Mitotic Catastrophe Induced in HeLa Tumor Cells by Photodynamic Therapy with Methyl-aminolevulinate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cell Toxicity
2.2. Subcellular Localization and Production of PpIX
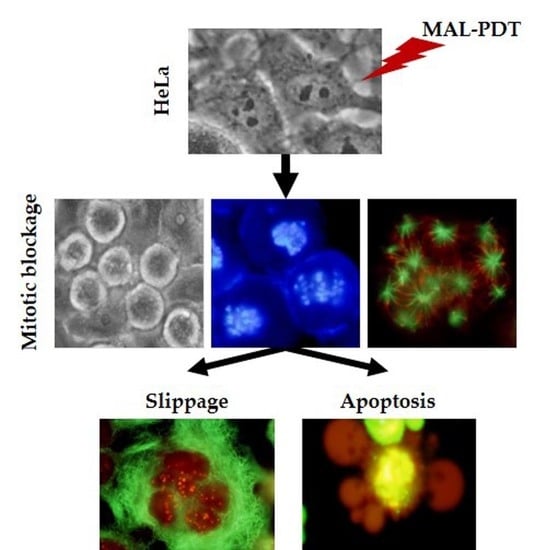
2.3. Alterations in Cellular and Nuclear Morphology Triggered by PDT
2.4. MAL-PDT Induces Microtubule Alterations in the HeLa Line
2.5. Localization and Expression of Proteins Involved in Cell Division after MAL-PDT
2.6. Mechanism of Cell Death
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Reagents and Antibodies
4.3. Treatments
4.4. Cellular Toxicity
4.5. Morphological Studies
4.6. Subcellular Localization of MAL
4.7. Determination of Intracellular Synthesis of PpIX
4.8. Cell Cycle Evaluation
4.9. Immunostaining
4.10. Western Blots
4.11. Optical Microscopy
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALA | 5-aminolevulinic acid |
| AO | Acridine Orange |
| AURK A | Aurora kinase A |
| AURK B | Aurora kinase B |
| EB | Ethidium Bromide |
| IF | Immunofluorescence |
| MAL | Methyl-aminolevulinate |
| MC | Mitotic Catastrophe |
| MTs | Microtubules |
| Nc | Nocodazole |
| PDT | Photodynamic Therapy |
| PpIX | Protoporphyrin IX |
| PS | Photosensitizer |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| Tx | Taxol |
| WB | Western Blot |
References
- Megna, M.; Fabbrocini, G.; Marasca, C.; Monfrecola, G. Photodynamic Therapy and Skin Appendage Disorders: A Review. Skin Appendage Disord. 2017, 2, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, R.; Lee, J.; Yang, S.G. Clinical development of photodynamic agents and therapeutic applications. Biomater. Res. 2018, 22, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgkinson, N.; Kruger, C.A.; Abrahamse, H. Targeted photodynamic therapy as potential treatment modality for the eradication of colon cancer and colon cancer stem cells. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, D.K.; Lee, P.K. Photodynamic Therapy for Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers. Cancers 2016, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.R.; Lau, R.W.H.; Ng, C.S.H. Catheter-based alternative treatment for early-stage lung cancer with a high-risk for morbidity. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S1864–S1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Straten, D.; Mashayekhi, V.; de Bruijn, H.S.; Oliveira, S.; Robinson, D.J. Oncologic Photodynamic Therapy: Basic Principles, Current Clinical Status and Future Directions. Cancers 2017, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamse, H.; Hamblin, M.R. New photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fonda-Pascual, P.; Moreno-Arrones, O.M.; Alegre-Sanchez, A.; Saceda-Corralo, D.; Buendia-Castaño, D.; Pindado-Ortega, C.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, P.; Velazquez-Kennedy, K.; Calvo-Sánchez, M.I.; Harto-Castaño, A.; et al. In situ production of ROS in the skin by photodynamic therapy as a powerful tool in clinical dermatology. Methods 2016, 109, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, C.; Dubec, M.; Donne, K.; Bashford, T. Effect of wavelength and beam width on penetration in light-tissue interaction using computational methods. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Zheng, H.; Chan, M.T.V.; Wu, W.K.K. Immune consequences induced by photodynamic therapy in non-melanoma skin cancers: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 20569–20574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, C.; Longo, J.P.F.; Azevedo, R.B.; Zhang, H.; Muehlmann, L.A. An updated overview on the development of new photosensitizers for anticancer photodynamic therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B. 2018, 8, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, C.; Kruger, C.A.; Abrahamse, H. Photodynamic Therapy for Metastatic Melanoma Treatment: A Review. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, C.A.; Hawkins, D.; Abrahamse, H. Photodynamic therapy (PDT): A short review on cellular mechanisms and cancer research applications for PDT. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2009, 96, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.R.; Neves, M.G.; Tomé, A.C.; Iglesias-de la Cruz, M.C.; Zamarrón, A.; Carrasco, E.; González, S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Torres, T.; Guldi, D.M.; et al. Glycophthalocyanines as photosensitizers for triggering mitotic catastrophe and apoptosis in cancer cells. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mroz, P.; Yaroslavsky, A.; Kharkwal, G.B.; Hamblin, M.R. Cell death pathways in photodynamic therapy of cancer. Cancers 2011, 3, 2516–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghe, T.V.; Linkermann, A.; Jouan-Lanhouet, S.; Walczak, H.; Vandenabeele, P. Regulated necrosis: The expanding network of nonapoptotic cell death pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrahamse, H.; Tynga, I.S.M. Photodynamic Therapy, a Potential Therapy for Improve Cancer Management. In Breast Cancer and Surgery, 1st ed.; Bulut, N., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; Chapter 10; pp. 