Protein Subcellular Localization with Gaussian Kernel Discriminant Analysis and Its Kernel Parameter Selection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
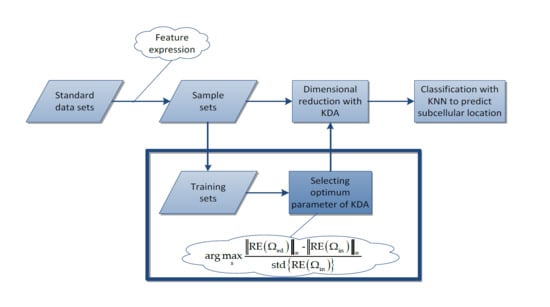
- First, for each standard data set, we use the PsePSSM algorithm and the PSSM-S algorithm to extract features, respectively. Then totally we obtain four sample sets, which are GN-1000 (Gram-negative with PsePSSM which contains 1000 features), GN-220 (Gram-negative with PSSM-S which contains 220 features), GP-1000 (Gram-positive with PsePSSM which contains 1000 features) and GP-220 (Gram-positive with PsePSSM which contains 220 features).
- Second, we use the proposed method to select the optimum kernel parameter for the Gaussian KDA model and then use KDA to reduce the dimension of sample sets. The same procedure is also carried out for the traditional grid-searching method to form a comparison with the proposed method.
- Finally, we use the KNN algorithm to classify the reduced dimensional sample sets and use some criterions to evaluate the results and give the comparison results.
2.1. The Comparison Results of the Overall Accuracy
2.1.1. The Accuracy Comparison between the Proposed Method and the Grid-Searching Method
2.1.2. The Comparison between Methods with and without KDA
2.2. The Robustness of the Proposed Method
2.3. Evaluating the Proposed Method with Some Regular Evaluation Criterions
3. Methods
3.1. Protein Subcellular Localization Prediction Based on KDA
3.2. Algorithm Principle
3.3. Kernel Discriminant Analysis (KDA) and Its Reconstruction Error
3.4. The Proposed Method for Selecting the Optimum Gaussian Kernel Parameter
3.4.1. The Method for Selecting Internal and Edge Samples
3.4.2. The Proposed Method
4. Materials
4.1. Standard Data Sets
4.2. Feature Expressions and Sample Sets
4.2.1. Pseudo Position-Specific Scoring Matrix (PsePSSM)
4.2.2. PSSM-S
4.2.3. Sample Sets
4.3. Evaluation Criterion
4.4. The Grid Searching Method Used as Contrast
- Compute the kernel matrix for each parameter .
- Use the Gaussian KDA to reduce the dimension of .
- Use the KNN algorithm to classify the reduced dimensional samples.
- Calculate the classification accuracy.
- Repeat the above four steps until all parameters in have been traversed. The parameter corresponding to the highest classification accuracy is selected as the optimum parameter.
