Astragalus membranaceus Extract Attenuates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via NF-κB Activation and Nrf2 Response
Abstract
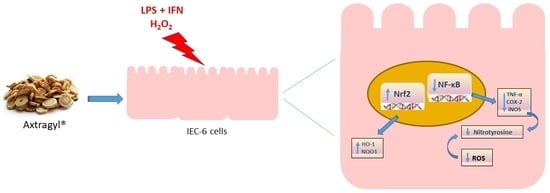
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Did Not Have Any Antiproliferative Activity on IEC-6 Cells
2.2. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Reduced Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) Levels in Lipopolysaccharide from E. coli (LPS) + Interferon-γ (IFN)-Stimulated IEC-6
2.3. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Reduced Cycloxygenase-2 (COX-2) and Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Expression and Nitrotyrosine Formation in LPS + IFN-Stimulated IEC-6
2.4. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Reduced p65 Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) Translocation in LPS + IFN-Stimulated IEC-6
2.5. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Reduced ROS Release by IEC-6 Cells
2.6. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Induced Nuclear Factor (Erythroid-Derived 2)-Like 2 (Nrf2) Activation and Heme Oxygenase 1 (HO-1), NAD(P)H Quinone Dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1) Expression in IEC-6 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Treatment
4.5. Antiproliferative Activity
4.6. TNF-α Determination
4.7. Measurement of COX-2, iNOS, HO-1, NQO1 Expression and Nitrotyrosine Formation by Cytofluorimetry
4.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis for NF-κB and Nrf2 by Confocal Microscopy
4.9. Intracellular ROS Release Measurement
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, B.L.; Chandra, S.; Shih, D.Q. Skin manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matricon, J.; Barnich, N.; Ardid, D. Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Self/Nonself 2010, 1, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanauer, S.B. Inflammatory bowel disease: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and therapeutic opportunities. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2006, 12, S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Cao, S.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in intestinal epithelial cell function and inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 328791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R.; Janeway, C., Jr. Innate immunity. New Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, L.B.; Rana, T.S.; Anand, K.K. Current status of the systematics of Astragalus L. (Fabaceae) with special reference to the Himalayan species in India. Taiwania 2008, 53, 338–355. [Google Scholar]
- Mabberley, D.J. Mabberley’s Plant-Book: A Portable Dictionary of Plants, Their Classification and Uses, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 77–476. [Google Scholar]
- State Pharmacopoeia Commission of the PRC. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Ha, H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.T.; Kwon, S.C.; Park, S.W. Induction of growth hormone by the roots of Astragalus membranaceus in pituitary cell culture. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zee-Cheng, R.K. Shi-quan-da-bu-tang (ten significant tonic decoction), SQT. A potent Chinese biological response modifier in cancer immunotherapy, potentiation and detoxifi-cation of anticancer drugs. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1992, 14, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.X.; Li, L.; Lou, J.; Yang, W.X.; Lei, T.W.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, J.; Cheng, M.L.; Huang, L.H. The protective effects of traditional Chinese medicine prescription, Han-Dan-Gan-Le, on CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1998, 26, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, D.; Hughes, K.; Jones, K. Astragalus. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2002, 8, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.C.S.; Leung, K.N. In vitro and in vivo immunomodulating and immunorestorative effects of Astragalus membranaceus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 113, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hei, Z.Q.; Zhang, J.J.; Lin, S.Q.; Liu, K.X.; Chen, B.X. Effects of Astragalus membranaceus injection on nitric oxide and endothelin concentration of intestinal mucosa after hemorrhage shock-reperfusion in rats. