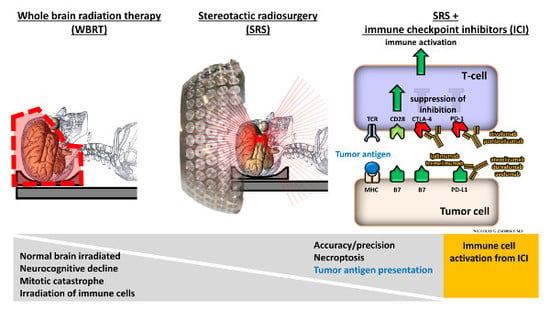
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Management of Brain Metastases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Traditional Treatment of Brain Metastases
3. Stereotactic Radiosurgery
4. Stereotactic Radiosurgery in the Definitive and Post-Operative Setting
5. Impact of Radiation Therapy on the Immune System
6. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
7. Rationale for Combining SRS and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Treating Brain Metastases
8. Existing Clinical Data Supporting Combining SRS with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
9. Planned and Ongoing Prospective Randomized Control Trials Assessing the Safety and Efficacy of Combination Therapy with SRS and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| WBRT | Whole brain radiation therapy |
| SRS | Stereotactic radiosurgery |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| RPA | Recursive partitioning analysis |
| KPS | Karnofsky Performance Status |
| DS-GPA | Diagnosis Specific–Graded Prognostic Assessment |
| Gy | Gray |
| LC | Local control |
| OS | Overall survival |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| RT | Radiation therapy |
| LINAC | Linear accelerator |
| NCCN | National Comprehensive Cancer Network |
| APC | Antigen presenting cells |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 |
| dsDNA | Double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid |
| STING | STimulator of INterferon Genes |
| DC | Dendritic cells |
| IFN | Interferon |
| ICD | Immunogenic cell death |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor β |
| Tregs | T regulatory cells |
| TAMs | Tumor associated macrophages |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| PD-1 | Programmed death cell protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death ligand-1 |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| RCC | Renal cell carcinoma |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| SCLC | Small cell lung cancer |
| BBB | Blood brain barrier |
| VLA-4 | Very late antigen-4 |
| LFA-1 | Leukocyte-function-associated antigen-1 |
| H | Histology |
| M | Melanoma |
| N | Total number of patients |
| NR | Not reported |
| USA | United States of America |
References
- Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Sloan, A.E.; Davis, F.G.; Vigneau, F.D.; Lai, P.; Sawaya, R.E. Incidence proportions of brain metastases in patients diagnosed (1973 to 2001) in the metropolitan detroit cancer surveillance system. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2865–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, B.A.; Ward, E.; McCarthy, B.J.; Schymura, M.J.; Ries, L.A.; Eheman, C.; Jemal, A.; Anderson, R.N.; Ajani, U.A.; Edwards, B.K. Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2007, featuring tumors of the brain and other nervous system. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 714–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabors, L.B.; Portnow, J.; Ammirati, M.; Baehring, J.; Brem, H.; Butowski, N.; Fenstermaker, R.A.; Forsyth, P.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.; Holdhoff, M.; et al. Nccn practice guidelines in oncology—Central nervous system cancers, version 1.2017. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2017, 15, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvold, N.D.; Lee, E.Q.; Mehta, M.P.; Margolin, K.; Alexander, B.M.; Lin, N.U.; Anders, C.K.; Soffietti, R.; Camidge, D.R.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; et al. Updates in the management of brain metastases. Neuro. Oncol. 2016, 18, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanghvi, S.M.; Lischalk, J.W.; Cai, L.; Collins, S.; Nair, M.; Collins, B.; Unger, K. Clinical outcomes of gastrointestinal brain metastases treated with radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifiletti, D.M.; Patel, N.; Lee, C.C.; Romano, A.M.; Sheehan, J.P. Stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of brain metastases from gastrointestinal primaries. J. Neurooncol. 