Novel Redox-Dependent Esterase Activity (EC 3.1.1.2) for DJ-1: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cloning and Overexpression of Recombinant hDJ-1 and Its Mutants C106D and M26I
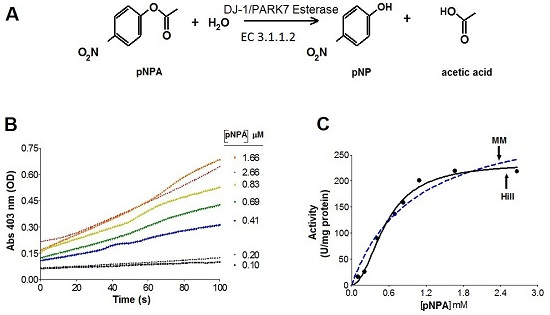
2.2. Kinetics Parameters of Esterase Activity of hDJ-1 and Its Enhancement by Oxidation
2.3. The Esterase Activity of hDJ-1 Is Enhanced by Exposure to Reactive Oxygen Species
2.4. Thiols Are Needed for the Esterase Activity of hDJ-1
2.5. Molecular Docking Studies Suggest a Mechanism by Which hDJ-1 Binds to pNPA
3. Discussion
3.1. Recombinant hDJ-1 Is Proteolytically Processed in E. coli
3.2. hDJ-1 Possesses Intrinsic Esterase Activity
3.3. Reactive Oxygene Species Enhance the Esterase Activity of hDJ-1
3.4. Oxidation of Solvent-Exposed Cysteines Are Required for the Esterase Activity of hDJ-1
3.5. Molecular Docking Studies Predict that C106 in hDJ-1 Mediates Catalysis of Esters
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cloning, Mutagenesis and Purification of Recombinant hDJ-1
4.2. Evaluation of the Hydrolysis of pNPA by hDJ-1 and Lipase
4.3. Analysis of the Oxidation of hDJ-1
4.4. Molecular Docking Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Duijn, C.M.; Dekker, M.C.; Bonifati, V.; Galjaard, R.J.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Snijders, P.J.; Testers, L.; Breedveld, G.J.; Horstink, M.; Sandkuijl, L.A.; et al. Park7, a novel locus for autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism, on chromosome 1p36. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, C.M.; McNally, R.S.; Conti, B.J.; Mak, T.W.; Ting, J.P.-Y. DJ-1, a cancer- and Parkinson’s disease-associated protein, stabilizes the antioxidant transcriptional master regulator Nrf2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15091–15096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariga, H.; Takahashi-Niki, K.; Kato, I.; Maita, H.; Niki, T.; Iguchi-Ariga, S.M.M. Neuroprotective function of DJ-1 in Parkinson’s disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 683920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, P.; Ambrosi, G.; Gammoh, O.; Blandini, F.; Cereda, C.; Milani, P.; Ambrosi, G.; Gammoh, O.; Blandini, F.; Cereda, C. SOD1 and DJ-1 Converge at Nrf2 Pathway: A Clue for Antioxidant Therapeutic Potential in Neurodegeneration. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 836760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Cookson, M.R. Evolutionary and functional relationships within the DJ1 superfamily. BMC Evol. Biol. 2004, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucas, J.I.; Marín, I. A new evolutionary paradigm for the Parkinson disease gene DJ-1. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.A. The role of cysteine oxidation in DJ-1 function and dysfunction. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, L.; Chin, L.S. Parkinson disease protein DJ-1 converts from a zymogen to a protease by carboxyl-terminal cleavage. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 2395–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.A.; Collins, J.L.; Hod, Y.; Ringe, D.; Petsko, G.A. The 1.1-Å resolution crystal structure of DJ-1, the protein mutated in autosomal recessive early onset Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9256–9261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.; Kim, J.; Ha, S.; Kwon, K.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Ryu, K.S.; Park, C. Stereospecific mechanism of DJ-1 glyoxalases inferred from their hemithioacetal-containing crystal structures. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 5447–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witt, A.C.; Lakshminarasimhan, M.; Remington, B.C.; Hasim, S.; Pozharski, E.; Wilson, M.A. Cysteine pKa depression by a protonated glutamic acid in human DJ-1. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 7430–7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Michel, H.A.; Diaz-Sanchez, A.G.; Martinez-Martinez, A.; Hesse, B. Investigations of sulfur chemical status with synchrotron micro focused X-ray fluorescence and X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Protein Pept. Lett. 2016, 23, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldridge, W. The esterases: perspectives and problems. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1993, 87, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.G.; Manthey, M.K.; Le Brocque, D.S.; Hayes, P.J. A microtiter plate assay for the characterization of serine proteases by their esterase activity. Anal. Biochem. 1994, 220, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.M.; Clark, D.S.; Blanch, H.W. Papain kinetics in the presence of a water-miscible organic solvent. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1991, 37, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Hamakubo, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Hara, Y.; Fujimura, H.; Imai, Y.; Iwanari, H.; Mochizuki, Y.; Shichiri, M.; et al. Preparation and application of monoclonal antibodies against oxidized DJ-1. Significant elevation of oxidized DJ-1 in erythrocytes of early-stage Parkinson disease patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 465, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madian, A.G.; Hindupur, J.; Hulleman, J.D.; Diaz-Maldonado, N.; Mishra, V.R.; Guigard, E.; Kay, C.M.; Rochet, J.-C.; Regnier, F.E. Effect of single amino acid substitution on oxidative modifications of the Parkinson’s disease-related protein, DJ-1. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, M111.010892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinumi, T.; Kimata, J.; Taira, T.; Ariga, H.; Niki, E. Cysteine-106 of DJ-1 is the most sensitive cysteine residue to hydrogen peroxide-mediated oxidation in vivo in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 317, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermoso, J.; Pignol, D.; Kerfelec, B.; Crenon, I.; Chapus, C.; Fontecilla-Camps, J.C. Lipase activation by nonionic detergents. The crystal structure of the porcine lipase-colipase-tetraethylene glycol monooctyl ether complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18007–18016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UCSF CHIMERA. Available online: https://www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera/ (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera-A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinbo, Y.; Niki, T.; Taira, T.; Ooe, H.; Takahashi-Niki, K.; Maita, C.; Seino, C.; Iguchi-Ariga, S.M.M.; Ariga, H. Proper SUMO-1 conjugation is essential to DJ-1 to exert its full activities. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reproduction-2DPage. Entry: IPI00298547. Available online: http://reprod.njmu.edu.cn/cgi-bin/2d/2d.cgi?ac=IPI00298547#[1] (accessed 1 on June 2016).
