Similarity and Differences in Inflammation-Related Characteristics of the Peripheral Immune System of Patients with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases
Abstract
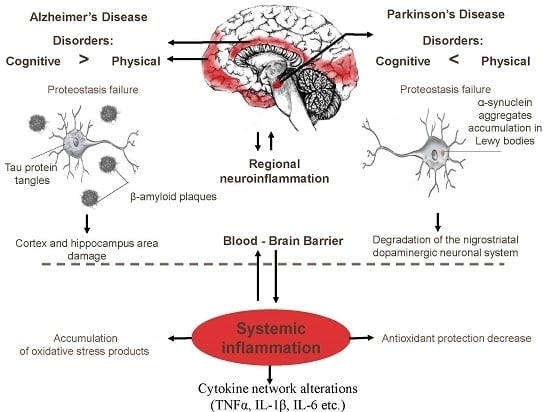
:1. Introduction
2. Inflammation as A Main Immune Process Associated with AD and PD
3. Alterations of Peripheral Cytokine Profiles in PD and AD
4. The Role of Oxidative Stress in PD and AD: Products of Oxidative Stress in the Peripheral Blood as Biomarkers of PD and AD
5. HSP70 as A Possible Biomarker for Neurodegenerative Diseases
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selkoe, D.J. Cell biology of protein misfolding: The examples of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.M.; Wong, E.S.; Lim, K.L. Protein misfolding and aggregation in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2119–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; Wahlster, L.; McLean, P.J. Molecular chaperones in Parkinson’s disease—Present and future. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2011, 1, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-β and tau: The trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Tanji, K.; Odagiri, S.; Miki, Y.; Mori, F.; Takahashi, H. The Lewy body in Parkinson’s disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 47, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Natteru, P.A.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Saeed, D.; Zahoor, H.; Zaheer, S.; Iyer, S.S.; Zaheer, A. Neuroinflammation induces neurodegeneration. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Spine 2016, 1, 1003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Szeto, J.Y.; Lewis, S.J. Current Treatment Options for Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease Dementia. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitz, J.M. Parkinson’s disease: A review. Front. Biosci. 2014, 6, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.; de Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzhemer’s disease. Lancet 2016, 388, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurosinski, P.; Guggisberg, M.; Götz, J. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease—Overlapping or synergistic pathologies? Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Wittenberg, R. Clinical and cost effectiveness of services for early diagnosis and intervention in dementia. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2009, 24, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.; Luber-Narod, J.; Styren, S.D.; Civin, W.H. Expression of immune system-associated antigens by cells of the human central nervous system: Relationship to the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 1988, 9, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortekaas, R.; Leenders, K.L.; Van Oostrom, J.C.; Vaalburg, W.; Bart, J.; Willemsen, A.T.; Hendrikse, N.H. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in parkinsonian midbrain in vivo. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitton, P.S. Inflammation as a causative factor in the aetiology of Parkinson’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 50, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phani, S.; Loike, J.D.; Przedborski, S. Neurodegeneration and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Zaheer, S.; Ahmed, M.E.; Raikwar, S.P.; Zahoor, H.; Saeed, D.; Natteru, P.A.; Iyer, S.; et al. Brain and peripheral atypical inflammatory mediators potentiate neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, K.R.; Guillot-Sestier, M.V.; Town, T. The role of the immune system in neurodegenerative disorders: Adaptive or maladaptive? Brain Res. 2014, 1617, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Bonafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; de Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E.; de Benedictis, G. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 908, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, V.H. The influence of systemic inflammation on inflammation in the brain: Implications for chronic neurodegenerative disease. Brain Behav. Immun. 