Cancer Salivary Biomarkers for Tumours Distant to the Oral Cavity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Systemic Cancer and Saliva
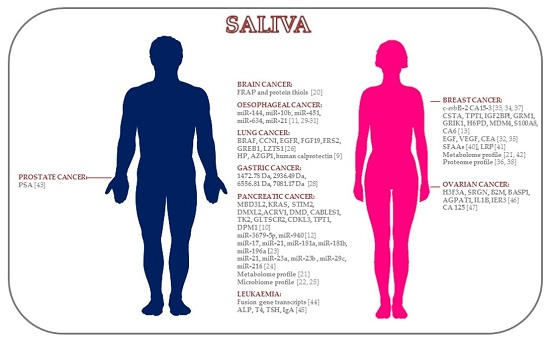
2.1. Brain Cancer
2.2. Pancreatic Cancer
2.3. Lung Cancer
2.4. Gastric Cancer
2.5. Oesophageal Cancer
2.6. Breast Cancer
2.7. Prostate Cancer
2.8. Leukemic Cancer
2.9. Ovarian Cancer
3. Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilkinson, E. Earlier cancer diagnosis would reduce NHS costs. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, M.P.; Allemani, C. Cancer: The elephant in the room. Lancet 2015, 385, 1047–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.T. Salivary Diagnostics: Amazing as it might seem, doctors can detect and monitor diseases using molecules found in a sample of spit. Am. Sci. 2008, 96, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, J.A.; Yan, W.; Ramachandran, P.; Wong, D.T. Comparative human salivary and plasma proteomes. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, N.; Wong, D.T. Saliva: Diagnostics and therapeutic perspectives. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Chan, T.M.; Lin, X.; Kim, Y.; Wong, D.T.W.; Xiao, X. The landscape of microRNA, Piwi-interacting RNA, and circular RNA in human saliva. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, C.A.; Schafer, J.J.; Yakob, M.; Lima, P.; Camargo, P.; Wong, D.T.W. Saliva diagnostics: Utilizing oral fluids to determine health status. Monogr. Oral Sci. 2014, 24, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henson, B.S.; Wong, D.T. Collection, storage, and processing of saliva samples for downstream molecular applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 666, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Lee, J.M.; Garon, E.B.; Wong, D.T.W. Proteomic analysis of human saliva from lung cancer patients using two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, M111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Farrell, J.J.; Zhou, H.; Elashoff, D.; Akin, D.; Park, N.H.; Chia, D.; Wong, D.T. Salivary transcriptomic biomarkers for detection of resectable pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.; Qin, Y.; Duan, Y.; Gong, B.; Li, Z. Salivary microRNAs as promising biomarkers for detection of esophageal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Yin, X.; Gong, B.; Nie, W.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Z. Salivary microRNAs show potential as a noninvasive biomarker for detecting resectable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xiao, H.; Karlan, S.; Zhou, H.; Gross, J.; Elashoff, D.; Akin, D.; Yan, X.; Chia, D.; Karlan, B.; et al. Discovery and preclinical validation of salivary transcriptomic and proteomic biomarkers for the non-invasive detection of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Zhou, H.; Kim, B.W.; Wong, D.T. Salivary transcriptomic biomarkers for detection of ovarian cancer: For serous papillary adenocarcinoma. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.J.; Yu, T.; Nabili, V.; Brinkman, B.M.N.; Henry, S.; Wang, J.; Wong, D.T. RNAprotect saliva: An optimal room-temperature stabilization reagent for the salivary transcriptome. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 2303–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Park, N.J.; Hu, S.; Wong, D.T. A universal pre-analytic solution for concurrent stabilization of salivary proteins, RNA and DNA at ambient temperature. Arch. Oral Biol. 2009, 54, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Wong, D.T.W. Method development for proteome stabilization in human saliva. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 722, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, L.C.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Adelson, P.D.; Arango, J.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.; Carlson, E.; Carter, B.S.; Majem, B.; Chen, C.C.; et al. Meeting report: Discussions and preliminary findings on extracellular RNA measurement methods from laboratories in the NIH extracellular RNA communication consortium. