Therapeutic Effect of Exogenous Truncated IK Protein in Inflammatory Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Exogenous tIK Protein Is Expressed in an Insect Cell Culture System
2.2. Treatment with tIK Protein Prevents the Differentiation of Naïve CD4+ T Cells into Th17 Cells
2.3. Treatment with tIK Protein Suppresses the Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines after CD4+ T Cell Activation
2.4. Treatment with tIK Protein Induces Expression of A20, a Negative Regulator of Inflammation in CD4+ T Cells
2.5. Treatment with tIK Protein Affects the Activation of Various Transcription Factors
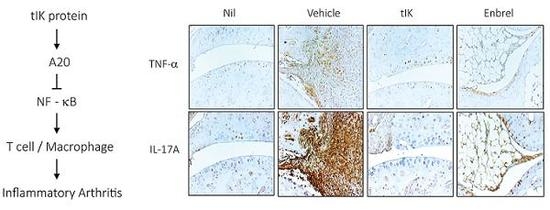
2.6. Exogenous tIK Protein Alleviates the Inflammatory Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Arthritis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Expression and Purification of tIK Protein
4.2. Th17 Cell Differentiation
4.3. Immunoblot Analysis
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.7. Animals
4.8. Arthritis Model
4.9. Treatment of Animals
4.10. Histopathology of Arthritis
4.11. Plate Array for Profiling of Transcription Factor Activation
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP | activator protein |
| BCA | bicinchoninic acid protein |
| CAIA | collagen antibody-induced arthritis |
| cAMP | cyclic AMP |
| CBF | core binding factor |
| CIA | collagen-induced arthritis |
| CIITA | class II transactivator |
| CVB3 | Coxsackievirus B3 |
| HIF | hypoxia inducing factor |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| IFN-γ | interferon-γ |
| IL | interleukin |
| IL1RaKO | interleukin-1 receptor antagonist knockout |
| i.p. | intraperitoneally |
| IRF | interferon regulatory factor |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MACS | magnetic activated cell sorting |
| MHC | major histocompatibility complex |
| NFAT | nuclear factor of activated T cells |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PMA | phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate |
| qPCR | quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| RIPA | radioimmunoprecipitation assay |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| Tg | transgenic |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| WT | wild-type |
References
- Cella, M.; Engering, A.; Pinet, V.; Pieters, J.; Lanzavecchia, A. Inflammatory stimuli induce accumulation of MHC class II complexes on dendritic cells. Nature 1997, 21, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holling, T.M.; Schooten, E.; Den Elsen, P.J. Function and regulation of MHC class II molecules in T-lymphocytes: Of mice and men. Hum. Immunol. 2004, 65, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neefjes, J.; Jongsma, M.L.; Paul, P.; Bakke, O. Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedrenne, J.; Assier, E.; Pereno, R.; Bouzinba-Segard, H.; Azzarone, B.; Jasmin, C.; Charron, D.; Krief, P. Inhibitor (IK) of IFN-g induced HLA class II antigens expression also inhibits HLA class II constitutive expression in the human Raji B cell line. Oncogene 1997, 14, 1453–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seko, Y.; Tsuchimochi, H.; Nakamura, T.; Okumura, K.; Naito, S.; Imataka, K.; Fujii, J.; Takaku, F.; Yazaki, Y. Expression of major histocompatibility complex class I antigen in murine ventricular myocytes infected with Coxsackievirus B3. Circ. Res. 1990, 67, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.L.; Kim, Y.J.; Na, H.N.; Park, M.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Yun, C.W.; Nam, J.H. IK induced by Coxsackievirus B3 infection transiently downregulates expression of MHC Class II through increasing cAMP. Viral Immunol. 2013, 26, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, S.C.L.; Simmonds, M.J. The HLA region and autoimmune disease: Associations and mechanisms of action. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 453–465. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, M.M.A.; Stevens, C.R.; Walsh, E.C.; De Jager, P.L.; Goyette, P.; Plenge, R.M.; Vyse, T.J.; Rioux, J.D. Defining the role of the MHC in autoimmunity: A review and pooled analysis. PLoS Genet. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, S.; Santamaria, P. MHC class II polymorphisms, autoreactive T-cells, and autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraoka, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Kohno, M.; Inoue, A.; Miyazaki, T.; Terada, M.; Nose, M.; Yasukawa, M. IK cytokine ameliorates the progression of lupus nephritis in MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3591–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.L.; Lee, S.M.; Min, J.K.; Moon, S.J.; Kim, I.; Kang, K.W.; Park, S.; Choi, S.; Jung, H.N.; Lee, D.H.; et al. IK acts an immunoregulator of inflammatory arthritis by suppressing Th17 cell differentiation and macrophage activation. Sci. Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffen, S.L. Role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Cur. Rheumatol. Rep. 2009, 11, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Dong, C. IL-17 cytokines in immunity and inflammation. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabgah, A.G.; Fattahi, E.; Shahneh, F.Z. Interleukin-17 in human inflammatory diseases. Postep. Dermatol. Alergol. 2014, 31, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradowska-Gorycka, A.; Haladyj, E. Th17-Cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Autoimmune Disord. Ther. 2015, 1, 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Assier, E.; Bouzinba-Segard, H.; Stolzenberg, M.C.; Stephens, R.; Bardos, J.; Freemont, P.; Charron, D.; Trowsdale, J.; Rich, T. Isolation, sequencing and expression of RED, a novel human gene encoding an acidic–basic dipeptide repeat. Gene 1999, 230, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakil, A.E.; Wang, Z.E.; Ryan, J.C.; Fowell, D.J.; Locksley, R.M. Interferon gamma derived from CD4(+) T cells is sufficient to mediate T helper cell type 1 development. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachigian, L.M. Collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2512–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, D.D.; Latham, K.A.; Rosloniec, E.F. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutamekalin, P.; Saito., T.; Yamaki., K.; Mizutani, N.; Brand, D.D.; Waritani, T.; Terato, K.; Yoshino, S. Collagen antibody-induced arthritis in mice: Development of a new arthritogenic 5-clone cocktail of monoclonal anti-type II collagen antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 343, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosloniec, E.F.; Cremer, M.; Kang, A.; Myers, L.K. Collagen-induced arthritis. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catrysse, L.; Vereecke, L.; Beyaert, R.; Loo, G. A20 in inflammation and autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2014, 35, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vereecke, L.; Beyaert, R.; Loo, G. Genetic relationships between A20/TNFAIP3, chronic inflammation and autoimmune disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, A.; Malynn, B.A. A20: Linking a complex regulator of ubiquitylation to immunity and human disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shembade, N.; Harhaj, E.W. Regulation of NF-kB signaling by the A20 deubiquitinase. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2012, 9, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, N.I.; Yoon, H.Y.; Lee, Y.R.; Won, M.; Chung, M.J.; Park, J.W.; Hur, G.M.; Lee, H.K.; Park, B.H. A20 attenuates allergic airway inflammation in mice. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hah, Y.S.; Lee, Y.R.; Jun, J.S.; Lim, H.S.; Kim, H.O.; Jeong, Y.G.; Hur, G.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Chung, M.J.; Park, J.W.; et al. A20 suppresses inflammatory responses and bone destruction in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2313–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, B.D.; Adeyemo, A.; O’Leary, M.E.; Bottaro, A. Animal models of rheumatoid pain: Experimental systems and insights. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitamura, M.; Nakano, N.; Yonekawa, T.; Shan, L.; Kaise, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamashita, K.; Kikkawa, H.; Kinoshita, M. T cells are involved in the development of arthritis induced by anti-type II collagen antibody. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rincon, M.; FlaveIl, R.A. AP-1 transcriptional activity requires both T-cell receptor-mediated and co-stimulatory signals in primary T lymphocytes. EMBO 1994, 13, 4370–4381. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Al-Kuhlani, M.; Johnston, S.C.; Ojcius, D.; Chou, J.; Dean, D. Transcription factor complex AP-1 mediates inflammation initiated by Chlamydia pneumoniae Infection. Cell Microbiol. 2013, 15, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Son, Y.J.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. AP-1-targeted anti-inflammatory activities of the nanostructured, self-assembling S5 peptide. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Boyle, D.L.; Manning, A.M.; Firestein, G.S. AP-1 and NF-kB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity 1998, 28, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; John, R.; Chen, J.; Richardson, J.A.; Shelton, J.M.; Bennett, M.; Zhou, X.J.; Nagami, G.T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Q.Q.; et al. RF-1 promotes inflammation early after ischemic acute kidney injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.H.; Gao, L.B.; Pan, X.M.; Li, C.; Liang, W.B.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L. Association between IRF-5 polymorphisms and risk of acute coronary syndrome. DNA Cell Biol. 2009, 29, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P.S.; Bhagat, G.; Pernis, A.B. IRF4 and its regulators: Evolving insights into the pathogenesis of inflammatory arthritis? Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernis, A.B. The role of IRF-4 in B and T cell activation and differentiation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002, 22, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macian, F. NFAT proteins: Key regulators of T-cell development and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onizawa, M.; Oshima, S.; Schulze-Topphoff, U.; Oses-Prieto, J.A.; Lu, T.; Tavares, R.; Prodhomme, T.; Duong, B.; Whang, M.I.; Advincula, R.; et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 restricts ubiquitination of the kinase RIPK3 and protects cells from necroptosis. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.J. The primary mechanism of the IL-10-regulated anti-inflammatory response is to selectively inhibit transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 8686–8691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couper, K.N.; Blount, D.G.; Riley, E.M. IL-10: The master regulator of immunity to infection. J. Immunol. 2009, 180, 5771–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppelman, B.; Neefjes, J.J.; de Vries, J.E.; Malefyt, R.W. Interleukin-10 down-regulates MHC Class IIαβ peptide complexes at the plasma membrane of monocytes by affecting arrival and recycling. Immunity 1997, 7, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjabi, S.; Zenewicz, L.A.; Kamanaka, M.; Flavell, R.A. Anti- and pro-inflammatory roles of TGF-β, IL-10, and IL-22 in immunity and autoimmunity. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 9, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, F.; Bajtner, E.; Rintisch, C.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Sack, U.; Holmdahl, R. Methotrexate ameliorates T cell dependent autoimmune arthritis and encephalomyelitis but not antibody induced or fibroblast induced arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Svensson, L.; Holmdahl, R. Collagen type II-specific monoclonal antibody-induced arthritis in mice: Description of the disease and the influence of age, sex, and genes. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.C.; Carter, P.J. Therapeutic antibodies for autoimmunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 300–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.R.; Singh, J.A. The use of biologics in rheumatoid arthritis: Current and emerging paradigms of care. Clin. Ther. 2011, 33, 679–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, A.; Seok, S.H. Ethical guidelines for use of experimental animals in biomedical research. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 2013, 43, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.; Park, H.; Jung, S.; Kim, E.-K.; Cho, M.-L.; Min, J.-K.; Moon, S.-J.; Lee, S.-M.; Cho, J.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; et al. Therapeutic Effect of Exogenous Truncated IK Protein in Inflammatory Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091976
Choi S, Park H, Jung S, Kim E-K, Cho M-L, Min J-K, Moon S-J, Lee S-M, Cho J-H, Lee D-H, et al. Therapeutic Effect of Exogenous Truncated IK Protein in Inflammatory Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091976
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Seulgi, HyeLim Park, SeoYeon Jung, Eun-Kyung Kim, Mi-La Cho, Jun-Ki Min, Su-Jin Moon, Sang-Myeong Lee, Jang-Hee Cho, Dong-Hee Lee, and et al. 2017. "Therapeutic Effect of Exogenous Truncated IK Protein in Inflammatory Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091976
APA StyleChoi, S., Park, H., Jung, S., Kim, E. -K., Cho, M. -L., Min, J. -K., Moon, S. -J., Lee, S. -M., Cho, J. -H., Lee, D. -H., & Nam, J. -H. (2017). Therapeutic Effect of Exogenous Truncated IK Protein in Inflammatory Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1976. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091976