Proteomic Analysis Reveals Coordinated Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis through Signal Transduction and Sugar Metabolism in Black Rice Leaf
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. General Information on iTRAQ Analysis
2.2. Comparative Analysis of Protein Expression at Five Developmental Stages
2.3. Cluster Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins
2.4. Validation Using Quantitative RT-PCR
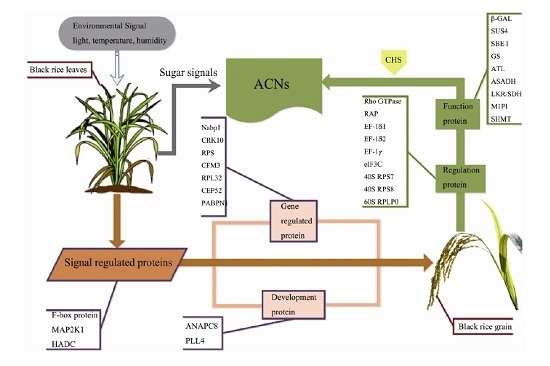
3. Discussion
3.1. Signal Regulation-Related Proteins
3.2. Phytohormone Proteins
3.3. Gene Expression Regulatory Proteins
3.4. Carbohydrate Metabolism-Related Proteins
3.5. Development-Associated Protein
3.6. Other Proteins
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Sampling
4.2. Protein Extraction and Digestion
4.3. iTRAQ Labeling and Strong Cation Exchange
4.4. LC-MSMS Analysis
4.5. Database Search and Protein Quantification
4.6. Bioinformatics Functional Analysis
4.7. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sompong, R.; Siebenhandl-Ehn, S.; Linsberger-Martin, G.; Berghofer, E. Physicochemical and antioxidative properties of red and black rice varieties from Thailand, China and Sri Lanka. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Sasaki, N.; Ohmiya, A. Biosynthesis of plant pigments: Anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant J. 2008, 54, 733–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, J.A.; Kasum, C.M. Dietary flavonoids: Bioavailability, metabolic effects, and safety. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2002, 22, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broun, P. Transcription factors as tools for metabolic engineering in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Ishimaru, M.; Ding, C.; Yakushiji, H.; Goto, N. Comparison of UDP-glucose: Flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase (UFGT) gene sequences between white grapes (Vitis vinifera) and their sports with red skin. Plant Sci. 2001, 160, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czemmel, S.; Heppel, S.C.; Bogs, J. R2R3 MYB transcription factors: Key regulators of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in grapevine. Protoplasma 2012, 249, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.S.; Xu, C.J.; Zhang, W.S.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Lin-Wang, K.; Ferguson, I.B.; Allan, A.C.; Chen, K.S. Coordinated regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) fruit by a R2R3 MYB transcription factor. Planta 2010, 231, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.G.; Kim, J.H.; Min, S.Y.; Shin, K.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Ryu, S.N.; Ahn, J.H. Anthocyanin content in rice is related to expression levels of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes. J. Plant Biol. 2007, 50, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boss, P.K.; Davies, C.; Robinson, S.P. Analysis of the expression of anthocyanin pathway genes in developing Vitis vinifera L. cv Shiraz grape berries and the implications for pathway regulation. Plant Physiol. 1996, 111, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroni, K.; Tonelli, C. Recent advances on the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis in reproductive organs. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, I.S.; Fennell, A.Y.; Haynes, P.A. Protein identification and quantification from riverbank grape, Vitis riparia: Comparing SDS-PAGE and FASP-GPF techniques for shotgun proteomic analysis. Proteomics 2015, 15, 3061–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erde, J.; Loo, R.R.; Loo, J.A. Enhanced FASP (eFASP) to increase proteome coverage and sample recovery for quantitative proteomic experiments. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.H.; Huang, Y.N.; Xu, M.; Cheng, Z.X.; Zhang, D.S.; Zheng, J.G. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics analysis of black rice grain development reveals metabolic pathways associated with anthocyanin biosynthesis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loreti, E.; Povero, G.; Novi, G.; Solfanelli, C.; Alpi, A.; Perata, P. Gibberellins, jasmonate and abscisic acid modulate the sucrose-induced expression of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2008, 179, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.T.; Qi, Y.P.; Lu, Y.B.; Guo, P.; Sang, W.; Feng, H.; Zhang, H.X.; Chen, L.S. TRAQ protein profile analysis of Citrus sinensis roots in response to long-term boron-deficiency. J. Proteom. 2013, 93, 179–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradet-Balade, B.; Boulmé, F.; Beug, H.; Müllner, E.W.; Garcia-Sanz, J.A. Translation control: Bridging the gap between genomics and proteomics. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajduch, M.; Ganapathy, A.; Stein, J.W.; Thelen, J.J. A systematic proteomic study of seed filling in soybean. Establishment of high-resolution two-dimensional reference maps, expression profiles, and an interactive proteome database. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 1397–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Stepaniants, S.B.; Mao, M.; Weng, L.; Feetham, M.C.; Doyle, M.J.; Yi, E.C.; Dai, H.Y.; Eng, J.; Thorsson, V.; et al. Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of gene expression in mammalian cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Vargas, F.; Jiménez, A.R.; Paredes-López, O. Natural pigments: Carotenoids, anthocyanins, and betalains-characteristics, biosynthesis, processing, and stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 173–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, S.I. Control of plant development and gene expression by sugar signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005, 8, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolland, F.; Baena-Gonzalez, E.; Sheen, J. Sugar sensing and signaling in plants: Conserved and novel mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 675–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, N.W.; Lewis, D.H.; Zhang, H.; Schwinn, K.E.; Jameson, P.E.; Davies, K.M. Members of an R2R3-MYB transcription factor family in Petunia are developmentally and environmentally regulated to control complex floral and vegetative pigmentation patterning. Plant J. 2011, 65, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espley, R.V.; Hellens, R.P.; Putterill, J.; Stevenson, D.E.; Kutty-Amma, S.; Allan, A.C. Red colouration in apple fruit is due to the activity of the MYB transcription factor, MdMYB10. Plant J. 2007, 49, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trakhtenberg, S.; Hangun-Balkir, Y.; Warner, J.C.; Bruno, F.F.; Kumar, J.; Nagarajan, R.; Samuelson, L.A. Photo-cross-linked immobilization of polyelectrolytes for enzymatic construction of conductive nanocomposites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 9100–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daub, M.E.; Ehrenshaft, M. The photoactivated Cercospora toxin cercosporin: Contributions to plant disease and fundamental biology. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2000, 38, 461–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.C.; Lee, C.T. Enhanced enzymatic activity through photoreversible conformational changes. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 14557–14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stracke, R.; Favory, J.J.; Gruber, H.; Bartelniewoehner, L.; Bartels, S.; Binkert, M.; Funk, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Ulm, R. The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor HY5 regulates expression of the PFG1/MYB12 gene in response to light and ultraviolet-B radiation. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.L.; Chen, C.S.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.H.; Li, P.M.; Ma, F.W. Reactive oxygen species produced via plasma membrane NADPH oxidase regulate anthocyanin synthesis in apple peel. Planta 2014, 240, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ban, Z.J.; Li, X.H.; Wu, M.Y.; Wang, A.L.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Jiang, Y.H. Differential expression of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes and transcription factor PcMYB10 in pears (Pyrus communis L.). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46070. [Google Scholar]
- Telias, A.; Bradeen, J.M.; Luby, J.J.; Hoover, E.E.; Allen, A.C. Regulation of anthocyanin accumulation in apple peel. Hortic. Rev. 2011, 38, 357–391. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Song, T.T.; Wan, H.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Yao, Y.C. McMYB10 regulates coloration via activating McF3H and later structural genes in ever-red leaf crabapple. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 948–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Cao, S.; Shi, L.; Chen, W.; Su, X.; Yang, Z. Blue light irradiation affects anthocyanin content and enzyme activities involved in postharvest strawberry fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4778–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.K.; Geul, B.; Choi, S.B.; Yoo, S.D.; Park, Y.I. Photosynthesis-dependent anthocyanin pigmentation in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potuschak, T.; Lechner, E.; Parmentier, Y.; Yanagisawa, S.; Grava, S.; Koncz, C.; Genschik, P. EIN3-dependent regulation of plant ethylene hormone signaling by two Arabidopsis F box proteins: EBF1 and EBF2. Cell 2003, 115, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Jang, J. F-box proteins in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimura, K.; Shinozaki, K.; Tena, G.; Sheen, J.; Henry, Y.; Champion, A.; Kreis, M.; Zhang, S.Q.; Hirt, H.; Wilson, C. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plants: A new nomenclature. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Bolouri Moghaddam, M.R.; Van den Ende, W. Sweet immunity in the plant circadian regulatory network. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1439–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memelink, J.; Kijne, J.W.; van der Heijden, R.; Verpoorte, R. Genetic modification of plant secondary metabolite pathways using transcriptional regulators. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2001, 72, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cowan, K.J.; Storey, K.B. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: New signaling pathways functioning in cellular responses to environmental stress. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, B.P.; Westerheide, S.D.; Baldwin, A.S. The p65 (RelA) subunit of NF-κB interacts with the histone deacetylase (HDAC) corepressors HDAC1 and HDAC2 to negatively regulate gene expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 7065–7077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberharter, A.; Becker, P.B. Histone acetylation: A switch between repressive and permissive chromatin. Second in review series on chromatin dynamics. EMBO Rep. 2002, 3, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; To, T.K.; Nishioka, T.; Seki, M. Chromatin regulation functions in plant abiotic stress responses. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santner, A.; Calderon-Villalobos, L.I.A.; Estelle, M. Plant hormones are versatile chemical regulators of plant growth. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazan, K.; Manners, J.M. Jasmonate signaling: Toward an integrated view. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Garcia, Y.; Romero-Cascales, I.; Gil-Muñoz, R.; Fernández-Fernández, J.I.; Lopez-Roca, J.M.; Gómez-Plaza, E. Improving grape phenolic content and wine chromatic characteristics through the use of two different elicitors: Methyl jasmonate versus benzothiadiazole. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Jin, P.; Cao, S.; Shang, H.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, Y. Methyl jasmonate reduces decay and enhances antioxidant capacity in Chinese bayberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5809–5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, P.; Vrhovsek, U.; Muth, J.; Segala, C.; Romualdi, C.; Fontana, P.; Pruefer, D.; Stefanini, M.; Moser, C.; Mattivi, F. Ripening and genotype control stilbene accumulation in healthy grapes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11773–11785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, H.; Urao, T.; Ito, T.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainz, M.B.; Grotewold, E.; Chandler, V.L. Evidence for direct activation of an anthocyanin promoter by the maize C1 protein and comparison of DNA binding by related Myb domain proteins. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, H.; Clendennen, S.K.; Caldwell, C.G.; Liu, X.L.; Connors, K.; Matheis, N.; Schuster, D.K.; Menasco, D.J.; Wagoner, W.; Lightner, J. Activation tagging in tomato identifies a transcriptional regulator of anthocyanin biosynthesis, modification, and transport. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1689–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Chen, Z. Identification of genes encoding receptor-like protein kinases as possible targets of pathogen-and salicylic acid-induced WRKY DNA-binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2000, 24, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Fan, B.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z. An important role of an inducible RNA-dependent RNA polymerase in plant antiviral defense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6516–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmay, T.; Hamilton, A.; Rudd, S.; Angell, S.; Baulcombe, D.C. An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene in Arabidopsis is required for posttranscriptional gene silencing mediated by a transgene but not by a virus. Cell 2000, 101, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrocchio, F.; Wing, J.F.; Leppen, H.; Mol, J.; Koes, R.E. Regulatory genes controlling anthocyanin pigmentation are functionally conserved among plant species and have distinct sets of target genes. Plant Cell 1993, 5, 1497–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.F.; Hua, D.P.; Chen, Z.Z.; Zhou, Z.J.; Gong, Z.Z. Elongator mediates ABA responses, oxidative stress resistance and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009, 60, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Longevialle, A.F.; Small, I.D.; Lurin, C. Nuclearly encoded splicing factors implicated in RNA splicing in higher plant organelles. Mol. Plant 2010, 3, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, S.C.; Tumer, N.E. Silencing of ribosomal protein L3 genes in N. tabacum reveals coordinate expression and significant alterations in plant growth, development and ribosome biogenesis. Plant J. 2004, 39, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Kim, G.T.; Shinozaki, K. Disruption of an Arabidopsis cytoplasmic ribosomal protein S13-homologous gene by transposon-mediated mutagenesis causes aberrant growth and development. Plant J. 2000, 22, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A.; Szick-Miranda, K.; Chang, I.F.; Guyot, R.; Blanc, G.; Cooke, R.; Delseny, M.; Bailey-Serres, J. The organization of cytoplasmic ribosomal protein genes in the Arabidopsis genome. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 398–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santner, A.; Estelle, M. The ubiquitin-proteasome system regulates plant hormone signaling. Plant J. 2010, 61, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprunck, S.; Baumann, U.; Edwards, K.; Langridge, P.; Dresselhaus, T. The transcript composition of egg cells changes significantly following fertilization in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant J. 2005, 41, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzeri, V.; Calvenzani, V.; Petroni, K.; Tonelli, C.; Castagna, A.; Ranieri, A. Carotenoid profiling and biosynthetic gene expression in flesh and peel of wild-type and hp-1 tomato fruit under UV-B depletion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4960–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnasooriya, S.N.; Porter, K.J.; Montgomery, B.L. Tissue-and isoform-specific phytochrome regulation of light-dependent anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirochika, H. Contribution of the Tos17 retrotransposon to rice functional genomics. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001, 4, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bennetzen, J.L. Retrotransposons: Central players in the structure, evolution and function of plant genomes. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 509–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butelli, E.; Licciardello, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Mackay, S.; Bailey, P.; Reforgiato-Recupero, G.; Martin, C. Retrotransposons control fruit-specific, cold-dependent accumulation of anthocyanins in blood oranges. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsy, M.R.; Jouve, L.; Hausman, J.F.; Hoffmann, L.; Stewart, J.M. Alteration of oxidative and carbohydrate metabolism under abiotic stress in two rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes contrasting in chilling tolerance. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 164, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillejo, M.A.; Amiour, N.; Dumas-Gaudot, E.; Rubiales, D.; Jorrı́n, J.V. A proteomic approach to studying plant response to crenate broomrape (Orobanche crenata) in pea (Pisum sativum). Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, H.; Yamane, H.; Maeshima, M.; Komatsu, S. Characterization of fructose- bisphosphate aldolase regulated by gibberellin in roots of rice seedling. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 56, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weckwerth, W.; Loureiro, M.E.; Wenzel, K.; Fiehn, O. Differential metabolic networks unravel the effects of silent plant phenotypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7809–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeekens, S.; Ma, J.; Hanson, J.; Rolland, F. Sugar signals and molecular networks controlling plant growth. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmer, D.P.; Haigler, C.H. The regulation of metabolic flux to cellulose, a major sink for carbon in plants. Metab. Eng. 2002, 4, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, T.; Motyka, V.; Laucou, V.; Smets, R.; van Onckelen, H.; Schmülling, T. Cytokinin-deficient transgenic Arabidopsis plants show multiple developmental alterations indicating opposite functions of cytokinins in the regulation of shoot and root meristem activity. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2532–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñeiro, M.; Jarillo, J.A. Ubiquitination in the control of photoperiodic flowering. Plant Sci. 2013, 198, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennman, A.; Oliw, E.H. Secretion of two novel enzymes, manganese 9S-lipoxygenase and epoxy alcohol synthase, by the rice pathogen Magnaporthe salvinii. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, L.E.; Bittnereddy, P.D.; Langley, C.H.; Holub, E.B.; Michelmore, R.W.; Beynon, J.L. The maintenance of extreme amino acid diversity at the disease resistance gene, RPP13, in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 2004, 166, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.B.; Li, T.; Deng, Z.Y.; Chong, K.; Xue, Y.B.; Wang, T. Dynamic proteomic analysis reveals a switch between central carbon metabolism and alcoholic fermentation in rice filling grains. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 908–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote) omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Zhu, B.Q.; Zhang, Y.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Li, C.Y.; Su, Y.H.; Ba, C.F. The research of applying primer premier 5.0 to design PCR primer. J. Jinzhou Med. Coll. 2004, 25, 43–46. [Google Scholar]







| Map ID | Map Name | Diffs | Refs | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ko00940 | Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis | 21 | 39 | 9.28 × 10−5 |
| ko04075 | Plant hormone signal transduction | 9 | 13 | 9.34 × 10−4 |
| ko00790 | Folate biosynthesis | 3 | 3 | 1.54 × 10−2 |
| ko01040 | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | 6 | 10 | 1.92 × 10−2 |
| ko00591 | Linoleic acid metabolism | 5 | 8 | 2.67 × 10−2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Xu, M.; Cheng, Z.; Zheng, J. Proteomic Analysis Reveals Coordinated Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis through Signal Transduction and Sugar Metabolism in Black Rice Leaf. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122722
Chen L, Huang Y, Xu M, Cheng Z, Zheng J. Proteomic Analysis Reveals Coordinated Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis through Signal Transduction and Sugar Metabolism in Black Rice Leaf. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122722
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Linghua, Yining Huang, Ming Xu, Zuxin Cheng, and Jingui Zheng. 2017. "Proteomic Analysis Reveals Coordinated Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis through Signal Transduction and Sugar Metabolism in Black Rice Leaf" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122722
APA StyleChen, L., Huang, Y., Xu, M., Cheng, Z., & Zheng, J. (2017). Proteomic Analysis Reveals Coordinated Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis through Signal Transduction and Sugar Metabolism in Black Rice Leaf. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122722