Shp2 Plays a Critical Role in IL-6-Induced EMT in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Exogenous IL-6 Induces EMT and Increases Cell Migration In Vitro
2.2. Stable Expression of IL-6 in T47D Cells Induces EMT In Vitro
2.3. Overexpression of IL-6 Promotes Tumor Metastasis In Vivo
2.4. Knockdown of Shp2 Decreases Invasion and Migration Capacities In Vitro
2.5. Knockdown of Shp2 Attenuated EMT Induced by IL-6 In Vitro
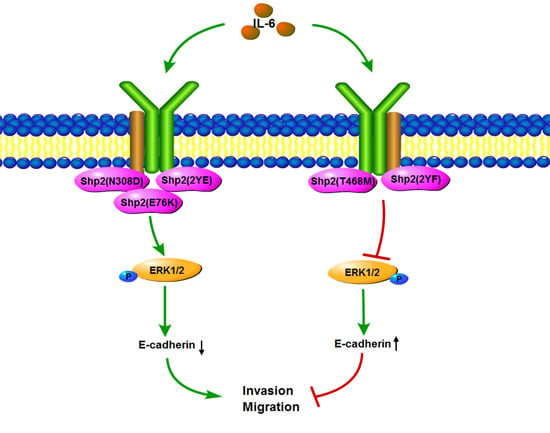
2.6. Phosphatase Activity and Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Shp2 Regulate IL-6-Induced EMT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell lines and Culture
4.2. siRNA Transfection
4.3. Vector Construction, Transfection, and Stable Cell Line Acquisition
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Wound Healing Assay
4.6. Transwell Invasion Assay
4.7. Tumor Metastasis Experiment In Vivo
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EMT | Epithelial mesenchymal transition |
| Shp2 | Src-homology 2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 2 |
| PTP | Protein tyrosine phosphatase |
References
- Chan, R.J.; Feng, G.S. PTPN11 is the first identified proto-oncogene that encodes a tyrosine phosphatase. Blood 2007, 109, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.; Kalaitzidis, D.; Neel, B.G. The tyrosine phosphatase Shp2 (PTPN11) in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aceto, N.; Sausgruber, N.; Brinkhaus, H.; Gaidatzis, D.; Martiny-Baron, G.; Mazzarol, G.; Confalonieri, S.; Quarto, M.; Hu, G.; Balwierz, P.J.; et al. Tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 promotes breast cancer progression and maintains tumor-initiating cells via activation of key transcription factors and a positive feedback signaling loop. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Wakayama, Y.; Tanino, M.; Orba, Y.; Sawa, H.; Hatakeyama, M.; Tanaka, S.; Sabe, H.; Mochizuki, N. Involvement of EphA2-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of Shp2 in Shp2-regulated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5292–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, A.M.; Tang, T.L.; Sugimoto, S.; Walsh, C.T.; Neel, B.G. Protein-tyrosine-phosphatase SHPTP2 couples platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta to Ras. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 7335–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Shen, K.; Cole, P.A. Chemical dissection of the effects of tyrosine phosphorylation of SHP-2. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 5461–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, N.; Montagner, A.; Lee, W.H.; Miteva, M.; Vidal, M.; Vidaud, M.; Parfait, B.; Raynal, P. Reduced phosphatase activity of Shp-2 in LEOPARD syndrome: Consequences for PI3K binding on Gab1. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, K.; Gaengel, K.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Kamiya, K.; Kim, I.K.; Ying, H.; Weber, U.; Perkins, L.A.; Tartaglia, M.; Mlodzik, M.; et al. Transgenic Drosophila models of Noonan syndrome causing PTPN11 gain-of-function mutations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Meyerson, H.J.; Yang, W.; Neel, B.G.; Qu, C.K. Gain-of-function mutations of Ptpn11 (Shp2) cause aberrant mitosis and increase susceptibility to DNA damage-induced malignancies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matalkah, F.; Martin, E.; Zhao, H.; Agazie, Y.M. SHP2 acts both upstream and downstream of multiple receptor tyrosine kinases to promote basal-like and triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, Z.L.; Zou, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Liang, L.; Zeng, G.; Chen, S. SHP2 and UGP2 are Biomarkers for Progression and Poor Prognosis of Gallbladder Cancer. Cancer Investig. 2016, 34, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Munoz, I.; Figuerola, E.; Sanchez-Molina, S.; Rodriguez, E.; Fernandez-Marino, A.I.; Pardo-Pastor, C.; Bahamonde, M.I.; Fernández-Fernández, J.M.; García-Domínguez, D.J.; Hontecillas-Prieto, L.; et al. RING1B contributes to Ewing sarcoma development by repressing the NaV1.6 sodium channel and the NF-κB pathway, independently of the fusion oncoprotein. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46283–46300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.D.; Yu, J.J.; Kong, T.A.; Spiotto, M.T.; Lin, J.M. Interleukin-6 activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, which inhibits apoptosis in human prostate cancer cell lines. Prostate 2000, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, Y.; Shah, N.; Lee, J.S.; Markoutsa, E.; Jie, C.; Liu, S.; Botbyl, R.; Reisman, D.; Xu, P.; Chen, H. A novel double-negative feedback loop between miR-489 and the HER2-Shp2-MAPK signaling axis regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18295–18308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, Y.; Song, L.; Yin, Y.; Kong, W.; Chen, X.; Ouyang, X. Expression and prognosis value of Shp2 in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 7853–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.C.; Chiang, W.F.; Huang, H.H.; Shen, Y.Y.; Chiang, H.C. Src-homology 2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 2 promotes oral cancer invasion and metastasis. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhao, H.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Z.; et al. Shp2 promotes metastasis of prostate cancer by attenuating the PAR3/PAR6/aPKC polarity protein complex and enhancing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.D.; Agazie, Y.M. Inhibition of SHP2 leads to mesenchymal to epithelial transition in breast cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonato, J.M.; Lan, I.S.; Lazzara, M.J. EGF augments TGFβ-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by promoting Shp2 binding to GAB1. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 3898–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; He, L.; Xu, Q.; Sun, X.; Teng, L.; Cheng, H.; Ke, Y. Shp2 positively regulates TGFβ1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition modulated by its novel interacting protein Hook1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34152–34160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneshiro, S.; Ebina, K.; Shi, K.; Higuchi, C.; Hirao, M.; Okamoto, M.; Koizumi, K.; Morimoto, T.; Yoshikawa, H.; Hashimoto, J. IL-6 negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation through the SHP2/MEK2 and SHP2/Akt2 pathways in vitro. J. Bone Min. Metab. 2014, 32, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Zhang, X.T.; Liu, X.L.; Fan, L.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Liang, X.H.; Wang, J.B.; Mei, Q.B.; Zhang, F.; et al. WSTF promotes proliferation and invasion of lung cancer cells by inducing EMT via PI3K/Akt and IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathways. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, A.; Kumar, B.; Datta, J.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, P. IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, N.J.; Sasser, A.K.; Axel, A.E.; Vesuna, F.; Raman, V.; Ramirez, N.; Oberyszyn, T.M.; Hall, B.M. Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.; Lee, O.Y.; Park, Y.; Seo, M.W.; Lee, D.S. IL-1beta induces IL-6 production and increases invasiveness and estrogen-independent growth in a TG2-dependent manner in human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.O.; Yang, X.; Duan, S.; Tsai, Y.; Strojny, L.R.; Keng, P.; Chen, Y. IL-6 promotes growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of CD133+ cells of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6626–6638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Merz, C.; von Massenhausen, A.; Queisser, A.; Vogel, W.; Andren, O.; Kirfel, J.; Duensing, S.; Perner, S.; Nowak, M. IL-6 Overexpression in ERG-Positive Prostate Cancer Is Mediated by Prostaglandin Receptor EP2. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, B.J.; Grail, D.; Nheu, T.; Najdovska, M.; Wang, B.; Waring, P.; Inglese, M.; McLoughlin, R.M.; Jones, S.A.; Topley, N.; et al. Hyperactivation of STAT3 in gp130 mutant mice promotes gastric hyperproliferation and desensitizes TGF-β signaling. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judd, L.M.; Alderman, B.M.; Howlett, M.; Shulkes, A.; Dow, C.; Moverley, J.; Grail, D.; Jenkins, B.J.; Ernst, M.; Giraud, A.S. Gastric cancer development in mice lacking the SHP2 binding site on the IL-6 family co-receptor gp130. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Fei, G.H.; Hu, J.G.; Hu, X.W. A study on the effect of IL-6 gene polymorphism on the prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar]
- Saglam, O.; Unal, Z.S.; Subasi, C.; Ulukaya, E.; Karaoz, E. IL-6 originated from breast cancer tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells may contribute to carcinogenesis. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 5667–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Li, A.S.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, D.; Guan, D.; Zou, H. Different associations of CD45 isoforms with STAT3, PKC and ERK regulate IL-6-induced proliferation in myeloma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, A.M.; Hausdorff, S.F.; O’Reilly, A.M.; Freeman, R.M.; Neel, B.G. Multiple requirements for SHPTP2 in epidermal growth factor-mediated cell cycle progression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, M.; Gelb, B.D. Germ-line and somatic PTPN11 mutations in human disease. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 48, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraakman, M.J.; Kammoun, H.L.; Allen, T.L.; Deswaerte, V.; Henstridge, D.C.; Estevez, E.; Matthews, V.B.; Neill, B.; White, D.A.; Murphy, A.J.; et al. Blocking IL-6 trans-signaling prevents high-fat diet-induced adipose tissue macrophage recruitment but does not improve insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Mehta, H.; Drevets, D.A.; Coggeshall, K.M. IL-6 increases B-cell IgG production in a feed-forward proinflammatory mechanism to skew hematopoiesis and elevate myeloid production. Blood 2010, 115, 4699–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, R.; Dey, G.; Mandal, M. Cancer development, chemoresistance, epithelial to mesenchymal transition and stem cells: A snapshot of IL-6 mediated involvement. Cancer Lett. 2016, 375, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.; Liang, S.; Ghosh, S.; Hornsby, P.J.; Li, R. Interleukin 6 secreted from adipose stromal cells promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2745–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Weng, M.; Qin, Y.; Jiang, A.; Ma, F.; Quan, Z. Expression of interleukin-6 is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and survival rates in gallbladder cancer. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; El-Ghonaimy, E.A.; Hassan, H.; Mahana, N.; Mahmoud, M.A.; El-Mamlouk, T.; El-Shinawi, M.; Mohameda, M.M. Hormonal-receptor positive breast cancer: IL-6 augments invasion and lymph node metastasis via stimulating cathepsin B expression. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazdrak, K.; Adachi, T.; Alam, R. Src homology 2 protein tyrosine phosphatase (SHPTP2)/Src homology 2 phosphatase 2 (SHP2) tyrosine phosphatase is a positive regulator of the interleukin 5 receptor signal transduction pathways leading to the prolongation of eosinophil survival. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.M.; Liu, H.Q.; Liu, S.R.; Tang, S.P.; Yang, L.; Feng, G.S. SHP-2 promoting migration and metastasis of MCF-7 with loss of E-cadherin, dephosphorylation of FAK and secretion of MMP-9 induced by IL-1beta in vivo and in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 89, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, Z.R.; Schaller, M.D.; Agazie, Y.M. The tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 regulates focal adhesion kinase to promote EGF-induced lamellipodia persistence and cell migration. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratne, A.; Thai, B.L.; Di Guglielmo, G.M. Atypical protein kinase C phosphorylates Par6 and facilitates transforming growth factor beta-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 874–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneeberger, V.E.; Ren, Y.; Luetteke, N.; Huang, Q.; Chen, L.; Lawrence, H.R.; Lawrence, N.J.; Haura, E.B.; Koomen, J.M.; Coppola, D.; et al. Inhibition of Shp2 suppresses mutant EGFR-induced lung tumors in transgenic mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6191–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Huang, S.; Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, D. Upregulation of Src homology phosphotyrosyl phosphatase 2 (Shp2) expression in oral cancer and knockdown of Shp2 expression inhibit tumor cell viability and invasion in vitro. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2014, 117, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, B.T.; Wang, L.; Gold, M.G.; Skidgel, R.A.; O’Bryan, J.P.; Carnegie, G.K. Protein Kinase A (PKA) Phosphorylation of Shp2 Protein Inhibits Its Phosphatase Activity and Modulates Ligand Specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 12058–12067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.Q.; Lin, Q.; Zhuang, X.; Cai, L.L.; Ruan, R.S.; Lu, Z.X.; Tzeng, C.M. Structure, function, and pathogenesis of SHP2 in developmental disorders and tumorigenesis. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2014, 14, 567–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Wei, X.; Yang, Y.; Qi, R.Z.; Ying, G.; Zhang, N.; Niu, R. Anxa2 plays a critical role in enhanced invasiveness of the multidrug resistant human breast cancer cells. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5041–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ji, W.; Tian, R.; Zhang, F.; Niu, R. Shp2 Plays a Critical Role in IL-6-Induced EMT in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020395
Sun X, Zhang J, Wang Z, Ji W, Tian R, Zhang F, Niu R. Shp2 Plays a Critical Role in IL-6-Induced EMT in Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020395
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Xuan, Jie Zhang, Zhiyong Wang, Wei Ji, Ran Tian, Fei Zhang, and Ruifang Niu. 2017. "Shp2 Plays a Critical Role in IL-6-Induced EMT in Breast Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020395
APA StyleSun, X., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., Ji, W., Tian, R., Zhang, F., & Niu, R. (2017). Shp2 Plays a Critical Role in IL-6-Induced EMT in Breast Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020395