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spielmann, N.; Ilsley, D.; Gu, J.; Lea, K.; Brockman, J.; Heater, S.; Setterquist, R.; Wong, D.T.W. The human salivary RNA transcriptome revealed by massively parallel sequencing. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suma, H.R.; Prabhu, K.; Shenoy, R.P.; Annaswamy, R.; Rao, S.; Rao, A. Estimation of salivary protein thiols and total antioxidant power of saliva in brain tumour patients. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2010, 6, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Wong, D.T.; Hirayama, A.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M. Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Chia, D.; Elashoff, D.; Akin, D.; Paster, B.J.; Joshipura, K.; Wong, D.T.W. Variations of oral microbiota are associated with pancreatic diseases including pancreatic cancer. Gut 2012, 61, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, L.M.; Chen, Z. MicroRNA expression in salivary supernatant of patients with pancreatic cancer and its relationship with ZHENG. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 756347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humeau, M.; Vignolle-Vidoni, A.; Sicard, F.; Martins, F.; Bournet, B.; Buscail, L.; Torrisani, J.; Cordelier, P. Salivary microRNA in pancreatic cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, P.J.; Fletcher, E.M.; Gibbons, S.M.; Bouvet, M.; Doran, K.S.; Kelley, S.T. Characterization of the salivary microbiome in patients with pancreatic cancer. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, H.; Santiago, S.; Lee, J.M.; Garon, E.B.; Yang, J.; Brinkmann, O.; Yan, X.; Akin, D.; et al. Development of transcriptomic biomarker signature in human saliva to detect lung cancer. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 3341–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, T.; Lin, J. Spectral analysis of human saliva for detection of lung cancer using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 037003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Wang, J.G.; Zhang, X.L. Diagnostic model of saliva protein finger print analysis of patients with gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.C.; Li, D.F.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.J. Saliva supernatant miR-21: A novel potential biomarker for esophageal cancer detection. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 6145–6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Hou, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yi, Y.; Lin, W. miRNA-144 in the saliva is a genetic marker for early diagnosis of esophageal cancer. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2013, 33, 1783–1786. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Ye, P.; Zhang, W.; Rao, J.; Xie, Z. Diagnostic values of salivary versus and plasma microRNA-21 for early esophageal cancer. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2014, 34, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navarro, M.A.; Mesía, R.; Díez-Gibert, O.; Rueda, A.; Ojeda, B.; Alonso, M.C. Epidermal growth factor in plasma and saliva of patients with active breast cancer and breast cancer patients in follow-up compared with healthy women. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1997, 42, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streckfus, C.; Bigler, L.; Tucci, M.; Thigpen, J.T. A preliminary study of CA15-3, c-erbB-2, epidermal growth factor receptor, cathepsin-D, and p53 in saliva among women with breast carcinoma. Cancer Investig. 2000, 18, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streckfus, C.; Bigler, L.; Dellinger, T.; Dai, X.; Kingman, A.; Thigpen, J.T. The presence of soluble c-erbB-2 in saliva and serum among women with breast carcinoma: A preliminary study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2363–2370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M.N.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Elashoff, D.; Wong, D.T. Salivary protein factors are elevated in breast cancer patients. Mol. Med. Rep. 2008, 1, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streckfus, C.F.; Mayorga-Wark, O.; Arreola, D.; Edwards, C.; Bigler, L.; Dubinsky, W.P. Breast cancer related proteins are present in saliva and are modulated secondary to ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer Investig. 