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi 2004, 29, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hei, Z.Q.; Huang, H.Q.; Zhang, J.J.; Chen, B.X.; Li, X.Y. Protective effect of Astragalus membranaceus on intestinal mucosa reperfusion injury after hemorrhagic shock in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 4986–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, X.L.; Hei, Z.Q.; Huang, H.Q.; Chen, L.X.; Li, S.R.; Cai, J. Effect of Astragalus membranaceus injection on the activity of the intestinal mucosal mast cells after hemorrhagic shock-reperfusion in rats. Chin. Med. J. 2006, 119, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Q.; Shi, Q.; Duan, J.A.; Dong, T.T.X.; Tsim, K.W.K. Chemical analysis of Radix Astragali (Huangqi) in China: A comparison with its adulterants and seasonal variations. J. Agric. Food Chemistry 2002, 50, 4861–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, M.; Kim, E.H.; Chun, M.; Kang, S.; Shim, B.; Yu, Y.B.; Jeong, G.; Lee, J.S. Astragali Radix elicits anti-inflammation via activation of MKP-1, concomitant with attenuation of p38 and Erk. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 115, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.; Qi, L.W.; Li, B.; Gao, W.; Li, P. Radix Astragali (Astraglaus): Latest advancements and trends in chemistry, analysis, pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Curr. Org. Chem. 2010, 14, 1792–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.Z.; Lu, Y.; Gui, D.K.; Peng, A.; Chen, J.; Gu, Y. Aqueous extract of Astragali Radix ameliorates proteinuria in adriamycin nephropathy rats through inhibition of oxidative stress and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.Q.; Hu, S.J.; Qiu, L.H.; Zhu, J.H.; Xie, X.J.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Z.H.; Xia, Q.; Bian, K. Effects of Astragalus membranaceus and its main components on the acute phase endothelial dysfunction induced by homocysteine. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2007, 46, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Qian, X.H.; Zhao, D.H.; Fu, S.Z. Effects of Astragalus polysaccharide on the erythroid lineage and microarray analysis in K562 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.H.; Xu, X.X.; Pan, R.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y.B.; Xia, Y.F.; Murata, K.; Matsuda, H.; Dai, Y. Saponin fraction from Astragalus membranaceus roots protects mice against polymicrobial sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture by inhibiting inflammation and upregulating protein C pathway. J. Nat. Med. 2009, 63, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; He, H.; Ge, H.; Wu, Y.; Shen, Z. Astragalus Polysaccharide Attenuates Murine Colitis through Inhibiton of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.L.; Ren, H.J.; Liu, M.M.; Li, X.G.; Sun, D.L.; Li, N.; Ming, L. Modulation of intestinal epithelial cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation in vitro by Astragalus polysaccharides. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, S.T.; Bernardo, D.; Mann, E.R.; Al-Hassi, H.O.; Knight, S.C.; Hart, A.L. Mechanisms of action of anti-tumor necrosis factor-α agents in Crohn’s disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, C.; Neumann, H.; Neurath, M.F.; Becker, C. Apoptosis, necrosis and necroptosis: Cell death regulation in the intestinal epithelium. Gut 2013, 62, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fries, W.; Muja, C.; Crisafulli, C.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Mazzon, E. Dynamics of enterocyte tight junctions: Effect of experimental colitis and two different anti-TNF strategies. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G938–G947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, J.K.; Chik, C.W. The protective action of radix Astragalus membranaceus against hapten-induced colitis through modulation of cytokines. Cytokine 2009, 47, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.Q.; Sun, W.Z. Study on regulation effects of TNF-α, IL-8 and sIL-2r content to patients of ulcerative colitis by mediation method. J. Harbin Univ. Commun. Nat. Sci. 2002, 18, 248–250. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Fidalgo, S.; Cárdeno, A.; Villegas, I.; Talero, E.; de la Lastra, C.A. Dietary supplementation of resveratrol attenuates chronic colonic inflammation in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 633, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianchi, F.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Vinci, M.C.; Messerini, L.; Comin, C.E.; Navarra, G.; Perigli, G.; Centorrino, T.; Marzocco, S.; Lenzi, E.; et al. Heterogeneous expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase within colorectal tumors: Correlation with tumor angiogenesis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, P.C.; Auyeung, K.K.; Chan, L.Y.; Ko, J.K. Astragalus saponins downregulate vascular endothelial growth factor under cobalt chloride-stimulated hypoxia in colon cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentine, J.F.; Tannahill, C.L.; Stevenot, S.A.; Sallustio, J.E.; Nick, H.S.; Eaker, E.Y. Colitis and interleukin 1â up-regulated inducible nitric oxide synthase and superoxide dismutase in rat myenteric neurons. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmilewitz, D.; Stamler, J.S.; Bachwich, D.; Karmeli, F.; Ackerman, Z.; Podolsky, D.K. Enhanced colonic nitric oxide generation and nitric oxide synthase activity in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Gut 1995, 36, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schopfer, F.J.; Baker, P.R.; Freeman, B.A. NO-dependent protein nitration: A cell signaling event or an oxidative inflammatory response? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003, 28, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Han, O.K.; Park, C.W.; Yang, C.H.; Jeon, T.W.; Yo, W.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.J. Pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression and nitric oxide regulation of aqueous extracted Astragali Radix in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF-kappaB: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atreya, I.; Atreya, R.; Neurath, M.F. NF-κB in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 263, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Liu, F.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, P. Astragalus polysaccharides protect against dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis by inhibiting NF-κВ activation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Mitra, S.; Crowe, S.E. Oxidative Stress: An Essential Factor in the Pathogenesis of Gastrointestinal Mucosal Diseases. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Shao, H.; Lin, S.; Zhang, J.J.; Xu, K.Q. Treatment with Astragalus membranaceus produces antioxidative effects and attenuates intestinal mucosa injury induced by intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2011, 39, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad, M.; Shabbir, A.; Wojcikowski, K.; Wohlmuth, H.; Gobe, G.C. The Antioxidant Effects of Radix Astragali (Astragalus membranaceus and Related Species) in Protecting Tissues from Injury and Disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2016, 17, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uruno, A.; Motohashi, H. The Keap1-Nrf2 system as an in vivo sensor for electrophiles. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2011, 25, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osburn, W.O.; Karim, B.; Dolan, P.M.; Liu, G.; Yamamoto, M.; Huso, D.L.; Kensler, T.W. Increased colonic inflammatory injury and formation of aberrant crypt foci in Nrf2-deficient mice upon dextran sulfate treatment. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, T.O.; Huang, M.T.; Prawan, A.; Liu, Y.; Hao, X.; Yu, S.; Cheung, W.K.L.; Chan, J.Y.; Reddy, B.S.; Yang, C.S.; et al. Increased susceptibility of Nrf2 knockout mice to colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2008, 1, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Qian, C.; Tang, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; You, Q.; Hu, R. 3-(2-Oxo-2-phenylethylidene)-2,3,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinolin-4(11bH)-one (compound 1), a novel potent Nrf2/ARE inducer, protects against DSS-induced colitis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 101, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, L.; Lei, S.; Luo, H. Luteolin ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice possibly through activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 40, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B.; Jin, Y.; Tian, Y.; Xin, Y.; Duan, Z. The Protective Effect of Heme Oxygenase-1 against Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction in Cholestatic Liver Injury Is Associated with NF-κB Inhibition. Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, P.; Huang, F.; Jin, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H.; Wu, X. Astragaloside IV protects blood-brain barrier integrity from LPS-induced disruption via activating Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 340, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Zanardelli, M.; Bartolucci, G.; Karioti, A.; Bilia, A.R.; Vannacci, A.; Mugelli, A.; Ghelardini, C. In Vitro Evidence for the Use of Astragali Radix Extracts as Adjuvant against Oxaliplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Pacini, A.; Micheli, L.; Femia, A.P.; Maresca, M.; Zanardelli, M.; Vannacci, A.; Gallo, E.; Bilia, A.R.; Caderni, G.; et al. Astragali radix: Could it be an adjuvant for oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy? Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, B.M.; Xu, W.; Dai, H.; Tu, P.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.M. A study on the immune receptors for polysaccharides from the roots of Astragalus membranaceus, a Chinese medicinal herb. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 320, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Hu, Y.; Sun, J.; Kong, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Comparative study on adjuvanticity of compound Chinese herbal medicinal ingredients. Vaccine 2005, 23, 3704–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.H.; Xiang, D.Y.; He, Y.J.; Xu, C.X.; Zhang, P.Z. Influence of radix Astragali on the noise-caused change in hepatic glycogencontent of rats. J. Chin. Mater. Med 1989, 14, 750–752. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Xiong, H.E. Inhibitive effect of injection Radix Astragali in epidemic hemorrhagic fever virus infection. Hunan Yike Daxue Xuebao 1990, 15, 250–252. [Google Scholar]
