS generation and increase of caspase-3 activity. Cell. Biol. Int. 2016, 40, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Ko, J.H.; Yun, J.-H.; Kim, J.-A.; Kim, T.E.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, K.H.; Oh, J.Y. Stanniocalcin-1 protects retinal ganglion cells by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative damage. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Li, W.Z.; Shi, Y.W.; Zhou, B.F.; Ma, R.; Li, W.P. Danshensu protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury and inhibits the apoptosis of H9c2 cells by reducing the calcium overload through the p-JNK-NF-κB-TRPC6 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Dou, P.C.; Tan, S.Y. Osthole ameliorates acute myocardial infarction in rats by decreasing the expression of inflammatory-related cytokines, diminishing MMP-2 expression and activating p-ERK. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, A.; Ishida, Y.; Wada, T.; Hisaoka, T.; Morikawa, Y.; Sugaya, T.; Mukaida, N.; Kondo, T. The absence of interleukin-6 enhanced arsenite-induced renal injury by promoting autophagy of tubular epithelial cells with aberrant extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Oh, Y.B.; Park, B.M.; Park, W.H.; Kim, S.H. Urotensin II protects ischemic reperfusion injury of hearts through ROS and antioxidant pathway. Peptides 2012, 36, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Zemans, R.; Correll, K.; Yang, I.V.; Ahmad, A.; Gao, B.; Mason, R.J. Stanniocalcin-1 is induced by hypoxia inducible factor in rat alveolar epithelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 452, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Garcia, G.; Lou, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Truong, L.D.; DiMattia, G.; Lan, X.R.; Lan, H.Y.; Wang, Y.; Sheikh-Hamad, D. Anti-inflammatory and renal protective actions of stanniocalcin-1 in a model of anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1368–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellis, J.; Bick, R.; Garcia, G.; Truong, L.; Tsao, C.C.; Etemadmoghadam, D.; Poindexter, B.; Feng, L.; Johnson, R.J.; Sheikh-Hamad, D. Stanniocalcin-1, an inhibitor of macrophage chemotaxis and chemokinesis. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2004, 286, F356–F362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Jamaluddin, M.S.; Yan, S.; Sheikh-Hamad, D.; Yao, Q. Human stanniocalcin-1 blocks TNF-α-induced monolayer permeability in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.Y.; Wang, N.P.; Kerendi, F.; Halkos, M.; Kin, H.; Guyton, R.A.; Vinten-Johansen, J.; Zhao, Z.Q. Hypoxic postconditioning reduces cardiomyocyte loss by inhibiting ROS generation and intracellular Ca2+ overload. Am. J. Physiol. Heart. Circ. Physiol. 2005, 288, H1900–H1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-H.; Li, Y.-C.; Ip, S.-W.; Hsu, S.-C.; Chang, N.-W.; Tang, N.-Y.; Yu, C.-S.; Chou, S.-T.; Lin, S.-S.; Lin, C.-C. The role of Ca2+ in baicalein-induced apoptosis in human breast MDA-MB-231 cancer cells through mitochondria-and caspase-3-dependent pathway. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1701–1711. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basu, K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, I.; Datta, K. Nuclear morphology and c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 expression differentiate serum-starved oxidative stress signalling from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in retinal neuronal cell line. Cell. Biol. Int. 2012, 36, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, S.; Hueper, K.; Kirsch, T.; Greite, R.; Klemann, C.; Mengel, M.; Meier, M.; Menne, J.; Leitges, M.; Susnik, N.; et al. Renal PKC-epsilon deficiency attenuates acute kidney injury and ischemic allograft injury via TNF-α-dependent inhibition of apoptosis and inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2014, 307, F718–F726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.S.; Han, S.J.