MicroRNA-331-3p Suppresses Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation and E6/E7 Expression by Targeting NRP2
Abstract
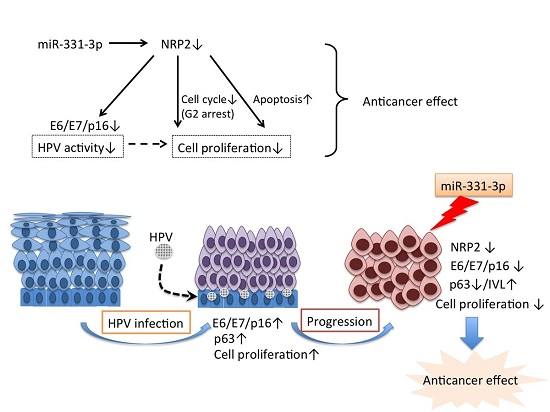
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. miR-331-3p Overexpression Suppresses Cell Proliferation in Cervical Cancer Cells
2.2. miR-331-3p Significantly Decreases the Expression of HPV-Related Proteins E6 and E7
2.3. Inhibition of Cell Proliferation by miR-331-3p Is Directly Mediated by NRP2 Expression in SKG-II Cells
2.4. Suppression of NRP2 by miR-331-3p Induces G2/M-Phase Cell Cycle Arrest
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. miRNA Precursor and siRNA Transfection in Cervical Cell Lines
4.3. qRT-PCR Analysis of miRNA and mRNA
4.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.5. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.6. Cell Viability and Cell Cycle Analysis
4.7. Western Blot and Immunocytochemistory Assay
4.8. TdT-Mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muñoz, N.; Castellsagué, X.; de González, A.B.; Gissmann, L. Chapter 1: HPV in the etiology of human cancer. Vaccine 2006, 24, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses causing cancer : Evasion from host-cell control in early events in carcinogenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, N. Human papillomavirus-16 E5 protein: Oncogenic role and therapeutic value. Cell. Oncol. 2012, 35, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Deng, D.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S.; Meng, L.; Ma, D. Human papillomavirus 16/18 E5 promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and accelerates tumor growth in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narisawa-Saito, M.; Kiyono, T. Basic mechanisms of high-risk human papillomavirus-induced carcinogenesis: Roles of E6 and E7 proteins. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longworth, M.S.; Laimins, L.A. Pathogenesis of human papillomaviruses in differentiating epithelia. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.S.; Rajasekaran, N.; Song, S.Y.; Kim, Y.D.; Hong, S.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, Y.L.; Shin, Y.K. Human papillomavirus E6/E7-specific siRNA potentiates the effect of radiotherapy for cervical cancer in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12243–12260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.P.; Shih, I.; Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell 2003, 115, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, R.; Fabbri, M.; Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2006, 12, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Shimada, K.; Tatsumi, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Konishi, N. Syndecan-1 responsive microRNA-126 and 149 regulate cell proliferation in prostate cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Shimada, K.; Tatsumi, Y.; Hatakeyama, K.; Obayashi, C.; Fujimoto, K.; Konishi, N. MicroRNA-145 promotes differentiation in human urothelial carcinoma through down-regulation of syndecan-1. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Shimada, K.; Tatsumi, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Fujimoto, K.; Konishi, N. Syndecan-1 up-regulates microRNA-331–3p and mediates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 55, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fkih Mhamed, I.; Privat, M.; Ponelle, F.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Kenani, A.; Bignon, Y.J. Identification of miR-10b, miR-26a, miR-146a and miR-153 as potential triple-negative breast cancer biomarkers. Cell. Oncol. 2015, 38, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J.; Peng, F.; Guo, X.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C. MicroRNA-138–5p regulates pancreatic cancer cell growth through targeting FOXC1. Cell. Oncol. 2015, 38, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riquelme, I.; Tapia, O.; Leal, P.; Sandoval, A.; Varga, M.G.; Letelier, P.; Buchegger, K.; Bizama, C.; Espinoza, J.A.; Peek, R.M.; et al. miR-101–2, miR-125b-2 and miR-451a act as potential tumor suppressors in gastric cancer through regulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell. Oncol. 2016, 39, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, K.; Zheng, W.; Mo, X.; Liu, F.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Hu, X. Dysregulated microRNAs involved in the progression of cervical neoplasm. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 292, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Gong, W. Increased exosomal microRNA-21 and microRNA-146a levels in the cervicovaginal lavage specimens of patients with cervical cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 758–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Yan, Q.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wan, X. Interferon-β induced microRNA-129–5p down-regulates HPV-18 E6 and E7 viral gene expression by targeting SP1 in cervical cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Sui, L.