Alternative Splicing of hTERT Pre-mRNA: A Potential Strategy for the Regulation of Telomerase Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
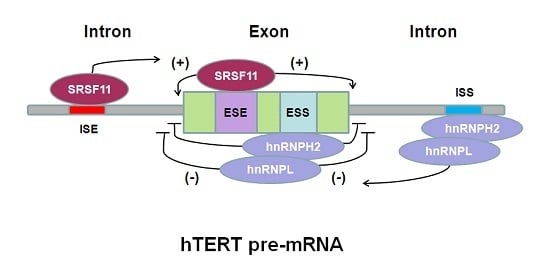
2. Alternative Splicing of hTERT Pre-mRNA
3. Alternative Splicing of hTERT Pre-mRNA in the Development of Human Embryo and Human Embryonic Stem Cells
4. Expression, Distribution and Biological Functions of hTERT ASVs in Cancer and Other Diseases
5. hTERT Pre-mRNA Alternative Splicing in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Cancer
6. hTERT Pre-mRNA Alternative Splicing Regulation in Cancer Therapy
7. Conclusions and Prospects
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blackburn, E.H. Telomere states and cell fates. Nature 2000, 408, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.; Ludlow, A.T.; Min, J.; Robin, J.D.; Stadler, G.; Mender, I.; Lai, T.P.; Zhang, N.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Regulation of the Human Telomerase Gene TERT by Telomere Position Effect-Over Long Distances (TPE-OLD): Implications for Aging and Cancer. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e2000016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.J.; Rube, H.T.; Xavier-Magalhães, A.; Costa, B.M.; Mancini, A.; Song, J.S.; Costello, J.F. Understanding TERT Promoter Mutations: A Common Path to Immortality. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akıncılar, S.C.; Khattar, E.; Boon, P.L.; Unal, B.; Fullwood, M.J.; Tergaonkar, V. Long-Range Chromatin Interactions Drive Mutant TERT Promoter Activation. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrdlickova, R.; Nehyba, J.; Bose, H.R., Jr. Alternatively spliced telomerase reverse transcriptase variants lacking telomerase activity stimulate cell proliferation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 4283–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichroeb, J.H.; Kim, J.; Betts, D.H. The role of telomeres andtelomerasereverse transcriptase isoforms in pluripotency induction and maintenance. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Quantitation of telomerase components and hTERT mRNA splicing patterns in immortal human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4818–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincz, L.F.; Mudge, L.M.; Scorgie, F.E.; Sakoff, J.A.; Hamilton, C.S.; Seldon, M. Quantification of hTERT splice variants in melanoma by SYBR green real-time polymerase chain reaction indicates a negative regulatory role for the beta deletion variant. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollmann, F.M. Physiological and pathological significance of human telomerase reverse transcriptase splice variants. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1965–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wick, M.; Zubov, D.; Hagen, G. Genomic organization and promoter characterization of the gene encoding the human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT). Gene 1999, 232, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Hu, J.F.; Vu, T.H.; Giudice, L.C.; Hoffman, A.R. Tissue-specific alternate splicing of human telomerase reverse transcriptase(hTERT) influences telomere lengths during human development. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listerman, I.; Sun, J.; Gazzaniga, F.S.; Lukas, J.L.; Blackburn, E.H. The major reverse transcriptase-incompetent splice variant of the human telomerase activity inhibits telomerase activity but protects from apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2817–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; White, D.M.; Aisner, D.L.; Baur, J.A.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. An alternate splicing variant of the human telomerase catalytic subunit inhibits telomerase activity. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisatomi, H.; Ohyashiki, K.; Ohyashiki, J.H.; Nagao, K.; Kanamaru, T.; Hirata, H.; Hibi, N.; Tsukada, Y. Expression profile of a γ-deletion variant of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene. Neoplasia 2003, 5, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaner, G.A.; Hu, J.F.; Vu, T.H.; Giudice, L.C.; Hoffman, A.R. Telomerase activity in human development is regulated by human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) transcription and by alternate splicing of hTERT transcripts. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4168–4172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Radan, L.; Hughes, C.S.; Teichroeb, J.H.; Vieira Zamora, F.M.; Jewer, M.; Postovit, L.M.; Betts, D.H. Microenvironmental regulation of telomerase isoforms in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2014, 23, 2046–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrogiannou, E.; Strati, A.; Stathopoulou, A.; Tsaroucha, E.G.; Kaklamanis, L.; Lianidou, E.S. Real-time RT-PCR quantification of human telomerase reverse transcriptase splice variants in tumor cell lines and non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, K.; Katsumata, K.; Aizawa, Y.; Saito, N.; Hirata, H.; Sasaki, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Hikiji, K.; Koiwa, T.; Hisatomi, H. Differential alternative splicing expressions of telomerase reverse transcriptase in gastrointestinal cell lines. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 11, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, J.Y.; Morris, A.G.; Nwokolo, C.U. HTERT mRNA partially regulates telomerase activity in gastric adenocarcinoma and adjacent normal gastric mucosa. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, J.Y.; Morris, A.G.; Nwokolo, C.U. Telomerase, hTERT and splice variants in Barrett’s oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 17, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, B.Q.; Zhong, H.H.; Tian, X.X.; Fang, W.G. Quantification of alternative splicing variants of human telomerase reverse transcriptase and correlations with telomerase activity in lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Meeker, A.K.; Kowalski, J.; Tsai, H.L.; Somervell, H.; Heaphy, C.; Sangenario, L.E.; Prasad, N.; Westra, W.H.; Zeiger, M.A.; et al. Telomere length is related to alternative splice patterns of telomerase in thyroid tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Wan, X.; Takahashi, Y.; Shinohara, A.; Tamaya, T. Alternatively spliced variant deleting exons 7 and 8 of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene is dominantly expressed in the uterus. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2001, 7, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Wu, L.; Sun, H.; Ren, X.; Epling-Burnette, P.K.; Yang, L. MDS shows a higher expression of hTERT and alternative splice variants in unactivated T-cells. Oncotarget 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, M.; Parker, A.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Forster, J.; Kokhaei, P.; Hansson, L.; Osterborg, A.; Mellstedt, H. Telomere length and expression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase splice variants in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 2013, 41, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrin, L.; Trentin, L.; Degan, M.; Corradini, I.; Bertorelle, R.; Carli, P.; Maschio, N.; Bo, M.D.; Noventa, F.; Gattei, V.; et al. Telomerase expression in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia predicts survival and delineates subgroups of patients with the same igVH mutation status and different outcome. Leukemia 2007, 21, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colgin, L.M.; Wilkinson, C.; Englezou, A.; Kilian, A.; Robinson, M.O.; Reddel, R.R. The hTERT α splice variant is a dominant negative inhibitor of telomerase activity. Neoplasia 2000, 2, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.W.; Piatyszek, M.A.; Prowse, K.R.; Harley, C.B.; West, M.D.; Ho, P.L.; Coviello, G.M.; Wright, W.E.; Weinrich, S.L.; Shay, J.W. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 1994, 266, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiyama, E.; Yamaoka, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Ando, H.; Suita, S.; Horie, H.; Kaneko, M.; Sasaki, F.; Hashizume, K.; et al. High expression of telomerase is an independent prognostic indicator of poor outcome in hepatoblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poremba, C.; Heine, B.; Diallo, R.; Heinecke, A.; Wai, D.; Schaefer, K.L.; Braun, Y.; Schuck, A.; Lanvers, C.; Bànkfalvi, A.; et al. Telomerase as a prognostic marker in breast cancer: High-throughput tissue microarray analysis of hTERT and hTR. J. Pathol. 2002, 198, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsumoto, N.; Hiyama, E.; Murakami, Y.; Imamura, Y.; Shay, J.W.; Matsuura, Y.; Yokoyama, T. High telomerase activity is an independent prognostic indicator of poor outcome in colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2696–2701. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, B.M. Splice variants as cancer biomarkers. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Chen, R.J. Prevalence of telomerase activity in human cancer. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2011, 110, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mender, I.; Shay, J.W. Telomerase Repeated Amplification Protocol (TRAP). Bio-Protocol 2015, 5, E1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, M.; Kamma, H.; Wu, W.; Hamasaki, M.; Kaneko, S.; Horiguchi, H.; Matsui-Horiguchi, M.; Satoh, H. Expression and alternative splicing pattern of human telomerase reverse transcriptase in human lung cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2004, 24, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krams, M.; Hero, B.; Berthold, F.; Parwaresch, R.; Harms, D.; Rudolph, P. Full-length telomerase reverse transcriptase messenger RNA is an independent prognostic factor in neuroblastoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.C.; Tergaonkar, V. Telomerase: Central regulator of all of all of the hallmarks of cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.S.; Chen, L.; Foster, C.; Kainthla, R.; Shay, J.W.; Wright, W.E. Regulation of telomerase alternative splicing: A target for chemotherapy. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.; Lemarteleur, T.; Lacroix, L.; Mailliet, P.; Mergny, J.L.; Riou, J.F. Telomerase downregulation induced by the G-quadruplex ligand12459 in A549 cells is mediated by hTERTRNA alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, C.; Folini, M.; Gandellini, P.; Daprai, L.; Daidone, M.G.; Zaffaroni, N. Oligomer-mediated modulation of hTERT alternative splicing induces telomerase inhibition and cell growth decline in human prostate cancer cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 1764–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buseman, C.M.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Is telomerase a viable target in cancer? Mutat. Res. 2012, 730, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.B.; Graham, M.E.; Lovrecz, G.O.; Bache, N.; Robinson, P.J.; Reddel, R.R. Protein composition of catalytically active human telomerase from immortal cells. Science 2007, 315, 1850–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.S.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Alternative splicing regulation of telomerase: A new paradigm? Trends Genet. 2014, 30, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Typical hTERT mRNA Variants | Telomerase Activity | Tissue-Specificity | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full-length hTERT mRNA | Yes | No | promote telomerase activity |
| α-deletion ASV | No | Yes | Inhibit telomerase activity |
| β-deletion ASV | No | Yes | Inhibit telomerase activity but protect from apoptosis |
| γ-deletion ASV | No | Yes | Inhibit telomerase activity |
| αβ-deletion ASV | No | Yes | Unclear |
| αγ-deletion, βγ-deletion and αβγ-deletion ASV | No | Unclear | Unclear |
| Δ4–13 | No | Unclear | Extra-telomeric functions, stimulate cell proliferation |
| Insertion ASVs | No | Unclear | Unclear |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chang, G.; Wang, F.; Wang, F.; Geng, X. Alternative Splicing of hTERT Pre-mRNA: A Potential Strategy for the Regulation of Telomerase Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030567
Liu X, Wang Y, Chang G, Wang F, Wang F, Geng X. Alternative Splicing of hTERT Pre-mRNA: A Potential Strategy for the Regulation of Telomerase Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(3):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030567
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuewen, Yuchuan Wang, Guangming Chang, Feng Wang, Fei Wang, and Xin Geng. 2017. "Alternative Splicing of hTERT Pre-mRNA: A Potential Strategy for the Regulation of Telomerase Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 3: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030567
APA StyleLiu, X., Wang, Y., Chang, G., Wang, F., Wang, F., & Geng, X. (2017). Alternative Splicing of hTERT Pre-mRNA: A Potential Strategy for the Regulation of Telomerase Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(3), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030567