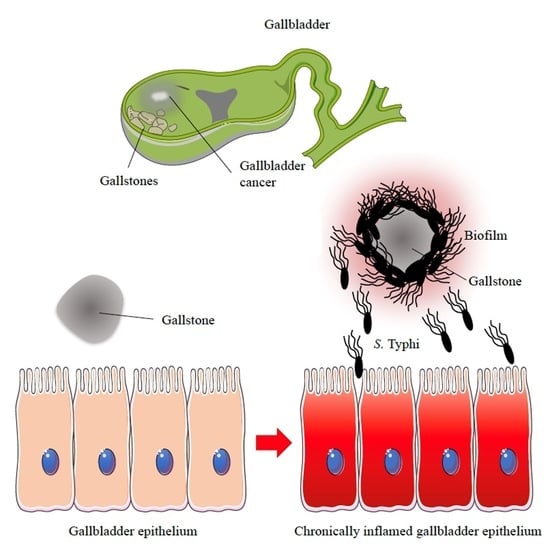
Biofilm Producing Salmonella Typhi: Chronic Colonization and Development of Gallbladder Cancer
Abstract
:1. Epidemiology and Risk Factors
2. Potential Carcinogenic Activity of S. Typhi
3. Biofilm-Mediated S. Typhi Persistence in the Gallbladder
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crump, J.A.; Sjölund-Karlsson, M.; Gordon, M.A.; Parry, C.M. Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Antimicrobial Management of Invasive Salmonella Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 901–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parry, C.M.; Hien, T.T.; Dougan, G.; White, N.J.; Farrar, J.J. Typhoid fever. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1770–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, B.M.; Pullen, R.L. Typhoid: Clinical analysis of 360 cases. Arch. Intern. Med. 1946, 78, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, A.P.; Basnyat, B.; Thwaites, G.E.; Campbell, J.I.; Farrar, J.J.; Zimmerman, M.D. Emerging trends in enteric fever in Nepal: 9124 cases confirmed by blood culture 1993–2003. Trans R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, P.; Kamat, R. A 10-year-old girl with a rash and abdominal pain. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 615–616, 683–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapha, O.; Kanj, S.; Araj, G.; Mroueh, S.; Dbeibo, G.; Seoud, M. Genital ulceration associated with typhoid fever. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 200, e6–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, J.A.; Luby, S.P.; Mintz, E.D. The global burden of typhoid fever. Bull. World Health Organ. 2004, 82, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buckle, G.C.; Walker, C.L.; Black, R.E. Typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever: Systematic review to estimate global morbidity and mortality for 2010. J. Glob. Health. 2012, 2, 010401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, J.A.; Mintz, E.D. Global trends in typhoid and paratyphoid Fever. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogasale, V.; Maskery, B.; Ochiai, R.L.; Lee, J.S.; Mogasale, V.V.; Ramani, E.; Kim, Y.E.; Park, J.K.; Wierzba, T.F. Burden of typhoid fever in low-income and middle-income countries: A systematic, literature-based update with risk-factor adjustment. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e570–e580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.; Hussell, T.; Dougan, G. Chronic bacterial infections: Living with unwanted guests. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinbar, A.; Altmann, G.; Tulcinsky, D.B. The treatment of chronic biliary Salmonella carriers. Am. J. Med. 1969, 47, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.M.; Black, R.E.; Lanata, C. Precise estimation of the numbers of chronic carriers of Salmonella typhi in Santiago, Chile, an endemic area. J. Infect. Dis. 1982, 146, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monack, D.M. Helicobacter and salmonella persistent infection strategies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a010348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caygill, C.P.; Hill, M.J.; Braddick, M.; Sharp, J.C. Cancer mortality in chronic typhoid and paratyphoid carriers. Lancet 1994, 343, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, U.; Garg, P.K.; Kumar, R.; Tandon, R.K. Typhoid carriers among patients with gallstones are at increased risk for carcinoma of the gallbladder. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, G.; Singh, Y.K.; Kumar, K.; Gulati, A.K.; Shukla, V.K.; Khanna, A.K.; Tripathi, S.K.; Jain, A.K.; Kumar, M.; Singh, T.B. Association of carcinoma of the gallbladder with typhoid carriage in a typhoid endemic area using nested PCR. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2008, 2, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Escobedo, G.; Marshall, J.M.; Gunn, J.S. Chronic and acute infection of the gall bladder by Salmonella Typhi: Understanding the carrier state. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, J.S.; Marshall, J.M.; Baker, S.; Dongol, S.; Charles, R.C.; Ryan, E.T. Salmonella chronic carriage: Epidemiology, diagnosis, and gallbladder persistence. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundal, R.; Shaffer, E.A. Gallbladder cancer: Epidemiology and outcome. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, K.L.; Gupta, A.