Investigating the Role of MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Co-regulatory Networks in Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MicroRNA Differential Expression in AOMS
2.2. MicroRNA Target Analysis
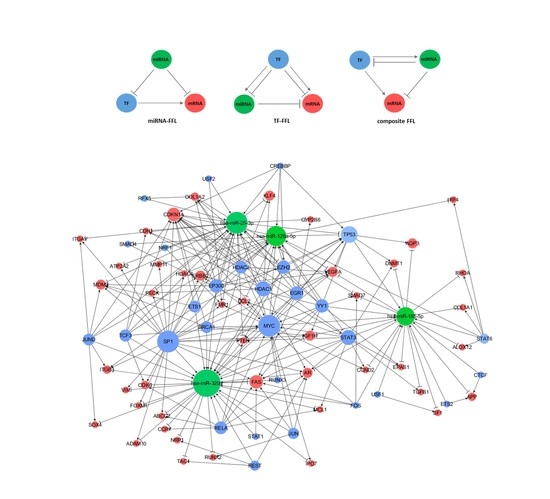
2.3. miRNA-TF Co-regulatory Network
2.4. Functional Enrichment and Pathway Analysis
2.5. Target Validation of miR-125a by Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. Reverse Transcription and Microfluidic qPCR
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. MicroRNA Target Analysis
4.6. Transcription Factor Target Analysis
4.7. Functional and Pathway Analysis
4.8. Luciferase Reporter Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| miRNA | microRNA |
| TF | Transcription Factor |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| PedMS | Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis |
| AOMS | Adult-Onset Multiple Sclerosis |
| FBL | Feedback Loop |
| FFL | Feed-Forward Loop |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| HC | Healthy Control |
| DE | Differentially Expressed |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| R | Renilla |
| FF | Firefly |
References
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, Y.-J.; Kim, J.H. Understanding cooperativity of microRNAs via microRNA association networks. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, W.-L.; Kleinhanz, R.R.; Schadt, E.E. Characterizing the role of miRNAs within gene regulatory networks using integrative genomics techniques. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Yuasa, Y. Multiple-to-multiple relationships between microRNAs and target genes in gastric cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, M.; Qiu, C.; Cui, Q. TransmiR: A transcription factor–microRNA regulation database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 38, D119–D122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, M.; Ranjbar, B.; Ganjalikhany, M.R.; Khan, F.M.; Schmitz, U.; Wolkenhauer, O.; Gupta, S.K. MicroRNA and transcription factor gene regulatory network analysis reveals key regulatory elements associated with prostate cancer progression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Luo, J.; Liu, C.; Niu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, H.; Ding, Y.; Sun, J. Investigating MicroRNA and transcription factor co-regulatory networks in colorectal cancer. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-M.; Kuang, S.; Xiong, X.; Gao, T.; Liu, C.; Guo, A.-Y. Transcription factor and microRNA co-regulatory loops: Important regulatory motifs in biological processes and diseases. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 16, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Shi, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, W.; Li, X. MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Mediated Regulatory Network Analysis Reveals Critical Regulators and Regulatory Modules in Myocardial Infarction. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiesleben, S.; Hecker, M.; Zettl, U.K.; Fuellen, G.; Taher, L. Analysis of microRNA and gene expression profiles in multiple sclerosis: Integrating interaction data to uncover regulatory mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.M.; Guerau-de-Arellano, M.; Costinean, S.; Williams, J.L.; Bottoni, A.; Cox, G.M.; Satoskar, A.R.; Croce, C.M.; Racke, M.K.; Lovett-Racke, A.E. miR-29ab1 deficiency identifies a negative feedback loop controlling Th1 bias that is dysregulated in multiple sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2012, 1103171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermersch, P.; Berger, T.; Gold, R.; Lukas, C.; Rovira, A.; Meesen, B.; Chard, D.; Comabella, M.; Palace, J.; Trojano, M. The clinical perspective: How to personalise treatment in MS and how may biomarkers including imaging contribute to this? Mult. Scler. 2016, 22, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oksenberg, J.R.; Baranzini, S.E. Multiple sclerosis genetics--is the glass half full, or half empty? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitnis, T.; Glanz, B.; Jaffin, S.; Healy, B. Demographics of pediatric-onset multiple sclerosis in an MS center population from the Northeastern United States. Mult. Scler. J. 2009, 15, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banwell, B.; Krupp, L.; Kennedy, J.; Tellier, R.; Tenembaum, S.; Ness, J.; Belman, A.; Boiko, A.; Bykova, O.; Waubant, E. Clinical features and viral serologies in children with multiple sclerosis: A multinational observational study. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghezzi, A.; Pozzilli, C.; Liguori, M.; Marrosu, M.G.; Milani, N.; Milanese, C.; Simone, I.; Zaffaroni, M. Prospective study of multiple sclerosis with early onset. Mult. Scler. J. 2002, 8, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, M.H.; Parratt, J.D.E.; Pollard, J.D.; Prineas, J.W. MS: Is it one disease? Int. MS J. 2009, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liguori, M.; Nuzziello, N.; Licciulli, F.; Consiglio, A.; Simone, M.; Viterbo, R.G.; Creanza, T.M.; Ancona, N.; Tortorella, C.; Margari, L. Combined microRNA and mRNA expression analysis in pediatric multiple sclerosis: An integrated approach to uncover novel pathogenic mechanisms of the disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 27, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punga, T.; Bartoccioni, E.; Lewandowska, M.; Damato, V.; Evoli, A.; Punga, A.R. Disease specific enrichment of circulating let-7 family microRNA in MuSK+ myasthenia gravis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 292, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, R.; Hernis, A.; Agostini, S.; Rovaris, M.; Caputo, D.; Clerici, M. MicroRNA-572 expression in multiple sclerosis patients with different patterns of clinical progression. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bossel Ben-Moshe, N.; Avraham, R.; Kedmi, M.; Zeisel, A.; Yitzhaky, A.; Yarden, Y.; Domany, E. Context-specific microRNA analysis: Identification of functional microRNAs and their mRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10614–10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouillard, A.D.; Gundersen, G.W.; Fernandez, N.F.; Wang, Z.; Monteiro, C.D.; McDermott, M.G.; Ma’ayan, A. The harmonizome: A collection of processed datasets gathered to serve and mine knowledge about genes and proteins. Database 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev, K.; Paul, A.; Healy, B.; von Glenn, F.; Diaz-Cruz, C.; Gholipour, T.; Mazzola, M.A.; Raheja, R.; Nejad, P.; Glanz, B.I. Comprehensive evaluation of serum microRNAs as biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, e267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.; Leidinger, P.; Steinmeyer, F.; Stähler, C.; Franke, A.; Hemmrich-Stanisak, G.; Kappel, A.; Wright, I.; Dörr, J.; Paul, F. Comprehensive analysis of microRNA profiles in multiple sclerosis including next-generation sequencing. Mult. Scler. J. 2014, 20, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Culla, M.; Irizar, H.; Sáenz-Cuesta, M.; Castillo-Triviño, T.; Osorio-Querejeta, I.; Sepúlveda, L.; De Munain, A.L.; Olascoaga, J.; Otaegui, D. SncRNA (microRNA & snoRNA) opposite expression pattern found in multiple sclerosis relapse and remission is sex dependent. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sievers, C.; Meira, M.; Hoffmann, F.; Fontoura, P.; Kappos, L.; Lindberg, R.L. Altered microRNA expression in B lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis: Towards a better understanding of treatment effects. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 144, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santis, G.; Ferracin, M.; Biondani, A.; Caniatti, L.; Rosaria Tola, M.; Castellazzi, M.; Zagatti, B.; Battistini, L.; Borsellino, G.; Fainardi, E.; et al. Altered miRNA expression in T regulatory cells in course of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 226, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otaegui, D.; Baranzini, S.E.; Armañanzas, R.; Calvo, B.; Muñoz-Culla, M.; Khankhanian, P.; Inza, I.; Lozano, J.A.; Castillo-Triviño, T.; Asensio, A. Differential micro RNA expression in PBMC from multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Junker, A.; Krumbholz, M.; Eisele, S.; Mohan, H.; Augstein, F.; Bittner, R.; Lassmann, H.; Wekerle, H.; Hohlfeld, R.; Meinl, E. MicroRNA profiling of multiple sclerosis lesions identifies modulators of the regulatory protein CD47. Brain 2009, 132, 3342–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutta, R.; Chomyk, A.M.; Chang, A.; Ribaudo, M.V.; Deckard, S.A.; Doud, M.K.; Edberg, D.D.; Bai, B.; Li, M.; Baranzini, S.E.; et al. Hippocampal demyelination and memory dysfunction are associated with increased levels of the neuronal microRNA miR-124 and reduced AMPA receptors. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 637–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmaj, I.; Mycko, M.P.; Raine, C.S.; Selmaj, K.W. The role of exosomes in CNS inflammation and their involvement in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 306, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimkhani, S.; Vafaee, F.; Young, P.E.; Hur, S.S.; Hawke, S.; Devenney, E.; Beadnall, H.; Barnett, M.H.; Suter, C.M.; Buckland, M.E. Exosomal microRNA signatures in multiple sclerosis reflect disease status. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vargas-Lowy, D.; Chitnis, T. Pathogenesis of pediatric multiple sclerosis. J. Child Neurol. 2012, 27, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, L.; Mu, P.; Li, Y.; Singh, N.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P. Expression, regulation and function of microRNAs in multiple sclerosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Chen, G. miRNAs participate in MS pathological processes and its therapeutic response. Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 4578230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecca, D.; Marangon, D.; Coppolino, G.T.; Méndez, A.M.; Finardi, A.; Dalla Costa, G.; Martinelli, V.; Furlan, R.; Abbracchio, M.P. MiR-125a-3p timely inhibits oligodendroglial maturation and is pathologically up-regulated in human multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Wang, W.-Z.; Zhang, X.-M.; Yue, H.; Li, B.; Lin, L.; Fu, J. MicroRNA expression aberration in Chinese patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 52, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reijerkerk, A.; Lopez-Ramirez, M.A.; van Het Hof, B.; Drexhage, J.A.; Kamphuis, W.W.; Kooij, G.; Vos, J.B.; van der Pouw Kraan, T.C.; van Zonneveld, A.J.; Horrevoets, A.J. MicroRNAs regulate human brain endothelial cell-barrier function in inflammation: Implications for multiple sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 6857–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jager, P.L.; Srivastava, G.; Lunnon, K.; Burgess, J.; Schalkwyk, L.C.; Yu, L.; Eaton, M.L.; Keenan, B.T.; Ernst, J.; McCabe, C. Alzheimer’s disease: Early alterations in brain DNA methylation at ANK1, BIN1, RHBDF2 and other loci. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murga, M.; Fernández-Capetillo, O.; Field, S.J.; Moreno, B.; Luis, R.; Fujiwara, Y.; Balomenos, D.; Vicario, A.; Carrera, A.C.; Orkin, S.H. Mutation of E2F2 in mice causes enhanced T lymphocyte proliferation, leading to the development of autoimmunity. Immunity 2001, 15, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.W.; Field, S.J.; Gore, L.; Thompson, M.; Yang, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Cardiff, R.D.; Greenberg, M.; Orkin, S.H.; DeGregori, J. E2F1 and E2F2 determine thresholds for antigen-induced T-cell proliferation and suppress tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 8547–8564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, C.; Wang, S.J.H.; Yoo, S.H.; Harden, N. Adducin at the neuromuscular junction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Hanging on for dear life. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E.A.; Fowler, C.D.; Kidd, G.J.; Chang, A.; Rudick, R.; Fisher, E.; Trapp, B.D. Imaging correlates of decreased axonal Na+/K+ ATPase in chronic multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 63, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, R.; Di Dario, M.; Cordiglieri, C.; Musio, S.; La Mantia, L.; Milanese, C.; Di Stefano, A.L.; Crabbio, M.; Franciotta, D.; Bergamaschi, R. Gender-based blood transcriptomes and interactomes in multiple sclerosis: Involvement of SP1 dependent gene transcription. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 38, J144–J155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Karin, M. Dangerous liaisons: STAT3 and NF-κB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pashaei, E.; Pashaei, E.; Ahmady, M.; Ozen, M.; Aydin, N. Meta-analysis of miRNA expression profiles for prostate cancer recurrence following radical prostatectomy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Qin, H.; Zhao, Q.; He, X.-X. Emerging role of transcription factor-microRNA-target gene feed-forward loops in cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2015, 3, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zettl, U.K.; Kuhlmann, T.; Brück, W. Bcl-2 expressing T lymphocytes in multiple sclerosis lesions. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1998, 24, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Fu, J. Identifying characteristic miRNAs-genes and risk pathways of multiple sclerosis based on bioinformatics analysis. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristjansdottir, G.; Sandling, J.K.; Bonetti, A.; Roos, I.M.; Milani, L.; Wang, C.; Gustafsdottir, S.M.; Sigurdsson, S.; Lundmark, A.; Tienari, P.J. Interferon regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) gene variants are associated with multiple sclerosis in three distinct populations. J. Med. Genet. 2008, 45, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agirrezabal, I.; Palacios, R.; Moreno, B.; Sepulcre, J.; Abernathy, A.; Saiz, A.; Llufriu, S.; Comabella, M.; Montalban, X.; Martinez, A. Increased expression of dedicator-cytokinesis-10, caspase-2 and Synaptotagmin-like 2 is associated with clinical disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Demyelinating Disord. 