Molecular Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis: Current Evidence and Future Directions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
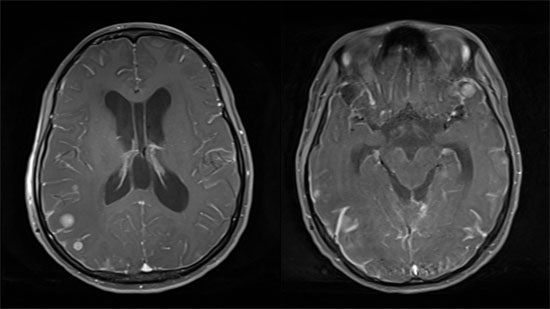
2. Clinical Manifestation and Diagnosis
3. Treatment
3.1. Intrathecal and Systemic Chemotherapy
3.2. Radiotherapy and Surgery
4. Molecular-Targeted Agents in Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis (LMC)
4.1. Lung Cancer Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations
4.2. Lung Cancer Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Translocation
4.3. Breast Cancer Patients with Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) Amplification
4.4. CD20 Positive Lymphoma Patients and BRAF Mutated Melanoma Patients
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chamberlain, M.; Soffietti, R.; Raizer, J.; Ruda, R.; Brandsma, D.; Boogerd, W.; Taillibert, S.; Groves, M.D.; Le Rhun, E.; Junck, L.; et al. Leptomeningeal metastasis: A response assessment in neuro-oncology critical review of endpoints and response criteria of published randomized clinical trials. Neuro-Oncol. 2014, 16, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeckle, K.A. Neoplastic meningitis from systemic malignancies: Diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. Semin. Oncol. 2006, 33, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waki, F.; Ando, M.; Takashima, A.; Yonemori, K.; Nokihara, H.; Miyake, M.; Tateishi, U.; Tsuta, K.; Shimada, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; et al. Prognostic factors and clinical outcomes in patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors. J. Neuro Oncol. 2009, 93, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, M.H.; Al-Sarraf, M.; Baker, L.H.; Vaitkevicius, V.K. Malignant melanoma and central nervous system metastases: Incidence, diagnosis, treatment and survival. Cancer 1978, 42, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, S.T.; Aisner, J.; Makuch, R.W.; Matthews, M.J.; Ihde, D.C.; Whitacre, M.; Glatstein, E.J.; Wiernik, P.H.; Lichter, A.S.; Bunn, P.A., Jr. Carcinomatous leptomeningitis in small cell lung cancer: A clinicopathologic review of the national cancer institute experience. Medicine 1982, 61, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.L.; Perez, H.R.; Jacks, L.M.; Panageas, K.S.; Deangelis, L.M. Leptomeningeal metastases in the mri era. Neurology 2010, 74, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserstrom, W.R.; Glass, J.P.; Posner, J.B. Diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastases from solid tumors: Experience with 90 patients. Cancer 1982, 49, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchins, R.N.; Bell, D.R.; Woods, R.L.; Levi, J.A. A prospective randomized trial of single-agent versus combination chemotherapy in meningeal carcinomatosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 1987, 5, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gwak, H.S.; Joo, J.; Kim, S.; Yoo, H.; Shin, S.H.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, S.H. Analysis of treatment outcomes of intraventricular chemotherapy in 105 patients for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, B.J.; Oberheim-Bush, N.A.; Kesari, S. Leptomeningeal metastasis in breast cancer—A systematic review. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3740–3747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glantz, M.J.; van Horn, A.; Fisher, R.; Chamberlain, M.C. Route of intracerebrospinal fluid chemotherapy administration and efficacy of therapy in neoplastic meningitis. Cancer 2010, 116, 1947–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, S.A.; Finkelstein, D.M.; Ruckdeschel, J.C.; Trump, D.L.; Moynihan, T.; Ettinger, D.S. Randomized prospective comparison of intraventricular methotrexate and thiotepa in patients with previously untreated neoplastic meningitis. Eastern cooperative oncology group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993, 11, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glantz, M.J.; LaFollette, S.; Jaeckle, K.A.; Shapiro, W.; Swinnen, L.; Rozental, J.R.; Phuphanich, S.; Rogers, L.R.; Gutheil, J.C.; Batchelor, T.; et al. Randomized trial of a slow-release versus a standard formulation of cytarabine for the intrathecal treatment of lymphomatous meningitis. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 3110–3116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glantz, M.J.; Jaeckle, K.A.; Chamberlain, M.C.; Phuphanich, S.; Recht, L.; Swinnen, L.J.; Maria, B.; LaFollette, S.; Schumann, G.B.; Cole, B.F.; et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing intrathecal sustained-release cytarabine (DepoCyt) to intrathecal methotrexate in patients with neoplastic meningitis from solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 3394–3402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boogerd, W.; van den Bent, M.J.; Koehler, P.J.; Heimans, J.J.; van der Sande, J.J.; Aaronson, N.K.; Hart, A.A.; Benraadt, J.; Vecht, C.J. The relevance of intraventricular chemotherapy for leptomeningeal metastasis in breast cancer: A randomised study. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 2726–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riess, J.W.; Nagpal, S.; Iv, M.; Zeineh, M.; Gubens, M.A.; Ramchandran, K.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A. Prolonged survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in the modern treatment era. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.I.; Nam, D.H.; Ahn, Y.C.; Han, J.H.; Sun, J.M.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; Ahn, M.J. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in non-small-cell lung cancer patients: Impact on survival and correlated prognostic factors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Hong, R.; Shi, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, J. Leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors: A single center experience in Chinese patients. J. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 115, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, J.H.; Bang, S.M.; Chung, J.H.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.S. Clinical outcomes of leptomeningeal metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer in the modern chemotherapy era. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, M.C. Leptomeningeal metastasis. Semin. Neurol. 2010, 30, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlidis, N. The diagnostic and therapeutic management of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, iv285–iv291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Azevedo, C.R.; Cruz, M.R.; Chinen, L.T.; Peres, S.V.; Peterlevitz, M.A.; de Azevedo Pereira, A.E.; Fanelli, M.F.; Gimenes, D.L. Meningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer: Prognostic factors and outcome. J. Neuro Oncol. 2011, 104, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizazi, K.; Asselain, B.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Jouve, M.; Dieras, V.; Palangie, T.; Beuzeboc, P.; Dorval, T.; Pouillart, P. Meningeal carcinomatosis in patients with breast carcinoma: Clinical features, prognostic factors, and results of a high-dose intrathecal methotrexate regimen. Cancer 1996, 77, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Piao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Hao, X. The concentration of CYFRA 21-1, NSE and CEA in cerebro-spinal fluid can be useful indicators for diagnosis of meningeal carcinomatosis of lung cancer. Cancer Biomark. A Dis. Markers 2013, 13, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, M.D.; Hess, K.R.; Puduvalli, V.K.; Colman, H.; Conrad, C.A.; Gilbert, M.R.; Weinberg, J.; Cristofanilli, M.; Yung, W.K.; Liu, T.J. Biomarkers of disease: Cerebrospinal fluid vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and stromal cell derived factor (SDF)-1 levels in patients with neoplastic meningitis (nm) due to breast cancer, lung cancer and melanoma. J. Neuro Oncol. 2009, 94, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Melisko, M.E.; Magbanua, M.J.; Kablanian, A.T.; Scott, J.H.; Rugo, H.S.; Park, J.W. Detection of cerebrospinal fluid tumor cells and its clinical relevance in leptomeningeal metastasis of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 154, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Mayor, R.; Ng, C.K.; Weigelt, B.; Martinez-Ricarte, F.; Torrejon, D.; Oliveira, M.; Arias, A.; Raventos, C.; Tang, J.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid-derived circulating tumour DNA better represents the genomic alterations of brain tumours than plasma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freilich, R.J.; Krol, G.; Deangelis, L.M. Neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collie, D.A.; Brush, J.P.; Lammie, G.A.; Grant, R.; Kunkler, I.; Leonard, R.; Gregor, A.; Sellar, R.J. Imaging features of leptomeningeal metastases. Clin. Radiol. 1999, 54, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straathof, C.S.; de Bruin, H.G.; Dippel, D.W.; Vecht, C.J. The diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in leptomeningeal metastasis. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauls, S.; Fischer, A.C.; Brambs, H.J.; Fetscher, S.; Hoche, W.; Bommer, M. Use of magnetic resonance imaging to detect neoplastic meningitis: Limited use in leukemia and lymphoma but convincing results in solid tumors. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, Y.J.; Cho, H.R.; Kim, T.M.; Keam, B.; Kim, J.W.; Wen, H.; Park, C.K.; Lee, S.H.; Im, S.A.; Kim, J.E.; et al. An NMR metabolomics approach for the diagnosis of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in lung adenocarcinoma cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer. 2015, 136, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, B.T.; Davis, T.P. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regina, A.; Demeule, M.; Laplante, A.; Jodoin, J.; Dagenais, C.; Berthelet, F.; Moghrabi, A.; Beliveau, R. Multidrug resistance in brain tumors: Roles of the blood-brain barrier. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2001, 20, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.D.; Price, J.E.; Fujimaki, T.; Bucana, C.D.; Fidler, I.J. Differential permeability of the blood-brain barrier in experimental brain metastases produced by human neoplasms implanted into nude mice. Am. J. Pathol. 1992, 141, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.F.; Lin, C.H.; Kuo, C.H.; Chen, W.W.; Yeh, D.C.; Liao, H.W.; Huang, S.M.; Cheng, A.L.; Lu, Y.S. A pilot study of bevacizumab combined with etoposide and cisplatin in breast cancer patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berweiler, U.; Krone, A.; Tonn, J.C. Reservoir systems for intraventricular chemotherapy. J. Neuro Oncol. 1998, 38, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, D.I.; Bilsky, M.H.; Souweidane, M.M.; Bzdil, J.; Gutin, P.H. Ommaya reservoirs for the treatment of leptomeningeal metastases. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glantz, M.J.; Hall, W.A.; Cole, B.F.; Chozick, B.S.; Shannon, C.M.; Wahlberg, L.; Akerley, W.; Marin, L.; Choy, H. Diagnosis, management, and survival of patients with leptomeningeal cancer based on cerebrospinal fluid-flow status. Cancer 1995, 75, 2919–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Yun, T.; Park, S.R.; Jung, J.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, T.Y.; Heo, D.S.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, N.K. Comparison of intrathecal chemotherapy for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis of a solid tumor: Methotrexate alone versus methotrexate in combination with cytosine arabinoside and hydrocortisone. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 33, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, M.C.; Kormanik, P.A.; Barba, D. Complications associated with intraventricular chemotherapy in patients with leptomeningeal metastases. J. Neurosurg. 1997, 87, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, P.G.; Reiner, A.S.; Szenberg, O.R.; Clarke, J.L.; Panageas, K.S.; Perez, H.R.; Kris, M.G.; Chan, T.A.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Omuro, A.M. Leptomeningeal metastasis from non-small cell lung cancer: Survival and the impact of whole brain radiotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 382–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnicka, H.; Niwinska, A.; Murawska, M. Breast cancer leptomeningeal metastasis—The role of multimodality treatment. J. Neuro Oncol. 2007, 84, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, B.C.; Brown, L.T.; Komotar, R.J.; McKhann, G.M. Frameless stereotactic Ommaya reservoir placement: Efficacy and complication comparison with frame-based technique. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2016, 93, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Matsuoka, M.; Sutani, A.; Gemma, A.; Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Okinaga, S.; Nagashima, M.; Oizumi, S.; Uematsu, K.; et al. Frequency of and variables associated with the EGFR mutation and its subtypes. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosell, R.; Moran, T.; Queralt, C.; Porta, R.; Cardenal, F.; Camps, C.; Majem, M.; Lopez-Vivanco, G.; Isla, D.; Provencio, M.; et al. Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Thongprasert, S.; Yang, C.H.; Chu, D.T.; Saijo, N.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Han, B.; Margono, B.; Ichinose, Y.; et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, A.F.; Kahle, K.T.; Wang, D.L.; Joshi, V.A.; Willers, H.; Engelman, J.A.; Lynch, T.J.; Sequist, L.V. EGFR mutation status and survival after diagnosis of brain metastasis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Neuro-Oncol. 2010, 12, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Shin, D.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Keam, B.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, H.G.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, Y.W.; et al. Additional prognostic role of EGFR activating mutations in lung adenocarcinoma patients with brain metastasis: Integrating with lung specific gpa score. Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.C.; Lee, J.H.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, Y.F.; Chang, C.H.; Ho, C.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Yu, C.J.; Yang, J.C. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for non-small-cell lung cancer patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1754–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Togashi, Y.; Masago, K.; Masuda, S.; Mizuno, T.; Fukudo, M.; Ikemi, Y.; Sakamori, Y.; Nagai, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Katsura, T.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 70, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackman, D.M.; Cioffredi, L.A.; Jacobs, L.; Sharmeen, F.; Morse, L.K.; Lucca, J.; Plotkin, S.R.; Marcoux, P.J.; Rabin, M.S.; Lynch, T.J.; et al. A phase I trial of high dose gefitinib for patients with leptomeningeal metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4527–4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, T.; Hata, A.; Takeshita, J.; Fujita, S.; Hayashi, M.; Tomii, K.; Katakami, N. High-dose erlotinib for refractory leptomeningeal metastases after failure of standard-dose EGFR-TKIs. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 75, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Keam, B.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, D.H.; Heo, D.S. Erlotinib versus gefitinib for control of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffknecht, P.; Tufman, A.; Wehler, T.; Pelzer, T.; Wiewrodt, R.; Schutz, M.; Serke, M.; Stohlmacher-Williams, J.; Marten, A.; Maria Huber, R.; et al. Efficacy of the irreversible ErbB family blocker afatinib in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI)-pretreated non-small-cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases or leptomeningeal disease. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanjo, S.; Ebi, H.; Arai, S.; Takeuchi, S.; Yamada, T.; Mochizuki, S.; Okada, Y.; Nakada, M.; Murakami, T.; Yano, S. High efficacy of third generation EGFR inhibitor azd9291 in a leptomeningeal carcinomatosis model with EGFR-mutant lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3847–3856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; Cho, B.C.; Lee, J.-S.; Ye, X.; Yin, X.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Ahn, M.-J. Osimertinib activity in patients (pts) with leptomeningeal (LM) disease from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Updated results from bloom, a phase I study. In Proceeding of the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, McCormick Place, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–7 June 2016; p. 9002.
- Ahn, M.-J.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, T.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Ratnayake, J.; Carlie, D.J.; Yin, X.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.C.-H. Phase I study of AZD3759, a CNS penetrable EGFR inhibitor, for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with brain metastasis (BM) and leptomeningeal metastasis (LM). In Proceeding of the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, McCormick Place, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–7 June 2016; p. 9003.
- Solomon, B.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Camidge, D.R. ALK gene rearrangements: A new therapeutic target in a molecularly defined subset of non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 1450–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Ou, S.H.; Logan, J.; Borges, L.F.; Shaw, A.T. The central nervous system as a sanctuary site in ALK-positive non-small-cell lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, D.B.; Kobayashi, S.; Pandya, S.S.; Yeo, W.L.; Shen, Z.; Tan, W.; Wilner, K.D. CSF concentration of the anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor crizotinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, e443–e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Mehra, R.; Tan, D.S.; Felip, E.; Chow, L.Q.; Camidge, D.R.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Sharma, S.; de Pas, T.; et al. Ceritinib in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1189–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrondeau, J.; Ammari, S.; Besse, B.; Soria, J.C. LDK378 compassionate use for treating carcinomatous meningitis in an ALK translocated non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, e62–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, S.H.; Ahn, J.S.; de Petris, L.; Govindan, R.; Yang, J.C.; Hughes, B.; Lena, H.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Bearz, A.; Ramirez, S.V.; et al. Alectinib in crizotinib-refractory ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase II global study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Gandhi, L.; Gadgeel, S.; Riely, G.J.; Cetnar, J.; West, H.; Camidge, D.R.; Socinski, M.A.; Chiappori, A.; Mekhail, T.; et al. Alectinib in ALK-positive, crizotinib-resistant, non-small-cell lung cancer: A single-group, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Gandhi, L.; Riely, G.J.; Chiappori, A.A.; West, H.L.; Azada, M.C.; Morcos, P.N.; Lee, R.M.; Garcia, L.; Yu, L.; et al. Safety and activity of alectinib against systemic disease and brain metastases in patients with crizotinib-resistant ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (AF-002JG): Results from the dose-finding portion of a phase 1/2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.H.; Sommers, K.R.; Azada, M.C.; Garon, E.B. Alectinib induces a durable (>15 months) complete response in an ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer patient who progressed on crizotinib with diffuse leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Oncologist 2015, 20, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Sherman, C.A.; Willoughby, K.; Logan, J.; Kennedy, E.; Brastianos, P.K.; Chi, A.S.; Shaw, A.T. Alectinib salvages cns relapses in ALK-positive lung cancer patients previously treated with crizotinib and ceritinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kort, A.; Sparidans, R.W.; Wagenaar, E.