2015, 124, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieder, C.; Spanne, O.; Mehta, M.P.; Grosu, A.L.; Geinitz, H. Presentation, patterns of care, and survival in patients with brain metastases: What has changed in the last 20 years? Cancer 2011, 117, 2505–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, L.; Scott, C.; Rotman, M.; Asbell, S.; Phillips, T.; Wasserman, T.; McKenna, W.G.; Byhardt, R. Recursive partitioning analysis (rpa) of prognostic factors in three radiation therapy oncology group (rtog) brain metastases trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 37, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Kased, N.; Roberge, D.; Xu, Z.; Shanley, R.; Luo, X.; Sneed, P.K.; Chao, S.T.; Weil, R.J.; Suh, J.; et al. Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: An accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgelt, B.; Gelber, R.; Kramer, S.; Brady, L.W.; Chang, C.H.; Davis, L.W.; Perez, C.A.; Hendrickson, F.R. The palliation of brain metastases: Final results of the first two studies by the radiation therapy oncology group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1980, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneed, P.K.; Larson, D.A.; Wara, W.M. Radiotherapy for cerebral metastases. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 1996, 7, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchell, R.A.; Tibbs, P.A.; Regine, W.F.; Dempsey, R.J.; Mohiuddin, M.; Kryscio, R.J.; Markesbery, W.R.; Foon, K.A.; Young, B. Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: A randomized trial. JAMA 1998, 280, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, C.M.; Suki, D.; Feiz-Erfan, I.; Mahajan, A.; Chang, E.; Sawaya, R.; Lang, F.F. Adjuvant whole-brain radiation therapy after surgical resection of single brain metastases. Neuro. Oncol. 2010, 12, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kocher, M.; Soffietti, R.; Abacioglu, U.; Villa, S.; Fauchon, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Fariselli, L.; Tzuk-Shina, T.; Kortmann, R.D.; Carrie, C.; et al. Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: Results of the eortc 22952–26001 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, E.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Hess, K.R.; Allen, P.K.; Lang, F.F.; Kornguth, D.G.; Arbuckle, R.B.; Swint, J.M.; Shiu, A.S.; Maor, M.H.; et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G., 2nd; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Pugh, S.; Laack, N.N.; Wefel, J.S.; Khuntia, D.; Meyers, C.; Choucair, A.; Fox, S.; Suh, J.H.; Roberge, D.; et al. Memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuro. Oncol. 2013, 15, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Inbar, O.; Melmer, P.; Lee, C.C.; Xu, Z.; Schlesinger, D.; Sheehan, J.P. Leukoencephalopathy in long term brain metastases survivors treated with radiosurgery. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 126, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McTyre, E.; Scott, J.; Chinnaiyan, P. Whole brain radiotherapy for brain metastasis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, S236–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abe, E.; Aoyama, H. The role of whole brain radiation therapy for the management of brain metastases in the era of stereotactic radiosurgery. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 14, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Zeng, R.; Yang, K.H.; Tian, J.H.; Wu, X.L.; Dai, Q.; Niu, X.D.; Ma, D.W. Whole brain radiotherapy combined with stereotactic radiotherapy versus stereotactic radiotherapy alone for brain metastases: A meta-analysis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.L.; Tome, W.A.; Caine, C.; Corn, B.; Kanner, A.; Rowley, H.; Kundapur, V.; DeNittis, A.; Greenspoon, J.N.; et al. Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (rtog 0933): A phase ii multi-institutional trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3810–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patchell, R.A.; Tibbs, P.A.; Walsh, J.W.; Dempsey, R.J.; Maruyama, Y.; Kryscio, R.J.; Markesbery, W.R.; Macdonald, J.S.; Young, B. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Ballman, K.V.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Whitton, A.C.; Greenspoon, J.; Parney, I.F.; Laack, N.N.I.; Ashman, J.B.; et al. Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (ncctg n107c/cec.3): A multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Ahmed, S.; McAleer, M.F.; Weinberg, J.S.; Li, J.; Brown, P.; Settle, S.; Prabhu, S.S.; Lang, F.F.; Levine, N.; et al. Post-operative stereotactic radiosurgery versus observation for completely resected brain metastases: A single-centre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D.W.; Scott, C.B.; Sperduto, P.W.; Flanders, A.E.; Gaspar, L.E.; Schell, M.C.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Demas, W.; Ryu, J.; Bahary, J.P.; et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: Phase iii results of the rtog 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 2004, 363, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.T.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Barnett, G.H.; Stevens, G.H.; Murphy, E.S.; Stockham, A.L.; Shiue, K.; Suh, J.H. Challenges with the diagnosis and treatment of cerebral radiation necrosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Auh, S.L.; Wang, Y.; Burnette, B.; Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Beckett, M.; Sharma, R.; Chin, R.; Tu, T.; et al. Therapeutic effects of ablative radiation on local tumor require cd8+ T cells: Changing strategies for cancer treatment. Blood 2009, 114, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, M.Z.; Galloway, A.E.; Kawashima, N.; Dewyngaert, J.K.; Babb, J.S.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Fractionated but not single-dose radiotherapy induces an immune-mediated abscopal effect when combined with anti-ctla-4 antibody. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5379–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanpouille-Box, C.; Alard, A.; Aryankalayil, M.J.; Sarfraz, Y.; Diamond, J.M.; Schneider, R.J.; Inghirami, G.; Coleman, C.N.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. DNA exonuclease trex1 regulates radiotherapy-induced tumour immunogenicity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, E.B.; Pellicciotta, I.; Demaria, S.; Barcellos-Hoff, M.H.; Formenti, S.C. The convergence of radiation and immunogenic cell death signaling pathways. Front Oncol. 2012, 2, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wennerberg, E.; Lhuillier, C.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Pilones, K.A.; Garcia-Martinez, E.; Rudqvist, N.P.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Barriers to radiation-induced in situ tumor vaccination. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, H.M.; Daly, M.E.; Azghadi, S.; Stewart, S.L.; Oesterich, L.; Schlom, J.; Donahue, R.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Chen, Q.; Rao, S.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiation therapy induces systemic differences in peripheral blood immunophenotype dependent on irradiated site. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 101, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Thomas, L.; Bondarenko, I.; O’Day, S.; Weber, J.; Garbe, C.; Lebbe, C.; Baurain, J.F.; Testori, A.; Grob, J.J.; et al. Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csoszi, T.; Fulop, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for pd-l1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crino, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.R.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.E.; Chow, L.Q.; Vokes, E.E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, J.B.; Sturm, E. Conditions determining the transplantability of tissues in the brain. J. Exp. Med. 1923, 38, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widner, H.; Brundin, P. Immunological aspects of grafting in the mammalian central nervous system. A review and speculative synthesis. Brain Res. 1988, 472, 287–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medawar, P.B. Immunity to homologous grafted skin; the fate of skin homografts transplanted to the brain, to subcutaneous tissue, and to the anterior chamber of the eye. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1948, 29, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, H.S.; Suk, K. The function and integrity of the neurovascular unit rests upon the integration of the vascular and inflammatory cell systems. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2005, 2, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ransohoff, R.M.; Kivisakk, P.; Kidd, G. Three or more routes for leukocyte migration into the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, M.J.; Doose, J.M.; Melchior, B.; Schmid, C.D.; Ploix, C.C. Cns immune privilege: Hiding in plain sight. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 213, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoll, G.; Jander, S.; Schroeter, M. Detrimental and beneficial effects of injury-induced inflammation and cytokine expression in the nervous system. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2002, 513, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carman, C.V.; Springer, T.A. A transmigratory cup in leukocyte diapedesis both through individual vascular endothelial cells and between them. J. Cell. Biol. 2004, 167, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujinami, R.S.; Oldstone, M.B. Amino acid homology between the encephalitogenic site of myelin basic protein and virus: Mechanism for autoimmunity. Science 1985, 230, 1043–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, M.C.; Lee, S.M.; Kalume, F.; Morcos, Y.; Dohan, F.C., Jr.; Hasty, K.A.; Callaway, J.C.; Zunt, J.; Desiderio, D.; Stuart, J.M. Autoimmunity due to molecular mimicry as a cause of neurological disease. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deli, M.A.; Abraham, C.S.; Kataoka, Y.; Niwa, M. Permeability studies on in vitro blood-brain barrier models: Physiology, pathology, and pharmacology. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 25, 59–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronk, J.C.; Filiano, A.J.; Louveau, A.; Marin, I.; Marsh, R.; Ji, E.; Goldman, D.H.; Smirnov, I.; Geraci, N.; Acton, S.; et al. Peripherally derived macrophages can engraft the brain independent of irradiation and maintain an identity distinct from microglia. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1627–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnus, T.; Schreiner, B.; Korn, T.; Jack, C.; Guo, H.; Antel, J.; Ifergan, I.; Chen, L.; Bischof, F.; Bar-Or, A.; et al. Microglial expression of the b7 family member b7 homolog 1 confers strong immune inhibition: Implications for immune responses and autoimmunity in the cns. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2537–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwidzinski, E.; Bunse, J.; Aktas, O.; Richter, D.; Mutlu, L.; Zipp, F.; Nitsch, R.; Bechmann, I. Indolamine 2,3-dioxygenase is expressed in the cns and down-regulates autoimmune inflammation. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1347–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulzewsky, F.; Pelz, A.; Feng, X.; Synowitz, M.; Markovic, D.; Langmann, T.; Holtman, I.R.; Wang, X.; Eggen, B.J.; Boddeke, H.W.; et al. Glioma-associated microglia/macrophages display an expression profile different from m1 and m2 polarization and highly express gpnmb and spp1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrusiewicz, K.; Rodriguez, B.; Wei, J.; Hashimoto, Y.; Healy, L.M.; Maiti, S.N.; Thomas, G.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Q.; Elakkad, A.; et al. Glioblastoma-infiltrated innate immune cells resemble m0 macrophage phenotype. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e85841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, N.; Saio, M.; Suwa, T.; Kitoh, Y.; Bai, J.; Nonaka, K.; Ouyang, G.F.; Okada, M.; Balazs, M.; Adany, R.