Proteome Profiling of the Exhaled Breath Condensate after Long-Term Spaceflights
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
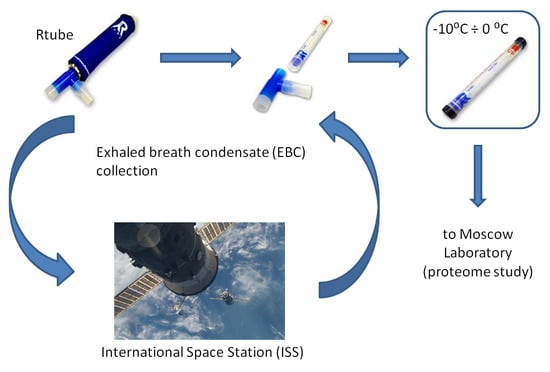
3.1. Samples Collection
3.2. LC-MS/MS Proteomic Analysis
3.3. Data Analysis
3.4. Collection of Microbiological Samples
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stein, T.P. Weight, muscle and bone loss during space flight: Another perspective. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 2171–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, M.; Seki, M.; Takahashi, R.; Yamada, S.; Higashibata, A.; Majima, H.J.; Sudoh, M.; Mukai, C.; Ishioka, N. Effects of a closed space environment on gene expression in hair follicles of astronauts in the International Space Station. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Meigal, A. Interplanetary space flight compared with fetal/neonatal motor strategy: Theoretical and practical implications. Pathophysiology 2012, 19, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononikhin, A.S.; Starodubtseva, N.L.; Pastushkova, L.K.; Kashirina, D.N.; Fedorchenko, K.Y.; Brhozovsky, A.G.; Popov, I.A.; Larina, I.M.; Nikolaev, E.N. Spaceflight induced changes in the human proteome. Expert. Rev. Proteom. 2017, 14, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcellos-Hoff, M.H.; Blakely, E.A.; Burma, S.; Fornace, A.J.; Gerson, S.; Hlatky, L.; Kirsch, D.G.; Luderer, U.; Shay, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Concepts and challenges in cancer risk prediction for the space radiation environment. Life Sci. Sp. Res. 2015, 6, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, R.J.; Day, S.M. Mortality among U.S. astronauts: 1980-2009. Aviat. Sp. Environ. Med. 2010, 81, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerma, M. Space radiation and cardiovascular disease risk. World J. Cardiol. 2015, 7, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Roberts, M.; Castro, S.; Oubre, C.; Makimura, K.; Leys, N.; Grohmann, E.; Sugita, T.; Ichijo, T.; Nasu, M. Microbial Monitoring of Crewed Habitats in Space—Current Status and Future Perspectives. Microbes Env. 2014, 29, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, C.; Wehland, M.; Pietsch, J.; Aleshcheva, G.; Wise, P.; Van Loon, J.; Magnusson, N.; Infanger, M.; Grosse, J.; Eilles, C.; et al. The impact of simulated and real microgravity on bone cells and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganov, D.I.; Teiber, J.F.; Speelman, A.; Osawa, Y.; Sunahara, R.; La Du, B.N. Human paraoxonases (PON1, PON2, and PON3) are lactonases with overlapping and distinct substrate specificities. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, A.M.; Altiero, T.; Corsetto, P.A.; Montorfano, G.; Guidetti, R.; Rebecchi, L. Space flight effects on antioxidant molecules in dry tardigrades: The TARDIKISS experiment. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, D.; Pietsch, J.; Richter, M.; Peter, W.; Strauch, S.M.; Lebert, M.; Magnusson, N.E.; Wise5, P.; Bauer, J. The impact of microgravity-based proteomics research. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2014, 11, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzhozovskiy, A.; Kononikhin, A.; Indeykina, M.; Pastushkova, L.; Popov, I.A.; Nikolaev, E.N.; Larina, I.M. Label-free study of cosmonaut’s urinary proteome changes after long-duration spaceflights. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 23, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, J.; Xie, P.; Xu, G. Discovery and validation of plasma biomarkers for major depressive disorder classification based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradi, M.; Pignatti, P.; Manini, P.; Andreoli, R.; Goldoni, M.; Poppa, M.; Moscatto, G.; Balbi, B.; Mutti, A. Comparison between exhaled and sputum oxidative stress biomarkers in chronic airway inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 24, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononikhin, A.S.; Starodubtseva, N.L.; Chagovets, V.V.; Ryndin, A.Y.; Burov, A.A.; Popov, I.A.; Bugrova, A.E.; Dautov, R.A.; Tokareva, A.O.; Podurovskaya, Y.L.; et al. Exhaled breath condensate analysis from intubated newborns by nano-HPLC coupled to high resolution MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1047, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, J. Exhaled breath condensate: An evolving tool for noninvasive evaluation of lung disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, I.; Hunt, J.; Barnes, P.J.; Alving, K.; Antczak, A.; Baraldi, E.; Becher, G.; van Beurden, W.J.C.; Corradi, M.; Dekhuijzen, R.; et al. Exhaled breath condensate: Methodological recommendations and unresolved questions. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 523–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurova, V.S.; Anaev, E.C.; Kononikhin, A.S.; Popov, I.A.; Fedorchenko, K.Y.; Nikolaev, E.N.; Varfolomeev, S.D.; Chuchalin, A.G. Mass spectrometric monitoring of exhaled breath condensate proteome of a patient after lung transplantation. Russ. Chem. Bull. Int. Ed. 2010, 59, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, M.; Cataneo, R.N.; Chaturvedi, A.; Kaplan, P.D.; Libardoni, M.; Mundada, M.; Patel, U.; Zhang, X. Detection of an Extended Human Volatome with Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, C.; Turner, C. Breath Analysis in Disease Diagnosis: Methodological Considerations and Applications. Metabolites 2014, 4, 465–498. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, M.; Montuschi, P.; Donnelly, L.E.; Pesci, A.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Barnes, P.J. Increased nitrosothiols in exhaled breath condensate in inflammatory airway diseases. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 163, 854–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.P.; Innes, J.A.; Greening, A.P. Nitrite levels in breath condensate of patients with cystic. Thorax 1998, 53, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balint, B.; Donnelly, L.E.; Hanazawa, T.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Barnes, P.J. Increased nitric oxide metabolites in exhaled breath condensate after exposure to tobacco smoke. Thorax 2001, 56, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kharitonov, S.; Yates, D.; Barnes, P. Inhaled Glucocorticoids Decrease Nitric Oxide in Exhaled Air of Asthmatic Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukides, S.; Horvath, I.; Wodehouse, T.; Cole, P.J.; Barnes, P.J. Brief Communications Elevated Levels of Expired Breath Hydrogen Peroxide in Bronchiectasis. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jöbsis, Q.; Raatgeep, H.C.; Schellekens, S.L.; Kroesbergen, A.; Hop, W.C.J.; De Jongste, J.C. Hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide in exhaled air of children with cystic fibrosis during antibiotic treatment. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 16, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, A.; van Herwaarden, C.L.; Dekker, I.; Dekhuijzen, P.N.; Aarts, L.P.; Aben, K.K.; Wielders, P.L. Increased exhalation of hydrogen peroxide in patients with stable and unstable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 154, 813–816. [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman, A.W.; Black, H.R.; Royall, J.A. Expired Breath Hydrogen Peroxide Is a Marker of Acute Airway Inflammation in Pediatric Patients with Asthma. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 2011, 148, 955–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanak, M.; Gielicz, A.; Nagraba, K.; Kaszuba, M.; Kumik, J.; Szczeklik, A. Targeted eicosanoids lipidomics of exhaled breath condensate in healthy subjects. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 1796–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Peralbo, M.A.; Calderón Santiago, M.; Priego-Capote, F.; Luque De Castro, M.D. Study of exhaled breath condensate sample preparation for metabolomics analysis by LC-MS/MS in high resolution mode. Talanta 2015, 144, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montuschi, P.; Collins, J.V.; Ciabattoni, G.; Lazzeri, N.; Corradi, M.; Kharitonov, S.A.; Barnes, P.J. Exhaled 8-isoprostane as an in vivo biomarker of lung oxidative stress in patients with COPD and healthy smokers. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 1175–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojoo, J.C.; Mulrennan, S.A.; Kastelik, J.A.; Morice, A.H.; Redington, A.E. Exhaled breath condensate pH and exhaled nitric oxide in allergic asthma and in cystic fibrosis. Thorax 2005, 60, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaughan, J.; Ngamtrakulpanit, L.; Pajewski, T.N.; Turner, R.; Nguyen, T.A.; Smith, A.; Urban, P.; Hom, S.; Gaston, B.; Hunt, J. Exhaled breath condensate pH is a robust and reproducible assay of airway acidity. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walsh, B.K.; Davis, M.D.; Hunt, J.F.; Kheir, J.N.; Smallwood, C.D.; Arnold, J.H. The effects of lung recruitment maneuvers on exhaled breath condensate pH. J. Breath Res. 2015, 9, 036009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullmann, T.; Barta, I.; Csiszé, E.; Antus, B.; Horváth, I. Differential cytokine pattern in the exhaled breath of patients with lung cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2008, 14, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Sánchez, L.M.; Jurado-Gámez, B.; Feu-Collado, N.; Valverde, A.; Cañas, A.; Fernández-Rueda, J.L.; Aranda, E.; Rodríguez-Ariza, A. Exhaled breath condensate biomarkers for the early diagnosis of lung cancer using proteomics. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L664–L676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fedorchenko, K.Y.; Ryabokon, A.M.; Kononikhin, A.S.; Mitrofanov, S.I.; Barmin, V.V.; Pikina, O.V.; Anafiev, E.K.; Gaciok, I.V.; Popov, I.A.; Nikolaev, E.N.; et al. Early diagnostics of lung cancer based on analysis of protom of exhausted breath condensate. Moscow Univ. Bull. 2016, 57, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Homberg, M.; Magin, T.M. Beyond Expectations: Novel Insights into Epidermal Keratin Function and Regulation, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 311, pp. 265–306. [Google Scholar]
- Lee Motoyama, J.P.; Kim-Motoyama, H.; Kim, P.; Nakagama, H.; Miyagawa, K.; Suzuki, K. Identification of dermcidin in human gestational tissue and characterization of its proteolytic activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, V.K. Microbiological status of cosmonauts during orbital spaceflights on Salyut and Mir orbital stations. Acta Astronaut. 2005, 56, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, V.K.; Solovieva, Z.O.; Skedina, M.A.; Papp, L.G. Evaluation of the effectiveness of automated analysis of the state of microflora of testers in conditions of 7 daily “dry” immersion. Aviakosm Ekol. Med. 2011, 45, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyin, V.K.; Shumilina, G.A.; Soloviev, Z.O.; Nosovsky, A.M.; Kaminskaya, E.V. Some indicators of the condition of the oral cavity and teeth of the cosmonauts during flights at the international space station. Aviakosm Ekol. Med. 2016, 50, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, H.J.; Tabaksblat, L.M.; Enghild, J.J.; Dahl, R. Human skin keratins are the major proteins in exhaled breath condensate. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurova, V.S.; Anaev, E.C.; Kononikhin, A.S.; Fedorchenko, K.Y.; Popov, I.A.; Kalupov, T.L.; Bratanov, D.O.; Nikolaev, E.N.; Varfolomeev, S.D. Proteomics of exhaled breath: Methodological nuances and pitfalls. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononikhin, A.S.; Fedorchenko, K.Y.; Ryabokon, A.M.; Starodubtseva, N.L.; Popov, I.A.; Zavialova, M.G.; Anaev, E.C.; Chuchalin, A.G.; Varfolomeev, S.D.; Nikolaev, E.N. Proteomic analysis of exhaled breath condensate for diagnosis of pathologies of the respiratory system. Biomeditsinskaya Khimiya 2015, 61, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brzhozovskiy, A.G.; Kononikhin, A.S.; Pastushkova, L.C.; Larina, I.M.; Nikolaev, E.N. The Effects of Spaceflight Factors on the Human Plasma Proteome, Including Both Real Space Missions and Ground-Based Experiments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidi, E.M.; Lappas, A.S.; Tzortzi, A.S.; Behrakis, P.K. Exhaled Breath Condensate: Technical and Diagnostic Aspects. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 435160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizca, J.A.; Csordas, A.; Griss, J.; Lavidas, I.; Mayer, G.; Perez-riverol, Y.; Reisinger, F.; Ternent, T.; Xu, Q.; Wang, R.; et al. 2016 update of the PRIDE database and its related tools. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2016, 44, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Mering, C.; Huynen, M.; Jaeggi, D.; Schmidt, S.; Bork, P.; Snel, B. STRING: A database of predicted functional associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Protein IDs | Protein Names | Gene Names | Background | 1 Day After Landing | 7 Day After Landing | Peptides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P04264 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 | KRT1 | 17.6 ± 1.5 | 18.4 ± 0.3 | 17.8 ± 0.6 | 34 |
