Endothelial Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthetase-1 Upregulates Vascularity and Endothelial Interleukin-1β in Deteriorative Progression of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. mPGES-1 Was Induced in CD31+ VECs and Facilitated Demyelination and Paralysis
2.2. CD31+ VEC Invasion in the EAE Spinal Cord Was Facilitated by mPGES-1
2.3. IL-1β Upregulation in CD31+ VECs in EAE Spinal Cords Was Regulated by mPGES-1
2.4. Induction of EP Receptors in CD31+ VECs in the EAE Spinal Cord
2.5. IL-1R1 Upregulation in CD31+ VECs in EAE Spinal Cords Was Not Regulated by mPGES-1
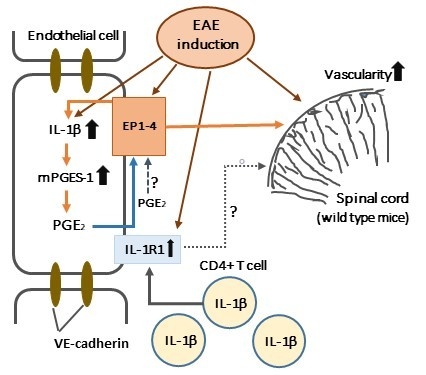
3. Discussion
3.1. Vascularity and mPGES-1 Expression in EAE
3.2. Effect of IL-1β on EAE and Endothelial IL-1β Production
3.3. Expression and Effect of Endothelial EP Receptors
3.4. IL-1β Production Through EP Receptor Activation
3.5. Relationship between IL-1β and COX-2/mPGES-1
3.6. Expression of Endothelial IL-1R1
3.7. A Mechanism of EAE Aggravation Induced by mPGES-1
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. Induction and Assessment of EAE
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Image Analysis
4.5. Histopathology
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| PGE2 | prostaglandin E2 |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| mPGES-1 | microsomal prostaglandin E synthetase-1 |
| GPCRs | G-protein-coupled receptors |
| EP | E-prostanoid |
| VECs | vascular endothelial cells |
| KA | kainic acid |
| EAE | experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| MOG35–55 | myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein35–55 peptide |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IL-1RN | interleukin-1 receptor antagonist |
| IL-1R1 | interleukin-1 receptor 1 |
| CD4+ T cells | CD4-positive T cells |
| CD31+ | CD31-positive |
| mPGES-1−/− | microsomal prostaglandin synthetase-1-deficient |
| wt | wild-type |
| H–E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| LFB | luxol fast blue |
| IL-1R1+ | IL-1R1-positive |
| BBB | blood-brain barrier |
| MMPs | matrix metalloproteinases |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| mPGES-2 | microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-2 |
| cPGES | cytosolic PGE2 synthase |
| EP receptor+ | EP receptor-positive |
| VE-cadherin | vascular endothelial-cadherin |
| FITC | fluorescein isothiocyanate |
References
- Yamagata, K.; Matsumura, K.; Inoue, W.; Shiraki, T.; Suzuki, K.; Yasuda, S.; Sugiura, H.; Cao, C.; Watanabe, Y.; Kobayashi, S. Coexpression of microsomal-type prostaglandin E synthase with cyclooxygenase-2 in brain endothelial cells of rats during endotoxin-induced fever. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 2669–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemiya, T.; Matsumura, K.; Sugiura, H.; Maehara, M.; Yasuda, S.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; Yamagata, K. Endothelial microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 exacerbates neuronal loss induced by kainate. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.W.; Hill, K.E.; Watt, H.E.; Carlson, N.G. Inflammatory cell expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in the multiple sclerosis lesion. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 149, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deininger, M.H.; Schluesener, H.J. Cyclooxygenases-1 and -2 are differentially localized to microglia and endothelium in rat EAE and glioma. J. Neuroimmunol. 1999, 95, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, I.; Kerlero de Rosbo, N.; Ben-Nun, A. A myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein peptide induces typical chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in H-2b mice: Fine specificity and T cell receptor Vβ expression of encephalitogenic T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuerten, S.; Kostova-Bales, D.A.; Frenzel, L.P.; Tigno, J.T.; Tary-Lehmann, M.; Angelov, D.N.; Lehmann, P.V. MP4- and MOG:35-55-induced EAE in C57BL/6 mice differentially targets brain, spinal cord and cerebellum. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 189, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, C.; Gordon, D.; Turk, J.L. Prostaglandin and thromboxane levels in central nervous system tissues from rats during the induction and development of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE). Immunopharmacology 1984, 7, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusic, S.; Leach, M.W.; Pelker, J.W.; Azoitei, M.L.; Uozumi, N.; Cui, J.; Shen, M.W.; DeClercq, C.M.; Miyashiro, J.S.; Carito, B.A.; et al. Cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha-deficient mice are resistant to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kihara, Y.; Matsushita, T.; Kita, Y.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; Kira, J.; Ishii, S.; Shimizu, T. Targeted lipidomics reveals mPGES-1-PGE2 as a therapeutic target for multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21807–21812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, C.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kohyama, K.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; Yamagata, K.; Takemiya, T. Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 aggravates inflammation and demyelination in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Miyake, S.; Mizuno, M.; Oka, N.; Kusunoki, S.; Yamamura, T. Selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib prevents experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through COX-2-independent pathway. Brain 2006, 129, 1984–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muthian, G.; Raikwar, H.P.; Johnson, C.; Rajasingh, J.; Kalgutkar, A.; Marnett, L.J.; Bright, J.J. COX-2 inhibitors modulate IL-12 signaling through JAK-STAT pathway leading to Th1 response in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 26, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Shu, Y.Y.; Zhu, Y.N.; Fu, Y.F.; Tang, W.; Zhong, X.G.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.F.; Ren, J.; Wang, M.W.; et al. COX-2 inhibitors ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis through modulating IFN-gamma and IL-10 production by inhibiting T-bet expression. J. Neuroimmunol. 2007, 186, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.; Near, S.L. Protective effect of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) on experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. J. Neuroimmunol. 1995, 61, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffenbauer, J.; Streit, W.J.; Butfiloski, E.; LaBow, M.; Edwards, C., 3rd; Moldawer, L.L. The induction of EAE is only partially dependent on TNF receptor signaling but requires the IL-1 type I receptor. Clin. Immunol. 2000, 95, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemiya, T.; Takeuchi, C.; Kawakami, M. Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 facilitates an intercellular interaction between CD4(+) T cells through IL-1beta autocrine function in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, G.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Neuroinflammation. Glia 2002, 39, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mun-Bryce, S.; Rosenberg, G.A. Gelatinase B modulates selective opening of the blood-brain barrier during inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, R1203–R1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madri, J.A.; Graesser, D.; Haas, T. The roles of adhesion molecules and proteinases in lymphocyte transendothelial migration. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1996, 74, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seabrook, T.J.; Littlewood-Evans, A.; Brinkmann, V.; Pollinger, B.; Schnell, C.; Hiestand, P.C. Angiogenesis is present in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and pro-angiogenic factors are increased in multiple sclerosis lesions. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigau, V.; Morin, M.; Rousset, M.C.; de Bock, F.; Lebrun, A.; Coubes, P.; Picot, M.C.; Baldy-Moulinier, M.; Bockaert, J.; Crespel, A.; et al. Angiogenesis is associated with blood-brain barrier permeability in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 2007, 130, 1942–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortiz, G.G.; Pacheco-Moises, F.P.; Macias-Islas, M.A.; Flores-Alvarado, L.J.; Mireles-Ramirez, M.A.; Gonzalez-Renovato, E.D.; Hernandez-Navarro, V.E.; Sanchez-Lopez, A.L.; Alatorre-Jimenez, M.A. Role of the blood-brain barrier in multiple sclerosis. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roscoe, W.A.; Welsh, M.E.; Carter, D.E.; Karlik, S.J. VEGF and angiogenesis in acute and chronic MOG(35-55) peptide induced EAE. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 209, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muramatsu, R.; Takahashi, C.; Miyake, S.; Fujimura, H.; Mochizuki, H.; Yamashita, T. Angiogenesis induced by CNS inflammation promotes neuronal remodeling through vessel-derived prostacyclin. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1658–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brumm, A.J.; Carmichael, S.T. Not just a rush of blood to the head. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1609–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dore-Duffy, P.; Donaldson, J.O.; Koff, T.; Longo, M.; Perry, W. Prostaglandin release in multiple sclerosis: Correlation with disease activity. Neurology 1986, 36, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberg, J.A.; Demers, L.M.; Romano, P.J.; Tenser, R.B. Prostaglandin production in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1990, 4, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobsson, P.J.; Thoren, S.; Morgenstern, R.; Samuelsson, B. Identification of human prostaglandin E synthase: A microsomal, glutathione-dependent, inducible enzyme, constituting a potential novel drug target. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7220–7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanikawa, N.; Ohmiya, Y.; Ohkubo, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Kangawa, K.; Kojima, M.; Ito, S.; Watanabe, K. Identification and characterization of a novel type of membrane-associated prostaglandin E synthase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 291, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanioka, T.; Nakatani, Y.; Semmyo, N.; Murakami, M.; Kudo, I. Molecular identification of cytosolic prostaglandin E2 synthase that is functionally coupled with cyclooxygenase-1 in immediate prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32775–32782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, M.; Naraba, H.; Tanioka, T.; Semmyo, N.; Nakatani, Y.; Kojima, F.; Ikeda, T.; Fueki, M.; Ueno, A.; Oh, S.; et al. Regulation of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by inducible membrane-associated prostaglandin E2 synthase that acts in concert with cyclooxygenase-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32783–32792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Anacker, C.; Suarez-Mier, G.B.; Wang, Q.; Andreasson, K. Function of prostaglandin E2 EP receptors in the acute outcome of rodent hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 504, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frankowski, J.C.; DeMars, K.M.; Ahmad, A.S.; Hawkins, K.E.; Yang, C.; Leclerc, J.L.; Dore, S.