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, A. Gallbladder cancer epidemiology, pathogenesis and molecular genetics: Recent update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 3978–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraja, V.; Eslick, G. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The relationship between chronic Salmonella Typhi carrier status and gall-bladder cancer. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenfels, A.B.; Walker, A.M.; Althaus, D.P.; Townsend, G.; Domellöf, L. Gallstone growth, size, and risk of gallbladder cancer: An interracial study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1989, 18, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, A.K. Gallstone size and the risk of gallbladder cancer. JAMA 1983, 250, 2323–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, G.; Gulati, A.K.; Shukla, V.K. Role of bacteria in carcinogenesis, with special reference to carcinoma of the gallbladder. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5395–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelrod, L.; Munster, A.M.; O′Brien, T.F. Typhoid cholecystitis and gallbladder carcinoma after interval of 67 years. JAMA 1971, 217, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshiol, J.; Wozniak, A.; Cook, P.; Adaniel, C.; Acevedo, J.; Azócar, L.; Hsing, A.W.; Roa, J.C.; Pasetti, M.F.; Miquel, J.F.; et al. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi and gallbladder cancer: A case-control study and meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3235–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strom, B.L.; Soloway, R.D.; Rios-Dalenz, J.L.; Rodriguez-Martinez, H.A.; West, S.L.; Kinman, J.L.; Polansky, M.; Berlin, J.A. Risk factors for gallbladder cancer. An international collaborative case-control study. Cancer 1995, 76, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, G.; Singh, H.; Shukla, V.K. Chronic typhoid carriage and carcinoma of the gallbladder. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 1997, 6, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, V.K.; Singh, H.; Pandey, M.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Nath, G. Carcinoma of the gallbladder-is it a sequel of typhoid? Dig. Dis. Sci. 2000, 45, 900–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewari, M.; Mishra, R.R.; Shukla, H.S. Salmonella typhi and gallbladder cancer: Report from an endemic region. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2010, 9, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mager, D.L. Bacteria and cancer: Cause, coincidence or cure? A review. J. Transl. Med. 2006, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, R.W.; Rosales-Reyes, R.; Ramirez-Aguilar Mde, L.; Chapa-Azuela, O.; Alpuche-Aranda, C.; Gunn, J.S. Gallstones play a significant role in Salmonella spp. gallbladder colonization and carriage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4353–4358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, R.W.; Gibson, D.L.; Kay, W.W.; Gunn, J.S. Identification of a bile-induced exopolysaccharide required for Salmonella biofilm formation on gallstone surfaces. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 5341–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Stoodley, P. Evolving concepts in biofilm infections. Cell Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, C.C.; Chang, S.J.; Gao, X.; Geiger, T.; Stack, G.; Galán, J.E. Emerging insights into the biology of typhoid toxin. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 35, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuron, M.D.; Boesze-Battaglia, K.; Dlakić, M.; Shenker, B.J. The Cytolethal distending toxin contributes to microbial virulence and disease pathogenesis by acting as a tri-perditious toxin. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickett, C.L.; Whitehouse, C.A. The cytolethal distending toxin family. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelastam, M.; Frisan, T. Cytolethal distending toxins. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 152, 111–133. [Google Scholar]
