The Candida albicans Inhibitory Activity of the Extract from Papaya (Carica papaya L.) Seed Relates to Mitochondria Dysfunction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. C. albicans Inhibitory
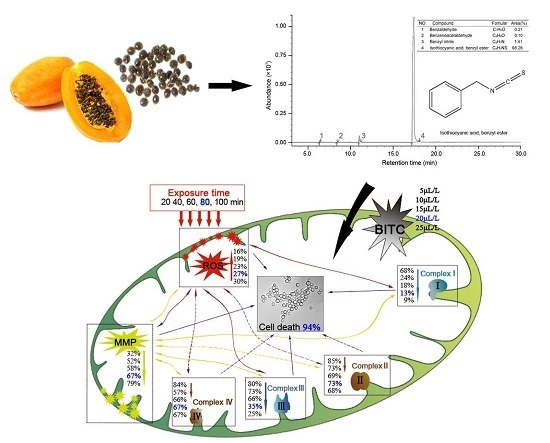
2.2. ROS Increase
2.3. MMP Decrease
2.4. The Activity of Mitochondrial Complex Enzymes
2.5. Chemical Composition of the Extract
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Extraction
4.2. Chemical and Reagents
4.3. Microorganism and Culture Condition
4.4. C. albicans Inhibitory Activity
4.5. Isolation of Mitochondria
4.6. Measurement of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Formation
4.7. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP)
4.8. Assay for Mitochondrial Enzyme Activities
4.9. GC-MS Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yon, R.M. Papaya: Fruit Development, Postharvest Physiology, Handling and Marketing in ASEAN; ASEAN Food Handling Bureau: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, H.; Tang, C.-S. The chemistry and biochemistry of papaya. Trop. Foods 1979, 1, 33–55. [Google Scholar]
- Salunkhe, D.K.; Kadam, S. Handbook of Fruit Science and Technology: Production, Composition, Storage, and Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- O’brien, R.D. Fats and Oils: Formulating and Processing for Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Adebiyi, A.; Ganesan Adaikan, P.; Prasad, R. Tocolytic and toxic activity of papaya seed extract on isolated rat uterus. Life Sci. 2003, 74, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, R.; Jamir, N. Ethnobotanical studies in Nagaland. I. Medicinal plants. Econ. Bot. 1982, 36, 176–181. [Google Scholar]
- Puangsri, T.; Abdulkarim, S.; Ghazali, H. Properties of Carica papaya L. (papaya) seed oil following extractions using solvent and aqueous enzymatic methods. J. Food Lipids 2005, 12, 62–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blekas, G.; Tsimidou, M.; Boskou, D. Contribution of α-tocopherol to olive oil stability. Food Chem. 1995, 52, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malacrida, C.R.; Kimura, M.; Jorge, N. Characterization of a high oleic oil extracted from papaya (Carica papaya L.) seeds. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 31, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson Salaué, L.; Camilo, C.; Torija, M.E. Caracterización del aceite de coquito de palma chilena (Jubaea chilensis). Grasas Y Aceites 2008, 59, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Emeruwa, A. Antibacterial substance from Carica papaya fruit extract. J. Nat. Prod. 1982, 45, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinoy, N.; D’souza, J.; Padman, P. Effects of crude aqueous extract of Carica papaya seeds in male albino mice. Reproduct. Toxicol. 1994, 8, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohiya, N.; Goyal, R.B. Antifertility investigations on the crude chloroform extract of Carica papaya Linn. seeds in male albino rats. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 1992, 30, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lohiya, N.; Manivannan, B.; Bhande, S.; Panneerdoss, S.; Garg, S. Perspectives of contraceptive choices for men. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 43, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chinoy, N.; Padman, P. Antifertility investigations on the benzene extract of Carica papaya seeds in male albino rats. J. Med. Aromat. Plants Sci. 1996, 18, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Lohiya, N.K.; Manivannan, B.; Garg, S. Toxicological investigations on the methanol sub-fraction of the seeds of Carica papaya as a male contraceptive in albino rats. Reproduct. Toxicol. 2006, 22, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermanshai, R.; McCarry, B.E.; Rosenfeld, J.; Summers, P.S.; Weretilnyk, E.A.; Sorger, G.J. Benzyl isothiocyanate is the chief or sole anthelmintic in papaya seed extracts. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderone, R.A.; Clancy, C.J. Candida and Candidiasis; ASM Press: Bel Air, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Achkar, J.M.; Fries, B.C. Candida infections of the genitourinary tract. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudlaugsson, O.; Gillespie, S.; Lee, K.; Berg, J.V.; Hu, J.; Messer, S.; Herwaldt, L.; Pfaller, M.; Diekema, D. Attributable mortality of nosocomial candidemia, revisited. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 1172–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çıtak, S.; Özçelik, B.; Cesur, S.; Abbasoglu, U. In vitro susceptibility of Candida species isolated from blood culture to some antifungal agents. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 58, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne, C.J.; Wong, R.W.; Samaranayake, L.P. Potent anti-microbial activity of traditional Chinese medicine herbs against Candida species. Mycoses 2008, 51, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Ma, Y.; Yi, G.; Wu, J.; Zhou, L.; Guo, H. Chemical composition and antifungal activity of Carica Papaya Linn. seeds essential oil against Candida spp. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, O.; Ali, M. Phytochemical and antifungal profiles of the seeds of Carica papaya L. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 73, 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, O.; Matee, M.; Moshi, M.; Simon, E.; Mugusi, F.; Mikx, F.; Helderman, W.; Rijs, A.; van der Ven, A.; Verweij, P. Species distribution and in vitro antifungal susceptibility of oral yeast isolates from Tanzanian HIV-infected patients with primary and recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.-Z.; Cheng, A.-X.; Sun, L.-M.; Sun, S.-J.; Lou, H.-X. Plagiochin E, an antifungal bis (bibenzyl), exerts its antifungal activity through mitochondrial dysfunction-induced reactive oxygen species accumulation in Candida albicans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1790, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H.-X.; Lu, R.-R.; Bao, J.