2004, 18, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, R.; Santana, I.; Bras, J.M.; Santiago, M.; Santiago, B.; Paiva, A.; Oliveira, C. Peripheral Inflammatory Cytokines as Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Neurodegener. Dis. 2007, 4, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo, P.; Martin-Aragon, S.; Benedi, J.; Susín, C.; Felici, E.; Gil, P.; Ribera, J.M.; Villar, A.M. Differences of peripheral inflammatory markers between mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Immunol. Lett. 2008, 117, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonotis, K.; Krikki, E.; Holeva, V.; Aggouridaki, C.; Costa, V.; Baloyannis, S. Systemic Immune Aberrations in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 193, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, C.; El-Okl, M.; Williams, A.L.; Cunningham, C.; Wilcockson, D.; Perry, V.H. Systemic infection, interleukin 1β and cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 788–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Block, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Breese, G.R.; Hong, J.; Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 2007, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncharova, L.B.; Tarakano, A.O. Molecular networks of brain and immunity. Brain Res. Rev. 2007, 55, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, V.H.; Cunningham, C.; Holmes, C. Systemic infections and inflammation affect chronic neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denes, A.; Thornton, P.; Rothwell, N.J.; Allan, S.M. Inflammation and brain injury: Acute cerebral ischaemia, peripheral and central inflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosley, R.L.; Hutter-Saunders, J.A.; Stone, D.K.; Gendelman, H.E. Inflammation and adaptive immunity in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, 009381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, C.; Butchart, J. Systemic inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogland, I.C.; Houbolt, C.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D. Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: Systematic review of animal experiments. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, C.; Cunningham, C.; Zotova, E.; Woolford, J.; Dean, C.; Kerr, S.; Culliford, D.; Perry, V.H. Systemic inflammation and disease progression in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2009, 73, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.V.; McGavern, D.B. Immune surveillance of the CNS following infection and injury. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calsolaro, V.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Current evidence and future directions. Alzheimers Dement. 2016, 12, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodore, S.; Cao, S.; McLean, P.J.; Standaert, D.G. Targeted overexpression of human α-synuclein triggers microglial activation and an adaptive immune response in a mouse model of Parkinson disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Sue, L.I.; Vedders, L.; Lue, L.; White, C.L.; Akiyama, H.; Caviness, J.N.; Shill, H.A.; Sabbagh, M.N.; et al. Arizona Parkinson’s Disease Consortium. Multi-organ distribution of phosphorylated a-synuclein histopathology in subjects with Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 119, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskvina, V.; Harold, D.; Russo, G.; Vedernikov, A.; Sharma, M.; Saad, M.; Holmans, P.; Bras, J.M.; Bettella, F.; Keller, M.F.; et al. IPDGC and GERAD Investigators. Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies of Alzheimer Disease and of Parkinson Disease to Determine If These 2 Diseases Share a Common Genetic Risk. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, M.; Parikh, I.; Vasquez, J.B.; Smith, C.; Tai, L.; Bu, G.; LaDu, M.J.; Fardo, D.W.; Rebeck, G.W.; Estus, S. Genetics ignite focus on microglial inflammation in Alzheimers’ disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griciuc, A.; Serrano-Pozzo, A.; Parrado, A.R.; Lesinski, A.N.; Asselin, C.N.; Mullin, K.; Hooli, B.; Choi, S.H.; Hyman, B.T.; Tanzi, R.E. Alzheimer’s disease risk gene CD33 inhibits microglial uptake of amyloid β. Neuron 2013, 78, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, R.; Wojtas, A.; Bras, J.; Carrasquillo, M.; Rogaeva, E.; Majounie, E.; Cruchaga, C.; Sassi, C.; Kauwe, J.S.; Younkin, S.; et al. The Alzheimer Genetic Analysis Group*. TREM2 variants in Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, E.C.; Vyas, S.; Hunot, S. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18 (Suppl. S1), S210–S212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, N.P.; de Miranda, A.S.; Teixeira, A.L. Insights into Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: From biomarkers to anti-Inflammatory based therapies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 628192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamza, T.H.; Zabetian, C.P.; Tenesa, A.; Laederach, A.; Montimurro, J.; Yearout, D.; Kay, D.M.; Doheny, K.F.; Paschall, J.; Pugh, E.; et al. Common genetic variation in the HLA region is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, S.; Coetzee, G.A. Parkinson’s disease-associated genetic variation is linked to quantitative expression of inflammatory genes. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wissemann, W.T.; Hill-Burns, E.M.; Zabetian, C.P.; Factor, S.A.; Patsopoulos, N.; Hoglund, B.; Holcomb, C.; Donahue, R.J.; Thomson, G.; Erlich, H.; et al. Association of Parkinson Disease with Structural and Regulatory Variants in the HLA Region. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, A.S.; Cao, S.; Rowse, A.L.; Thome, A.D.; Li, X.; Mangieri, L.R.; Cron, R.Q.; Shacka, J.J.; Raman, C.; Standaert, D.G. MHCII is required for α-synuclein-induced activation of microglia, CD4 T cell proliferation and dopaminergic neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 9592–9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebrián, C.; Loike, J.D.; Sulzer, D. Neuronal MHC-I expression and its implications in synaptic function, axonal regeneration and Parkinson’s and other brain diseases. Front. Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payami, H.; Schellenberg, G.D.; Zareparsi, S.; Kaye, J.; Sexton, G.J.; Head, M.A.; Matsuyama, S.S.; Jarvik, L.F.; Miller, B.; McManus, D.Q.; et al. Evidence for association of HLA-A2 allele with onset age of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 1997, 49, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.L.; Tang, N.L.; Tam, C.W.; Lui, V.W.; Suen, E.W.; Chiu, H.F.; Lam, L.C. Association between HLA-A alleles and Alzheimer’s disease in a southern Chinese community. Dement. Geriatr. Cognit. Disord. 2008, 26, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, G.W.; Scott, W.K.; Komo, S.; Yamaoka, L.H.; Farrer, L.A.; Auerbach, S.H.; Saunders, A.M.; Roses, A.D.; Haines, J.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A. No association between the HLA-A2 allele and Alzheimer disease. Neurogenetics 1999, 2, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araria-Goumidi, L.; Lambert, J.C.; Cottel, D.; Amouyel, P.; Chartier-Harlin, M.C. No association of the HLA-A2 allele with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 335, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listì, F.; Candore, G.; Balistreri, C.R.; Grimaldi, M.P.; Orlando, V.; Vasto, S.; Colonna-Romano, G.; Lio, D.; Licastro, F.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Association between the HLA-A2 allele and Alzheimer disease. Rejuvenation Res. 2006, 9, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cifuentes, R.A.; Murillo-Rojas, J. Alzheimer’s Disease and HLA-A2: Linking neurodegenerative to immune processes through an In silico approach. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 791238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medana, I.M.; Gallimore, A.; Oxenius, A.; Martinic, M.M.; Wekerle, H.; Neumann, H. MHC class I-restricted killing of neurons by virus-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes is effected through the Fas/FasL but not the perforin pathway. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 3623–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.A.; Sage, J.R.; Wood, S.C.; Davenport, C.M.; Anagnostaras, S.G.; Boulanger, L.M. MHC class I immune proteins are critical for hippocampus-dependent memory and gate NMDAR-dependent hippocampal long-term depression. Learn. Mem. 2013, 20, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glynn, M.W.; Elmer, B.M.; Garay, P.A.; Liu, X.B.; Needleman, L.A.; El-Sabeawy, F.; McAllister, A.K. MHCI negatively regulates synapse density during the establishment of cortical connections. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, A.; Cacabelos, R.; Sanpedro, C.; García-Fantini, M.; Aleixandre, M. Serum TNF-α Levels Are Increased and Correlate Negatively with Free IGF-I in Alzheimer Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuliani, G.; Ranzini, M.; Guerra, G.; Rossi, L.; Munari, M.R.; Zurlo, A.; Volpato, S.; Atti, A.R.; Blè, A.; Fellin, R. Plasma Cytokines Profile in Older Subjects with Late Onset Alzheimer’s Disease or Vascular Dementia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkhelfa, M.; Rafa, H.; Medjeber, O.; Arroul-Lammali, A.; Behairi, N.; Abada-Bendib, M.; Makrelouf, M.; Belarbi, S.; Masmoudi, A.N.; Tazir, M.; et al. IFN-γ and TNF-α Are Involved during Alzheimer Disease Progression and Correlate with Nitric Oxide Production: A Study in Algerian Patients. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swardfager, W.; Lanctôt, K.; Rothenburg, L.; Wong, A.; Cappell, J.; Herrmann, N. A meta-analysis of cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodacki, B.; Staszewski, J.; Toczyłowska, B.; Kozłowska, E.; Drela, N.; Chalimoniuk, M.; Stępien, A. Serum Interleukin (IL-2, IL-10, IL-6, IL-4), TNFα and INFγ Concentrations Are Elevated in Patients with Atypical and Idiopathic Parkinsonism. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 441, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziorowski, D.; Tomasiuk, R.; Szlufik, S.; Friedman, A. Inflammatory Cytokines and NT-proCNP in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Cytokine 2012, 60, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.