- Haghjoo, E.; Galan, J.E. Salmonella typhi encodes a functional cytolethal distending toxin that is delivered into host cells by a bacterial-internalization pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4614–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán, J.E. Typhoid toxin provides a window into typhoid fever and the biology of Salmonella Typhi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6338–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara-Tejero, M.; Galán, J.E. A bacterial toxin that controls cell cycle progression as a deoxyribonuclease I-like protein. Science 2000, 290, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, X. Regulators in the DNA damage response. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 594, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, W.M.; Lior, H. A new heat-labile cytolethal distending toxin (CLDT) produced by Escherichia coli isolates from clinical material. Microb. Pathog. 1988, 4, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Bayles, D.O. The contribution of cytolethal distending toxin to bacterial pathogenesis. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 32, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Sharipo, A.; Chaves-Olarte, E.; Masucci, M.G.; Levitsky, V.; Thelestam, M.; Frisan, T. The Haemophilus ducreyi cytolethal distending toxin activates sensors of DNA damage and repair complexes in proliferating and non-proliferating cells. Cell Microbiol. 2002, 4, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, R.; Card, R.; Nunes, C.; AbuOun, M.; Bagnall, M.C.; Nunez, J.; Mendonça, N.; Anjum, M.F.; da Silva, G.J. Virulence characterization of Salmonella enterica by a New microarray: Detection and evaluation of the cytolethal distending toxin gene activity in the un usual host S. Typhimurium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Gao, X.; Galan, J.E. Structure and function of the Salmonella Typhi chimaeric A(2)B(5) typhoid toxin. Nature 2013, 499, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Song, J.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Chen, X.; Varki, N.; Naito-Matsui, Y.; Galan, J.E.; Varki, A. Host adaptation of a bacterial toxin from the human pathogen Salmonella Typhi. Cell 2014, 159, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, A.; Lee, S.; Yang, Y.A.; Song, J. The Role of Typhoid Toxin in Salmonella Typhi Virulence. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2017, 90, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spano, S.; Ugalde, J.E.; Galan, J.E. Delivery of a Salmonella typhi exotoxin from a host intracellular compartment. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, R.; Levi, L.; Rouf, S.F.; Puiac, S.; Rhen, M.; Frisan, T. Salmonella enterica delivers its genotoxin through outer membrane vesicles secreted from infected cells. Cell Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2034–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.; Wiedmann, M. Dynamic Duo-The Salmonella Cytolethal Distending Toxin Combines ADP-Ribosyltransferase and Nuclease Activities in a Novel Form of the Cytolethal Distending Toxin. Toxins 2016, 8, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locht, C.; Coutte, L.; Mielcarek, N. The ins and outs of pertussis toxin. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 4668–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suez, J.; Porwollik, S.; Dagan, A.; Marzel, A.; Schorr, Y.I.; Desai, P.T.; Agmon, V.; McClelland, M.; Rahav, G.; Gal-Mor, O. Virulence gene profiling and pathogenicity characterization of non-typhoidal Salmonella accounted for invasive disease in humans. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisan, T. Bacterial genotoxins: The long journey to the nucleus of mammalian cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwell, C.A.; Dreyfus, L.A. DNAase I homologous residues in CdtB are critical for cytolethal distending toxin-mediated cell cycle arrest. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 37, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesic, D.; Hsu, Y.; Stebbins, C.E. Assembly and function of a bacterial genotoxin. Nature 2004, 429, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Komoto, J.; Saiki, K.; Konishi, K.; Takusagawa, F. Variation of loop sequence alters stability of cytolethal distending toxin (CDT): Crystal structure of CDT from Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hontz, J.S.; Villar-Lecumberri, M.T.; Potter, B.M.; Yoder, M.D.; Dreyfus, L A.; Laity, J.H. Differences in crystal and solution structures of the cytolethal distending toxin B subunit: Relevance to nuclear translocation and functional activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25365–25372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassane, D.C.; Lee, R.B.; Mendenhall, M.D.; Pickett, C.L. Cytolethal distending toxin demonstrates genotoxic activity in a yeast model. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 5752–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisan, T.; Cortes-Bratti, X.; Chaves-Olarte, E.; Stenerlow, B.; Thelestam, M. The Haemophilus ducreyi cytolethal distending toxin induces DNA double strand breaks and promotes ATM-dependent activation of RhoA. Cell Microbiol. 2003, 5, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Domenico, E.G.; Romano, E.; del Porto, P.; Ascenzioni, F. Multifunctional role of ATM/Tel1 kinase in genome stability: From the DNA damage response to telomere maintenance. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 787404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasso, F.; Frisan, T. Bacterial Genotoxins: Merging the DNA Damage Response into Infection Biology. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1762–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes-Bratti, X.; Karlsson, C.; Lagergard, T.; Thelestam, M.; Frisan, T.; Lagergård, T. The Haemophilus ducreyi cytolethal distending toxin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via the DNA damage checkpoint pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 5296–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Koseki, T.; Yamato, K.; Saiki, K.; Konishi, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Ishikawa, I.; Nishihara, T. p53-Independent Expression of p21CIP1/WAF1 in Plasmacytic Cells during G2 Cell Cycle Arrest Induced by Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans Cytolethal Distending Toxin. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Tominaga, K.; Sukedai, M.; Okinaga, T.; Iwanaga, K.; Nishihara, T.; Fukuda, J. Delivery of cytolethal distending toxinB induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in gingival squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2004, 112, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas-Ramos, G.; Petit, C.R.; Marcq, I.; Boury, M.; Oswald, E.; Nougayrède, J.P. Escherichia coli induces DNA damage in vivo and triggers genomic instability in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010, 107, 11537–11542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazkova, H.; Krejcikova, K.; Moudry, P.; Frisan, T.; Hodny, Z.; Bartek, J. Bacterial intoxication evokes cellular senescence with persistent DNA damage and cytokine signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubbs, A.; Nussenzweig, A. Endogenous DNA Damage as a Source of Genomic Instability in Cancer. Cell 2017, 168, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, L.; Carr, H.S.; Richter-Dahlfors, A.; Masucci, M.G.; Thelestam, M.; Frost, J.A.; Frisan, T. A bacterial cytotoxin identifies the RhoA exchange factor Net1 as a key effector in the response to DNA damage. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M. Nuclear factor-[kappa]B in cancer development and progression. Nature 2006, 441, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Bel Belluz, L.; Guidi, R.; Pateras, I.S.; Levi, L.; Mihaljevic, B.; Rouf, S.F.; Wrande, M.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; Nastasi, C.; et al. The Typhoid Toxin Promotes Host Survival and the Establishment of a Persistent Asymptomatic Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidi, R.; del Bel Belluz, L.; Frisan, T. Bacterial genotoxin functions as immune-modulator and promotes host survival. Microb Cell. 2016, 3, 355–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbort, C.J.; Soeiro-Pereira, P.V.; von Bernuth, H.; Kaindl, A.M.; Costa-Carvalho, B.T.; Condino-Neto, A.; Reichenbach, J.; Roesler, J.; Zychlinsky, A.; Amulic, B. Neutrophil oxidative burst activates ATM to regulate cytokine production and apoptosis. Blood. 