2008, 26, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agha-Hosseini, F.; Mirzaii-Dizgah, I.; Rahimi, A. Correlation of serum and salivary CA15-3 levels in patients with breast cancer. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2009, 14, e521–e524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streckfus, C.F.; Storthz, K.A.; Bigler, L.; Dubinsky, W.P. A Comparison of the Proteomic Expression in Pooled Saliva Specimens from Individuals Diagnosed with Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast with and without Lymph Node Involvement. J. Oncol. 2009, 2009, 737619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.Q.; Wu, Z.Z.; Wu, W.K. Identification of salivary biomarkers in breast cancer patients with thick white or thick yellow tongue fur using isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitative proteomics. J. Chin. Integr. Med. 2011, 9, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Wang, X. Investigation of salivary free amino acid profile for early diagnosis of breast cancer with ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 447, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, N.; Streckfus, C.F. The expression of lung resistance protein in saliva: A novel prognostic indicator protein for carcinoma of the breast. Cancer Investig. 2015, 33, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, T.; Tsutsui, H.; Shimizu, I.; Toyama, T.; Yoshimoto, N.; Endo, Y.; Inoue, K.; Todoroki, K.; Min, J.Z.; Mizuno, H.; et al. Diagnostic approach to breast cancer patients based on target metabolomics in saliva by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 452, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiiki, N.; Tokuyama, S.; Sato, C.; Kondo, Y.; Saruta, J.; Mori, Y.; Shiiki, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Tsukinoki, K. Association between saliva PSA and serum PSA in conditions with prostate adenocarcinoma. Biomarkers 2011, 16, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Song, N.; Ni, R.; Zhao, J.; Hu, J.; Lu, Q.; Li, Q. Saliva as a sampling source for the detection of leukemic fusion transcripts. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, R.N.M.; Oliveira-Junior, J.J.; Mouchrek-Filho, J.C.E.; Liberio, S.A.; Lima, M.V.V.; Paim, D.B.S.; Brito, C.X.L.; Mendonça, C.; Nascimento, F.R.F.; Pereira, A.L.A. Salivary evaluation of pediatric patients with cancer, before and after antineoplasic treatment. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2012, 41, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Suh, D.H.; Kim, M.K.; Chung, H.H.; Song, Y.S. Ovarian cancer biomarker discovery based on genomic approaches. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 18, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.X.; Schwartz, P.E.; Li, F.Q. Saliva and serum CA 125 assays for detecting malignant ovarian tumours. Obstet. Gynecol. 1990, 75, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Globocan. Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Default.aspx (accessed on 28 May 2015).
- Ray, A.; Manjila, S.; Hdeib, A.M.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Nock, C.J.; Cohen, M.L.; Sloan, A.E. Extracranial metastasis of gliobastoma: Three illustrative cases and current review of the molecular pathology and management strategies. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayutham, P.K.; Adhikary, S.D.; Babu, S.K.; Vedantam, R.; Korula, G.; Ramachandran, A. Oxidative stress-associated hypertension in surgically induced brain injury patients: Effects of β-blocker and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 179, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreher, D.; Junod, A.F. Role of oxygen free radicals in cancer development. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32A, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frampton, A.E.; Krell, J.; Jamieson, N.B.; Gall, T.M.H.; Giovannetti, E.; Funel, N.; Mato Prado, M.; Krell, D.; Habib, N.A.; Castellano, L.; et al. microRNAs with prognostic significance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 1389–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Miyamae, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Morimura, R.; Hirajima, S.; Okajima, W.; Ohashi, T.; Imamura, T.; Konishi, H.; et al. Malignant potential in pancreatic neoplasm; new insights provided by circulating miR-223 in plasma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2015, 15, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Sun, Y.W.; Liu, D.J.; Zhang, J.F.; Li, J.; Hua, R. MicroRNAs in stool samples as potential screening biomarkers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 4, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Raimondo, M.; Guha, S.; Chen, J.; Diao, L.; Dong, X.; Wallace, M.B.; Killary, A.M.; Frazier, M.L.; Woodward, T.A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in pancreatic juice as candidate biomarkers of pancreatic cancer. J. Cancer 2014, 5, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, S.; Raulefs, S.; Bruns, P.; Afonso-Grunz, F.; Plötner, A.; Thermann, R.; Jäger, C.; Schlitter, A.M.; Kong, B.; Regel, I.; et al. Next-generation sequencing reveals novel differentially regulated mRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs, sdRNAs and a piRNA in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachagani, S.; Macha, M.A.; Heimann, N.; Seshacharyulu, P.; Haridas, D.; Chugh, S.; Batra, S.K. Clinical implications of miRNAs in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.A.; Baxter, D.H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, D.Y.; Huang, K.H.; Lee, M.J.; Galas, D.J.; Wang, K. The microRNA spectrum in 12 body fluids. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, Y.; Taketomi, Y.; Murakami, M.; Tsujimoto, M.; Yanoshita, R. Small RNA transcriptomes of two types of exosomes in human whole saliva determined by next generation sequencing. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Lu, L.; Qiu, Y.; Ni, Q.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Y.T.; Risch, H.A.; Yu, H.; Jia, W. Plasma metabolite biomarkers for the detection of pancreatic cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.; Kim, Y.; Chia, D.; Spielmann, N.; Eibl, G.; Elashoff, D.; Wei, F.; Lin, Y.L.; Moro, A.; Grogan, T.; et al. Role of pancreatic cancer-derived exosomes in salivary biomarker development. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26888–26897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Chang, P.; LeBlanc, A.; Li, D.; Abbruzzesse, J.L.; Frazier, M.L.; Killary, A.M.; Sen, S. MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abue, M.; Yokoyama, M.; Shibuya, R.; Tamai, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sato, I.; Tanaka, N.; Hamada, S.; Shimosegawa, T.; Sugamura, K.; et al. Circulating miR-483-3p and miR-21 is highly expressed in plasma of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 46, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Dubaybo, H.; Brand, R.E. Differential expression of microRNAs in tissues and plasma co-exists as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2015, 7, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belstrøm, D.; Fiehn, N.E.; Nielsen, C.H.; Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Paster, B.J.; Twetman, S.; Holmstrup, P. Differentiation of salivary bacterial profiles of subjects with periodontitis and dental caries. J. Oral Microbiol. 2015, 7, 27429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, M.W.; Raji, O.Y.; Field, J.K. Lung cancer screening: Identifying the high risk cohort. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, S156–S162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Lin, C.C.; Joon, A.; Feng, Z.; Troche, G.; Lira, M.E.; Chia, D.; Mao, M.; Ho, C.L.; Su, W.C.; et al. Noninvasive saliva-based EGFR gene mutation detection in patients with lung cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbannayya, Y.; Mir, S.A.; Renuse, S.; Manda, S.S.; Pinto, S.M.; Puttamallesh, V.N.; Solanki, H.S.; Manju, H.C.; Syed, N.; Sharma, R.; et al. Identification of differentially expressed serum proteins in gastric adenocarcinoma. J. Proteom. 