- Braca, A.; Dal Piaz, F.; Marzocco, S.; Autore, G.; Vassallo, A.; De Tommasi, N. Triterpene derivatives as inhibitors of protein involved in the inflammatory process: Molecules interfering with phospholipase A2, cycloxygenase, and lipoxygenase. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 302–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hou, X.; Xu, R.; Liu, C.; Tu, M. Research review on the pharmacological effects of astragaloside IV. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 31, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L.; Zheng, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S. Review of the botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi). Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.J.; Liu, H.K.; Hsiao, P.C.; Kuo, L.M.Y.; Lee, I.J.; Wu, T.S.; Chiou, W.F.; Kuo, Y.H. New isoflavonoid glycosides and related constituents from Astragali Radix (Astragalus membranaceus) and their inhibitory activity on nitric oxide production. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Song, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S. Studies on principal components and antioxidant activity of different Radix Astragali samples using high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization multiple-stage tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2009, 78, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaroni, A. Pre- and postnatal development of differentiated functions in rat intestinal epithelial cells. Dev. Biol. 1985, 111, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, G.; Fontanella, B.; Severino, L.; Quaroni, A.; Autore, G.; Marzocco, S. Nivalenol and deoxynivalenol affect rat intestinal epithelial cells: A concentration related study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepe, G.; Sommella, E.; Ventre, G.; Scala, M.C.; Adesso, S.; Ostacolo, C.; Marzocco, S.; Novellino, E.; Campiglia, P. Antioxidant peptides released from gastrointestinal digestion of “Stracchino” soft cheese: Characterization, in vitro intestinal protection and bioavailability. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesso, S.; Autore, G.; Quaroni, A.; Popolo, A.; Severino, L.; Marzocco, S. The Food Contaminants Nivalenol and Deoxynivalenol Induce Inflammation in Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Regulating Reactive Oxygen Species Release. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesso, S.; Magnus, T.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Campolo, M.; Rissiek, B.; Paciello, O.; Autore, G.; Pinto, A.; Marzocco, S. Indoxyl Sulfate Affects Glial Function Increasing Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Chronic Kidney Disease: Interaction between Astrocytes and Microglia. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 12, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzocco, S.; Calabrone, L.; Adesso, S.; Larocca, M.; Franceschelli, S.; Autore, G.; Martelli, G.; Rossano, R. Anti-inflammatory activity of horseradish (Armoracia rusticana) root extracts in LPS-stimulated macrophages. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 3778–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzocco, S.; Adesso, S.; Alilou, M.; Stuppner, H.; Schwaiger, S. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Potential of the Root Extract and Constituents of Doronicum austriacum. Molecules 2017, 22, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adesso, S.; Russo, R.; Quaroni, A.; Autore, G.; Marzocco, S. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Attenuates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via NF-κB Activation and Nrf2 Response. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030800
Adesso S, Russo R, Quaroni A, Autore G, Marzocco S. Astragalus membranaceus Extract Attenuates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via NF-κB Activation and Nrf2 Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030800
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdesso, Simona, Rosario Russo, Andrea Quaroni, Giuseppina Autore, and Stefania Marzocco. 2018. "Astragalus membranaceus Extract Attenuates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via NF-κB Activation and Nrf2 Response" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030800
APA StyleAdesso, S., Russo, R., Quaroni, A., Autore, G., & Marzocco, S. (2018). Astragalus membranaceus Extract Attenuates Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells via NF-κB Activation and Nrf2 Response. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030800