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, S.; Lipschutz, J.H.; Park, K.M. Activation of ERK accelerates repair of renal tubular epithelial cells, whereas it inhibits progression of fibrosis following ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 1998–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, D.Y.; Sha, W.G.; Shen, L.; Lu, G.Y.; Yin, X.; Wang, M.J. High glucose induces renal tubular epithelial injury via Sirt1/NF-κB/microR-29/Keap1 signal pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O'Neill, S.; Humphries, D.; Tse, G.; Marson, L.P.; Dhaliwal, K.; Hughes, J.; Ross, J.A.; Wigmore, S.J.; Harrison, E.M. Heat shock protein 90 inhibition abrogates TLR4-mediated NF-κB activity and reduces renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, G.A.; Postescu, I.D.; Bolfa, P.; Catoi, C.; Muresan, A.; Clichici, S. Inhibition of UVB-induced skin phototoxicity by a grape seed extract as modulator of nitrosative stress, ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway and apoptosis, in SKH-1 mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 57, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFuria, J.; Chen, P.; Shea, T.B. Divergent effects of the MEKK-1/JNK pathway on NB2a/d1 differentiation: Some activity is required for outgrowth and stabilization of neurites but overactivation inhibits both phenomena. Brain Res. 2006, 1123, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, P.; Huang, Q.; Ou, Y.; Du, X.; Li, K.; Tao, Y.; Yin, H. Aloe-emodin-mediated photodynamic therapy induces autophagy and apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cell line MG63 through the ROS/JNK signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 3209–3215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Wu, B.; Li, J.; Yao, X.Y.; Zhu, P.; Chen, Z.N. CD147 promotes IKK/IκB/NF-κB pathway to resist TNF-induced apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2016, 94, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.Y.; Ma, X. Tamoxifen reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells, apoptosis and inhibits IKK/NF-κB pathway after spinal cord injury in rats. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 35, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargavan, B.; Woollard, S.M.; Kanmogne, G.D. Data in support of NF-κB and JNK pathways involvement in TLR3-mediated HIV-1 transactivation, expression of IL-6 and transcription factors associated with HIV-1 replication. Data Brief. 2016, 6, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Qian, Y.; Geng, L.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, S. Involvement of ERK and JNK pathways in IFN-γ-induced B7-DC expression on tumor cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afonso, V.; Santos, G.; Collin, P.; Khatib, A.M.; Mitrovic, D.R.; Lomri, N.; Leitman, D.C.; Lomri, A. Tumor necrosis factor-α down-regulates human Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase 1 promoter via JNK/AP-1 signaling pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayne, K. Revised guide for the care and use of laboratory animals available. American Physiological Society. Physiologist 1996, 39, 199 and 208–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balahoroglu, R.; Dulger, H.H.; Ozbek, H.; Bayram, I.; Sekeroglu, M.R. Protective effects of antioxidants on the experimental liver and kidney toxicity in mice. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, A3. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.L.; Choi, J.H.; Seo, J.H.; Kil, J.H.; Park, K.Y. Antioxidative effects of fermented sesame sauce against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in LLC-PK1 porcine renal tubule cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2014, 8, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.K.; Ma, K.L.; Yuan, Y.H.; Mu, Z.; Song, X.Y.; Niu, F.; Han, N.; Chen, N.H. Targeted overexpression of α-synuclein by rAAV2/1 vectors induces progressive nigrostriatal degeneration and increases vulnerability to MPTP in mouse. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Shang, H.; Liu, Y. Stanniocalcin-1 Protects a Mouse Model from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Affecting ROS-Mediated Multiple Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071051
Liu D, Shang H, Liu Y. Stanniocalcin-1 Protects a Mouse Model from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Affecting ROS-Mediated Multiple Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(7):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071051
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dajun, Huiping Shang, and Ying Liu. 2016. "Stanniocalcin-1 Protects a Mouse Model from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Affecting ROS-Mediated Multiple Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 7: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071051
APA StyleLiu, D., Shang, H., & Liu, Y. (2016). Stanniocalcin-1 Protects a Mouse Model from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Affecting ROS-Mediated Multiple Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(7), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071051