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating myeloid-derived suppressor cells are pleiotropic-inflamed monocytes/macrophages that bear m1- and m2-type characteristics. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon-Muvdi, T.; Theodros, D.; Luksik, A.S.; Maxwell, R.; Kim, E.; Jackson, C.M.; Belcaid, Z.; Ganguly, S.; Tyler, B.; Brem, H.; et al. Dendritic cell activation enhances anti-pd-1 mediated immunotherapy against glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20681–20697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggart, D.; Andreou, T.; Scott, K.J.; Williams, J.; Rippaus, N.; Brownlie, R.J.; Ilett, E.J.; Salmond, R.J.; Melcher, A.; Lorger, M. Anti-pd-1/anti-ctla-4 efficacy in melanoma brain metastases depends on extracranial disease and augmentation of cd8(+) t cell trafficking. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E1540–E1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.M.; Kochel, C.M.; Nirschl, C.J.; Durham, N.M.; Ruzevick, J.; Alme, A.; Francica, B.J.; Elias, J.; Daniels, A.; Dubensky, T.W., Jr.; et al. Systemic tolerance mediated by melanoma brain tumors is reversible by radiotherapy and vaccination. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1161–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chongsathidkiet, P.; Jackson, C.; Koyama, S.; Loebel, F.; Cui, X.; Farber, S.H.; Woroniecka, K.; Elsamadicy, A.A.; Dechant, C.A.; Kemeny, H.R.; et al. Sequestration of t cells in bone marrow in the setting of glioblastoma and other intracranial tumors. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Understanding responses to stereotactic body radiotherapy and pembrolizumab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2661–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, M.; Tam, M.; Ott, P.A.; Pavlick, A.C.; Rush, S.C.; Donahue, B.R.; Golfinos, J.G.; Parker, E.C.; Huang, P.P.; Narayana, A. Ipilimumab in melanoma with limited brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Melanoma Res. 2013, 23, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silk, A.W.; Bassetti, M.F.; West, B.T.; Tsien, C.I.; Lao, C.D. Ipilimumab and radiation therapy for melanoma brain metastases. Cancer Med. 2013, 2, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, K.A.; Stallworth, D.G.; Kim, Y.; Johnstone, P.A.; Harrison, L.B.; Caudell, J.J.; Yu, H.H.; Etame, A.B.; Weber, J.S.; Gibney, G.T. Clinical outcomes of melanoma brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiation and anti-pd-1 therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiess, A.P.; Wolchok, J.D.; Barker, C.A.; Postow, M.A.; Tabar, V.; Huse, J.T.; Chan, T.A.; Yamada, Y.; Beal, K. Stereotactic radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases in patients receiving ipilimumab: Safety profile and efficacy of combined treatment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, J.D.; Mahadevan, A.; Floyd, S.R.; Dyer, M.A.; Catalano, P.J.; Alexander, B.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Kaplan, I.D. Ipilmumab and cranial radiation in metastatic melanoma patients: A case series and review. J. Immunother. Cancer 2015, 3, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.M.; Yu, J.B.; Kluger, H.M.; Chiang, V.L. Timing and type of immune checkpoint therapy affect the early radiographic response of melanoma brain metastases to stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer 2016, 122, 3051–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, E.S.; Postow, M.A.; Wolchok, J.D.; Young, R.J.; Ballangrud, A.; Chan, T.A.; Yamada, Y.; Beal, K. Melanoma brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery and concurrent pembrolizumab display marked regression; efficacy and safety of combined treatment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, E.S.; Lo, S.; Drummond, M.; Fogarty, G.B.; Menzies, A.M.; Guminski, A.; Shivalingam, B.; Clarke, K.; Long, G.V.; Hong, A.M. Survival of patients with melanoma brain metastasis treated with stereotactic radiosurgery and active systemic drug therapies. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen-Inbar, O.; Shih, H.H.; Xu, Z.; Schlesinger, D.; Sheehan, J.P. The effect of timing of stereotactic radiosurgery treatment of melanoma brain metastases treated with ipilimumab. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudy-Marqueste, C.; Dussouil, A.S.; Carron, R.; Troin, L.; Malissen, N.; Loundou, A.; Monestier, S.; Mallet, S.; Richard, M.A.; Regis, J.M.; et al. Survival of melanoma patients treated with targeted therapy and immunotherapy after systematic upfront control of brain metastases by radiosurgery. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 84, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.R.; Shoukat, S.; Oliver, D.E.; Chowdhary, M.; Rizzo, M.; Lawson, D.H.; Khosa, F.; Liu, Y.; Khan, M.K. Ipilimumab and stereotactic radiosurgery versus stereotactic radiosurgery alone for newly diagnosed melanoma brain metastases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 40, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrepnik, T.; Sundararajan, S.; Cui, H.; Stea, B. Improved time to disease progression in the brain in patients with melanoma brain metastases treated with concurrent delivery of radiosurgery and ipilimumab. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1283461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, N.L.; Wuthrick, E.J.; Kim, H.; Palmer, J.D.; Garg, S.; Eldredge-Hindy, H.; Daskalakis, C.; Feeney, K.J.; Mastrangelo, M.J.; Kim, L.J.; et al. Phase 1 study of ipilimumab combined with whole brain radiation therapy or radiosurgery for melanoma patients with brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, S.; Mahmood, M.; Mullen, D.; Yang, D.; Tsien, C.I.; Huang, J.; Perkins, S.M.; Rich, K.; Chicoine, M.; Leuthardt, E.; et al. Distant intracranial failure in melanoma brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery in the era of immunotherapy and targeted agents. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 2, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuf, M.B.; Amsbaugh, M.J.; Burton, E.; Chesney, J.; Woo, S. Peri-srs administration of immune checkpoint therapy for melanoma metastatic to the brain: Investigating efficacy and the effects of relative treatment timing on lesion response. World Neurosurg. 2017, 100, 632–640.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, K.A.; Kim, S.; Arrington, J.; Naghavi, A.O.; Dilling, T.J.; Creelan, B.C.; Antonia, S.J.; Caudell, J.J.; Harrison, L.B.; Sahebjam, S.; et al. Outcomes targeting the pd-1/pd-l1 axis in conjunction with stereotactic radiation for patients with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Douglass, J.; Kleinberg, L.; Ye, X.; Marciscano, A.E.; Forde, P.M.; Brahmer, J.; Lipson, E.; Sharfman, W.; Hammers, H.; et al. Concurrent immune checkpoint inhibitors and stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, and renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrer, E.J.; Peterson, J.; Brown, P.D.; Sheehan, J.P.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Trifiletti, D.M. Treatment of brain metastases with stereotactic radiosurgery and immune checkpoint inhibitors: An international meta-analysis of individual patient data. Radiother. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Drug | Target | FDA Approved Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Ipilimumab | CTLA-4 | Metastatic Melanoma |
| Pembrolizumab | PD-1 | Metastatic Melanoma, NSCLC, Head and Neck Cancer, Hodgkin Lymphoma, Urothelial Carcinoma, Gastric Cancer, Cervical Cancer |
| Nivolumab | PD-1 | Metastatic Melanoma, NSCLC, RCC, Hodgkin Lymphoma, Head and Neck Cancer, Urothelial Carcinoma, CRC, HCC, SCLC |
| Atezolizumab | PD-L1 | Bladder Cancer, NSCLC |
| Ipilimumab + Nivolumab | CTLA-4 + PD-1 | RCC, CRC |
| Study | H | Arm | N | ICI Target | DS-GPA | 1-Year OS (%) | 1-Year LC (%) | 1-Year RBC (%) | RN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mathew et al., 2013 [61]. | M | NR | 25 | CTLA-4 | NR | 32.6 | 40 | 16 | NR |
| Silk et al., 2013 [62]. | M | NR | 17 | CTLA-4 | 25% (0-1); 39.3% (2); 25% (3); 10.7% (4) | 82.3 | NR | NR | NR |
| Ahmed et al., 2016 [63]. | M | NR | 26 | PD-1 | 27% (1-2); 19% (3-4) | 74.7 | 82 | 45.9 | NR |