2016, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinowska-Lyszczarz, A.; Losy, J. The role of neurotrophins in multiple sclerosis—pathological and clinical implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 13713–13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esper, R.M.; Loeb, J.A. Neurotrophins induce neuregulin release through protein kinase Cδ activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26251–26260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mencel, M.; Nash, M.; Jacobson, C. Neuregulin upregulates microglial α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression in immortalized cell lines: Implications for regulating neuroinflammation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; He, W.; Hu, X.; Shen, Y.; Cao, J.; Wei, Z.; Luan, Y.; He, L.; Jiang, F.; Tao, Y. A role for ErbB signaling in the induction of reactive astrogliosis. Cell Dis. 2017, 3, 17044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Banwell, B.; Clanet, M.; Cohen, J.A.; Filippi, M.; Fujihara, K.; Havrdova, E.; Hutchinson, M.; Kappos, L. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Kostoulas, N.; Vlachos, I.S.; Vergoulis, T.; Reczko, M.; Filippidis, C.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-microT web server v5.0: Service integration into miRNA functional analysis workflows. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W169–W173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, A.; Xu, H.; Krishnan, J.; Berger, S.I.; Mazloom, A.R.; Ma’ayan, A. ChEA: Transcription factor regulation inferred from integrating genome-wide ChIP-X experiments. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2438–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, E.P. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matys, V.; Kel-Margoulis, O.V.; Fricke, E.; Liebich, I.; Land, S.; Barre-Dirrie, A.; Reuter, I.; Chekmenev, D.; Krull, M.; Hornischer, K. TRANSFAC® and its module TRANSCompel®: Transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D108–D110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daily, K.; Patel, V.R.; Rigor, P.; Xie, X.; Baldi, P. MotifMap: Integrative genome-wide maps of regulatory motif sites for model species. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Fornes, O.; Stigliani, A.; Gheorghe, M.; Castro-Mondragon, J.A.; van der Lee, R.; Bessy, A.; Cheneby, J.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Tan, G. JASPAR 2018: Update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles and its web framework. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D260–D266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Cho, J.-W.; Lee, S.; Yun, A.; Kim, H.; Bae, D.; Yang, S.; Kim, C.Y.; Lee, M.; Kim, E. TRRUST v2: An expanded reference database of human and mouse transcriptional regulatory interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 46, D380–D386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| AOMS (no. 58) | HC (no. 20) | |
|---|---|---|
| Female/Male Ratio | 2.7 | 2.3 |
| Age (y, mean ± SD) | 37.8 ± 11.3 | 43.2 ± 3.1 |
| Age at MS Onset (y, mean ± SD) | 34.3 ± 9.6 | |
| MS Course (RR/SP/PP) | 54/4/0 | |
| Disease Duration (y, mean ± SD) | 13.4 ± 9.3 | |
| EDSS Score | 2.7 ± 1.1 | |
| DMT (y/n) | 56/2 |
| miRNA | qPCR | ROC | Target * | TF | miRNA-TF co-regulatory Networks | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| logFC | p-value | AUC | p-value | FBL | miRNA-FFL | TF-FFL | Composite FFL | |||
| miR-320a | 0.8383653 | 0.0018 | 0.735 | 0.0001 | 157 | 141 | 4 | 6 | 52 | 9 |
| miR-125a-5p | 0.9214846 | 0.0059 | 0.708 | 0.0016 | 140 | 40 | 2 | 9 | 28 | 6 |
| miR-652-3p | 0.5953385 | 0.0078 | 0.701 | 0.0017 | 2 | 5 | ||||
| miR-185-5p | 0.5878233 | 0.0080 | 0.719 | 0.0002 | 220 | 49 | 1 | 2 | 20 | |
| miR-942-5p | 0.7367637 | 0.0083 | 0.699 | 0.0016 | 95 | |||||
| miR-25-3p | 0.5819802 | 0.0124 | 0.689 | 0.0034 | 119 | 79 | 1 | 4 | 52 | 10 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nuzziello, N.; Vilardo, L.; Pelucchi, P.; Consiglio, A.; Liuni, S.; Trojano, M.; Liguori, M. Investigating the Role of MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Co-regulatory Networks in Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3652. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113652
Nuzziello N, Vilardo L, Pelucchi P, Consiglio A, Liuni S, Trojano M, Liguori M. Investigating the Role of MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Co-regulatory Networks in Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3652. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113652
Chicago/Turabian StyleNuzziello, Nicoletta, Laura Vilardo, Paride Pelucchi, Arianna Consiglio, Sabino Liuni, Maria Trojano, and Maria Liguori. 2018. "Investigating the Role of MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Co-regulatory Networks in Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3652. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113652
APA StyleNuzziello, N., Vilardo, L., Pelucchi, P., Consiglio, A., Liuni, S., Trojano, M., & Liguori, M. (2018). Investigating the Role of MicroRNA and Transcription Factor Co-regulatory Networks in Multiple Sclerosis Pathogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3652. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113652