Mast Cells Interact with Endothelial Cells to Accelerate In Vitro Angiogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
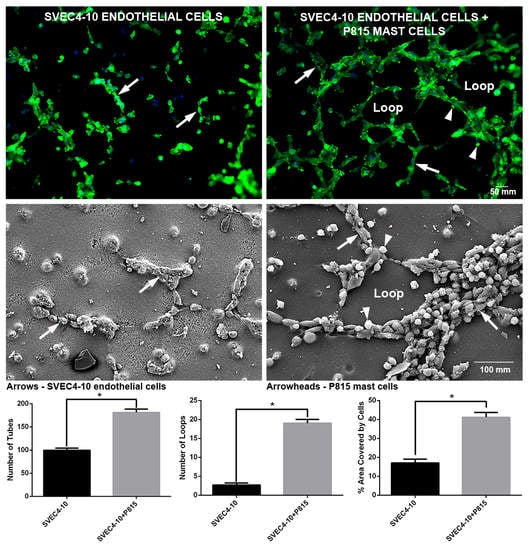
2.1. Mast Cells Accelerate In Vitro Angiogenesis
2.2. Mast Cells and Endothelial Cells Are Associated
2.3. Gap Junctions Connect Endothelial Cells and Mast Cells
2.4. Angiogenic Factors Are Released by Endothelial Cells in the Presence of Mast Cells
2.5. Conditioned Medium from the Co-Cultures Increases Tube Formation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells
4.2. In Vitro Angiogenesis: Tube Formation Assay
4.3. CellTracker™ Cell Labelling
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. Fluorescent Labeling
4.6. Expression Profile of Angiogenesis Related Proteins
4.7. Electron Microscopy
4.7.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4.7.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.8. Immunoblotting
4.9. β-Hexosamidase Assay
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baer, C.; Squadrito, M.L.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L.; de Palma, M. Reciprocal interactions between endothelial cells and macrophages in angiogenic vascular niches. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodarev, N.N.; Yu, J.; Labay, E.; Darga, T.; Brown, C.K.; Mauceri, H.J.; Yassari, R.; Gupta, N.; Weichselbaum, R.R. Tumour-endothelium interactions in co-culture: Coordinated changes of gene expression profiles and phenotypic properties of endothelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Groopman, J.E.; Wang, J.F. Extracellular matrix regulates endothelial functions through interaction of VEGFR-3 and integrin α5β1. J. Cell Physiol. 2005, 202, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuger, J.; Phillipson, M. Targeting vascular and leukocyte communication in angiogenesis, inflammation and fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freudenberg, U.; Zieris, A.; Chwalek, K.; Tsurkan, M.V.; Maitz, M.F.; Atallah, P.; Levental, K.R.; Eming, S.A.; Werner, C. Heparin desulfation modulates VEGF release and angiogenesis in diabetic wounds. J. Control Release 2015, 220, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebner, S.; Cavallaro, U.; Dejana, E. The multiple languages of endothelial cell-to-cell communication. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalamon, V.; Fiori, M.C.; Figueroa, V.A.; Oliva, C.A.; del Rio, R.; Gonzalez, W.; Canan, J.; Elgoyhen, A.B.; Altenberg, G.A.; Retamal, M.A. Gap-junctional channel and hemichannel activity of two recently identified connexin 26 mutants associated with deafness. Pflugers Arch. 2016, 468, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, X.F.; Duling, B.R. Gap junctions in the control of vascular function. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzoni, G.; Dejana, E. Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions: Molecular organization and role in vascular homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 869–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leithe, E. Regulation of connexins by the ubiquitin system: Implications for intercellular communication and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1865, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oviedo-Orta, E.; Howard Evans, W. Gap junctions and connexin-mediated communication in the immune system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1662, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radeva, M.Y.; Waschke, J. Mind the gap: Mechanisms regulating the endothelial barrier. Acta Physiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuringer, D.; Boucher, J.; Jego, G.; Pernet, N.; Cronier, L.; Hammann, A.; Solary, E.; Garrido, C. Transfer of functional micrornas between glioblastoma and microvascular endothelial cells through gap junctions. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 73925–73934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.G.; Zhang, F.X.; Chen, M.L.; Zhu, H.J.; Yang, B.; Cao, K.J. Cx43 in mesenchymal stem cells promotes angiogenesis of the infarcted heart independent of gap junctions. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.; Laxton, V.; Srivastava, S.; Chan, Y.W.; Tse, G. The role of gap junctions in inflammatory and neoplastic disorders. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, A.M.; Snyder, E.G.; Taffet, S.M. Connexins and pannexins in the immune system and lymphatic organs. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2015, 72, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vliagoftis, H.; Ebeling, C.; Ilarraza, R.; Mahmudi-Azer, S.; Abel, M.; Adamko, D.; Befus, A.D.; Moqbel, R. Connexin 43 expression on peripheral blood eosinophils: Role of gap junctions in transendothelial migration. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 803257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danese, S.; Sans, M.; de la Motte, C.; Graziani, C.; West, G.; Phillips, M.H.; Pola, R.; Rutella, S.; Willis, J.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Angiogenesis as a novel component of inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 2060–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bremnes, R.M.; Dønnem, T.; Al-Saad, S.; Al-Shibli, K.; Andersen, S.; Sirera, R.; Camps, C.; Marinez, I.; Busund, L.T. The role of tumor stroma in cancer progression and prognosis: Emphasis on carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamur, M.C.; Grodzki, A.C.; Berenstein, E.H.; Hamawy, M.M.; Siraganian, R.P.; Oliver, C. Identification and characterization of undifferentiated mast cells in mouse bone marrow. Blood 2005, 105, 4282–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soucie, E.; Brenet, F.; Dubreuil, P. Molecular basis of mast cell disease. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 63, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, E.Z.; Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C. Mast cell function: A new vision of an old cell. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 698–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krystel-Whittemore, M.; Dileepan, K.N.; Wood, J.G. Mast cell: A multi-functional master cell. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilfillan, A.M.; Austin, S.J.; Metcalfe, D.D. Mast cell biology: Introduction and overview. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 716, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C. Origin, maturation and recruitment of mast cell precursors. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 1390–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, H.; Tian, D.; Li, X.; Ning, Y.; Yin, L. Tryptase promotes atherosclerotic plaque haemorrhage in ApoE-/-mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, R.J.; Meng, H.; Marchese, M.J.; Ren, S.; Schwartz, L.B.; Tonnesen, M.G.; Gruber, B.L. Human mast cells stimulate vascular tube formation. Tryptase is a novel, potent angiogenic factor. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.W.; Tedla, N.; Lloyd, A.R.; Wakefield, D.; McNeil, P.H. Mast cell activation and migration to lymph nodes during induction of an immune response in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1617–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, D.A.; Borges, A.C.; Santana, A.C.; Oliver, C.; Jamur, M.C. Mast cell proteases 6 and 7 stimulate angiogenesis by inducing endothelial cells to release angiogenic factors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Białas, M.; Dyduch, G.; Szpor, J.; Demczuk, S.; Okoń, K. Microvascular density and mast cells in benign and malignant pheochromocytomas. Pol. J. Pathol. 2012, 63, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyduch, G.; Kaczmarczyk, K.; Okoń, K. Mast cells and cancer: Enemies or allies? Pol. J. Pathol. 2012, 63, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cimpean, A.M.; Tamma, R.; Ruggieri, S.; Nico, B.; Toma, A.; Ribatti, D. Mast cells in breast cancer angiogenesis. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 115, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varricchi, G.; Galdiero, M.R.; Loffredo, S.; Marone, G.; Iannone, R.; Granata, F. Are mast cells masters in cancer? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Ranieri, G. Tryptase, a novel angiogenic factor stored in mast cell granules. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 332, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, S.K.; Dasgupta, S.; Mandal, P.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Chakraborty, D. Is there any role of mast cell density and microvessel density in cervical squamous cell carcinoma? A histologic study with special reference to cd-34 immunomarker staining. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2014, 35, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, D.K.; Noelle, R.J. The roles of mast cells in anticancer immunity. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2012, 61, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hua, Y.; Shen, Q.; Ding, S.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, X. Role of mast cells in gynecological neoplasms. Front. Biosci. 2013, 18, 773–781. [Google Scholar]