| Kiess et al., 2015 [64]. | M | SRS → ICI | 19 | CTLA-4 | 3 (median) | 56 | 87 | 36 | NR |
| SRS = ICI | 15 | 65 | 100 | 31 | NR | ||||
| ICI → SRS | 12 | 50 | 89 | 8 | NR | ||||
| Schoenfeld et al., 2015 [65]. | M | SRS → ICI | 5 | CTLA-4 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| SRS = ICI | 4 | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||
| ICI → SRS | 7 | NR | NR | NR | NR | ||||
| Qian et al., 2015 [66]. | M | SRS ≠ ICI | 22 | CTLA-4 or PD-1 | 3 (median) | 44.4 | NR | NR | NR |
| SRS = ICI | 33 | 2 (median) | 62.5 | NR | NR | NR | |||
| Ahmed et al., 2017 [76]. | NSCLC | NR | 17 | PD-1 | 59% (0-1.5); 41% (2-3) | 40.0 | 96.0 | 0.0 | NR |
| Anderson et al., 2017 [67]. | M | NR | 11 | PD-1 | 3 (median) | NR | NR | NR | 0 |
| Choong et al., 2017 [68]. | M | NR | 39 | CTLA-4 or PD-1 | NR | 54.9 | NR | NR | 5 |
| Cohen-Inbar et al., 2017 [69]. | M | SRS = ICI; SRS → ICI | 32 | CTLA-4 | 2.5% (0-1); 53% (2); 18.8% (3); 15.6% (4) | 59.0 | 54.4 | 25.8 | 31 |
| ICI → SRS | 14 | 14.3% (0-1); 64.3% (2); 0% (3); 21.4% (4) | 33.0 | 16.5 | 26.8 | 7 | |||
| Gaudy-Marqueste et al., 2017 [70]. | M | SRS → ICI | 43 | CTLA-4 or PD-1 | NR | 52.4 | NR | NR | NR |
| Patel et al., 2017 [71]. | M | NR | 20 | CTLA-4 | 10% (1); 35% (2); 30% (3); 25% (4) | 37.1 | 71.4 | 12.7 | NR |
| Skrepnik et al., 2017 [72]. | M | NR | 25 | CTLA-4 | NR | 83.0 | 94.8 | 72.0 | 12 |
| Williams et al., 2017 [73]. | M | NR | 11 | CTLA-4 | NR | 60.0 | NR | NR | 0 |
| Yusuf et al., 2017 [75]. | M | SRS = ICI | 12 | CTLA-4 or PD-1 | NR | 45.0 | 87.6 | 46.4 | 2 |
| SRS ≠ ICI | 6 | 21.5 | NR | 0.0 | 0 | ||||
| Acharya et al., 2017 [74]. | M | NR | 18 | CTLA-4 and/or PD-1 | 6% (1); 28% (2); 39% (3); 0% (4) | 58.5 | 85.0 | 60.0 | NR |
| Chen et al., 2018 [77]. | M, NSCLC, RCC | SRS → ICI | 30 | CTLA-4 and/or PD-1 | NR | 63.6 | NR | NR | NR |
| SRS = ICI | 28 | 77.9 | 88.0 | NR | NR | ||||
| ICI → SRS | 23 | 50.7 | NR | NR | NR |
| Study | Phase | Country | Histology | SRS Dose | ICI Target | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02886585 | 2 | USA | Melanoma | NR | PD-1 | Overall Response Rate; Overall Survival; Extracranial Overall Response Rate |
| NCT02858869 | 1 | USA | Melanoma and NSCLC | 30 Gy/5 fractions 27 Gy/3 fractions 18-21 Gy/1 fraction | PD-1 | Dose-Limiting Toxicities |
| NCT02978404 | 2 | Canada | NSCLC and RCC | 15-20 Gy/1 fraction | PD-1 | Progression-Free Survival |
| NCT02696993 | 1 & 2 | USA | NSCLC | NR | CTLA-4 and PD-1 | Maximum Tolerated Dose; Dose-Limiting Toxicities |
| NCT03340129 | 2 | Australia | Melanoma | 16-22 Gy/1 fraction | CTLA-4 and PD-1 | Intracranial Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor |
| NCT02716948 | 1 | USA | Melanoma | NR | PD-1 | Incidence of Severe Adverse Effects |
| NCT02097732 | 2 | USA | Melanoma | NR | CTLA-4 | Local Control at 6 months |
| NCT01703507 | 1 | USA | Melanoma | NR | CTLA-4 | Maximum Tolerated Dose |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lehrer, E.J.; McGee, H.M.; Peterson, J.L.; Vallow, L.; Ruiz-Garcia, H.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Sharma, S.; Trifiletti, D.M. Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Management of Brain Metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103054
Lehrer EJ, McGee HM, Peterson JL, Vallow L, Ruiz-Garcia H, Zaorsky NG, Sharma S, Trifiletti DM. Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Management of Brain Metastases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103054
Chicago/Turabian StyleLehrer, Eric J., Heather M. McGee, Jennifer L. Peterson, Laura Vallow, Henry Ruiz-Garcia, Nicholas G. Zaorsky, Sonam Sharma, and Daniel M. Trifiletti. 2018. "Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Management of Brain Metastases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103054
APA StyleLehrer, E. J., McGee, H. M., Peterson, J. L., Vallow, L., Ruiz-Garcia, H., Zaorsky, N. G., Sharma, S., & Trifiletti, D. M. (2018). Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Management of Brain Metastases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103054