Biocompatible and Antimicrobial Electrospun Membranes Based on Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. GO Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Electrospun CS/PVA/GO Composite Nanofibrous Membranes Characterization
2.2.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.3. Degradation in a Simulated Biological Fluid (SBF)
2.2.4. SEM of the Electrospun CS/PVA/GO Composite Nanofibrous Membranes after Immersion in SBF
2.2.5. Antibacterial Activity
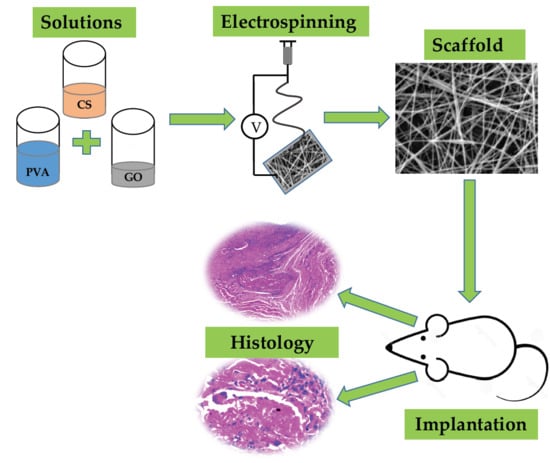
2.2.6. Biomodel Tests In Vivo
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. GO Synthesis
3.2.2. Preparation of Electrospun CS/PVA/GO Composite Nanofibrous Membranes
3.3. Characterization
3.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3.3. Degradation in Simulated Biological Fluid
3.3.4. Antimicrobial of Electrospun CS/PVA/GO Composite Nanofibrous Membranes Assay
3.3.5. Biomodels Test In Vivo
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abd-Khorsand, S.; Saber-Samandari, S.; Saber-Samandari, S. Development of nanocomposite scaffolds based on TiO2 doped in grafted chitosan/hydroxyapatite by freeze-drying method and evaluation of biocompatibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.S.; Mooney, D.J. Development of biocompatible synthetic extracellular matrices for tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Liu, C.; Yang, X. Biomimetic porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 80, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-Y.; Seo, S.-J.; Moon, H.-S.; Yoo, M.-K.; Park, I.-Y.; Kim, B.-C.; Cho, C.-S. Chitosan and its derivatives for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, R.; Mielke, S.L.; Paci, J.T.; Zhang, S.; Ballarini, R.; Schatz, G.C.; Belytschko, T. Coupled quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical modeling of the fracture of defective carbon nanotubes and graphene sheets. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 075412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, N.; Bentini, R.; Islam, I.; Cao, T.; Neto, A.H.C.; Rosa, V. Graphene: A Versatile Carbon-Based Material for Bone Tissue Engineering. Stem Cells Int. 2015, 2015, 804213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, K.P.; Bao, Q.; Ang, P.K.; Yang, J. The chemistry of graphene. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2277–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Liu, Z. Graphene in biomedicine: opportunities and challenges. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostarelos, K.; Novoselov, K.S. Exploring the interface of graphene and biology. Science 2014, 344, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenka, S.; Sant, V.; Sant, S. Graphene-based nanomaterials for drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control Release 2014, 173, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depan, D.; Misra, R.D.K. The interplay between nanostructured carbon-grafted chitosan scaffolds and protein adsorption on the cellular response of osteoblasts: Structure-function property relationship. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6084–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Martínez, V. Estudio de la estabilidad del óxido de grafeno con el tiempo. 2013. Available online: http://digibuo.uniovi.es/dspace/handle/10651/19083 (accessed on 2 March 2019).
