Human Microbiome Acquisition and Bioinformatic Challenges in Metagenomic Studies
Abstract
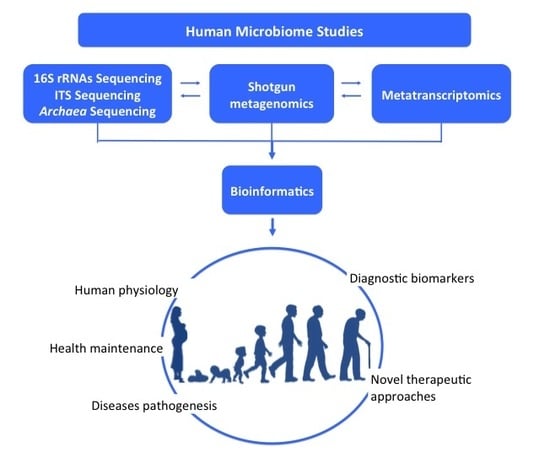
:1. Introduction
2. Human Microbiome Acquisition and Healthy Status Maintenance
3. Data Generation, Bioinformatic Issues, and Challenges in Metagenomic Studies
3.1. 16S Rrnas and ITS Sequencing
3.2. Shotgun Sequencing
3.3. Metatranscriptomics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| rRNA | ribosomal RNA |
| OTUs | Operational Taxonomic Units |
| QIIME | Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology |
| DADA2 | Divisive Amplicon Denoising Algorithm 2 |
| ZOTUs | zero-radius OTUs |
| Bp | base pair |
| PCoA | Principal Coordinates Analysis |
| PICRUSt | Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States |
| ITSs | Internal Transcribed Spacers |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PanPhlAn | pangenome-based phylogenomic analysis |
References
- Precone, V.; del Monaco, V.; Esposito, M.V.; de Palma, F.D.; Ruocco, A.; Salvatore, F.; D’Argenio, V. Cracking the code of human diseases using next-generation sequencing: Applications, challenges, and perspectives. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 161648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Argenio, V.; Salvatore, F. The role of the gut microbiome in the healthy adult status. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 451, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Pietro, M.; Filardo, S.; Porpora, M.G.; Recine, N.; Latino, M.A.; Sessa, R. HPV/Chlamydia trachomatis co-infection: Metagenomic analysis of cervical microbiota in asymptomatic women. New Microbiol. 2018, 41, pmid:29313867. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.M.; Jin, H.Z. Skin Microbiome: An Actor in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nycz, B.T.; Dominguez, S.R.; Friedman, D.; Hilden, J.M.; Diana, I.; Robertson, C.E.; Frank, D.N. Evaluation of bloodstream infections, Clostridium difficile infections, and gut microbiota in pediatric oncology patients. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, P.N.; Hasegawa, K.; Ajami, N.J.; Espinola, J.A.; Henke, D.M.; Petrosino, J.F.; Piedra, P.A.; Sullivan, A.F.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Shaw, C.A.; et al. The association between anterior nares and nasopharyngeal microbiota in infants hospitalized for bronchiolitis. Microbiome 2018, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, J.; Lee, C.; Ko, G. Oral Microbiota: Microbial Biomarkers of Metabolic Syndrome Independent of Host Genetic Factors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol 2017, 7, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.N.; Wang, J.P.; Liu, P.; Yang, Y.F.; Feng, J.; Han, Y. Faecal and mucosal microbiota in patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders: Correlation with toll-like receptor 2/toll-like receptor 4 expression. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6665–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Argenio, V.; Torino, M.; Precone, V.; Casaburi, G.; Esposito, M.V.; Iaffaldano, L.; Malapelle, U.; Troncone, G.; Coto, I.; Cavalcanti, P.; et al. The cause of death of a child in the 18th century solved by bone microbiome typing using laser microdissection and next generation sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassone-Corsi, M.; Raffatellu, M. No vacancy: How beneficial microbes cooperate with immunity to provide colonization resistance to pathogens. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4081–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selber-Hnatiw, S.; Rukundo, B.; Ahmadi, M.; Akoubi, H.; Al-Bizri, H.; Aliu, A.F.; Ambeaghen, T.U.; Avetisyan, L.; Bahar, I.; Baird, A.; et al. Human gut microbiota: Toward an ecology of disease. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarci, A.; Hasturk, H. Microbes and host response: A relationship in health and disease. Oral Dis. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Wu, G.D.; Albenberg, L.; Tomov, V.T. Gut microbiota and IBD: Causation or correlation? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, S.; Ferrario, C.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M.; Turroni, F. Obesity and microbiota: An example of an intricate relationship. Genes Nutr. 2017, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J.Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Argenio, V.; Precone, V.; Casaburi, G.; Miele, E.; Martinelli, M.; Staiano, A.; Salvatore, F.; Sacchetti, L. An altered gut microbiome profile in a child affected by Crohn’s disease normalized after nutritional therapy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 851–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Argenio, V.; Casaburi, G.; Precone, V.; Pagliuca, C.; Colicchio, R.; Sarnataro, D.; Discepolo, V.; Kim, S.M.; Russo, I.; del Vecchio Blanco, G.; et al. Metagenomics reveals dysbiosis and a potentially pathogenic N. flavescens strain in duodenum of adult celiac patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Argenio, V.; Casaburi, G.; Precone, V.; Pagliuca, C.; Colicchio, R.; Sarnataro, D.; Discepolo, V.; Kim, S.M.; Russo, I.; del Vecchio Blanco, G.; et al. No change in the mucosal gut microbiome is associated with celiac disease-specific microbiome alteration in adult patients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1659–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, V.T.; Lacroix, C.; Braegger, C.P.; Chassard, C. Lactate-utilizing community is associated with gut microbiota dysbiosis in colicky infants. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Gu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Jia, L.; Chen, C.; Han, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, P.; et al. Alterations of the Gut Microbiome in Hypertension. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, J.C.; Manasson, J.; Scher, J.U. The role of the gut microbiome in systemic inflammatory disease. BMJ 2018, 360, j5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklöf, V.; Löfgren-Burström, A.; Zingmark, C.; Edin, S.; Larsson, P.; Karling, P.; Alexeyev, O.; Rutegård, J.; Wikberg, M.L.; Palmqvist, R. Cancer-associated fecal microbial markers in colorectal cancer detection. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 41, 2528–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Muñoz, M.E.; Arrieta, M.C.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Walter, J. A critical assessment of the “sterile womb” and “in utero colonization” hypotheses: Implications for research on the pioneer infant microbiome. Microbiome 2017, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, J.M.; Murphy, K.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Kober, O.I.; Juge, N.; Avershina, E.; Rudi, K.; Narbad, A.; Jenmalm, M.C.; et al. The composition of the gut microbiota throughout life, with an emphasis on early life. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, M.C.; Rautava, S.; Aakko, J.; Isolauri, E.; Salminen, S. Human gut colonisation may be initiated in utero by distinct microbial communities in the placenta and amniotic fluid. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neu, J. The microbiome during pregnancy and early postnatal life. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016, 21, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinson, L.F.; Payne, M.S.; Keelan, J.A. Planting the seed: Origins, composition, and postnatal health significance of the fetal gastrointestinal microbiota. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 352–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, G.; Aldo, P.; Alvero, A.B. The unique immunological and microbial aspects of pregnancy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuriel-Ohayon, M.; Neuman, H.; Koren, O. Microbial changes during pregnancy, birth, and infancy. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, J.M.; Dattilo, A.M. Early development of intestinal microbiota: Implications for future health. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 41, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, S.; Sakwinska, O.; Soh, S.E.; Ngom-Bru, C.; Brück, W.M.; Berger, B.; Brüssow, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Yap, F.; Chong, Y.S.; et al. Dynamics of infant gut microbiota are influenced by delivery mode and gestational duration and are associated with subsequent adiposity. MBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Tsuji, H.; Takahashi, T.; Nomoto, K.; Kawashima, K.; Nagata, S.; Yamashiro, Y. Gut dysbiosis following C-section instigates higher colonisation of toxigenic Clostridium perfringens in infants. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.M.; Ma, J.; Prince, A.L.; Antony, K.M.; Seferovic, M.D.; Aagaard, K.M. Maturation of the infant microbiome community structure and function across multiple body sites and in relation to mode of delivery. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, K.M.; Foster, J.A.; Forney, L.J.; Schütte, U.M.; Beck, D.L.; Abdo, Z.; Fox, L.K.; Williams, J.E.; McGuire, M.K.; McGuire, M.A. Characterization of the diversity and temporal stability of bacterial communities in human milk. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, P.; Blacher, E.; Elinav, E.; Pettersson, S. Our gut microbiome: The evolving inner self. Cell 2017, 171, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erny, D.; Hrabě de Angelis, A.L.; Prinz, M. Communicating systems in the body: How microbiota and microglia cooperate. Immunology 2017, 150, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martí, J.M.; Martínez-Martínez, D.; Rubio, T.; Gracia, C.; Peña, M.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A.; P Garay, C. Health and disease imprinted in the time variability of the human microbiome. mSystems 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Z.; Du, W.T.; Xu, Y.L.; Cheng, S.Z.; Liu, Z.J. Gut microbiome-based medical methodologies for early-stage disease prevention. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D. Gut microbiota—At the intersection of everything? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 321–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvallet, C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Gurry, T.; Irizarry, R.A.; Alm, E.J. Meta-analysis of gut microbiome studies identifies disease-specific and shared responses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliev, I.D.; Leonardi, I. Fungal dysbiosis: Immunity and interactions at mucosal barriers. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koskinen, K.; Pausan, M.R.; Perras, A.K.; Beck, M.; Bang, C.; Mora, M.; Schilhabel, A.; Schmitz, R.; Moissl-Eichinger, C. First insights into the diverse human archaeome: Specific detection of archaea in the gastrointestinal tract, lung, and nose and on skin. MBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgin, H.W. The virome in mammalian physiology and disease. Cell 2014, 157, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadwell, K. Expanding the role of the virome: Commensalism in the gut. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 1951–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadwell, K. The virome in host health and disease. Immunity 2015, 42, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, J.K.; Waters, J.L.; Poole, A.C.; Sutter, J.L.; Koren, O.; Blekhman, R.; Beaumont, M.; Van Treuren, W.; Knight, R.; Bell, J.T.; et al. Human genetics shape the gut microbiome. Cell 2014, 159, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, J. Insights into study design and statistical analyses in translational microbiome studies. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Fish, J.A.; Chai, B.; McGarrell, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Brown, C.T.; Porras-Alfaro, A.; Kuske, C.R.; Tiedje, J.M. Ribosomal Database Project: Data and tools for high throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D633–D642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods. 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. UNOISE2: Improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. BioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; McDonald, D.; Navas-Molina, J.A.; Kopylova, E.; Morton, J.T.; Zech Xu, Z.; Kightley, E.P.; Thompson, L.R.; Hyde, E.R.; Gonzalez, A.; et al. Deblur rapidly resolves single-nucleotide community sequence patterns. mSystems 2017, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R. UniFrac—An online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.I.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwai, S.; Weinmaier, T.; Schmidt, B.L.; Albertson, D.G.; Poloso, N.J.; Dabbagh, K.; DeSantis, T.Z. Piphillin: Improved prediction of metagenomic content by direct inference from human microbiomes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4Fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhu, H.; Ruan, J.; Qian, W.; Fang, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Shan, G.; Kristiansen, K.; et al. De novo assembly of human genomes with massively parallel short read sequencing. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Birney, E. Velvet: Algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namiki, T.; Hachiya, T.; Tanaka, H.; Sakakibara, Y. MetaVelvet: An extension of Velvet assembler to de novo metagenome assembly from short sequence reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Leung, H.C.; Yiu, S.M.; Chin, F.Y. Meta-IDBA: A de Novo assembler for metagenomic data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laserson, J.; Jojic, V.; Koller, D. Genovo: De novo assembly for metagenomes. J. Comput. Biol. 2011, 18, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, S.; Treangen, T.J.; Pop, M. Bambus 2: Scaffolding metagenomes. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2964–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisvert, S.; Raymond, F.; Godzaridis, E.; Laviolette, F.; Corbeil, J. Ray Meta: Scalable de novo metagenome assembly and profiling. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampelli, S.; Soverini, M.; Turroni, S.; Quercia, S.; Biagi, E.; Brigidi, P.; Candela, M. ViromeScan: A new tool for metagenomic viral community profiling. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, M.; Ward, D.V.; Pasolli, E.; Tolio, T.; Zolfo, M.; Asnicar, F.; Truong, D.T.; Tett, A.; Morrow, A.L.; Segata, N. Strain-level microbial epidemiology and population genomics from shotgun metagenomics. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rho, M.; Tang, H.; Ye, Y. FragGeneScan: Predicting genes in short and error-prone reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M. Ab initio gene identification in metagenomic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, D.R.; Liu, B.; Delcher, A.L.