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Sun, H. MicroRNA-26a inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of cervical cancer cells by targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA 1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chu, H.; Lv, T.; Wang, L.; Kong, S.; Dai, S. MiR-342–3p suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting FOXM1 in human cervical cancer. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3298–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Yu, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, Z. MiR-101 inhibits the G1-to-S phase transition of cervical cancer cells by targeting Fos. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2014, 24, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Ou, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-196a promotes cervical cancer proliferation through the regulation of FOXO1 and p27Kip1. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, P.P.; Chen, Z.; Liu, M.; Tang, H. MiR-181b promotes cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis by repressing the expression of adenylyl cyclase 9 (AC9) in cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epis, M.R.; Giles, K.M.; Candy, P.A.; Webster, R.J.; Leedman, P.J. MiR-331–3p regulates expression of neuropilin-2 in glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 116, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epis, M.R.; Giles, K.M.; Kalinowski, F.C.; Barker, A.; Cohen, R.J.; Leedman, P.J. Regulation of expression of deoxyhypusine hydroxylase (DOHH), the enzyme that catalyzes the activation of eIF5A, by miR-331–3p and miR-642–5p in prostate cancer cell. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35251–35259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Sun, M.; Nie, F.Q.; Ge, Y.B.; Zhang, E.B.; Yin, D.D.; Kong, R.; Xia, R.; Lu, K.H.; Li, J.H.; et al. Lnc RNA HOTAIR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression by sponging miR-331–3p in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, D.J.; McDade, S.S.; Patel, D.; McCance, D.J. MicroRNA 203 expression in keratinocytes is dependent on regulation of p53 levels by E6. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10644–10652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, O.; McCluggage, W.G. The expression and diagnostic utility of p63 in the female genital tract. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2009, 16, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, J.E.; Arends, J.; van der Linden, P.J.; de Boer, B.A.; Helmerhorst, T.J. Cytokeratin 17 and p63 are markers of the HPV target cell, the cervical stem cell. Anticancer Res. 2004, 24, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Selvi, K.; Badhe, B.A.; Papa, D.; Ganesh, R.N. Role of p16, CK17, p63, and human papillomavirus in diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and distinction from its mimics. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 22, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyöngyösi, E.; Szalmás, A.; Ferenczi, A.; Kónya, J.; Gergely, L.; Veress, G. Effects of human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16 oncoproteins on the expression of involucrin in human keratinocytes. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keating, J.T.; Cviko, A.; Riethdorf, S.; Riethdorf, L.; Quade, B.J.; Sun, D.; Duensing, S.; Sheets, E.E.; Munger, K.; Crum, C.P. Ki-67, cyclin E, and p16INK4 are complimentary surrogate biomarkers for human papilloma virus-related cervical neoplasia. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2001, 25, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin-Drubin, M.E.; Park, D.; Munger, K. Tumor suppressor p16INK4A is necessary for survival of cervical carcinoma cell lines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16175–16180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S.; Trunk, M.; Schiffman, M.; Herrero, R.; Sherman, M.E.; Burk, R.D.; Hildesheim, A.; Bratti, M.C.; Wright, T.; Rodriguez, A.C.; et al. Validation of p16INK4a as a marker of oncogenic human papillomavirus infection in cervical biopsies from a population-based cohort in Costa Rica. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Sano, T.; Oyama, T.; Kashiwabara, K.; Fukuda, T.; Nakajima, T. Immunohistochemical overexpression of p16 protein associated with intact retinoblastoma protein expression in cervical cancer and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Pathol. Int. 1998, 48, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, S.; Hansson, B.; Norman, I.; Gaberi, V.; Mints, M.; Hjerpe, A.; Karlsen, F.; Johansson, B.O. Expression of E6/E7 mRNA from “high risk” human papillomavirus in relation to CIN grade, viral load and p16INK4a. Int. J. Oncol. 2006, 29, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqi, A.; Pasha, T.L.; McGrath, C.M.; Yu, G.H.; Zhang, P.; Gupta, P. Overexpression of p16INK4A in liquid-based specimens (SurePath) as marker of cervical dysplasia and neoplasia. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2002, 27, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustinucci, D.; Rossi, P.G.; Cesarini, E.; Broccolini, M.; Bulletti, S.; Carlani, A.; D′angelo, V.; D′amico, M.R.; di Dato, E.; Galeazzi, P.; et al. Use of cytology, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4a-Ki-67 to define the management of human papillomavirus (HPV)—Positive women in cervical cancer screening. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 145, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuschieri, K.; Wentzensen, N. Human papillomavirus mRNA and p16 detection as biomarkers for the improved diagnosis of cervical neoplasia. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 2536–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaes, R.; Friedrich, T.; Spitkovsky, D.; Ridder, R.; Rudy, W.; Petry, U.; Dallenbach-Hellweg, G.; Schmidt, D.; von Knebel Doeberitz, M. Overexpression of p16(INK4A) as a specific marker for dysplastic and neoplastic epithelial cells of the cervix uteri. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Sui, Y.; Zheng, X. miR-331–3p inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting HER2 through the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1075–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Guo, L.; Ji, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Cai, Q.; Li, J.; Gu, Q.; Liu, B.; et al. miRNA-331–3p directly targets E2F1 and induces growth arrest in human gastric cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, N.M.; Youssef, Y.M.; Fendler, A.; Stephan, C.; Jung, K.; Yousef, G.M. The miRNA-kallikrein axis of interaction: A new dimension in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer. Biol. Chem. 2012, 393, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.M.; Yang, H.; Fang, F.; Xu, J.F.; Yang, L.Y. MicroRNA-331–3p promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting pH domain and leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasarre, P.; Gemmill, R.M.; Potiron, V.A.; Roche, J.; Lu, X.; Barón, A.E.; Korch, C.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Lagana, A.; Howe, P.H.; et al. Neuropilin-2 is upregulated in lung cancer cells during TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 7111–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staton, C.A.; Koay, I.; Wu, J.M.; Hoh, L.; Reed, M.W.R.; Brown, N.J. Neuropilin-1 and neuropilin-2 expression in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence of colorectal cancer. Histopathology 2013, 62, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukahi, K.; Fukasawa, M.; Neufeld, G.; Itakura, J.; Korc, M. Aberrant expression of neuropilin-1 and -2 in human pancreatic cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Lu, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, W.; Cheng, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, J.; Long, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; et al. miR-1247 is correlated with prognosis of pancreatic cancer and inhibits cell proliferation by targeting neuropilins. Curr. Mol. Med. 2014, 14, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Futamura, M.; Kamino, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kitamura, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Ohnishi, S.; Masuda, Y.; Arakawa, H. Possible role of semaphorin 3F, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at 3p2l1.3, in p53-regulated tumor angiogenesis suppression. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, K.; Nakamura, M.; de Velasco, M.A.; Tanaka, M.; Ouji, Y.; Konishi, N. Syndecan-1, a new target molecule involved in progression of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujii, T.; Shimada, K.; Asano, A.; Tatsumi, Y.; Yamaguchi, N.; Yamazaki, M.; Konishi, N. MicroRNA-331-3p Suppresses Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation and E6/E7 Expression by Targeting NRP2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081351
Fujii T, Shimada K, Asano A, Tatsumi Y, Yamaguchi N, Yamazaki M, Konishi N. MicroRNA-331-3p Suppresses Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation and E6/E7 Expression by Targeting NRP2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081351
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujii, Tomomi, Keiji Shimada, Aya Asano, Yoshihiro Tatsumi, Naoko Yamaguchi, Masaharu Yamazaki, and Noboru Konishi. 2016. "MicroRNA-331-3p Suppresses Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation and E6/E7 Expression by Targeting NRP2" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081351
APA StyleFujii, T., Shimada, K., Asano, A., Tatsumi, Y., Yamaguchi, N., Yamazaki, M., & Konishi, N. (2016). MicroRNA-331-3p Suppresses Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation and E6/E7 Expression by Targeting NRP2. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081351