- Bei, P.H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Luo, X.; Yang, M.; Zhao, X. Graphene-Based Nanocomposites for Neural Tissue Engineering. Molecules 2019, 24, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Grande, C.D.; Rodrigues, D.F. Biodegradation of graphene oxide-polymer nanocomposite films in wastewater. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, C.; Lou, W.; Shentu, F. Fiber optic humidity sensor based on the graphene oxide/PVA composite film. Opt. Commun. 2016, 372, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zheng, H.; Liang, S.; Gao, C. Aligned PLLA nanofibrous scaffolds coated with graphene oxide for promoting neural cell growth. Acta Biomater. 2016, 37, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiacchiaretta, M.; Bramini, M.; Rocchi, A.; Armirotti, A.; Giordano, E.; Vázquez, E.; Bandiera, T.; Ferroni, S.; Cesca, F.; Benfenati, F. Graphene oxide upregulates the homeostatic functions of primary astrocytes and modulates astrocyte-to-neuron communication. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 5827–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E.; Abouei, E.; Hatamie, S.; Ghasemi, E. Accelerated differentiation of neural stem cells into neurons on ginseng-reduced graphene oxide sheets. Carbon 2014, 66, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Gao, H.; Zhu, G.; Cao, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y. The preparation and characterization of polycaprolactone/graphene oxide biocomposite nanofiber scaffolds and their application for directing cell behaviors. Carbon 2015, 95, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Tamayo, A.J.; Delgado Ospina, J.; Navia Porras, P.D.; Valencia Zapata, E.M.; Mina Hernandez, H.J.; Valencia, H.C.; Zuluaga, F.; Grande Tovar, D.C. Antimicrobial Films Based on Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Graphene Oxide for Biomedical Applications. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, C.; Valencia, C.; Zuluaga, F.; Valencia, M.; Mina, J.; Grande-Tovar, C. Synthesis and Application of Scaffolds of Chitosan-Graphene Oxide by the Freeze-Drying Method for Tissue Regeneration. Molecules 2018, 23, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio, D.L.; Valencia, C.H.; Valencia, C.; Zuluaga, F.; Valencia, M.E.; Mina, J.H.; Tovar, C.D.G. Evaluation of the Biocompatibility of CS-Graphene Oxide Compounds In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofaro, F.; Gigli, M.; Bloise, N.; Chen, H.; Bruni, G.; Munari, A.; Moroni, L.; Lotti, N.; Visai, L. Influence of the nanofiber chemistry and orientation of biodegradable poly(butylene succinate)-based scaffolds on osteoblast differentiation for bone tissue regeneration. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 8689–8703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Bachhuka, A.; Wei, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Vasilev, K.; Xiao, Y. Nanotopography-based strategy for the precise manipulation of osteoimmunomodulation in bone regeneration. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 18129–18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.C.; Park, S.K.; Kim, G.T.; Hwang, Y.J.; Lee, C.G.; Shin, H.S.; Lee, J.K. Development of high-efficiency nano filters made of nanofibers. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2006, 6, 1030–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; An, I.G.; Kim, C.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Nam, J. Do Electrospun dual-porosity structure and biodegradation morphology of Montmorillonite reinforced PLLA nanocomposite scaffolds. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3165–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, W.; Zhao, X.; Wen, S.; Sun, Y.; Han, J.; Zhang, H. Bone remodeling-inspired dual delivery electrospun nanofibers for promoting bone regeneration. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Ramakrishna, S. Advances in drug delivery via electrospun and electrosprayed nanomaterials. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2997. [Google Scholar]
- Mangadlao, J.D.; de Leon, A.C.C.; Felipe, M.J.L.; Cao, P.; Advincula, P.A.; Advincula, R.C. Grafted carbazole-assisted electrodeposition of graphene oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10266–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lei, P.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, D. Preparation and characterization of antibacterial electrospun chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide composite nanofibrous membrane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandele, A.M.; Ionita, M.; Crica, L.; Dinescu, S.; Costache, M.; Iovu, H. Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro studies of graphene oxide/chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.Y.; Tai, Z.X.; Sun, D.F.; Chen, J.T.; Ma, H.B.; Yan, X.B.; Liu, B.; Xue, Q.J. Fabrication and characterization of poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide nanofibrous biocomposite scaffolds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshirzadeh, B.; Anaraki, N.A.; Irani, M.; Rad, L.R.; Shamshiri, S. Controlled release of doxorubicin from electrospun PEO/chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite nanofibrous scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 48, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habiba, U.; Siddique, T.A.; Talebian, S.; Lee, J.J.L.; Salleh, A.; Ang, B.C.; Afifi, A.M. Effect of deacetylation on the property of electrospun chitosan/PVA nanofibrous membrane and removal of methyl orange, Fe(III) and Cr(VI) ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 177, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, H.R.; Park, C.H.; Tijing, L.D.; Amarjargal, A.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, C.S. Bimodal fiber diameter distributed graphene oxide/nylon-6 composite nanofibrous mats via electrospinning. Colloids Surf. A Phys. Eng. Asp. 2012, 407, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, L.E.J. Comportamiento viscoelástico de dispersiones de grafeno y líquidos iónicos. 2018. Available online: http://repositorio.upct.es/handle/10317/15 (accessed on 2 March 2019).