- Crivellato, E.; Nico, B.; Ribatti, D. Mast cells and tumour angiogenesis: New insight from experimental carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.; Huynh, V.; Hargrove, L.; Kennedy, L.; Graf-Eaton, A.; Owens, J.; Trzeciakowski, J.P.; Hodges, K.; DeMorrow, S.; Han, Y.; et al. Inhibition of mast cell-derived histamine decreases human cholangiocarcinoma growth and differentiation via c-Kit/stem cell factor-dependent signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinaccio, C.; Ingravallo, G.; Gaudio, F.; Perrone, T.; Nico, B.; Maoirano, E.; Specchia, G.; Ribatti, D. Microvascular density, CD68 and tryptase expression in human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 1374–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCicco-Skinner, K.L.; Henry, G.H.; Cataisson, C.; Tabib, T.; Gwilliam, J.C.; Watson, N.J.; Bullwinkle, E.M.; Falkenburg, L.; O’Neill, R.C.; Morin, A.; et al. Endothelial cell tube formation assay for the in vitro study of angiogenesis. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 91, e51312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaoutova, I.; Kleinman, H.K. In vitro angiogenesis: Endothelial cell tube formation on gelled basement membrane extract. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunderkötter, C.; Steinbrink, K.; Goebeler, M.; Bhardwaj, R.; Sorg, C. Macrophages and angiogenesis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1994, 55, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nucera, S.; Biziato, D.; de Palma, M. The interplay between macrophages and angiogenesis in development, tissue injury and regeneration. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffelt, S.B.; Hughes, R.; Lewis, C.E. Tumor-associated macrophages: Effectors of angiogenesis and tumor progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1796, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.E.; Hartmann, K.; Roers, A.; Krummel, M.F.; Locksley, R.M. Perivascular mast cells dynamically probe cutaneous blood vessels to capture immunoglobulin E. Immunity 2013, 38, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Almeida Buranello, P.A.; Moulin, M.R.; Souza, D.A.; Jamur, M.C.; Roque-Barreira, M.C.; Oliver, C. The lectin artinm induces recruitment of rat mast cells from the bone marrow to the peritoneal cavity. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9776. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, A.L.; Jackson, T.L.; Jiang, Y. A cell-based model exhibiting branching and anastomosis during tumor-induced angiogenesis. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 3105–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.W.; Bazou, D.; Munn, L.L. Anastomosis of endothelial sprouts forms new vessels in a tissue analogue of angiogenesis. Integr. Biol. 2012, 4, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Santana, A.; Shan, M.; Stroock, A.D. Endothelial cell dynamics during anastomosis in vitro. Integr. Biol. 2015, 7, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fantin, A.; Vieira, J.M.; Gestri, G.; Denti, L.; Schwarz, Q.; Prykhozhij, S.; Peri, F.; Wilson, S.W.; Ruhrberg, C. Tissue macrophages act as cellular chaperones for vascular anastomosis downstream of VEGF-mediated endothelial tip cell induction. Blood 2010, 116, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, X.F.; Isakson, B.E.; Duling, B.R. Connexins: Gaps in our knowledge of vascular function. Physiology 2004, 19, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brink, P.R.; Ricotta, J.; Christ, G.J. Biophysical characteristics of gap junctions in vascular wall cells: Implications for vascular biology and disease. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2000, 33, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leithe, E.; Mesnil, M.; Aasen, T. The connexin 43 C-terminus: A tail of many tales. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1860, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleisner, M.A.; Navarrete, M.; Hofmann, F.; Salazar-Onfray, F.; Tittarelli, A. Mind the gaps in tumor immunity: Impact of connexin-mediated intercellular connections. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, B.R.; Mulhaupt, F.; Veillard, N.; Gros, D.B.; Mach, F. Altered pattern of vascular connexin expression in atherosclerotic plaques. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polacek, D.; Bech, F.; McKinsey, J.F.; Davies, P.F. Connexin43 gene expression in the rabbit arterial wall: Effects of hypercholesterolemia, balloon injury and their combination. J. Vasc. Res. 1997, 34, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vliagoftis, H.; Hutson, A.M.; Mahmudi-Azer, S.; Kim, H.; Rumsaeng, V.; Oh, C.K.; Moqbel, R.; Metcalfe, D.D. Mast cells express connexins on their cytoplasmic membrane. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, X.F.; Isakson, B.E.; Duling, B.R. Vascular gap junctions in hypertension. Hypertension 2006, 48, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistorio, A.L.; Ehrlich, H.P. Modulatory effects of connexin-43 expression on gap junction intercellular communications with mast cells and fibroblasts. J. Cell Biochem. 2011, 112, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.R.; Au, K.; Saggers, G.C.; Karne, N.; Ehrlich, H.P. Rat mast cells communicate with fibroblasts via gap junction intercellular communications. J. Cell Biochem. 