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H. Brain accumulation of the EML4-ALK inhibitor ceritinib is restricted by p-glycoprotein (P-GP/ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 102, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.C.; Nguyen, L.N.; Sparidans, R.W.; Wagenaar, E.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H. Increased oral availability and brain accumulation of the ALK inhibitor crizotinib by coadministration of the P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) inhibitor elacridar. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1484–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takanashi, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Kondoh, O.; Sakamoto, H. Antitumor activity of the selective ALK inhibitor alectinib in models of intracranial metastases. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2014, 74, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Clark, G.M.; Wong, S.G.; Levin, W.J.; Ullrich, A.; McGuire, W.L. Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987, 235, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.S.; Fletcher, J.A. The HER-2/neu oncogene in breast cancer: Prognostic factor, predictive factor, and target for therapy. Oncologist 1998, 3, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Shak, S.; Fuchs, H.; Paton, V.; Bajamonde, A.; Fleming, T.; Eiermann, W.; Wolter, J.; Pegram, M.; et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagouri, F.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Bartsch, R.; Berghoff, A.S.; Chrysikos, D.; de Azambuja, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Preusser, M. Intrathecal administration of trastuzumab for the treatment of meningeal carcinomatosis in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: A systematic review and pooled analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestalozzi, B.C.; Brignoli, S. Trastuzumab in CSF. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 2349–2351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stemmler, H.J.; Schmitt, M.; Willems, A.; Bernhard, H.; Harbeck, N.; Heinemann, V. Ratio of trastuzumab levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid is altered in HER2-positive breast cancer patients with brain metastases and impairment of blood-brain barrier. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2007, 18, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mego, M.; Sycova-Mila, Z.; Obertova, J.; Rajec, J.; Liskova, S.; Palacka, P.; Porsok, S.; Mardiak, J. Intrathecal administration of trastuzumab with cytarabine and methotrexate in breast cancer patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Breast 2011, 20, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, C.; Davidson, A.; Bouganim, N.; Aloyz, R.; Panasci, L.C. Intrathecal trastuzumab and thiotepa for leptomeningeal spread of breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, O.; Ropert, S.; Alexandre, J.; Lemare, F.; Goldwasser, F. High-dose intrathecal trastuzumab for leptomeningeal metastases secondary to HER-2 overexpressing breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemmler, H.J.; Mengele, K.; Schmitt, M.; Harbeck, N.; Laessig, D.; Herrmann, K.A.; Schaffer, P.; Heinemann, V. Intrathecal trastuzumab (herceptin) and methotrexate for meningeal carcinomatosis in HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer: A case report. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2008, 19, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordbacheh, T.; Law, W.Y.; Smith, I.E. Sanctuary site leptomeningeal metastases in HER-2 positive breast cancer: A review in the era of trastuzumab. Breast 2016, 26, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raizer, J.; Pentsova, E.; Omuro, A.; Lin, N.; Nayak, L.; Quant, E.; Kumthekar, P. Phase I trial of intrathecal trastuzumab in HER2 positive leptomeningeal metastases. Neuro-Oncol. 2014, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusnak, D.W.; Affleck, K.; Cockerill, S.G.; Stubberfield, C.; Harris, R.; Page, M.; Smith, K.J.; Guntrip, S.B.; Carter, M.C.; Shaw, R.J.; et al. The characterization of novel, dual ErbB-2/EGFR, tyrosine kinase inhibitors: Potential therapy for cancer. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 7196–7203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geyer, C.E.; Forster, J.; Lindquist, D.; Chan, S.; Romieu, C.G.; Pienkowski, T.; Jagiello-Gruszfeld, A.; Crown, J.; Chan, A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Lapatinib plus capecitabine for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelot, T.; Romieu, G.; Campone, M.; Dieras, V.; Cropet, C.; Dalenc, F.; Jimenez, M.; Le Rhun, E.; Pierga, J.Y.; Goncalves, A.; et al. Lapatinib plus capecitabine in patients with previously untreated brain metastases from HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (landscape): A single-group phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivot, X.; Manikhas, A.; Zurawski, B.; Chmielowska, E.; Karaszewska, B.; Allerton, R.; Chan, S.; Fabi, A.; Bidoli, P.; Gori, S.; et