Epidermal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein: A Novel Marker in the Diagnosis of Dry Eye Disease in Sjögren Syndrome
Abstract
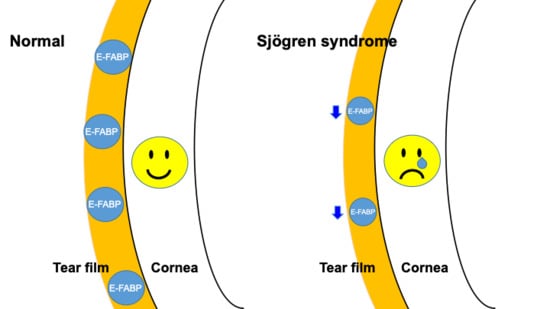
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Subjects and Examinations
2.2. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Concentration in Tears, Saliva, and Serum Measured by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.3. Dry Eye Symptom Questionnaire
2.4. Tear Function Examinations
2.5. Correlations between Tear Fatty Acid-Binding Protein and DED Parameters
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Subjects and Examinations
4.2. Collection of Tears, Saliva, and Serum
4.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.4. Dry Eye Symptom Questionnaire
4.5. Tear Function Examinations
4.5.1. Tear Break-Up Time
4.5.2. Ocular Surface Vital Staining
4.5.3. Schirmer Test-1
4.6. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sjogren, H. Zur Kenntnis Der Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca Ii. Acts Opthalmol. 1935, 13, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, H.; Asashima, H.; Takai, C.; Hagiwara, S.; Hagiya, C.; Yokosawa, M.; Hirota, T.; Umehara, H.; Kawakami, A.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Primary and secondary surveys on epidemiology of Sjögren syndrome in Japan. Mod. Rheumatol. 2014, 24, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillemer, S.R.; Matteson, E.L.; Jacobsson, L.T.; Martens, P.B.; Melton, L.J.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Fox, P.C. Incidence of physician-diagnosed primary Sjogren syndrome in residents of Olmsted County, Minnesota. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2001, 76, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibayashi, T.; Sugai, S.; Miyasaka, N.; Hayashi, Y.; Tsubota, K. Revised Japanese criteria for Sjögren syndrome. Mod Rheumatol. 2004, 14, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitali, C.; Bombardieri, S.; Jonsson, R.; Moutsopoulos, H.; Alexander, E.; Carsons, S.; Daniels, T.; Fox, P.C.; Fox, R.; Kassan, S.S.; et al. Classification criteria for Sjogren syndrome: A revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiboski, S.C.; Shiboski, C.H.; Criswell, L.A.; Bae, A.N.; Challacombe, S.; Lanfranchi, H.; Schiødt, M.; Umehara, H.; Vivino, F.; Zhao, Y.; et al. American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjogren’s syndrome: A. data-driven, expert consensus approach in the Sjogren International Collaborative Clinical Alliance cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcher, J.P.; Shiboski, C.H.; Shiboski, S.C.; Heidenreich, A.M.; Kitagawa, K.; Zhang, S.; Hamann, S.; Larkin, G.; McNamara, N.A.; Greenspan, J.S. A simplified quantitative method for assessing keratoconjunctivitis sicca from the Sjögren’s Syndrome International Registry. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 149, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, T.H.; Dogru, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kojima, T.; Kaido, M.; Ibrahim, O.M.; Sato, E.A.; Igarashi, A.; Ichihashi, Y.; Satake, Y.; et al. Evaluation of lipid oxidative stress status in Sjögren syndrome patients. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Shao, X.; Ni, Z.; Mou, S. L-FABP: A novel biomarker of kidney disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 445, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vupputuri, A.; Sekhar, S.; Krishnan, S.; Venugopal, K.; Natarajan, K.U. Heart-type fatty acid-binding protein (H-FABP) as an early diagnostic biomarker in patients with acute chest pain. Indian Heart J. 2015, 67, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohrfelt, A.; Andreasson, U.; Simon, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Edman, A.; Potter, W.; Holder, D.; Devanarayan, V.; Seeburger, J.; Smith, A.D.; et al. Screening for new biomarkers for subcortical vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2011, 1, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smathers, R.L.; Petersen, D.R. The human fatty acid-binding protein family: Evolutionary divergences and functions. Hum. Genom. 2011, 5, 170–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegenthaler, G.; Hotz, R.; Chatellard-Gruaz, D.; Jaconi, S.; Saurat, J.H. Characterization and expression of a novel human fatty acid-binding protein: The epidermal type (E-FABP). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 190, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owada, Y.; Yoshimoto, T.; Kondo, H. Spatio-temporally differential expression of genes for three members of fatty acid binding proteins in developing and mature rat brains. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1996, 12, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, R.F.; Seery, J.P.; Celis, J.E.; Frischauf, A.; Watt, F.M. PA-FABP, a novel marker of human epidermal transit amplifying cells revealed by 2D protein gel electrophoresis and cDNA array hybridisation. FEBS Lett. 2000, 486, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Tarawneh, S.K.; Border, M.B.; Dibble, C.F.; Bencharit, S. Defining salivary biomarkers using mass spectrometry-based proteomics: A systematic review. Omics 2011, 15, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, O.; Krief, G.; Konttinen, Y.T.; Zaks, B.; Wong, D.T.; Aframian, D.J.; Palmon, A. Identification of Sjögren syndrome oral fluid biomarker candidates following high-abundance protein depletion. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleissig, Y.; Deutsch, O.; Reichenberg, E.; Redlich, M.; Zaks, B.; Palmon, A.; Aframian, D.J. Different proteomic protein patterns in saliva of Sjögren syndrome patients. Oral Dis. 2009, 15, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, L.; Baldini, C.; Bazzichi, L.; Bombardieri, S.; Lucacchini, A. Proteomic diagnosis of Sjögren syndrome. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2007, 4, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Vissink, A.; Arellano, M.; Roozendaal, C.; Zhou, H.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Wong, D.T. Identification of autoantibody biomarkers for primary Sjögren syndrome using protein microarrays. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peluso, G.; De Santis, M.; Inzitari, R.; Fanali, C.; Cabras, T.; Messana, I.; Castagnola, M.; Ferraccioli, G.F. Proteomic study of salivary peptides and proteins in patients with Sjögren syndrome before and after pilocarpine treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, O.H.; Atkinson, J.C.; Hoehn, G.T.; Illei, G.G.; Hart, T.C. Identification of parotid salivary biomarkers in Sjögren syndrome by surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartuccio, L.; Salvin, S.; Fabris, M.; Maset, M.; Pontarini, E.; Isola, M.; De Vita, S. BLyS upregulation in Sjögren syndrome associated with lymphoproliferative disorders, higher ESSDAI score and B-cell clonal expansion in the salivary glands. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, A.; Suzuki, K.; Kassai, Y.; Gotou, Y.; Takiguchi, M.; Miyazaki, T.; Yoshimoto, K.; Yasuoka, H.; Yamaoka, K.; Morita, R.; et al. Identification of definitive serum biomarkers associated with disease activity in primary Sjögren syndrome. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Sheng, M.; Li, J.; Yan, G.; Lin, A.; Li, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, Y. Tear proteomic analysis of Sjogren syndrome patients with dry eye syndrome by two-dimensional-nano-liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.; Fujii, H.; Odani, S.; Sakakibara, J.; Yamamoto, A.; Ito, M.; Ono, T. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding a novel fatty acid-binding protein from rat skin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 200, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, C.; Beesley, C.; Foster, C.S.; Chen, H.; Rudland, P.S.; West, D.C.; Fujii, H.; Smith, P.H.; Ke, Y. Human cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein induces metastasis by up-regulating the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor gene in rat Rama 37 model cells Rama. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4357–4364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adamson, J.; Morgan, E.A.; Beesley, C.; Mei, Y.; Foster, C.S.; Fujii, H.; Rudland, P.S.; Smith, P.H.; Ke, Y. High-level expression of cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein in prostatic carcinomas and its effect on tumorigenicity. Oncogene 2003, 22, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veerkamp, J.H. Fatty acid-binding proteins of nervous tissue. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2001, 16, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suojalehto, H.; Kinaret, P.; Kilpeläinen, M.; Toskala, E.; Ahonen, N.; Wolff, H.; Alenius, H.; Puustinen, A. Level of fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5) is increased in sputum of allergic asthmatics and links to airway remodeling and inflammation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.M.; Holt, V.V.; Malpass, L.R.; Hines, I.N.; Wheeler, M.D. Fatty acid-binding protein 5 limits the anti-inflammatory response in murine macrophages. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Rao, E.; Yan, F.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Silverstein, K.A.; Liu, S.; Sauter, E.; Cleary, M.P.; et al. Fatty acid-binding protein E-FABP restricts tumor growth by promoting IFN-β responses in tumor-associated macrophages. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2986–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owada, Y.; Suzuki, I.; Noda, T.; Kondo, H. Analysis on the phenotype of E-FABP-gene knockout mice. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 239, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, E.; Owada, Y.; Ikawa, S.; Adachi, Y.; Egawa, T.; Nemoto, K.; Suzuki, K.; Hishinuma, T.; Kawashima, H.; Kondo, H.; et al. Epidermal FABP (FABP5) regulates keratinocyte differentiation by 13(S)-HODE-mediated activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbi, J.; Pardoll, D.; Pan, F. Metabolic control of the Treg/Th17 axis. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 252, 52–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, J.M.; Liu, Q.; Brittingham, K.C.; Liu, Y.; Gruenthal, M.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Stout, R.D.; Suttles, J. Deficiency of fatty acid-binding proteins in mice confers protection from development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, A.; Boisvert, W.A.; Lee, C.H.; Laffitte, B.A.; Barak, Y.; Joseph, S.B.; Liao, D.; Nagy, L.; Edwards, P.A.; Curtiss, L.K.; et al. A PPAR γ-LXR-ABCA1 pathway in macrophages is involved in cholesterol efflux and atherogenesis. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricote, M.; Li, A.C.; Willson, T.M.; Kelly, C.J.; Glass, C.K. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ is a negative regulator of macrophage activation. Nature 1998, 391, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, G.; Fong, A.L.; Ogawa, S.; Gamliel, A.; Li, A.C.; Perissi, V.; Rose, D.W.; Willson, T.M.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Glass, C.K. A SUMOylation-dependent pathway mediates transrepression of inflammatory response genes by PPAR-gamma. Nature 2005, 437, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogue, A.; Spire, C.; Brun, M.; Claude, N.; Guillouzo, A. Gene expression changes induced by PPAR gamma agonists in animal and human liver. PPAR Res. 2010, 2010, 325183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Tian, T.; Park, C.O.; Lofftus, S.Y.; Mei, S.; Liu, X.; Luo, C.; O’Malley, J.T.; Gehad, A.; Teague, J.E.; et al. Survival of tissue-resident memory T cells requires exogenous lipid uptake and metabolism. Nature 2017, 543, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carbone, F.R.; Mackay, L.K.; Heath, W.R.; Gebhardt, T. Distinct resident and recirculating memory T cell subsets in non-lymphoid tissues. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.A.; Watanabe, R.; Teague, J.E.; Schlapbach, C.; Tawa, M.C.; Adams, N.; Dorosario, A.A.; Chaney, K.S.; Cutler, C.S.; Leboeuf, N.R.; et al. Skin effector memory T cells do not recirculate and provide immune protection in alemtuzumab-treated CTCL patients. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 117ra7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.N.; Mackay, L.K. Tissue-resident memory T cells: Local specialists in immune defence. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.; Gehad, A.; Yang, C.; Scott, L.L.; Teague, J.E.; Schlapbach, C.; Elco, C.P.; Huang, V.; Matos, T.R.; Kupper, T.S.; et al. Human skin is protected by four functionally and phenotypically discrete populations of resident and recirculating memory T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 279ra39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bose, T.; Lee, R.; Hou, A.; Tong, L.; Chandy, K.G. Tissue resident memory T cells in the human conjunctiva and immune signatures in human dry eye disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, C.Q.; Cornelius, J.G.; Cooper, L.; Neff, J.; Tao, J.; Lee, B.H.; Peck, A.B. Identification of possible candidate genes regulating Sjögren syndrome-associated autoimmunity: A potential role for TNFSF4 in autoimmune exocrinopathy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.Q.; Sharma, A.; She, J.X.; McIndoe, R.A.; Peck, A.B. Differential gene expressions in the lacrimal gland during development and onset of keratoconjunctivitis sicca in Sjögren syndrome (SjS)-like disease of the C57BL/6.NOD-Aec1Aec2 mouse. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 88, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodde, B.M.; Sankar, V.; Kok, M.R.; Leakan, R.A.; Tak, P.P.; Pillemer, S.R. Serum lipid levels in Sjögren syndrome. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, Y. Aquaporin-5 water channel in lipid rafts of rat parotid glands. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killedar, S.J.; Eckenrode, S.E.; McIndoe, R.A.; She, J.X.; Nguyen, C.Q.; Peck, A.B.; Cha, S. Early pathogenic events associated with Sjögren syndrome (SjS)-like disease of the nod mouse using microarray analysis. Lab. Investig. 2006, 86, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldini, C.; Giusti, L.; Ciregia, F.; Da Valle, Y.; Giacomelli, C.; Donadio, E.; Sernissi, F.; Bazzichi, L.; Giannaccini, G.; Bombardieri, S.; et al. Proteomic analysis of saliva: A unique tool to distinguish primary Sjögren’s syndrome from secondary Sjögren syndrome and other sicca syndromes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, Y.; Spann, N.J.; Link, V.M.; Muse, E.D.; Strid, T.; Edillor, C.; Kolar, M.J.; Matsuzaka, T.; Hayakawa, S.; Tao, J.; et al. SREBP1 contributes to resolution of pro-inflammatory TLR4 signaling by reprogramming fatty acid metabolism. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakane, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yokoi, N.; Uchino, M.; Dogru, M.; Oishi, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Ohashi, Y. Development and validation of the Dry Eye-Related Quality-of-Life Score questionnaire. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013, 131, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Revised Japanese Criteria for Sjögren Syndrome (SS) (1999) |
|---|
| 1. Histopathology Definition: Positive for at least one of (A) or (B): (A) Focus score ≧ 1 (periductal lymphoid cell infiltration ≧ 50) in a 4-mm2 minor salivary gland biopsy (B) Focus score ≧ 1 (periductal lymphoid cell infiltration ≧ 50) in a 4-mm2 lacrimal gland biopsy |
| 2. Oral Examination Definition: Positive for at least one of (A) or (B): (A) Abnormal findings in sialography ≧ Stage I (diffuse punctate shadows of less than 1 mm) (B) Decreased salivary secretion (flow rate ≦ 10 mL/10 min according to the chewing gum test or ≦ 2 g/2 min according to the Saxon test) and decreased salivary function according to salivary gland scintigraphy |
| 3. Ocular Examination Definition: Positive for at least one of (A) or (B): (A) Schirmer’s test ≦ 5 mm/5 min and rose bengal test ≧ 3 according to the van Bijsterveld score (B) Schirmer’s test ≦ 5 mm/5 min and positive fluorescein staining test |
| 4. Serological Examination Definition: Positive for at least one of (A) or (B): (A) Anti-Ro/SS-A antibody (B) Anti-La/SS-B antibody |
| Diagnostic criteria: Diagnosis of SS can be made when the patient meets at least two of the above four criteria |
| Subject Subgroups | Tear E-FABP mean ± SD (μg/mL) | Saliva E-FABP mean ± SD (μg/mL) | Serum E-FABP mean ± SD (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SS | 89.41 ± 72.30 | 35.30 ± 24.84 | 1828 ± 1064 |
| non-SS | 674.7 ± 50.73 | 85.51 ± 63.75 | 1102 ± 873.3 |
| p value vs. SS | p = 0.2000 | p = 0.3333 | p = 0.4242 |
| p value vs. controls | p = 0.2857 | p = 0.1648 | p = 0.9999 |
| Normal controls | 4076 ± 5746 | 32.08 ± 38.31 | 1604 ± 1686 |
| p value vs. SS | p = 0.0088 * | p = 0.3075 | p = 0.3813 |
| Scores | Patients (n = 11 eyes) | Controls (n = 12 eyes) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEQS (pts) | 40.09 ± 30.66 | 7.67 ± 11.5 | 0.001 * |
| BUT (sec) | 2.36 ± 1.43 | 6.0 ± 1.28 | <0.0001 * |
| Schirmer (mm) | 2.73 ± 1.90 | 14.75 ± 10.73 | <0.0001 * |
| FS (pts) | 4.73 ± 2.72 | 0.08 ± 0.29 | <0.0001 * |
| LG (pts) | 6.46 ± 4.39 | 0.0 ± 0.0 | <0.0001 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinzawa, M.; Dogru, M.; Den, S.; Ichijima, T.; Higa, K.; Kojima, T.; Seta, N.; Nomura, T.; Tsubota, K.; Shimazaki, J. Epidermal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein: A Novel Marker in the Diagnosis of Dry Eye Disease in Sjögren Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113463
Shinzawa M, Dogru M, Den S, Ichijima T, Higa K, Kojima T, Seta N, Nomura T, Tsubota K, Shimazaki J. Epidermal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein: A Novel Marker in the Diagnosis of Dry Eye Disease in Sjögren Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113463
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinzawa, Megumi, Murat Dogru, Seika Den, Takehiro Ichijima, Kazunari Higa, Takashi Kojima, Noriyuki Seta, Takeshi Nomura, Kazuo Tsubota, and Jun Shimazaki. 2018. "Epidermal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein: A Novel Marker in the Diagnosis of Dry Eye Disease in Sjögren Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113463
APA StyleShinzawa, M., Dogru, M., Den, S., Ichijima, T., Higa, K., Kojima, T., Seta, N., Nomura, T., Tsubota, K., & Shimazaki, J. (2018). Epidermal Fatty Acid-Binding Protein: A Novel Marker in the Diagnosis of Dry Eye Disease in Sjögren Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3463. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113463