| P13645 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 | KRT10 | 16.2 ± 1.4 | 18.2 ± 0.4 | 16.1 ± 1.3 | 30 |
| P02533 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 | KRT14 | 15.4 ± 0.1 | 15.1 ± 1.4 | 14.5 ± 0.1 | 23 |
| P35908 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal | KRT2 | 16 ± 0.2 | 17 ± 0.4 | 15.4 ± 0.9 | 29 |
| P13647 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 5 | KRT5 | 14.1 ± 0.2 | 13.8 ± 1.1 | 13.6 ± 0.3 | 24 |
| P02538 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 6 | KRT6 | 14.1 ± 0.1 | 14.5 ± 1.5 | 13.1 ± 0 | 25 |
| P35527 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 | KRT9 | 17 ± 0 | 15.6 ± 1.2 | 16.5 ± 0.2 | 16 |
| Biotopes | Micro-Organisms | CFU |
|---|---|---|
| 45 days before spaceflight | ||
| Mouth | Enterobacterium sp. | 107 |
| Enterococcus sp. | 104 | |
| Dental plaque | Streptococcus sp. | 102 |
| Enterobacterium sp. | 105 | |
| Tongue | Enterobacterium sp | 103 |
| Streptococcus sp. | 102 | |
| Enterococcus sp. | 104 | |
| Cheek | Staphylococcus sp. | 104–105 |
| 1 day before spaceflight | ||
| Dental plaque | Staphylococcus sp. | 102 |
| Tongue | Enterococcus sp. | 106 |
| Cheek | Staphylococcus sp. | 104 |
| During the spaceflight | ||
| Mouth | Staphylococcus sp. | 102 |
| Dental plaque | Staphylococcus sp. | 103–107 |
| Tongue | Staphylococcus sp. | 102 |
| E.coli | 107 | |
| Cheek | Staphylococcus sp. | ~101 |
| Immediately after landing (R0) | ||
| Mouth | Enterococcus sp. | 101–106 |
| Staphylococcus sp. | 101 | |
| Dental plaque | Enterococcus sp. | 103–106 |
| Staphylococcus sp. | 103 | |
| Tongue | Staphylococcus sp. | 103 |
| Enterococcus sp. | 103 | |
| Cheek | Staphylococcus sp. | ~103 |
| 7 day after landing (R+7) | ||
| Mouth | Enterococcus sp. | 103–105 |
| S. Aureus | 104 Met S | |
| Dental plaque | Staphylococcus sp. | 101 |
| Enterococcus sp. | 105 | |
| Tongue | Enterococcus sp. | 105–108 |
| S. Aureus | 107 Met S. | |
| Cheek | Staphylococcus sp. | 101–106 |
| S. Aureus | 104 Met S | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kononikhin, A.S.; Brzhozovskiy, A.G.; Ryabokon, A.M.; Fedorchenko, K.; Zakharova, N.V.; Spasskii, A.I.; Popov, I.A.; Ilyin, V.K.; Solovyova, Z.O.; Pastushkova, L.K.; et al. Proteome Profiling of the Exhaled Breath Condensate after Long-Term Spaceflights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184518
Kononikhin AS, Brzhozovskiy AG, Ryabokon AM, Fedorchenko K, Zakharova NV, Spasskii AI, Popov IA, Ilyin VK, Solovyova ZO, Pastushkova LK, et al. Proteome Profiling of the Exhaled Breath Condensate after Long-Term Spaceflights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(18):4518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184518
Chicago/Turabian StyleKononikhin, Alexey S., Alexander G. Brzhozovskiy, Anna M. Ryabokon, Kristina Fedorchenko, Natalia V. Zakharova, Alexander I. Spasskii, Igor A. Popov, Vyacheslav K. Ilyin, Zoya O. Solovyova, Lyudmila Kh. Pastushkova, and et al. 2019. "Proteome Profiling of the Exhaled Breath Condensate after Long-Term Spaceflights" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 18: 4518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184518
APA StyleKononikhin, A. S., Brzhozovskiy, A. G., Ryabokon, A. M., Fedorchenko, K., Zakharova, N. V., Spasskii, A. I., Popov, I. A., Ilyin, V. K., Solovyova, Z. O., Pastushkova, L. K., Polyakov, A. V., Varfolomeev, S. D., Larina, I. M., & Nikolaev, E. N. (2019). Proteome Profiling of the Exhaled Breath Condensate after Long-Term Spaceflights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(18), 4518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20184518