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chou, K.C. Some Remarks on Predicting Multi-Label Attributes in Molecular Biosystems. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, B.; Xia, X.F.; Sun, Z.R. Bioinformatics Research in Subcellular Localization of Protein. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 34, 573–579. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.B.; Lai, J.H. Machine Learning-based Prediction of Subcellular Localization for Protein. Comput. Sci. 2009, 36, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Huh, W.K.; Falvo, J.V.; Gerke, L.C.; Carroll, A.S.; Howson, R.W.; Weissman, J.S.; O’Shea, E.K. Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature 2003, 425, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkley, T.P.J.; Watson, R.; Griffin, J.L.; Dupree, P.; Lilley, K.S. Localization of organelle proteins by isotope tagging (LOPIT). Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.A.; Ahmad, S.; Molla, M.K. Protein subcellular localization prediction using multiple kernel learning based support vector machine. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teso, S.; Passerini, A. Joint probabilistic-logical refinement of multiple protein feature predictors. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, S. Protein Sub-Nuclear Localization Based on Effective Fusion Representations and Dimension Reduction Algorithm LDA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 30343–30361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudat, G.; Anouar, F. Generalized Discriminant Analysis Using a Kernel Approach. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2385–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.N.; Wang, J.B.; Li, Y.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, Y.F.; Li, H. Person re-identification based on feature fusion and kernel local Fisher discriminant analysis. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 36, 2597–2600. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.C.; Wang, H.G.; Xu, W.L.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hang, L.I. Model selection of Gaussian kernel PCA for novelty detection. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. 2014, 136, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H.B. MemType-2L: A Web server for predicting membrane proteins and their types by incorporating evolution information through Pse-PSSM. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 360, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehzangi, A.; Heffernan, R.; Sharma, A.; Lyons, J.; Paliwal, K.; Sattar, A. Gram-positive and Gram-negative protein subcellular localization by incorporating evolutionary-based descriptors into Chou׳s general PseAAC. J. Theor. Biol. 2015, 364, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.B.; Chou, K.C. Gpos-PLoc: An ensemble classifier for predicting subcellular localization of Gram-positive bacterial proteins. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2007, 20, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, H. Kernel PCA for novelty detection. Pattern Recogn. 2007, 40, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Maguire, L. Selecting Critical Patterns Based on Local Geometrical and Statistical Information. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2010, 33, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.R.; Martinez, T.R. Reduction Techniques for Instance-Based Learning Algorithms. Mach. Learn. 2000, 38, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidi, R.; Astudillo, R.; Kolossa, D. Uncertain LDA: Including observation uncertainties in discriminative transforms. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. 2016, 38, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K. Data clustering: 50 years beyond K-means. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2010, 31, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.L.; Hu, Y.F. A Density-Based Method for Reducing the Amount of Training Data in kNN Text Classification. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 2004, 41, 539–545. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H.B. Cell-PLoc 2.0: An improved package of web-servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat. Sci. 2010, 2, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H.B. Large-Scale Predictions of Gram-Negative Bacterial Protein Subcellular Locations. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 5, 3420–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavousi, K.; Moshiri, B.; Sadeghi, M.; Araabi, B.N.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A. A protein fold classifier formed by fusing different modes of pseudo amino acid composition via PSSM. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2011, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.B.; Chou, K.C. Nuc-PLoc: A new web-server for predicting protein subnuclear localization by fusing PseAA composition and PsePSSM. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2007, 20, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yang, J. Using the nonlinear dimensionality reduction method for the prediction of subcellular localization of Gram-negative bacterial proteins. Mol. Divers. 2009, 13, 475. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.Y.; Tang, J.J.; Zou, Q. Local-DPP: An improved DNA-binding protein prediction method by exploring local evolutionary information. Inform. Sci. 2017, 384, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.B.; Chou, K.C. Gneg-mPLoc: A top-down strategy to enhance the quality of predicting subcellular localization of Gram-negative bacterial proteins. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 264, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, L.I.; Yao, Q.Z.; Luo, Z.M.; Tian, Y. Gird-pattern method for model selection of support vector machines. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2008, 44, 136–138. [Google Scholar]