2015, 126, 2842–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanu, T.; Spaapen, R.M.; Bakker, J.M.; Pratap, C.B.; Wu, L.E.; Hofland, I.; Broeks, A.; Shukla, V.K.; Kumar, M.; Janssen, H.; et al. Salmonella Manipulation of Host Signaling Pathways Provokes Cellular Transformation Associated with Gallbladder Carcinoma. Cell. Host. Microbe 2015, 17, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuijl, C.; Savage, N.D.; Marsman, M.; Tuin, A.W.; Janssen, L.; Egan, D.A.; Ketema, M.; van den Nieuwendijk, R.; van den Eeden, S.J.; Geluk, A.; et al. Intracellular bacterial growth is controlled by a kinase network around PKB/AKT1. Nature 2007, 450, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffatellu, M.; Wilson, R.P.; Chessa, D.; Andrews-Polymenis, H.; Tran, Q.T.; Lawhon, S.; Khare, S.; Adams, L.G.; Bäumler, A.J. SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD, and SopE2 contribute to Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium invasion of epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnaire, A.; Nadel, B.; Raoult, D.; Neefjes, J.; Gorvel, J.P. Collateral damage: Insights into bacterial mechanisms that predispose host cells to cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.K.; Sonkar, K.; Sinha, N.; Rebala, P.; Albani, A.E.; Behari, A.; Reddy, D.N.; Farooqui, A.; Kapoor, V.K. Gallstones: A Worldwide Multifaceted Disease and Its Correlations with Gallbladder Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.W.; Chan, R.C.; Cheng, A.F.; Sung, J.Y.; Leung, J.W. Common bile duct stones: A cause of chronic salmonellosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1992, 87, 1198–1199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S. Infection as a risk factor for gallbladder cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 93, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Escobedo, G.; Gunn, J.S. Identification of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium genes regulated during biofilm formation on cholesterol gallstone surfaces. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3770–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.M.; Flechtner, A.D.; La Perle, K.M.; Gunn, J.S. Visualization of extracellular matrix components within sectioned Salmonella biofilms on the surface of human gallstones. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongol, S.; Thompson, C.N.; Clare, S.; Nga, T.V.; Duy, P.T.; Karkey, A.; Arjyal, A.; Koirala, S.; Khatri, N.S.; Maskey, P.; et al. The microbiological and clinical characteristics of invasive Salmonella in gallbladders from cholecystectomy patients in Kathmandu, Nepal. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalai Chelvam, K.; Chai, L.C.; Thong, K.L. Variations in motility and biofilm formation of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Gut. Pathog. 2014, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levay, B.; Szabó, G.; Szijártó, A.; Gamal, E.M. The frequency of bacteria in human gallstones. Magy. Seb. 2013, 66, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hazrah, P.; Oahn, K.T.; Tewari, M.; Pandey, A.K.; Kumar, K.; Mohapatra, T.M.; Shukla, H.S. The frequency of live bacteria in gallstones. HPB 2004, 6, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouty, A.M.; Schwesinger, W.H.; Gunn, J.S. Biofilm formation and interaction with the surfaces of gallstones by Salmonella spp. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2640–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, C.; Weingarden, A.R.; Khoruts, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Interaction of gut microbiota with bile acid metabolism and its influence on disease states. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Cagliero, C.; Guo, B.; Barton, Y.W.; Maurel, M.C.; Payot, S.; Zhang, Q. Bile salts modulate expression of the CmeABC multidrug efflux pump in Campylobacter jejuni. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 7417–7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.G.; Tutt, C.B.; Duval, L.; Popov, V.; Nasr, A.B.; Michalski, J.; Scaletsky, I.C. Bile salts induce expression of the afimbrial LDA adhesin of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleator, R.D.; Wemekamp-Kamphuis, H.H.; Gahan, C.G.; Abee, T.; Hill, C. A PrfA-regulated bile exclusion system (BilE) is a novel virulence factor in Listeria monocytogenes. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1183–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almagro-Moreno, S.; Pruss, K.; Taylor, R.K. Intestinal Colonization Dynamics of Vibrio cholerae. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouty, A.M.; Brodsky, I.E.; Falkow, S.; Gunn, J.S. Bile-salt-mediated induction of antimicrobial and bile resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Microbiology 2004, 150, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walawalkar, Y.D.; Vaidya, Y.; Nayak, V. Response of Salmonella Typhi to bile-generated oxidative stress: Implication of quorum sensing and persister cell populations. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouty, A.M.; Gunn, J.S. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium invasion is repressed in the presence of bile. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 6763–6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.C.; Wang, M.; Andersen, S.K.; Ferreira, R.B.; Kappelhoff, R.; Han, J.; Borchers, C.H.; Finlay, B.B. Repression of Salmonella enterica phoP expression by small molecules from physiological bile. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 2286–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatta, M.; Pastoor, R.; Scheelbeek, P.F.; Sultan, A.R.; Dwiyanti, R.; Labeda, I.; Smits, H.L. Multi-locus variable-number tandem repeat profiling of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi isolates from blood cultures and gallbladder specimens from Makassar, South-Sulawesi, Indonesia. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinandan, C.S.; Elango, M.; Gnanadhas, D.P.; Chakravortty, D. Infiltration of Matrix-Non-producers Weakens the Salmonella Biofilm and Impairs Its Antimicrobial Tolerance and Pathogenicity. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejea, C.M.; Sears, C.L. Do biofilms confer a pro-carcinogenic state? Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.H.; Dejea, C.M.; Edler, D.; Hoang, L.T.; Santidrian, A.F.; Felding, B.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Cho, K.; Wick, E.C.; Hechenbleikner, E.M.; et al. Metabolism links bacterial biofilms and colon carcinogenesis. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Domenico, E.G.; Toma, L.; Provot, C.; Ascenzioni, F.; Sperduti, I.; Prignano, G.; Gallo, M.T.; Pimpinelli, F.; Bordignon, V.; Bernardi, T.; et al. Development of an in vitro Assay, Based on the BioFilm Ring Test®, for Rapid Profiling of Biofilm-Growing Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, W.; Trampuz, A.; Ochsner, P.E. Prosthetic-joint infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 351, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Høiby, N.; Ciofu, O.; Johansen, H.K.; Song, Z.J.; Moser, C.; Jensen, P.Ø.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Bjarnsholt, T. The clinical impact of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 3, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hengzhuang, W.; Wu, H.; Ciofu, O.; Song, Z.; Høiby, N. In vivo pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of colistin and imipenem in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2683–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Domenico, E.G.; Farulla, I.; Prignano, G.; Gallo, M.T.; Vespaziani, M.; Cavallo, I.; Sperduti, I.; Pontone, M.; Bordignon, V.; Cilli, L.; et al. Biofilm is a major virulence determinant in bacterial colonization of chronic skin ulcers independently from the multidrug resistant phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Domenico, E.G.; Toma, L.; Ensoli, F. The Biofilm Ring Test® at the bedside: Experimental applications. In Proceedings of the World Anti-Microbial Resistance Congress, Washington, DC, USA, 8–9 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Paulucci, F.; di Domenico, E.G.; Toma, L.; Ensoli, F. Evaluation of microbial biofilm formation on occipital and supraorbital nerve stimulators: Development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. In Proceedings of the Difficult Infections in Oncology and Dermatology, Rome, Italy, 23 June 2017. [Google Scholar]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Domenico, E.G.; Cavallo, I.; Pontone, M.; Toma, L.; Ensoli, F. Biofilm Producing Salmonella Typhi: Chronic Colonization and Development of Gallbladder Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091887
Di Domenico EG, Cavallo I, Pontone M, Toma L, Ensoli F. Biofilm Producing Salmonella Typhi: Chronic Colonization and Development of Gallbladder Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091887
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Domenico, Enea Gino, Ilaria Cavallo, Martina Pontone, Luigi Toma, and Fabrizio Ensoli. 2017. "Biofilm Producing Salmonella Typhi: Chronic Colonization and Development of Gallbladder Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091887
APA StyleDi Domenico, E. G., Cavallo, I., Pontone, M., Toma, L., & Ensoli, F. (2017). Biofilm Producing Salmonella Typhi: Chronic Colonization and Development of Gallbladder Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091887