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Yang, L.; Shi, H.; Du, W.; Qi, Y.; Qiu, C.; Liang, X.; Shi, W.; Liu, J. Endoplasmic reticulum-targeting photosensitizer Hypericin confers chemo-sensitization towards oxaliplatin through inducing pro-death autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 87, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessel, D. Apoptosis, Paraptosis and Autophagy: Death and Survival Pathways Associated with Photodynamic Therapy. Photochem. Photobiol. 2018, 95, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, M.S.; Zong, W.X. Chemotherapeutic approaches for targeting cell death pathways. Oncologist 2006, 11, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juarranz, A.; Espada, J.; Stockert, J.C.; Villanueva, A.; Polo, S.; Domínguez, V.; Cañete, M. Photodamage Induced by Zinc (II)-phthalocyanine to Microtubules, Actin, α-Actinin and Keratin of HeLa Cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 2001, 73, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenklová, V. Photodynamic therapy with TMPyP—Porphyrine induces mitotic catastrophe and microtubule disorganization in HeLa and G361 cells, a comprehensive view of the action of the photosensitizer. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 173, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, F.; Braig, S.; Moser, C.; Kubisch, R.; Busse, J.; Wagner, E.; Schmoeckel, E.; Mayr, D.; Schmitt, S.; Huettel, S.; et al. Targeting the actin cytoskeleton: Selective antitumor action via trapping PKCε. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, M.A.; Toso, R.J.; Thrower, D.; Wilson, L. Mechanism of mitotic block and inhibition of cell proliferation by taxol at low concentraions. PNAS 1993, 90, 9552–9556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.H.; Seemann, J. Nakiterpiosin targets tubulin and triggers mitotic catastrophe in human cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 3375–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello-Varona, S.; Stockert, J.C.; Cañete, M.; Acedo, P.; Villanueva, Á. Mitotic catastrophe induced in HeLa cells by photodynamic treatment with Zn (II)-phthalocyanine. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rello, S.; Stockert, J.C.; Moreno, V.; Gamez, A.; Pacheco, M.; Juarranz, A.; Cañete, M.; Villanueva, A. Morphological criteria to distinguish cell death induced by apoptotic and necrotic treatments. Apoptosis 2005, 10, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavallaris, M. Microtubules and resistance to tubulin-binding agents. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, M.A.; Wilson, L. Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicenas, J. The Aurora kinase inhibitors in cancer research and therapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 1995–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbaghi, M.; Gil-Gómez, G.; Guardia, C.; Servitja, S.; Arpi, O.; García-Alonso, S.; Menendez, S.; Arumi-Uria, M.; Serrano, L.; Salido, M.; et al. Defective cyclin B1 induction in trastuzumab-emtansine (T-DM1) acquired resistance in HER2-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 7006–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castedo, M.; Perfettini, J.L.; Roumier, T.; Andreau, K.; Medema, R.; Kroemer, G. Cell death by mitotic catastrophe: A molecular definition. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2825–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Li, Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Photodynamic therapy in dermatology beyond non-melanoma cancer: An update. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2017, 19, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyrrell, J.; Paterson, C.; Curnow, A. Regression Analysis of Protoporphyrin IX Measurements Obtained During Dermatological Photodynamic Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, L.L.; Lear, J.T. Photodynamic Therapy and Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. Cancers 2016, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Bernier, M.; Rodríguez-Barón, D.; Ruiz, F.R.; Segura-Palacios, J.M.; Martín, M.T. Long-term efficacy of photodynamic therapy with methyl aminolevulinate in treating Bowen’s disease in clinical practice: A retrospective cohort study (2006-2017). Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Yang, G.; Vasovic, V.; Cunderlikova, B.; Suo, Z.; Nesland, J.M.; Peng, Q. Subcellular localization pattern of protoporphyrin IX is an important determinant for its photodynamic efficiency of human carcinoma and normal cell lines. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2006, 84, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Huang, Z.