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Detrimental role of the EP1 prostanoid receptor in blood-brain barrier damage following experimental ischemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, K.; Kida, T.; Hori, M.; Ozaki, H.; Murata, T. Multiple roles of the PGE2 -EP receptor signal in vascular permeability. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4879–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalvi, S.; Nguyen, H.H.; On, N.; Mitchell, R.W.; Aukema, H.M.; Miller, D.W.; Hatch, G.M. Exogenous arachidonic acid mediates permeability of human brain microvessel endothelial cells through prostaglandin E2 activation of EP3 and EP4 receptors. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Lin, L.; Woodling, N.S.; Wang, Q.; Anacker, C.; Pan, T.; Merchant, M.; Andreasson, K. Signaling via the prostaglandin E(2) receptor EP4 exerts neuronal and vascular protection in a mouse model of cerebral ischemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4362–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levesque, S.A.; Pare, A.; Mailhot, B.; Bellver-Landete, V.; Kebir, H.; Lecuyer, M.A.; Alvarez, J.I.; Prat, A.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Keane, R.W.; et al. Myeloid cell transmigration across the CNS vasculature triggers IL-1beta-driven neuroinflammation during autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 929–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blamire, A.M.; Anthony, D.C.; Rajagopalan, B.; Sibson, N.R.; Perry, V.H.; Styles, P. Interleukin-1beta-induced changes in blood-brain barrier permeability, apparent diffusion coefficient, and cerebral blood volume in the rat brain: A magnetic resonance study. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8153–8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argaw, A.T.; Zhang, Y.; Snyder, B.J.; Zhao, M.L.; Kopp, N.; Lee, S.C.; Raine, C.S.; Brosnan, C.F.; John, G.R. IL-1β regulates blood-brain barrier permeability via reactivation of the hypoxia-angiogenesis program. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 5574–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correale, J.; Farez, M.F. The role of astrocytes in multiple sclerosis progression. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Sonobe, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Horiuchi, H.; Parajuli, B.; Kawanokuchi, J.; Mizuno, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Suzumura, A. Interleukin-1beta induces blood-brain barrier disruption by downregulating sonic hedgehog in astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murta, V.; Farias, M.I.; Pitossi, F.J.; Ferrari, C.C. Chronic systemic IL-1beta exacerbates central neuroinflammation independently of the blood-brain barrier integrity. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 278, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vainchtein, I.D.; Vinet, J.; Brouwer, N.; Brendecke, S.; Biagini, G.; Biber, K.; Boddeke, H.W.; Eggen, B.J. In acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, infiltrating macrophages are immune activated, whereas microglia remain immune suppressed. Glia 2014, 62, 1724–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, A.; Amiable, N.; de Rivero Vaccari, J.P.; Chae, J.J.; Keane, R.W.; Lacroix, S.; Vallieres, L. The inflammasome pyrin contributes to pertussis toxin-induced IL-1beta synthesis, neutrophil intravascular crawling and autoimmune encephalomyelitis. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarland, H.F.; Martin, R. Multiple sclerosis: A complicated picture of autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, B.N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.J.; Kang, Z.; Gulen, M.F.; Zepp, J.A.; Zhao, J.; Bian, G.; Do, J.S.; Min, B.; et al. T cell-intrinsic ASC critically promotes T(h)17-mediated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, M.; Sugata, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Matsumoto, R.; Nishibori, M.; Shimizu, K.; Maeda, M.; Kimura, Y.; Kariya, S.; Hattori, H.; et al. E prostanoid 2 (EP2)/EP4-mediated suppression of antigen-specific human T-cell responses by prostaglandin E2. Immunology 2006, 118, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslanka, T.; Spodniewska, A.; Barski, D.; Jasiecka, A.; Zuska-Prot, M.; Ziolkowski, H.; Markiewicz, W.; Jaroszewski, J.J. Prostaglandin E(2) down-regulates the expression of CD25 on bovine T cells, and this effect is mediated through the EP4 receptor. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 160, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreeramkumar, V.; Hons, M.; Punzon, C.; Stein, J.V.; Sancho, D.; Fresno, M.; Cuesta, N. Efficient T-cell priming and activation requires signaling through prostaglandin E2 (EP) receptors. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Genc, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Bazan, N.G.; Chen, C. Heterogeneous expression and regulation of hippocampal prostaglandin E2 receptors. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 81, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Matsumura, K.; Yamagata, K.; Watanabe, Y. Endothelial cells of the rat brain vasculature express cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in response to systemic interleukin-1 beta: A possible site of prostaglandin synthesis responsible for fever. Brain Res. 1996, 733, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serou, M.J.; DeCoster, M.A.; Bazan, N.G. Interleukin-1β activates expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase in primary hippocampal neuronal culture: Platelet-activating factor as a preferential mediator of cyclooxygenase-2 expression. J. Neurosci. Res. 1999, 58, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, T.A.; Moore, K.A.; Sapirstein, A.; Billet, S.; Allchorne, A.; Poole, S.; Bonventre, J.V.; Woolf, C.J. Interleukin-1β-mediated induction of COX-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. Nature 2001, 410, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laflamme, N.; Lacroix, S.; Rivest, S. An essential role of interleukin-1beta in mediating NF-kappaB activity and COX-2 transcription in cells of the blood-brain barrier in response to a systemic and localized inflammation but not during endotoxemia. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 10923–10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favrais, G.; Schwendimann, L.; Gressens, P.; Lelievre, V. Cyclooxygenase-2 mediates the sensitizing effects of systemic IL-1-beta on excitotoxic brain lesions in newborn mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 25, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casos, K.; Siguero, L.; Fernandez-Figueras, M.T.; Leon, X.; Sarda, M.P.; Vila, L.; Camacho, M. Tumor cells induce COX-2 and mPGES-1 expression in microvascular endothelial cells mainly by means of IL-1 receptor activation. Microvasc. Res. 2011, 81, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, A.M.; De Vries, H.E.; Kuiper, J.; Zijlstra, F.J.; De Boer, A.G.; Tilders, F.J.; Berkenbosch, F. Interleukin-1 receptors on rat brain endothelial cells: A role in neuroimmune interaction? FASEB J. 1996, 10, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohleb, E.S.; Patterson, J.M.; Sharma, V.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P.; Sheridan, J.F. Knockdown of interleukin-1 receptor type-1 on endothelial cells attenuated stress-induced neuroinflammation and prevented anxiety-like behavior. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Powell, N.; Zhang, H.; Belevych, N.; Ching, S.; Chen, Q.; Sheridan, J.; Whitacre, C.; Quan, N. Endothelial IL-1R1 is a critical mediator of EAE pathogenesis. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCandless, E.E.; Budde, M.; Lees, J.R.; Dorsey, D.; Lyng, E.; Klein, R.S. Il-1r signaling within the central nervous system regulates CXCL12 expression at the blood-brain barrier and disease severity during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. Lipopolysaccharide-dependent prostaglandin E(2) production is regulated by the glutathione-dependent prostaglandin E(2) synthase gene induced by the Toll-like receptor 4/MYD88/NF-IL6 pathway. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 5811–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuma, H.; Kohyama, K.; Park, I.K.; Miyakoshi, A.; Tanuma, N.; Matsumoto, Y. Clinicopathological study of a myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced demyelinating disease in LEW.1AV1 rats. Brain 2004, 127, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Storch, M.K.; Stefferl, A.; Brehm, U.; Weissert, R.; Wallstrom, E.; Kerschensteiner, M.; Olsson, T.; Linington, C.; Lassmann, H. Autoimmunity to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in rats mimics the spectrum of multiple sclerosis pathology. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takemiya, T.; Kawakami, M.; Takeuchi, C. Endothelial Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthetase-1 Upregulates Vascularity and Endothelial Interleukin-1β in Deteriorative Progression of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113647
Takemiya T, Kawakami M, Takeuchi C. Endothelial Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthetase-1 Upregulates Vascularity and Endothelial Interleukin-1β in Deteriorative Progression of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113647
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakemiya, Takako, Marumi Kawakami, and Chisen Takeuchi. 2018. "Endothelial Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthetase-1 Upregulates Vascularity and Endothelial Interleukin-1β in Deteriorative Progression of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113647
APA StyleTakemiya, T., Kawakami, M., & Takeuchi, C. (2018). Endothelial Microsomal Prostaglandin E Synthetase-1 Upregulates Vascularity and Endothelial Interleukin-1β in Deteriorative Progression of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113647