-D.; Tan, C.; Sun, Z. The mechanism underlying proliferation-inhibitory and apoptosis-inducing effects of curcumin on papillary thyroid cancer cells. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Yoshimoto, M.; Murata, Y.; Shimoishi, Y.; Asai, Y.; Park, E.Y.; Sato, K.; Nakamura, Y. Papaya seed represents a rich source of biologically active isothiocyanate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4407–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, Y.; Shi, Z.; Chen, W.; Ruan, M.; Zhu, H. Optimized formation of benzyl isothiocyanate by endogenous enzyme and its extraction from Carica papaya seed. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Lee, M.H.; Su, N.W. Characteristics of papaya seed oils obtained by extrusion-expelling processes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2348–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okeniyi, J.A.; Ogunlesi, T.A.; Oyelami, O.A.; Adeyemi, L.A. Effectiveness of dried Carica papaya seeds against human intestinal parasitosis: A pilot study. J. Med. Food 2007, 10, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, M.D.; Lozano-Chiu, M.; Rex, J.H. Point prevalence of oropharyngeal carriage of fluconazole-resistant Candida in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1997, 25, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakkol-Afshari, J.; Brook, A.; Mousavi, S.H. Study of cytotoxic and apoptogenic properties of saffron extract in human cancer cell lines. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3443–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, D.; Kondo, K.; Uehara, N.; Otokozawa, S.; Tsuji, N.; Yagihashi, A.; Watanabe, N. Endogenous reactive oxygen species is an important mediator of miconazole antifungal effect. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3113–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.G. Indole-3-carbinol generates reactive oxygen species and induces apoptosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 1602–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laparra, J.M.; Vélez, D.; Barberá, R.; Farré, R.; Montoro, R. As2O3 induced oxidative stress and cycle progression in a human intestinal epithelial cell line (Caco-2). Toxicology 2008, 22, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Chandel, N.S.; Williamson, E.K.; Schumacker, P.T.; Thompson, C.B. Bcl-xL regulates the membrane potential and volume homeostasis of mitochondria. Cell 1997, 91, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Shen, W.; Liu, Z.; Guan, S.; Liu, J.; Ding, S. Endurance exercise causes mitochondrial and oxidative stress in rat liver: Effects of a combination of mitochondrial targeting nutrients. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitkanen, S.; Robinson, B.H. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency leads to increased production of superoxide radicals and induction of superoxide dismutase. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Powolny, A.; Singh, S. Benzyl isothiocyanate targets mitochondrial respiratory chain to trigger reactive oxygen species-dependent apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30151–30163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasiappan, R.; Jutooru, I.; Karki, K.; Hedrick, E.; Safe, S.H. Benzylisothiocyanate (BITC) induces ROS-dependent repression of STAT3 by downregulation of specificity proteins in pancreatic cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 27122–27133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, R.; Zhang, R.; Srivastava, S. Generation of ROS by benzyl isothiocyanate results in the activation of MAPK leading to induction of apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2355. [Google Scholar]
- Eloff, J. A sensitive and quick microplate method to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration of plant extracts for bacteria. Planta Medica 1998, 64, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niimi, K.; Harding, D.; Parshot, R.; King, A.; Lun, D.; Decottignies, A.; Niimi, M.; Lin, S.; Cannon, R.; Goffeau, A. Chemosensitization of fluconazole resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and pathogenic fungi by a Doctapeptide derivative. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.L.; Zou, L.B.; Lin, S.; Shi, J.G.; Zhu, H.B. Anti-apoptotic effect of esculin on dopamine-induced cytotoxicity in the human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell line. Neuropharmacology 2007, 53, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trounce, I.A.; Kim, Y.L.; Jun, A.S.; Wallace, D.C. Assessment of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in patient muscle biopsies, lymphoblasts, and transmitochondrial cell lines. Methods Enzymol. 1996, 264, 484–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Picklo, M.J.; Amarnath, V.; McIntyre, J.O.; Graham, D.G.; Montine, T.J. 4-Hydroxy-2(E)-nonenal inhibits CNS mitochondrial respiration at multiple sites. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, K.M.; Szweda, L.I. Selective inactivation of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and pyruvate dehydrogenase: Reaction of lipoic acid with 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 15835–15841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Chen, W. The Candida albicans Inhibitory Activity of the Extract from Papaya (Carica papaya L.) Seed Relates to Mitochondria Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091858
Zhang T, Chen W. The Candida albicans Inhibitory Activity of the Extract from Papaya (Carica papaya L.) Seed Relates to Mitochondria Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091858
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao, and Weijun Chen. 2017. "The Candida albicans Inhibitory Activity of the Extract from Papaya (Carica papaya L.) Seed Relates to Mitochondria Dysfunction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091858
APA StyleZhang, T., & Chen, W. (2017). The Candida albicans Inhibitory Activity of the Extract from Papaya (Carica papaya L.) Seed Relates to Mitochondria Dysfunction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091858