2015, 127, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiam, K.; Wang, T.; Watson, D.I.; Mayne, G.C.; Irvine, T.S.; Bright, T.; Smith, L.; White, I.A.; Bowen, J.M.; Keefe, D.; et al. Circulating serum exosomal miRNAs as potential biomarkers for esophageal adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2015, 19, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Hirajima, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Miyamae, M.; Okajima, W.; Ohashi, T.; Arita, T.; Konishi, H.; Shiozaki, A.; et al. Plasma microRNA profiles: Identification of miR-25 as a novel diagnostic and monitoring biomarker in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1614–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hezova, R.; Kovarikova, A.; Srovnal, J.; Zemanova, M.; Harustiak, T.; Ehrmann, J.; Hajduch, M.; Svoboda, M.; Sachlova, M.; Slaby, O. Diagnostic and prognostic potential of miR-21, miR-29c, miR-148 and miR-203 in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.X.; Yu, Q.; Shi, Z.L.; Li, P.; Fu, S. Circulating microRNAs in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Association with locoregional staging and survival. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 7241–7250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mulrane, L.; Klinger, R.; McGee, S.F.; Gallagher, W.M.; O’Connor, D.P. microRNAs: A new class of breast cancer biomarkers. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigler, L.R.; Streckfus, C.F.; Copeland, L.; Burns, R.; Dai, X.; Kuhn, M.; Martin, P.; Bigler, S.A. The potential use of saliva to detect recurrence of disease in women with breast carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2002, 31, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streckfus, C.F.; Arreola, D.; Edwards, C.; Bigler, L. Salivary protein profiles among HER2/neu-receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer patients: Support for using salivary protein profiles for modeling breast cancer progression. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012, 413256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidi, F.; Bouziane, A.; Lakhdar, A.; Khabouze, S.; Amrani, M.; Rhrab, B.; Zaoui, F. Significant correlation between salivary and serum Ca 15–3 in healthy women and breast cancer patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 4659–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajkowska, M.; Głażewska, E.K.; Będkowska, G.E.; Chorąży, P.; Szmitkowski, M.; Ławicki, S. Diagnostic power of vascular endothelial growth factor and macrophage colony-stimulating factor in breast cancer patients based on ROC analysis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 5962946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ławicki, S.; Zajkowska, M.; Głażewska, E.K.; Będkowska, G.E.; Szmitkowski, M. Plasma levels and diagnostic utility of VEGF, MMP-9, and TIMP-1 in the diagnosis of patients with breast cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 911–919. [Google Scholar]
- Streckfus, C.F.; Bigler, L.R.; Zwick, M. The use of surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry to detect putative breast cancer markers in saliva: A feasibility study. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2006, 35, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzick, J.; Thorat, M.A.; Andriole, G.; Brawley, O.W.; Brown, P.H.; Culig, Z.; Eeles, R.A.; Ford, L.G.; Hamdy, F.C.; Holmberg, L.; et al. Prevention and early detection of prostate cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e484–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachakova, D.; Mitkova, A.; Popov, E.; Popov, I.; Vlahova, A.; Dikov, T.; Christova, S.; Mitev, V.; Slavov, C.; Kaneva, R. Combinations of serum prostate-specific antigen and plasma expression levels of let-7c, miR-30c, miR-141, and miR-375 as potential better diagnostic biomarkers for prostate cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2015, 34, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayatollahi, H.; Darabi Mahboub, M.R.; Mohammadian, N.; Parizadeh, M.R.; Kianoosh, T.; Khabbaz Khoob, M.; Kamalian, F. Ratios of free to total prostate-specific antigen and total prostate specific antigen to protein concentrations in saliva and serum of healthy men. Urol. J. 2007, 4, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turan, T.; Demir, S.; Aybek, H.; Atahan, O.; Tuncay, O.L.; Aybek, Z. Free and total prostate-specific antigen levels in saliva and the comparison with serum levels in men. Eur. Urol. 2000, 38, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, S.L.; Brown, P.A. Treatment of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 62, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershan, L.A.; Durham, P.L.; Skidmore, J.; Shimizu, J.; Cady, R.J.; Sheng, X.; Maloney, C.G. The role of salivary neuropeptides in pediatrics: Potential biomarkers for integrated therapies. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2015, 7, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streckfus, C.F.; Romaguera, J.; Guajardo-Streckfus, C. The use of salivary protein secretions as an in vivo model to study Mantel cell lymphoma progression and treatment. Cancer Investig. 2013, 31, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts Figures 2015; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, B.; Bi, R. Ovarian cancer: Biomarker proteomic diagnosis in progress. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Ke, C.; Yin, M.; Li, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, F.; Zhou, X.; et al. Identification of potential biomarkers for ovarian cancer by urinary metabolomic profiling. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lu, Z.; Unruh, A.K.; Ivan, C.; Baggerly, K.A.; Calin, G.A.; Li, Z.; Bast, R.C.; Le, X.F. Clinically relevant microRNAs in ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bast, R.C.; Spriggs, D.R. More than a biomarker: CA125 may contribute to ovarian cancer pathogenesis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 121, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ławicki, S.; Będkowska, G.E.; Gacuta-Szumarska, E.; Szmitkowski, M. The plasma concentration of VEGF, HE4 and CA125 as a new biomarkers panel in different stages and sub-types of epithelial ovarian tumors. J. Ovarian Res. 2013, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Cancer Location | Study Design | Patients (No.) | Saliva Collection | Methods | Biomarkers | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain Cancer | Biochemical | 28 C, 32 B, 42 HC | Unstimulated | Spectrophotometric | FRAP, protein thiols | [20] |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Transcriptomic | DP: 12 C, 12 HC | Unstimulated | DP: Affymetrix U133 Plus 2.0 Array | MBD3L2, KRAS, STIM2, DMXL2, ACRV1, DMD, CABLES1, TK2, GLTSCR2, CDKL3, TPT1, DPM1 | [10] |
| VP: 30 C, 30 P, 30 HC | VP: RT-qPCR | |||||
| Metabolomic | 18 C, 87 HC | Unstimulated | CE-TOF-MS | Leucine with isoleucine tryptophan, valine, glutamic acid, phenylalanine, glutamine, aspartic acid | [21] | |
| Microbial | DP: 10 C, 10 HC | Unstimulated | DP: HOMIM | Neisseria elongata, Streptococcus mitis, Granulicatella adiacens | [22] | |
| VP: 28 C, 27 P, 28 HC | VP: RT-qPCR | |||||
| miRNAs | 30 C, 32 HC | NA | miScript miRNA PCR array human, RT-qPCR | miR-17, miR-21, miR-181a, miR-181b, miR-196a | [23] | |
| miRNAs | DP: 8 C, 8 HC | Stimulated (citric acid) | DP: Human miRNA Microarray, release 19.0 (Agilent) | miR-3679-5p, miR-940 | [12] | |
| VP: 40 C, 20 B, 40 HC | VP: RT-qPCR | |||||
| miRNAs | 7 C, 4 P, 2 IPMN, 4 HC | NA | RT-qPCR using Fluidigm (Biomark) | miR-21, miR-23a, miR-23b, miR-29c, miR-216 | [24] | |
| Microbial | 8 C, 78 OD, 22 HC | NA | RT-qPCR | Leptotrichia sp. to Porphyromonas sp. | [25] | |
| Lung Cancer | Proteomic | DP: 10 C, 10 HC | Unstimulated | DP: 2D-DIGE-MS | HP, AZGP1, human calprotectin | [9] |
| VP: 26 C, 26 HC | VP: Western blotting, ELISA kits | |||||
| Transcriptomic | DP: 10 C, 10 HC | Unstimulated | DP: Affymetrix HG U133 Plus 2.0 Array | BRAF, CCNI, EGFR, FGF19, FRS2, GREB1, LZTS1 | [26] | |
