Calsenilin, a Presenilin Interactor, Regulates RhoA Signaling and Neurite Outgrowth
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Calsenilin Interacts with RhoA
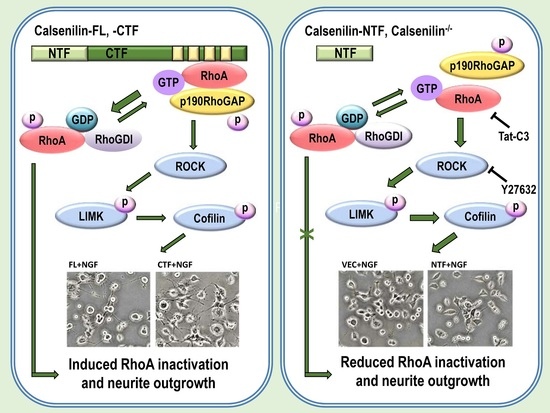
2.2. Calsenilin Regulates RhoA Activity and the RhoA-ROCK-LIMK-Cofilin Pathway by Facilitating an Interaction between RhoA and p190RhoGAP
2.3. RhoA Preferentially Interacts with Calsenilin-CTF and Regulates RhoA Activity and the RhoA-ROCK-LIMK-Cofilin Pathway
2.4. Calsenilin Regulates F-actin Formation
2.5. Calsenilin-CTF Induces Neurite Outgrowth through RhoA-Mediated Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture, Transfection, and Generation of Stable Cell Lines
4.2. Construction of Recombinant Plasmids
4.3. Animals
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.6. In Vitro Loading of GDP and GTPγS onto GTP-Binding Proteins
4.7. Glutathione-S-Transferase (GST)-Rhotekin-RBD Pull-Down Assay for RhoA Activation
4.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.9. Quantitation of F-Actin and G-Actin
4.10. Adhesion Assays
4.11. Neurite Outgrowth Analysis
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GAP | GTPase-activating protein |
| NGF | nerve growth factor |
| ROCK | Rho-associated kinase |
| RhoGDI | Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor |
| GST-Rhotekin-RBD | glutathione S-transferase-Rhotekin Rho-binding domain |
| DREAM | downstream regulatory element antagonist modulator |
| CREB | cAMP response element binding protein |
| WASP | Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome protein |
| PAK | p21-activated kinase |
| CDK5 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 |
References
- Buxbaum, J.D.; Choi, E.K.; Luo, Y.; Lilliehook, C.; Crowley, A.C.; Merriam, D.E.; Wasco, W. Calsenilin: A calcium-binding protein that interacts with the presenilins and regulates the levels of a presenilin fragment. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, N.F.; Thomson, E.E.; Choi, E.K.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Wasco, W. Intracellular calcium modulates the nuclear translocation of calsenilin. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.K.; Zaidi, N.F.; Miller, J.S.; Crowley, A.C.; Merriam, D.E.; Lilliehook, C.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Wasco, W. Calsenilin is a substrate for caspase-3 that preferentially interacts with the familial Alzheimer’s disease-associated C-terminal fragment of presenilin 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 19197–19204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.K.; Miller, J.S.; Zaidi, N.F.; Salih, E.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Wasco, W. Phosphorylation of calsenilin at Ser63 regulates its cleavage by caspase-3. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontan-Lozano, A.; Romero-Granados, R.; del-Pozo-Martin, Y.; Suarez-Pereira, I.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Penninger, J.M.; Carrion, A.M. Lack of DREAM protein enhances learning and memory and slows brain aging. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.J.; Mellstrom, B.; Wang, H.; Ren, M.; Domingo, S.; Kim, S.S.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, T.; Naranjo, J.R.; Zhuo, M. DREAM (downstream regulatory element antagonist modulator) contributes to synaptic depression and contextual fear memory. Mol. Brain Res. 2010, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, P.L.; Craig, T.A.; Atanasova, E.A.; Cui, G.; Owen, B.A.; Bergen, H.R., III; Mer, G.; Kumar, R. The potassium channel interacting protein 3 (DREAM/KChIP3) heterodimerizes with and regulates calmodulin function. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 39439–39448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etienne-Manneville, S.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 2002, 420, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, M.L.; Marshall, C.J.; Olson, M.F. RAS and RHO GTPases in G1-phase cell-cycle regulation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiering, D.; Hodgson, L. Dynamics of the Rho-family small GTPases in actin regulation and motility. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2011, 5, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.M.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPases in cancer cell biology. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, J.L.; Rehmann, H.; Wittinghofer, A. GEFs and GAPs: Critical elements in the control of small G proteins. Cell 2007, 129, 865–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govek, E.E.; Newey, S.E.; van Aelst, L. The role of the Rho GTPases in neuronal development. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L. RHO GTPASES in neuronal morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2000, 1, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, J.S.; Dotti, C.G. Breaking the neuronal sphere: Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in neuritogenesis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, E.; Dubey, B.N.; Zhang, S.C.; Gremer, L.; Dvorsky, R.; Moll, J.M.; Taha, M.S.; Nagel-Steger, L.; Piekorz, R.P.; Somlyo, A.V.; et al. Rho-kinase: Regulation, (dys)function, and inhibition. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, C.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, S.C.; Park, J.B. p190RhoGAP and Rap-dependent RhoGAP (ARAP3) inactivate RhoA in response to nerve growth factor leading to neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2010, 42, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, C.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Morii, H.; Mori, N.; Settleman, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.C.; Park, J.B. Neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells by basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is mediated by RhoA inactivation through p190RhoGAP and ARAP3. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 224, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, E.; Park, E.S.; Wasco, W.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, E.K. Calsenilin is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011, 405, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sit, S.T.; Manser, E. Rho GTPases and their role in organizing the actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.; Choi, J.K.; Na, Y.J.; Jang, B.; Wasco, W.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, E.K. Calsenilin regulates presenilin 1/γ-secretase-mediated N-cadherin epsilon-cleavage and β-catenin signaling. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 4174–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, C.Y.; Moon, M.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.G.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.K.; Kim, P.H.; Kim, H.C.; Meier, K.E.; et al. Control of neurite outgrowth by RhoA inactivation. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120, 684–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Manzanero, S.; Chang, J.W.; Choi, Y.; Baik, S.H.; Cheng, Y.L.; Li, Y.I.; Gwon, A.R.; Woo, H.N.; Jang, J.; et al. Calsenilin contributes to neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke. Brain Pathol. 2013, 23, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Pitcher, G.M.; Laviolette, S.R.; Whishaw, I.Q.; Tong, K.I.; Kockeritz, L.K.; Wada, T.; Joza, N.A.; Crackower, M.; Goncalves, J.; et al. DREAM is a critical transcriptional repressor for pain modulation. Cell 2002, 108, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.G.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, Y.H.; Kim, I.K.; Song, Y.H.; Woo, H.N.; Chung, C.W.; Jung, Y.K. Pro-apoptotic function of calsenilin/DREAM/KChIP3. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 589–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Katoh, H.; Yasui, H.; Mori, K.; Negishi, M. RhoA inhibits the nerve growth factor-induced Rac1 activation through Rho-associated kinase-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18977–18983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ottens, A.K.; Larner, S.F.; Kobeissy, F.H.; Williams, M.L.; Hayes, R.L.; Wang, K.K. Direct Rho-associated kinase inhibition induces cofilin dephosphorylation and neurite outgrowth in PC-12 cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2006, 11, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.; Lalli, G. Rho and Ras GTPases in axon growth, guidance, and branching. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, W.T.; Burridge, K. RhoA inactivation by p190RhoGAP regulates cell spreading and migration by promoting membrane protrusion and polarity. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontainhas, A.M.; Townes-Anderson, E. RhoA inactivation prevents photoreceptor axon retraction in an in vitro model of acute retinal detachment. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arber, S.; Barbayannis, F.A.; Hanser, H.; Schneider, C.; Stanyon, C.A.; Bernard, O.; Caroni, P. Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase. Nature 1998, 393, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, F.; Loeser, R.F. Biology and pathology of Rho GTPase, PI-3 kinase-Akt, and MAP kinase signaling pathways in chondrocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigyi, G.; Fischer, D.J.; Sebok, A.; Marshall, F.; Dyer, D.L.; Miledi, R. Lysophosphatidic acid-induced neurite retraction in PC12 cells: Neurite-protective effects of cyclic AMP signaling. J. Neurochem. 1996, 66, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spira, M.E.; Oren, R.; Dormann, A.; Ilouz, N.; Lev, S. Calcium, protease activation, and cytoskeleton remodeling underlie growth cone formation and neuronal regeneration. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2001, 21, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, D.J.; Grabham, P.W. Braking news: Calcium in the growth cone. Neuron 1999, 22, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, P.; Williams, G.; Williams, E.J. CAMs and axonal growth: A critical evaluation of the role of calcium and the MAPK cascade. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 16, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankiewicz, T.R.; Linseman, D.A. Rho family GTPases: Key players in neuronal development, neuronal survival, and neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.D.; Kiosses, W.B.; Schwartz, M.A. Regulation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho by cell adhesion and the cytoskeleton. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensel, N.; Ratzka, A.; Brinkmann, H.; Klimaschewski, L.; Grothe, C.; Claus, P. Analysis of the fibroblast growth factor system reveals alterations in a mouse model of spinal muscular atrophy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusser, N.; Gosmanova, E.; Zheng, Y.; Tigyi, G. Nerve growth factor signals through TrkA, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and Rac1 to inactivate RhoA during the initiation of neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 35840–35846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newey, S.E.; Velamoor, V.; Govek, E.E.; Van Aelst, L. Rho GTPases, dendritic structure, and mental retardation. J. Neurobiol. 2005, 64, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, Y.; Hartwig, J.H.; Stossel, T.P. FilGAP, a Rho- and ROCK-regulated GAP for Rac binds filamin A to control actin remodelling. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimnual, A.S.; Taylor, L.J.; Bar-Sagi, D. Redox-dependent downregulation of Rho by Rac. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarugi, P.; Cirri, P.; Taddei, L.; Giannoni, E.; Camici, G.; Manao, G.; Raugei, G.; Ramponi, G. The low Mr protein-tyrosine phosphatase is involved in Rho-mediated cytoskeleton rearrangement after integrin and platelet-derived growth factor stimulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 4640–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drubin, D.G.; Feinstein, S.C.; Shooter, E.M.; Kirschner, M.W. Nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells involves the coordinate induction of microtubule assembly and assembly-promoting factors. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 101, 1799–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.P.; Freudenrich, T.M.; Mundy, W.R. Assessment of PC12 cell differentiation and neurite growth: A comparison of morphological and neurochemical measures. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, C.Y.; Jin, J.K.; Koh, Y.H.; Chun, W.; Choi, I.G.; Kown, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, J.B. Neurites from PC12 cells are connected to each other by synapse-like structures. Synapse 2010, 64, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, L.A.; Tischler, A.S. Establishment of a noradrenergic clonal line of rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells which respond to nerve growth factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, D.; Heinemann, S.; Kidokoro, Y. Cholinergic metabolism and synapse formation by a rat nerve cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 2579–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckenbill-Edds, L.; Van Horn, C.; Greene, L.A. Fine structure of initial outgrowth of processes induced in a pheochromocytoma cell line (PC12) by nerve growth factor. J. Neurocytol. 1979, 8, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, N.F.; Kuplast, K.G.; Washicosky, K.J.; Kajiwara, Y.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Wasco, W. Calsenilin interacts with transcriptional co-repressor C-terminal binding protein(s). J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilliehook, C.; Bozdagi, O.; Yao, J.; Gomez-Ramirez, M.; Zaidi, N.F.; Wasco, W.; Gandy, S.; Santucci, A.C.; Haroutunian, V.; Huntley, G.W.; et al. Altered Aβ formation and long-term potentiation in a calsenilin knock-out. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 9097–9106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, E.K.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.S. A neuronal cell line that does not express either prion or doppel proteins. Neuroreport 2005, 16, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Fonseca, J.A.; Najera, O.; Martinez-Jurado, J.; Walker, E.M.; Varela-Ramirez, A.; Khan, A.M.; Miranda, M.; Lamango, N.S.; Roychowdhury, S. Nerve growth factor induces neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells by promoting Gβγ-microtubule interaction. BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-J.; Lee, W.-H.; Kim, M.-J.; Shin, S.; Jang, B.; Park, J.-B.; Wasco, W.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Kim, Y.-S.; Choi, E.-K. Calsenilin, a Presenilin Interactor, Regulates RhoA Signaling and Neurite Outgrowth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041196
Kim H-J, Lee W-H, Kim M-J, Shin S, Jang B, Park J-B, Wasco W, Buxbaum JD, Kim Y-S, Choi E-K. Calsenilin, a Presenilin Interactor, Regulates RhoA Signaling and Neurite Outgrowth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041196
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hee-Jun, Won-Haeng Lee, Mo-Jong Kim, Sunmee Shin, Byungki Jang, Jae-Bong Park, Wilma Wasco, Joseph D. Buxbaum, Yong-Sun Kim, and Eun-Kyoung Choi. 2018. "Calsenilin, a Presenilin Interactor, Regulates RhoA Signaling and Neurite Outgrowth" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041196
APA StyleKim, H. -J., Lee, W. -H., Kim, M. -J., Shin, S., Jang, B., Park, J. -B., Wasco, W., Buxbaum, J. D., Kim, Y. -S., & Choi, E. -K. (2018). Calsenilin, a Presenilin Interactor, Regulates RhoA Signaling and Neurite Outgrowth. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041196