-Y.; Zhang, S.-P.; Cao, C.; Loh, Y.P.; Cheng, Y. Aberrations in Peripheral Inflammatory Cytokine Levels in Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, S.; Britschgi, M.; Herbert, C.; Takeda-Uchimura, Y.; Boxer, A.; Blennow, K.; Friedman, L.F.; Galasko, D.R.; Jutel, M.; Karydas, A.; et al. Classification and prediction of clinical Alzheimer’s diagnosis based on plasma signaling proteins. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.C.; Ala, T.A.; Hu, S.; Crossley, K.B.; Sherman, R.E.; Peterson, P.K.; Frey, W.H. Serum Cytokine Levels in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1994, 1, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corsi, M.M.; Licastro, F.; Porcellini, E.; Dogliotti, G.; Galliera, E.; Lamont, J.L.; Innocenzi, P.J.; Fitzgerald, S.P. Reduced Plasma Levels of P-Selectin and L-Selectin in a Pilot Study from Alzheimer Disease: Relationship with Neuro-Degeneration. Biogerontology 2011, 12, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dursun, E.; Gezen-Ak, D.; Hanağas, H.; Bilgiç, B.; Lohmann, E.; Ertan, S.; Atasoy, İ.L.; Alaylıoğlu, M.; Araz, Ö.S.; Önal, B.; et al. The Interleukin 1 α, Interleukin 1 β, Interleukin 6 and α-2-Macroglobulin Serum Levels in Patients with Early or Late Onset Alzheimer’s Disease, Mild Cognitive Impairment or Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 283, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licastro, F.; Pedrini, S.; Caputo, L.; Annoni, G.; Davis, L.J.; Ferri, C.; Casadei, V.; Grimaldi, L.M. Increased Plasma Levels of Interleukin-1, Interleukin-6 and α-1-Antichymotrypsin in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: Peripheral Inflammation or Signals from the Brain? J. Neuroimmunol. 2000, 103, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, L.; Motta, M.; Di Rosa, M.; Anzaldi, M.; Malaguarnera, M. Interleukin-18 and Transforming Growth Factor-β 1 Plasma Levels in Alzheimer’s Disease and Vascular Dementia. Neuropathology 2006, 26, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, M.; Imbesi, R.; Di Rosa, M.; Stivala, F.; Malaguarnera, L. Altered Plasma Cytokine Levels in Alzheimer’s Disease: Correlation with the Disease Progression. Immunol. Lett. 2007, 114, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossù, P.; Ciaramella, A.; Salani, F.; Bizzoni, F.; Varsi, E.; Di Iulio, F.; Giubilei, F.; Gianni, W.; Trequattrini, A.; Moro, M.L.; et al. Interleukin-18 Produced by Peripheral Blood Cells Is Increased in Alzheimer’s Disease and Correlates with Cognitive Impairment. Brain Behav. Immun. 2008, 22, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, C.; Chromek, M.; Ahrengart, L.; Brauner, A.; Schultzberg, M.; Garlind, A. Soluble Interleukin-1 Receptor Type II, IL-18 and Caspase-1 in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Severe Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem. Int. 2005, 46, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, I.-U.; Kim, J.-S.; Chung, S.-W.; Lee, K.S. Is There an Association between the Level of High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease? A Comparison of Parkinson’s Disease Patients, Disease Controls and Healthy Individuals. Eur. Neurol. 2009, 62, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamza, T.; Barnett, J.B.; Li, B. Interleukin 12 a key immunoregulatory cytokine in infection applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin 1 and interleukin 18 as mediators of inflammation and the aging process. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 447S–455S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, S.H.; Wright, T.T.; Shen, Z.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Zhu, W.; Potempa, L.A.; Ji, S.R.; Szalai, A.J.; Wu, Y. C-reactive protein directly suppresses Th1 cell differentiation and alleviates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5243–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjöberg, A.P.; Trouw, L.A.; McGrath, F.D.; Hack, C.E.; Blom, A.M. Regulation of complement activation by C-reactive protein: Targeting of the inhibitory activity of C4b-binding protein. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 7612–7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Lin, J.X.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Leonard, W.J. Modulation of cytokine receptors by IL-2 broadly regulates differentiation into helper T cell lineages. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.H.; Im, S.H. Differential regulation of the IL-10 gene in Th1 and Th2 T cells. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1050, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, C.