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Gene prediction with Glimmer for metagenomic sequences augmented by classification and clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markowitz, V.M.; Chen, I.M.; Chu, K.; Szeto, E.; Palaniappan, K.; Pillay, M.; Ratner, A.; Huang, J.; Pagani, I.; Tringe, S.; et al. IMG/M 4 version of the integrated metagenome comparative analysis system. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D568–D573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Brady, A.; Mahurkar, A.; White, O.; Gevers, D.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. MetaRef: A pan-genomic database for comparative and community microbial genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Mao, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Mao, F.; Xu, Y. dbCAN: A web resource for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W445–W451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubucker, S.; Segata, N.; Goll, J.; Schubert, A.M.; Izard, J.; Cantarel, B.L.; Rodriguez-Mueller, B.; Zucker, J.; Thiagarajan, M.; Henrissat, B.; et al. Metabolic reconstruction for metagenomic data and its application to the human microbiome. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Argenio, V.; Notomista, E.; Petrillo, M.; Cantiello, P.; Cafaro, V.; Izzo, V.; Naso, B.; Cozzuto, L.; Durante, L.; Troncone, L.; et al. Complete sequencing of Novosphingobium sp. PP1Y reveals a biotechnologically meaningful metabolic pattern. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Argenio, V.; Petrillo, M.; Pasanisi, D.; Pagliarulo, C.; Colicchio, R.; Talà, A.; de Biase, M.S.; Zanfardino, M.; Scolamiero, E.; Pagliuca, C.; et al. The complete 12 Mb genome and transcriptome of Nonomuraea gerenzanensis with new insights into its duplicated “magic” RNA polymerase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradnam, K.R.; Fass, J.N.; Alexandrov, A.; Baranay, P.; Bechner, M.; Birol, I.; Boisvert, S.; Chapman, J.A.; Chapuis, G.; Chikhi, R. Assemblathon 2: Evaluating de novo methods of genome assembly in three vertebrate species. Gigascience 2013, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quince, C.; Walker, A.W.; Simpson, J.T.; Loman, N.J.; Segata, N. Shotgun metagenomics, from sampling to analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heintz-Buschart, A.; Wilmes, P. Human gut microbiome: Function matters. Trends Microbiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westreich, S.T.; Korf, I.; Mills, D.A.; Lemay, D.G. SAMSA: A comprehensive metatranscriptome analysis pipeline. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Danska, J.; Parkinson, J. Metatranscriptomic analysis of diverse microbial communities reveals core metabolic pathways and microbiome-specific functionality. Microbiome 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Function | Pipeline | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 16S Databases | Ribosomal Database Project | (Cole et al., 2014) [50] |
| Greengenes | (DeSantis et al., 2006) [51] | |
| Silva | (Quast et al., 2013) [52] | |
| OTUs clustering | Cd-hit | (Li et al., 2006) [53] |
| UCLUST | (Edgar et al., 2010) [54] | |
| Sub-OTU methods | DADA2 | (Callahan et al., 2016) [55] |
| UNOISE2 | (Edgar, 2016) [56] | |
| Deblur | (Amir et al., 2017) [57] | |
| Communities diversity comparison | UniFrac | (Lozupone et al., 2006) [58] |
| Functional profiles prediction | PICRUSt | (Langille et al., 2013) [59] |
| Piphillin | (Iwai et al., 2016) [60] | |
| Tax4Fun | (Aßhauer et al., 2015) [61] | |
| Metagenome assembly | SOAPdenovo | (Li et al., 2010) [62] |
| Velvet | (Zerbino et al., 2008) [63] | |
| MetaVelvet | (Namiki et al., 2012) [64] | |
| Meta-IBDA | (Peng et al., 2011) [65] | |
| Genovo | (Laserson et al., 2011) [66] | |
| Bambus2 | (Koren et al., 2011) [67] | |
| Ray-Meta | (Boisvert et al., 2012) [68] | |
| ViromeScan | (Rampelli et al., 2016) [69] | |
| PanPhlAn | (Scholz et al., 2016) [70] | |
| Gene identification | FragGeneScan | (Rho et al., 2010) [71] |
| MetaGeneMark | (Zhu et al., 2010) [72] | |
| Glimmer-MG | (Kelley et al., 2012) [73] | |
| Functional assignment | IMG database | (Markowitz et al., 2014) [74] |
| MetaRef | (Huang et al., 2014) [75] | |
| dbCAN | (Yin et al., 2012) [76] | |
| HUMAnN | (Abubucker et al., 2012) [77] |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Argenio, V. Human Microbiome Acquisition and Bioinformatic Challenges in Metagenomic Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020383
D’Argenio V. Human Microbiome Acquisition and Bioinformatic Challenges in Metagenomic Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020383
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Argenio, Valeria. 2018. "Human Microbiome Acquisition and Bioinformatic Challenges in Metagenomic Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020383
APA StyleD’Argenio, V. (2018). Human Microbiome Acquisition and Bioinformatic Challenges in Metagenomic Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020383