| VP: 23 C, 64 HC | VP: RT-qPCR | |||||
| Proteomic | 21 C, 20 HC | Unstimulated | Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy | Amino acids, nucleic acid bases | [27] | |
| Gastric Cancer | Proteomic | 23 C, 18 HC | NA | MALDI-TOF-MS | 1472.78 Da, 2936.49 Da, 6556.81 Da, 7081.17 Da | [28] |
| Oesophageal Cancer | miRNAs | DP: 8 EC, 4 HC | Stimulated (2% citric acid) | DP: RT-qPCR | miR-21 | [29] |
| VP: 32 C, 16 HC | VP: RT-qPCR | |||||
| miRNAs | DP: 7 C, 3 HC | Stimulated (2% citric acid) | DP: Agilent microarray | miR-144, miR-10b, miR-451, miR-21 | [11] | |
| VP: 39 C, 19 HC | VP: RT-qPCR | |||||
| miRNAs | 67 C, 50 HC | Stimulated (2% citric acid) | RT-qPCR | miR-144 | [30] | |
| miRNAs | 100 C, 50 HC | Stimulated (citric acid) | RT-qPCR | miR-21 | [31] | |
| Breast Cancer | Proteomic | 52 active BC, 22 non-active BC, 33 HC | Stimulated (lemon juice when necessary) | ER-EIA (Abbott) | EGF | [32] |
| Proteomic | 12 C, 8 B, 15 HC | Stimulated (cube of paraffin) | EIA kits, ELISA kits (Oncogene Research) | CA15-3, c-erbB-2 | [33] | |
| Proteomic | 30 C, 44 B, 57 HC | Stimulated (gum base) | ELISA kits and EIA kits | c-erbB-2 | [34] | |
| Proteomic | 49 C, 49 HC | Unstimulated | ELISA kits | VEGF, EGF, CEA | [35] | |
| Proteomic | 10 C, 10 B, 10 HC | Stimulated (paraffin or gum base) | IL-LC-MS/MS | 40 protein profiles | [36] | |
| Proteomic | 26 C, 35 HC | Unstimulated | EIA kits | CA15-3 | [37] | |
| Proteomic | 20 C, 10 HC | Stimulated (paraffin or gum base) | IL-LC-MS/MS | 20 proteins (Stage IIa) 28 proteins (Stage IIb) | [38] | |
| Transcriptomic | DP: 10 C, 10 HC | Unstimulated | DP: Affymetrix HG U133 Plus 2.0 Array | CSTA, TPT1, IGF2BP1, GRM1, GRIK1, H6PD, MDM4, S100A8 | [13] | |
| VP: 30 C, 63 HC | VP: RT-qPCR | |||||
| Proteomic | DP: 10 C, 10 HC | DP: 2D-DIGE | CA6 | |||
| VP: 30 C, 63 HC | VP: Western blotting | |||||
| Metabolomic | 30 C, 87 HC | Unstimulated | CE-MS | 28 metabolites | [21] | |
| Proteomic | 20 C, 10 HC | NA | LC-MS/MS | Protein profile | [39] | |
| Proteomic | 27 C, 28 HC | Unstimulated | UPLC-MS | 15 SFAAs | [40] | |
| Proteomic | 16 C, 16 HC | Stimulated (gum base) | Gel electrophoresis and western blotting | Lung resistance protein | [41] | |
| Metabolomic | 111 C, 61 HC | NA | UPLC-MS/MS | Polyamines | [42] | |
| Prostate Cancer | Proteomic | 11 high serum PSA prostate C, 20 low serum PSA prostate C | Stimulated (citrate-containing cotton) | ELISA | PSA | [43] |
| Leukaemia | Transcriptomic | 7 C, 20 HC | Stimulated (citric acid) | RT-qPCR | BCR-ABL, PML-RARα, AML-ETO | [44] |
| Biochemical | 32 C, 115 HC | Unstimulated | Biochemical analysis, EIA, chemoluminescence | ALP, T4, TSH, IgA | [45] | |
| Ovarian Cancer | Transcriptomic | DP: 11 C, 11 HC | Unstimulated | DP: Affymetrix HG U133 Plus 2.0 Array | H3F3A, SRGN, B2M, BASP1, AGPAT1, IL1B, IER3 | [46] |
| VP: 21 C, 35 HC | VP: RT-qPCR | |||||
| Proteomic | 92 B, 41 C, 55 HC | NA | Radioimmunoassay | CA 125 | [47] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rapado-González, Ó.; Majem, B.; Muinelo-Romay, L.; López-López, R.; Suarez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Cancer Salivary Biomarkers for Tumours Distant to the Oral Cavity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091531
Rapado-González Ó, Majem B, Muinelo-Romay L, López-López R, Suarez-Cunqueiro MM. Cancer Salivary Biomarkers for Tumours Distant to the Oral Cavity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(9):1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091531
Chicago/Turabian StyleRapado-González, Óscar, Blanca Majem, Laura Muinelo-Romay, Rafa López-López, and María Mercedes Suarez-Cunqueiro. 2016. "Cancer Salivary Biomarkers for Tumours Distant to the Oral Cavity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 9: 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091531
APA StyleRapado-González, Ó., Majem, B., Muinelo-Romay, L., López-López, R., & Suarez-Cunqueiro, M. M. (2016). Cancer Salivary Biomarkers for Tumours Distant to the Oral Cavity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(9), 1531. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091531