A Highly Efficient Cell Division-Specific CRISPR/Cas9 System Generates Homozygous Mutants for Multiple Genes in Arabidopsis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cell Division-Specific Promoters Improve the Production of CRISPR/Cas9-Induced Heritable Gene Modifications in Arabidopsis
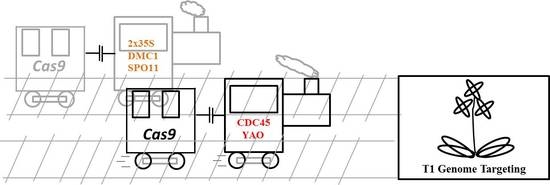
2.2. Development of a Multiplex CDC45 Promoter-Driven CRISPR/Cas9 System
2.3. Mutation Frequency of the sgRNA Module Transcribed by Different Pol III Promoters
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Transformation and Growth Conditions
Vector Construction
4.2. Mutation Detection
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alonso, J.M.; Ecker, J.R. Moving forward in reverse: Genetic technologies to enable genome-wide phenomic screens in Arabidopsis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, R.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; et al. A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaj, T.; Gersbach, C.A.; Barbas, C.F., 3rd. ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cong, L.; Ran, F.A.; Cox, D.; Lin, S.; Barretto, R.; Habib, N.; Hsu, P.D.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Marraffini, L.A.; et al. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013, 339, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Xi, J.J.; Qiu, J.L.; et al. Targeted genome modification of crop plants using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Zhang, B.; Ding, W.; Liu, X.; Yang, D.L.; Wei, P.; Cao, F.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, F.; Mao, Y.; et al. Efficient genome editing in plants using a CRISPR/Cas system. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N.; Zhang, B.; Gou, F.; Zhu, J.K. Application of the CRISPR-Cas system for efficient genome engineering in plants. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 2008–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekrasov, V.; Staskawicz, B.; Weigel, D.; Jones, J.D.; Kamoun, S. Targeted mutagenesis in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana using Cas9 RNA-guided endonuclease. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 691–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrangou, R.; Fremaux, C.; Deveau, H.; Richards, M.; Boyaval, P.; Moineau, S.; Romero, D.A.; Horvath, P. CRISPR provides acquired resistance against viruses in prokaryotes. Science 2007, 315, 1709–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyman, C.; Kanaar, R. DNA double-strand break repair: All’s well that ends well. Ann. Rev. Genet. 2006, 40, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterworth, W.M.; Drury, G.E.; Bray, C.M.; West, C.E. Repairing breaks in the plant genome: The importance of keeping it together. New Phytol. 2011, 192, 805–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, P.; Zhang, B.; Gou, F.; Feng, Z.; Mao, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N.; et al. The CRISPR/Cas9 system produces specific and homozygous targeted gene editing in rice in one generation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, Z.; Mao, Y.; Xu, N.; Zhang, B.; Wei, P.; Yang, D.L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, R.; Yang, L.; et al. Multigeneration analysis reveals the inheritance, specificity, and patterns of CRISPR/Cas-induced gene modifications in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4632–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.P.; Xing, H.L.; Dong, L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Han, C.Y.; Wang, X.C.; Chen, Q.J. Egg cell-specific promoter-controlled CRISPR/Cas9 efficiently generates homozygous mutants for multiple target genes in Arabidopsis in a single generation. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Wei, P.; Zhang, H.; Botella, J.R.; Zhu, J.K. Development of germ-line-specific CRISPR-Cas9 systems to improve the production of heritable gene modifications in Arabidopsis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Wei, S.; Wu, Y.; Hu, R.; Li, H.; Yang, W.; Xie, Q. High-efficiency genome editing in Arabidopsis using YAO promoter-driven CRISPR/Cas9 system. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 1820–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, A.; Ali, Z.; Mahfouz, M.M. High efficiency of targeted mutagenesis in Arabidopsis via meiotic promoter-driven expression of Cas9 endonuclease. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Stillman, B. Assembly of a complex containing Cdc45p, replication protein A, and Mcm2p at replication origins controlled by S-phase cyclin-dependent kinases and Cdc7p-Dbf4p kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 3086–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.; Grelon, M.; Vezon, D.; Oh, J.; Meyer, P.; Perennes, C.; Domenichini, S.; Bergounioux, C. A CDC45 homolog in Arabidopsis is essential for meiosis, as shown by RNA interference-induced gene silencing. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doutriaux, M.P.; Couteau, F.; Bergounioux, C.; White, C. Isolation and characterisation of the RAD51 and DMC1 homologs from Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Gen. Genet. MGG 1998, 257, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelon, M.; Vezon, D.; Gendrot, G.; Pelletier, G. AtSPO11-1 is necessary for efficient meiotic recombination in plants. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.J.; Liu, N.Y.; Shi, D.Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, W.C. YAO is a nucleolar WD40-repeat protein critical for embryogenesis and gametogenesis in Arabidopsis. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.S.; Kolevski, B.; Smyth, D.R. TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA2, a trichome and seed coat development gene of Arabidopsis, encodes a WRKY transcription factor. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, G.N.; Stone, D.; Pang, S.Z.; Creely, W.; Gonzalez, K.; Hinchee, M. Arabidopsis ovule is the target for Agrobacterium in planta vacuum infiltration transformation. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 1999, 19, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinek, M.; East, A.; Cheng, A.; Lin, S.; Ma, E.; Doudna, J. RNA-programmed genome editing in human cells. eLife 2013, 2, e00471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Mao, Y.; Ha, S.; Liu, W.; Botella, J.R.; Zhu, J.K. A multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 platform for fast and efficient editing of multiple genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 1519–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, R.; Mali, P.; Moosburner, M.; Church, G.M. Unraveling CRISPR-Cas9 genome engineering parameters via a library-on-library approach. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Wei, J.J.; Sabatini, D.M.; Lander, E.S. Genetic screens in human cells using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Science 2014, 343, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Davison, T.S.; Henz, S.R.; Pape, U.J.; Demar, M.; Vingron, M.; Scholkopf, B.; Weigel, D.; Lohmann, J.U. A gene expression map of Arabidopsis thaliana development. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Su, H.; Chen, W.; Lu, P. The application of a meiocyte-specific CRISPR/Cas9 (MSC) system and a suicide-MSC system in generating inheritable and stable mutations in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.L.; Dong, L.; Wang, Z.P.; Zhang, H.Y.; Han, C.Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.C.; Chen, Q.J. A CRISPR/Cas9 toolkit for multiplex genome editing in plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Shen, L.; Fu, Y.; Yan, C.; Wang, K. A simple CRISPR/Cas9 system for multiplex genome editing in rice. J. Genet. Genom. (Yi Chuan Xue Bao) 2015, 42, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, D.; Glazebrook, J. In planta transformation of Arabidopsis. CSH Protoc. 2006, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, L.J.; Nguyen, B. Use of polyethylene glycol for purification of DNA from leaf tissue of woody plants. BioTechniques 1993, 14, 734–736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Hua, K.; Gao, X.; Mao, Y.; Botella, J.R.; Zhu, J.-K. A Highly Efficient Cell Division-Specific CRISPR/Cas9 System Generates Homozygous Mutants for Multiple Genes in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123925
Feng Z, Zhang Z, Hua K, Gao X, Mao Y, Botella JR, Zhu J-K. A Highly Efficient Cell Division-Specific CRISPR/Cas9 System Generates Homozygous Mutants for Multiple Genes in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123925
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Zhengyan, Zhengjing Zhang, Kai Hua, Xifeng Gao, Yanfei Mao, Jose Ramon Botella, and Jian-Kang Zhu. 2018. "A Highly Efficient Cell Division-Specific CRISPR/Cas9 System Generates Homozygous Mutants for Multiple Genes in Arabidopsis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123925
APA StyleFeng, Z., Zhang, Z., Hua, K., Gao, X., Mao, Y., Botella, J. R., & Zhu, J. -K. (2018). A Highly Efficient Cell Division-Specific CRISPR/Cas9 System Generates Homozygous Mutants for Multiple Genes in Arabidopsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3925. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123925