- Advedissian, T.; Deshayes, F.; Poirier, F.; Viguier, M.; Richarme, G. The Parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1/Park7 prevents glycation damage in human keratinocyte. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Sleiman, P.M.; Healy, D.G.; Quinn, N.; Lees, A.J.; Wood, N.W. The role of pathogenic DJ-1 mutations in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Tong, L. Crystal structure of human DJ-1, a protein associated with early onset Parkinson’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31372–31379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richarme, G.; Mihoub, M.; Dairou, J.; Bui, L.C.; Leger, T.; Lamouri, A. Parkinsonism-associated protein DJ-1/park7 is a major protein deglycase that repairs methylglyoxal- and glyoxal-glycated cysteine, arginine, and lysine residues. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1885–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maita, C.; Maita, H.; Iguchi-Ariga, S.M.M.; Ariga, H. Monomer DJ-1 and its N-terminal sequence are necessary for mitochondrial localization of DJ-1 mutants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsugi, H.; Niki, T.; Takahashi-Niki, K.; Tanimura, K.; Yoshizawa-Kumagaye, K.; Tsunemi, M.; Iguchi-Ariga, S.M.M.; Ariga, H. Identification of the recognition sequence and target proteins for DJ-1 protease. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 2493–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y. Oxidized DJ-1 as a possible biomarker of Parkinson’s disease. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014, 54, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodson, M.W.; Guo, M. Pink1, Parkin, DJ-1 and mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2007, 17, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, Y.O.; Saito, Y.; Hamakubo, T.; Masuo, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Nishio, K.; Shichiri, M.; Miyasaka, T.; Iwanari, H.; Mochizuki, Y.; et al. Elevation of oxidized DJ-1 in the brain and erythrocytes of Parkinson disease model animals. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 483, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Caraveo, A.; Castillo-Michel, H.; Mejia-Carmona, G.E.; Pérez-Ishiwara, D.G.; Cotte, M.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Preliminary studies of the effects of psychological stress on circulating lymphocytes analyzed by synchrotron radiation based-Fourier transform infrared microspectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 128, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejia-Carmona, G.E.; Gosselink, K.L.; Pérez-Ishiwara, G.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Oxidant/antioxidant effects of chronic exposure to predator odor in prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and hypothalamus. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 406, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madzelan, P.; Labunska, T.; Wilson, M.A. Influence of peptide dipoles and hydrogen bonds on reactive cysteine pKa values in fission yeast DJ-1. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 4111–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenholm, H.L.; Spomer, W.E.; Wootton, J.F. Effects of acetylation on the activity of trypsin toward ester and amide substrates. Biochemistry 1969, 8, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, E.F.; Nutting, F. Inhibition of the proteinase and esterase activities of trypsin and chymotrypsin by diisopropyl fluorophosphate; crystallization of inhibited chymotrypsin. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 179, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.B. Thiolesterase activity of papain. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 221, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vázquez-Mayorga, E.; Díaz-Sánchez, Á.G.; Dagda, R.K.; Domínguez-Solís, C.A.; Dagda, R.Y.; Coronado-Ramírez, C.K.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Novel Redox-Dependent Esterase Activity (EC 3.1.1.2) for DJ-1: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081346
Vázquez-Mayorga E, Díaz-Sánchez ÁG, Dagda RK, Domínguez-Solís CA, Dagda RY, Coronado-Ramírez CK, Martínez-Martínez A. Novel Redox-Dependent Esterase Activity (EC 3.1.1.2) for DJ-1: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081346
Chicago/Turabian StyleVázquez-Mayorga, Emmanuel, Ángel G. Díaz-Sánchez, Ruben K. Dagda, Carlos A. Domínguez-Solís, Raul Y. Dagda, Cynthia K. Coronado-Ramírez, and Alejandro Martínez-Martínez. 2016. "Novel Redox-Dependent Esterase Activity (EC 3.1.1.2) for DJ-1: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081346
APA StyleVázquez-Mayorga, E., Díaz-Sánchez, Á. G., Dagda, R. K., Domínguez-Solís, C. A., Dagda, R. Y., Coronado-Ramírez, C. K., & Martínez-Martínez, A. (2016). Novel Redox-Dependent Esterase Activity (EC 3.1.1.2) for DJ-1: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081346