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Zeng, H. Kinetics and subcellular localization of 5-ALA-induced PpIX in DHL cells via two-photon excitation fluorescence microscopy. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.H.; Chung, C.W.; Choi, K.H.; Yoo, J.J.; Kim, D.H.; Jeong, Y.I.; Kang, D.H. Effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid-based photodynamic therapy via reactive oxygen species in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1357–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenpreisa, J.; Cragg, M.S. Mitotic death: A mechanism of survival. Cancer Cell Int. 2001, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagosklonny, M.V. Mitotic arrest and cell fate: Why and how mitotic inhibition of transcription drives mutually exclusive events. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forer, A.; Sheykhani, R.; Berns, M.W. Anaphase Chromosomes in Crane-Fly Spermatocytes Treated with Taxol (Paclitaxel) Accelerate When Their Kinetochore Microtubules Are Cut: Evidence for Spindle Matrix Involvement With Spindle Forces. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovinazzi, S.; Bellapu, D.; Morozov, V.M.; Ishov, A.M. Targeting mitotic exit with hyperthermia or APC/C inhibition to increase paclitaxel efficacy. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 2598–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chumduri, C.; Gillissen, B.; Richter, A.; Richter, A.; Milojkovic, A.; Overkamp, T.; Müller, A.; Pott, C.; Daniel, P.T. Apoptosis resistance, mitotic catastrophe, and loss of ploidy control in Burkitt lymphoma. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikonova, A.S.; Astsaturov, I.; Serebriiskii, I.G.; Dunbrack, R.L.; Golemis, E.A. Aurora A kinase (AURKA) in normal and pathological cell division. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 661–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmena, M.; Earnshaw, W.C. The cellular geography of aurora kinases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannu, V.; Rida, P.C.G.; Ogden, A.; Clewley, R.; Cheng, A.; Karna, P.; Lopus, M.; Mishra, R.C.; Zhou, J.; Aneja, R. Induction of robust de novo centrosome amplification, high-grade spindle multipolarity and metaphase catastrophe: A novel chemotherapeutic approach. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.J.; Fukui, M.; Zhu, B.T. Role of cyclin B1/Cdc2 up-regulation in the development of mitotic prometaphase arrest in human breast cancer cells treated with nocodazole. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgoulis, A.; Vorgias, C.; Chrousos, G.; Rogakou, E. Genome instability and γH2AX. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, L.; Read, S.H.; Dorstyn, L.; Lambrusco, L.; Kumar, S. Caspase-2 is required for cell death induced by cytoskeletal disruption. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3393–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castedo, M.; Perfettini, J.L.; Roumier, T.; Valent, A.; Raslova, H.; Yakushijin, K.; Horne, D.; Feunteun, J.; Lenoir, G.; Medema, R.; et al. Mitotic catastrophe constitutes a special case of apoptosis whose suppression entails aneuploidy. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4362–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmider, B.; Zyner, E.; Osiecka, R.; Ochocki, J. Induction of apoptosis and necrosis in A549 cells by the cis-Pt (II) complex of 3-aminoflavone in comparison with cis-DDP. Mutat. Res. 2004, 563, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| MAL Concentration (mM) | Light Dose (J/cm2) | HeLa | HaCaT |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | 98.9 ± 1.10 | 100 ± 1.95 |
| 0.3 | - | 97.4 ± 2.30 | 104 ± 0.01 |
| 1 | - | 104 ± 5.17 | 96.88 ± 8.16 |
| - | 6.75 | 99.4 ± 1.30 | 101.69 ± 3.68 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mascaraque, M.; Delgado-Wicke, P.; Damian, A.; Lucena, S.R.; Carrasco, E.; Juarranz, Á. Mitotic Catastrophe Induced in HeLa Tumor Cells by Photodynamic Therapy with Methyl-aminolevulinate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051229
Mascaraque M, Delgado-Wicke P, Damian A, Lucena SR, Carrasco E, Juarranz Á. Mitotic Catastrophe Induced in HeLa Tumor Cells by Photodynamic Therapy with Methyl-aminolevulinate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051229
Chicago/Turabian StyleMascaraque, Marta, Pablo Delgado-Wicke, Alejandra Damian, Silvia Rocío Lucena, Elisa Carrasco, and Ángeles Juarranz. 2019. "Mitotic Catastrophe Induced in HeLa Tumor Cells by Photodynamic Therapy with Methyl-aminolevulinate" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051229
APA StyleMascaraque, M., Delgado-Wicke, P., Damian, A., Lucena, S. R., Carrasco, E., & Juarranz, Á. (2019). Mitotic Catastrophe Induced in HeLa Tumor Cells by Photodynamic Therapy with Methyl-aminolevulinate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051229