2007, 100, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, T.T.; Saggers, G.C.; Moyer, K.E.; Ehrlich, H.P. Rat mast cells enhance fibroblast proliferation and fibroblast-populated collagen lattice contraction through gap junctional intercellular communications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 1478–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza Junior, D.A.; Santana, A.C.; da Silva, E.Z.; Oliver, C.; Jamur, M.C. The role of mast cell specific chymases and tryptases in tumor angiogenesis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Ranieri, G.; Nico, B.; Benagiano, V.; Crivellato, E. Tryptase and chymase are angiogenic in vivo in the chorioallantoic membrane assay. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, J.H.; Hirth, A.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S.; Distler, O. Angiogenic and angiostatic factors in the molecular control of angiogenesis. Q. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 47, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dunn, T.B.; Potter, M. A transplantable mast-cell neoplasm in the mouse. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1957, 18, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furuno, T.; Teshima, R.; Kitani, S.; Sawada, J.; Nakanishi, M. Surface expression of CD63 antigen (AD1 antigen) in P815 mastocytoma cells by transfected IgE receptors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 219, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.; Alber, G.; Varin-Blank, N.; Ludowyke, R.; Metzger, H. Transmembrane signaling in P815 mastocytoma cells by transfected ige receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 12444–12453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schindler, R.; Day, M.; Fischer, G.A. Culture of neoplastic mast cells and their synthesis of 5-hydroxytryptamine and histamine in vitro. Cancer Res. 1959, 19, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khoo, C.P.; Micklem, K.; Watt, S.M. A comparison of methods for quantifying angiogenesis in the matrigel assay in vitro. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2011, 17, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Park, Y.L.; Kim, N.; Oh, H.H.; Son, D.J.; Kim, M.Y.; Oak, C.Y.; Chung, C.Y.; Park, H.C.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Myeloid cell leukemia-1 is associated with tumor progression by inhibiting apoptosis and enhancing angiogenesis in colorectal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Askou, A.L.; Aagaard, L.; Kostic, C.; Arsenijevic, Y.; Hollensen, A.K.; Bek, T.; Jensen, T.G.; Mikkelsen, J.G.; Corydon, T.J. Multigenic lentiviral vectors for combined and tissue-specific expression of miRNA- and protein-based antiangiogenic factors. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2015, 2, 14064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Angiogenic Factor | SVEC4-10 Cells | SVEC4-10 + P815 Cells | Angiogenic Factor | SVEC4-10 Cells | SVEC4-10 + P815 Cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAMTS1 | − | + | MMP-8 | − | + |
| Amfiregulin | − | + | MMP-9 | − | + |
| Angiogenin | + | + | IGFBP-9 | − | + |
| Coagulation III | − | + | Osteopontin | − | + |
| CXCL16 | − | + | PDGF-AA | − | + |
| DPPIV/CD26 | − | + | PDGF | − | + |
| Endostatin | + | + | Pentraxin | − | + |
| Endothelin 1 | − | + | PF 4 | + | + |
| FGF-1 | − | + | PlGF-2 | − | + |
| FGF-2 | − | + | Prolactin | − | + |
| Hepatopoietin A | − | + | Proliferin | − | + |
| IGFBP-1 | − | + | SDF-1 CXCL12 | − | + |
| IGFBP-2 | − | + | Serpin E1 | − | + |
| IGFBP-3 | + | + | Serpin F1 | − | + |
| IL-1 | − | + | Trombospondin-2 | − | + |
| Leptin | − | + | TIMP-1 | − | + |
| MCP-1 | + | + | TIMP-4 | − | + |
| MIP-1 | − | + | VEGF VPF | − | + |
| MMP-3 | − | + | VEGF-B VRF | − | + |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Souza Junior, D.A.; Mazucato, V.M.; Santana, A.C.; Oliver, C.; Jamur, M.C. Mast Cells Interact with Endothelial Cells to Accelerate In Vitro Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122674
De Souza Junior DA, Mazucato VM, Santana AC, Oliver C, Jamur MC. Mast Cells Interact with Endothelial Cells to Accelerate In Vitro Angiogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122674
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Souza Junior, Devandir Antonio, Vivian Marino Mazucato, Ana Carolina Santana, Constance Oliver, and Maria Celia Jamur. 2017. "Mast Cells Interact with Endothelial Cells to Accelerate In Vitro Angiogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122674
APA StyleDe Souza Junior, D. A., Mazucato, V. M., Santana, A. C., Oliver, C., & Jamur, M. C. (2017). Mast Cells Interact with Endothelial Cells to Accelerate In Vitro Angiogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122674