| Sample Sets | Overall Accuracy | Ratio () | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GP-220 (PSSM-S) | The proposed method | 0.9924 | 0.7087 |
| Grid searching method | 0.9924 | ||
| GP-1000 (PsePSSM) | The proposed method | 0.9924 | 0.7362 |
| Grid searching method | 0.9924 | ||
| GN-220 (PSSM-S) | The proposed method | 0.9801 | 0.7416 |
| Grid searching method | 0.9801 | ||
| GN-1000 (PsePSSM) | The proposed method | 0.9574 | 0.7687 |
| Grid searching method | 0.9574 | ||
| Sample Set | Protein Subcellular Locations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Cell Wall | Cytoplasm | Extracell | |
| Sensitivity | ||||
| GP-220 | 1 | 0.9444 | 0.9904 | 0.9919 |
| GP-1000 | 0.9943 | 0.9444 | 1 | 0.9837 |
| Specificity | ||||
| GP-220 | 0.9943 | 1 | 1 | 09950 |
| GP-1000 | 0.9971 | 1 | 0.9937 | 0.9925 |
| Matthews coefficient correlation (MCC) | ||||
| GP-220 | 0.9914 | 0.9709 | 0.9920 | 0.9841 |
| GP-1000 | 0.9914 | 0.9709 | 0.9921 | 0.9840 |
| Overall accuracy (Q) | ||||
| GP-220 | 0.9924 | |||
| GP-1000 | 0.9924 | |||
| Sample Set | Protein Subcellular Locations | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | |
| Sensitivity | ||||||||
| GN-220 | 1 | 0.9699 | 1 | 0 | 0.9982 | 0 | 0.9677 | 1 |
| GN-1000 | 1 | 0.9323 | 1 | 0 | 0.9659 | 0 | 0.9516 | 0.9556 |
| Specificity | ||||||||
| GN-220 | 0.9924 | 0.9902 | 1 | 1 | 0.9978 | 1 | 1 | 0.9953 |
| GN-1000 | 0.9608 | 0.9872 | 1 | 1 | 0.9967 | 1 | 1 | 0.9992 |
| Matthews coefficient correlation () | ||||||||
| GN-220 | 0.9866 | 0.9324 | 1 | - | 0.9956 | - | 0.9823 | 0.9814 |
| GN-1000 | 0.9346 | 0.8957 | 1 | - | 0.9681 | - | 0.9733 | 0.9712 |
| Overall accuracy (Q) | ||||||||
| GN-220 | 0.9801 | |||||||
| GN-1000 | 0.9574 | |||||||
| Input: , the training set . |
|---|
| 1. Calculate the radius of neighborhood using Equation (11). |
| 2. Calculate the centroid of the th class according to Equation (9). |
| 3. Calculate the distances from all samples in training set to , respectively, and the median value of them. |
4. For each training sample of the set
|
| Output: the selected internal sample set , the selected edge sample set . |
| Input: A reasonable candidate set for Gaussian kernel parameter, , the training set , the number of retained eigenvectors . |
| 1. Get the internal sample set and the edge sample set from the training set using Algorithm 1. |
2. For each parameter
|
| 3. Select the optimum parameter |
| Output: the optimum Gaussian kernel parameter . |
| No. | Subcellular Localization | Number of Proteins |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | cell membrane | 174 |
| 2 | cell wall | 18 |
| 3 | cytoplasm | 208 |
| 4 | extracell | 123 |
| No. | Subcellular Localization | Number of Proteins |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | cytoplasm | 410 |
| 2 | extracell | 133 |
| 3 | fimbrium | 32 |
| 4 | flagellum | 12 |
| 5 | inner membrane | 557 |
| 6 | nucleoid | 8 |
| 7 | outer membrane | 124 |
| 8 | periplasm | 180 |
| Sample Sets | Benchmarks for Subcellular Locations | Extraction Feature Method | The Number of Classes | The Dimension of Feature Vector | The Number of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GN-1000 | Gram-negative | PsePSSM | 8 | 1000 | 1456 |
| GN-220 | Gram-negative | PSSM-S | 8 | 220 | 1456 |
| GP-1000 | Gram-positive | PsePSSM | 4 | 1000 | 523 |
| GP-220 | Gram-positive | PSSM-S | 4 | 220 | 523 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Nie, B.; Yue, K.; Fei, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, D. Protein Subcellular Localization with Gaussian Kernel Discriminant Analysis and Its Kernel Parameter Selection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122718
Wang S, Nie B, Yue K, Fei Y, Li W, Xu D. Protein Subcellular Localization with Gaussian Kernel Discriminant Analysis and Its Kernel Parameter Selection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122718
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shunfang, Bing Nie, Kun Yue, Yu Fei, Wenjia Li, and Dongshu Xu. 2017. "Protein Subcellular Localization with Gaussian Kernel Discriminant Analysis and Its Kernel Parameter Selection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122718
APA StyleWang, S., Nie, B., Yue, K., Fei, Y., Li, W., & Xu, D. (2017). Protein Subcellular Localization with Gaussian Kernel Discriminant Analysis and Its Kernel Parameter Selection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2718. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122718