- Cao, D.; Fu, Z.; Li, C. Heat and compression molded electrospun poly(l-lactide) membranes: Preparation and characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2011, 176, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Bi, X.; Xiao, C.; et al. Enhanced Physiochemical and Mechanical Performance of Chitosan-Grafted Graphene Oxide for Superior Osteoinductivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depan, D.; Girase, B.; Shah, J.S.; Misra, R.D.K. Structure-process-property relationship of the polar graphene oxide-mediated cellular response and stimulated growth of osteoblasts on hybrid chitosan network structure nanocomposite scaffolds. Acta. Biomater. 2011, 7, 3432–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.F.C. Caracterización físico-química y biológica de filmes de quitosano como transportadores de la rhBMP-2 en la regeneración del tejido óseo. 2014. Available online: https://eprints.ucm.es/28770/ (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Figueira-Maldonado, E. Degradación hidrolítica a diferentes pH de un material compuesto Poli(ácido láctico)/Quitosano. 2008. Available online: http://www.bib.usb.ve/tesis/000140588.pdf (accessed on 4 March 2019).
- Depan, D.; Shah, J.S.; Misra, R.D.K. Degradation mechanism, and increased stability of chitosan-based hybrid scaffolds cross-linked with nanostructured carbon: Process-structure-functional property relationship. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 2331–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiñana, I.T.; Cejudo, A.G.; Fernández, E. pH y amortiguadores: Tampones fisiológicos. Amortiguadoras 2001, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, M.; Ito, M. In vitro properties of a chitosan-bonded self-hardening paste with hydroxyapatite granules. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1996, 32, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelegueda, L.I.; Gliemmo, M.; Campos, C.A. Action of chitosan, nisin and sodium lactate on the inhibition and cell membrane damage of Listeria innocua and Shewanella putrefaciens. In Worldwide Research Efforts in the Fighting against Microbial Pathogens: From Basic Research to Technological Developments; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Brownwalker Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shan, C.; Zu, S.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Ge, Y. Preparation and characterization of chitosan–polyvinyl alcohol blend hydrogels for the controlled release of nano-insulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perreault, F.; de Faria, A.F.; Nejati, S.; Elimelech, M. Antimicrobial properties of graphene oxide nanosheets: why size matters. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7226–7236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, D.; Wang, B.; Zhao, R.; Guan, M.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, X.; Chai, Z.; Feng, W. Graphene oxide as an anaerobic membrane scaffold for the enhancement of B. adolescentis proliferation and antagonistic effects against pathogens E. coli and S. aureus. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 165101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Raj, S.; Kolanthai, E.; Sood, A.K.; Sampath, S.; Chatterjee, K. Chemical functionalization of graphene to augment stem cell osteogenesis and inhibit biofilm formation on polymer composites for orthopedic applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3237–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Vargas Castrillón, S.; Perreault, F.; de Faria, A.F.; Elimelech, M. Interaction of graphene oxide with bacterial cell membranes: insights from force spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2015, 2, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Peng, C.; Luo, W.; Lv, M.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. Graphene-based antibacterial paper. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4317–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Strain | 0% GO | 0.5% GO | 1.0% GO |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus cereus | --- | -- | + |
| Staphylococcus aureus | --- | -- | + |
| Salmonella spp | --- | -- | + |
| Escherichia coli | --- | -- | + |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamayo Marín, J.A.; Londoño, S.R.; Delgado, J.; Navia Porras, D.P.; Valencia Zapata, M.E.; Mina Hernandez, J.H.; Valencia, C.H.; Grande Tovar, C.D. Biocompatible and Antimicrobial Electrospun Membranes Based on Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Oxide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122987
Tamayo Marín JA, Londoño SR, Delgado J, Navia Porras DP, Valencia Zapata ME, Mina Hernandez JH, Valencia CH, Grande Tovar CD. Biocompatible and Antimicrobial Electrospun Membranes Based on Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Oxide. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(12):2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122987
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamayo Marín, Julián Andrés, Sebastián Ruiz Londoño, Johannes Delgado, Diana Paola Navia Porras, Mayra Eliana Valencia Zapata, José Herminsul Mina Hernandez, Carlos Humberto Valencia, and Carlos David Grande Tovar. 2019. "Biocompatible and Antimicrobial Electrospun Membranes Based on Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Oxide" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 12: 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122987
APA StyleTamayo Marín, J. A., Londoño, S. R., Delgado, J., Navia Porras, D. P., Valencia Zapata, M. E., Mina Hernandez, J. H., Valencia, C. H., & Grande Tovar, C. D. (2019). Biocompatible and Antimicrobial Electrospun Membranes Based on Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Graphene Oxide. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(12), 2987. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122987