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Born, J.; Marshall, L. Enhancing Influence of Intranasal Interleukin-6 on Slow-Wave Activity and Memory Consolidation during Sleep. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 3629–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Rey, A.; Balschun, D.; Wetzel, W.; Randolf, A.; Besedovsky, H.O. A cytokine network involving brain-borne IL-1β, IL-1ra, IL-18, IL-6 and TNFα operates during long-term potentiation and learning. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 33, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, A.M.; Mukandala, G.; Greig, N.H.; O’Connor, J.J. Tumor necrosis factor-α potentiates long-term potentiation in the rat dentate gyrus after acute hypoxia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2015, 93, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Kamiya, H.; Morimoto, Y. Synapse-specific effects of IL-1β on long-term potentiation in the mouse hippocampus. Biomed. Res. 2017, 38, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasko, I.; Veerhuis, R.; Stampfer-Kountchev, M.; Saurwein-Teissl, M.; Eikelenboom, P.; Grubeck-Loebenstein, B. Costimulatory effects of interferon-gamma and interleukin-1β or tumor necrosis factor α on the synthesis of Abeta1–40 and Abeta1–42 by human astrocytes. Neurobiol. Dis. 2000, 7, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giunta, B.; Fernandez, F.; Nikolic, W.V.; Obregon, D.; Rrapo, E.; Town, T.; Tan, J. Inflammaging as a prodrome to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, T.; Ziegler, A.C.; Dimitrion, P.; Zuo, L. Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 2525967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Farias, C.C.; Maes, M.; Bonifácio, K.L.; Bortolasci, C.C.; de Souza Nogueira, A.; Brinholi, F.F.; Matsumoto, A.K.; do Nascimento, M.A.; de Melo, L.B.; Nixdorf, S.L.; et al. Highly specific changes in antioxidant levels and lipid peroxidation in Parkinson’s disease and its progression: Disease and staging biomarkers and new drug targets. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 23, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Bader Lange, M.L.; Sultana, R. Involvements of the lipid peroxidation product, HNE, in the pathogenesis and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markesbery, W.R.; Lovell, M.A. DNA oxidation in Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbulla, L.F.; Song, P.; Mazzulli, J.R.; Zampese, E.; Wong, Y.C.; Jeon, S.; Santos, D.P.; Blanz, J.; Obermaier, C.D.; Strojny, C.; et al. Dopamine oxidation mediates mitochondrial and lysosomal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Science 2017, 357, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitte, J.; Michel, B.F.; Bongrand, P.; Gastaut, J.L. Oxidative stress level in circulating neutrophils is linked to neurodegenerative diseases. J. Clin. Immunol. 2004, 24, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Kanthasamy, A.; Ghosh, A.; Anantharam, V.; Kalyanaraman, B.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants for treatment of Parkinson’s disease: Preclinical and clinical outcomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 1282–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, P.I.; Carvalho, C.; Zhu, X.; Smith, M.A.; Perry, G. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a trigger of Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, R.; Mecocci, P.; Mangialasche, F.; Cecchetti, R.; Baglioni, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Increased protein and lipid oxidative damage in mitochondria isolated from lymphocytes from patients with Alzheimer’s disease: Insights into the role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease and initial investigations into a potential biomarker for this dementing disorder. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 24, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markesberya, W.R. Oxidative Stress Hypothesis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.M.; Thomas, A.T.; Connor, J.; Nolan, Y.M. Contributions of central and systemic inflammation to the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2154–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunomura, A.; Perry, G.; Aliev, G.; Hirai, K.; Takeda, A.; Balraj, E.K.; Jones, P.K.; Ghanbari, H.; Wataya, T.; Shimohama, S.; et al. Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigione, A.; Isaias, I.U.; Galbussera, A.; Brighina, L.; Begni, B.; Andreoni, S.; Pezzoli, G.; Antonini, A.; Ferrarese, C. Increased oxidative stress in lymphocytes from untreated Parkinson’s disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2009, 15, 327–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.M.; Liu, J.L.; Wu, Y.R.; Chen, Y.C.; Cheng, H.S.; Cheng, M.L.; Chiu, D.T. Increased damage in peripheral blood correlates with severity of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 33, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, J.