al. Cerebel (EGF111438): A phase III, randomized, open-label study of lapatinib plus capecitabine versus trastuzumab plus capecitabine in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1564–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiffier, B.; Lepage, E.; Briere, J.; Herbrecht, R.; Tilly, H.; Bouabdallah, R.; Morel, P.; van den Neste, E.; Salles, G.; Gaulard, P.; et al. Chop chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with chop alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feugier, P.; Virion, J.M.; Tilly, H.; Haioun, C.; Marit, G.; Macro, M.; Bordessoule, D.; Recher, C.; Blanc, M.; Molina, T.; et al. Incidence and risk factors for central nervous system occurrence in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: Influence of Rituximab. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Combs, D.; Rosenberg, J.; Levy, A.; McDermott, M.; Damon, L.; Ignoffo, R.; Aldape, K.; Shen, A.; Lee, D.; et al. Rituximab therapy for cns lymphomas: Targeting the leptomeningeal compartment. Blood 2003, 101, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenstein, J.L.; Fridlyand, J.; Abrey, L.; Shen, A.; Karch, J.; Wang, E.; Issa, S.; Damon, L.; Prados, M.; McDermott, M.; et al. Phase I study of intraventricular administration of rituximab in patients with recurrent cns and intraocular lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, H.; Pels, H.; Schmidt-Wolf, I.; Zeelen, U.; Germing, U.; Engert, A. Intraventricular treatment of relapsed central nervous system lymphoma with the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab. Haematologica 2004, 89, 753–754. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Floudas, C.S.; Chandra, A.B.; Xu, Y. Vemurafenib in leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from melanoma: A case report of near-complete response and prolonged survival. Melanoma Res. 2016, 26, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakji-Dupre, L.; Le Rhun, E.; Templier, C.; Desmedt, E.; Blanchet, B.; Mortier, L. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of vemurafenib in patients treated for brain metastatic BRAF-v600 mutated melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2015, 25, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| References | Design | N | Targeted Agent | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liao et al., 2015 [48] | Retrospective | 75 | Any EGFR TKI | EGFR TKI was effective in managing LMC of EGFR (+) patients. |
| Jackman et al., 2015 [50] | Phase I study | 7 | High-dose gefitinib | High-dose gefitinib was well tolerated and showed moderate CSF penetration. |
| Kawamura et al., 2015 [51] | Retrospective | 35 | High-dose erlotinib (N = 12) or Standard-dose EGFR TKI (N = 23) | High-dose erlotinib showed efficacy in patients with LMC. |
| Lee et al., 2013 [52] | Retrospective | 25 | Gefitinib (N = 11) or Erlotinib (N = 14) | Erlotinib had better control rate for LMC compared to gefitinib. |
| Hoggknecht et al., 2015 [53] | Retrospective | 100 (LMC or brain metastasis) | Afatinib | Afatinib showed clinical effect in patients with CNS metastasis (brain metastasis or LMC). |
| Nanjo et al., 2015 [54] | In vivo imaging | LMC mouse | Third generation TKI (AZD9291) | AZD9291 showed response in LMC mouse models refractory to EGFR TKI. |
| References | Design | N | Targeted Agent | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arrondeau et al., 2014 [60] | Case report | 1 | Ceritinib | Certinib showed clinical and radiographic improvement in LMC for over 5.5 months. |
| Ou et al., 2015 [64] | Case report | 1 | Alectinib | Alectinib induced durable (>15 months) complete response of LMC. |
| Gainor et al., 2015 [65] | Case series | 4 | Alectinib | 3 (75%) experienced clinical and radiographic improvement in LMC. Another one patients had stable intracranial disease for 4 months. |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.-W.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, J.W.; Keam, B. Molecular Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis: Current Evidence and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071074
Lee D-W, Lee K-H, Kim JW, Keam B. Molecular Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis: Current Evidence and Future Directions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(7):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071074
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dae-Won, Kyung-Hun Lee, Jin Wook Kim, and Bhumsuk Keam. 2016. "Molecular Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis: Current Evidence and Future Directions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 7: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071074
APA StyleLee, D. -W., Lee, K. -H., Kim, J. W., & Keam, B. (2016). Molecular Targeted Therapies for the Treatment of Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis: Current Evidence and Future Directions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(7), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071074