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K.; Banerjee, T.K.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Chakraborty, D.P.; Ray, B.C.; Rao, V.R. Plasma levels of lipid peroxides in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 13, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Padurariu, M.; Ciobica, A.; Hritcu, L.; Stoica, B.; Bild, W.; Stefanescu, C. Changes of some oxidative stress markers in the serum of patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 469, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moslemnezhad, A.; Mahjoub, S.; Moghadasi, M. Altered plasma marker of oxidative DNA damage and total antioxidant capacity in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2016, 7, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Mecocci, P.; Polidori, M.C.; Cherubini, A.; Ingegni, T.; Mattioli, P.; Catani, M.; Rinaldi, P.; Cecchetti, R.; Stahl, W.; Senin, U.; et al. Lymphocyte oxidative DNA damage and plasma antioxidants in Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwinska, A.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Czarny, P.; Toma, M.; Wigner, P.; Drzewoski, J.; Fabianowska-Majewska, K.; Szemraj, J.; Maes, M.; Galecki, P.; et al. The levels of 7,8-dihydrodeoxyguanosine (8-oxoG) and 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1)—A potential diagnostic biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 15, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schippling, S.; Kontush, A.; Arlt, S.; Buhmann, C.; Stürenburg, H.J.; Mann, U.; Müller-Thomsen, T.; Beisiegel, U. Increased lipoprotein oxidation in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthwal, M.K.; Srivastava, N.; Shukla, R.; Nag, D.; Seth, P.K.; Srimal, R.C.; Dikshit, M. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte nitrite content and antioxidant enzymes in Parkinson’s disease patients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1999, 100, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, H.; Bergman, M.; Djaldetti, R.; Bessler, H.; Djaldetti, M. Decreased phagocytic function in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 1999, 53, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shad, K.F.; Aghazadeh, Y.; Ahmad, S.; Kress, B. Peripheral markers of Alzheimer’s disease: Surveillance of white blood cells. Synapse 2013, 67, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenaro, E.; Pietronigro, E.; Della Bianca, V.; Piacentino, G.; Marongiu, L.; Budui, S.; Turano, E.; Rossi, B.; Angiari, S.; Dusi, S.; et al. Neutrophils promote Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and cognitive decline via LFA-1 integrin. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, P.F.; Fan, C.; Perou, C.M. Evaluating the comparability of gene expression in blood and brain. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2006, 141B, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molochnikov, L.; Rabey, M.; Dobronevsky, E.; Bonucelli, U.; Ceravolo, R.; Frosini, D.; Grünblatt, E.; Riederer, P.; Jacob, C.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; et al. A molecular signature in blood identifies early Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2012, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Booij, B.B.; Lindahl, T.; Wetterberg, P.; Skaane, N.V.; Sæbø, S.; Feten, G.; Rye, P.D.; Kristiansen, L.I.; Hagen, N.; Jensen, M.; et al. A gene expression pattern in blood for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 23, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yenari, M.A.; Giffard, R.G.; Sapolsky, R.M.; Steinberg, G.K. The Neuroprotective potential of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70). Mol. Med. Today 1999, 5, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giffard, R.G.; Xu, L.; Zhao, H.; Carrico, W.; Ouyang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Sapolsky, R.; Steinberg, G.; Hu, B.; Yenari, M.A. Chaperones, protein aggregation and brain protection from hypoxic/ischemic injury. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207 Pt 18, 3213–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magran’e, J.; Smith, R.C.; Walsh, K.; Querfurth, H.W. Heat shock protein 70 participates in the neuroprotective response to intracellularly expressed β-amyloid in neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, T.; Murao, N.; Namba, T.; Takehara, M.; Adachi, H.; Katsuno, M.; Sobue, G.; Matsushima, T.; Suzuki, T.; Mizushima, T. Suppression of Alzheimer’s disease-related phenotypes by expression of heat shock protein 70 in mice. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5225–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrucelli, L.; Dickson, D.; Kehoe, K.; Taylor, J.; Snyder, H.; Grover, A.; De Lucia, M.; McGowan, E.; Lewis, J.; Prihar, G.; et al. CHIP and HSP70 regulate tau ubiquitination, degradation and aggregation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinwal, U.K.; O’Leary, J.C., III; Borysov, S.I.; Jones, J.R.; Li, Q.; Koren, J., 3rd; Abisambra, J.F.; Vestal, G.D.; Lawson, L.Y.; Johnson, A.G.; et al. Hsc70 rapidly engages tau after microtubule destabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16798–16805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, K.R.; Ward, S.M.; Combs, B.; Voss, K.; Kanaan, N.M.; Morfini, G.; Brady, S.T.; Gamblin, T.C.; Binder, L.I. Heat shock protein 70 prevents both tau aggregation and the inhibitory effects of preexisting tau aggregates on fast axonal transport. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 10300–10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, T.K.; Paul, S. Protein-misfolding diseases and chaperone-based therapeutic approaches. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 1331–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, H.; Katsuno, M.; Waza, M.; Minamiyama, M.; Tanaka, F.; Sobue, G. Heat shock proteins in neurodegenerative diseases: Pathogenic roles and therapeutic implications. Int. J. Hyperth. 2009, 25, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xilouri, M.; Stefanis, L. Chaperone mediated autophagy to the rescue: A new-fangled target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 66, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigione, A.; Piazza, F.; Brighina, L.; Begni, B.; Galbussera, A.; Difrancesco, J.C.; Andreoni, S.; Piolti, R.; Ferrarese, C. α-synuclein nitration and autophagy response are induced in peripheral blood cells from patients with Parkinson disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 477, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, G.; Stefanoni, G.; Arosio, A.; Riva, C.; Melchionda, L.; Saracchi, E.; Fermi, S.; Brighina, L.; Ferrarese, C. Reduced expression of the chaperone-mediated autophagy carrier hsc70 protein in lymphomonocytes of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2014, 1546, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Noort, J.M. Stress proteins in CNS inflammation. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, B.; Jia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Ren, G.; Wang, H. The detection and role of heat shock protein 70 in various nondisease conditions and disease conditions: A literature review. Cell Stress Chaperones 2015, 20, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.D.; Fleshner, M. Releasing signals, secretory pathways and immune function of endogenous extracellular heat shock protein 72. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Eden, W.; van der Zee, R.; Prakken, B. Heat-shock proteins induce T-cell regulation of chronic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pockley, A.G.; Henderson, B.; Multhoff, G. Extracellular cell stress proteins as biomarkers of human disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njemini, R.; Demanet, C.; Mets, T. Inflammatory status as an important determinant of heat shock protein 70 serum concentrationsduring aging. Biogerontology 2004, 5, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalenko, E.I.; Boyko, A.A.; Semenkov, V.F.; Lutsenko, G.V.; Grechikhina, M.V.; Kanevskiy, L.M.; Azhikina, T.L.; Telford, W.G.; Sapozhnikov, A.M. ROS production, HSP70 levels and their relationship in neutrophils: Effects of age. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11800–11812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boyko, A.A.; Troyanova, N.I.; Kovalenko, E.I.; Sapozhnikov, A.M. Similarity and Differences in Inflammation-Related Characteristics of the Peripheral Immune System of Patients with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122633
Boyko AA, Troyanova NI, Kovalenko EI, Sapozhnikov AM. Similarity and Differences in Inflammation-Related Characteristics of the Peripheral Immune System of Patients with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122633
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoyko, Anna A., Natalya I. Troyanova, Elena I. Kovalenko, and Alexander M. Sapozhnikov. 2017. "Similarity and Differences in Inflammation-Related Characteristics of the Peripheral Immune System of Patients with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122633
APA StyleBoyko, A. A., Troyanova, N. I., Kovalenko, E. I., & Sapozhnikov, A. M. (2017). Similarity and Differences in Inflammation-Related Characteristics of the Peripheral Immune System of Patients with Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2633. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122633