Pharmacological Modulation of Steroid Activity in Hormone-Dependent Breast and Prostate Cancers: Effect of Some Plant Extract Derivatives
Abstract
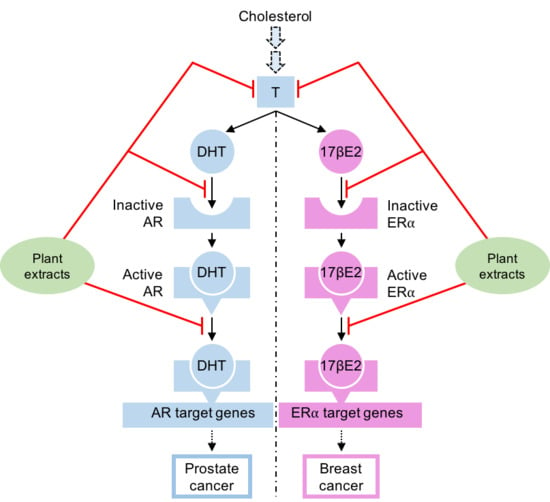
:1. Introduction
2. PCa and BCa, Two Hormone-Dependent Cancers
3. The Activity of Androgens and Estrogens
4. Pharmacological Treatments of BCa and PCa
4.1. Modulation of the Enzymes Involved in 17βE2 and DHT Synthesis
4.2. Antagonists of ERα and AR Transcriptional Activities
4.3. Antagonists of the Steroid Receptors and Inducers of Their Degradation
5. Natural Compounds Modulating the Steroid Activity
5.1. Natural Compounds Inhibiting the Steroid Synthesis
5.2. Natural Compounds Acting as AR or ERα Antagonists
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Δ4 | Δ4-androstenedion |
| 5⍺R | 5⍺-reductase |
| 17βE2 | estradiol |
| 17βHSD | 17β-hydroxy-steroid dehydrogenase |
| AR | androgen receptor |
| BCa | breast cancer |
| E1 | estrone |
| ER⍺ | estrogen receptor ⍺ |
| PCa | prostate cancer |
| SARM | specific androgen receptor modulator |
| SARD | specific androgen receptor degrader/down-regulator |
| SERM | specific estrogen receptor modulator |
| SERD | specific estrogen receptor degrader/down-regulator |
| T | testosterone |
References
- Lordan, R.; Tsoupras, A.; Zabetakis, I. The Potential Role of Dietary Platelet-Activating Factor Inhibitors in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Adv. Nutr. Bethesda Md 2019, 10, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gandellini, P.; Andriani, F.; Merlino, G.; D’Aiuto, F.; Roz, L.; Callari, M. Complexity in the tumour microenvironment: Cancer associated fibroblast gene expression patterns identify both common and unique features of tumour-stroma crosstalk across cancer types. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Amicis, F.; Chimento, A.; Montalto, F.I.; Casaburi, I.; Sirianni, R.; Pezzi, V. Steroid Receptor Signallings as Targets for Resveratrol Actions in Breast and Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, W.; Elemento, O. Cancer systems biology: Embracing complexity to develop better anticancer therapeutic strategies. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godzieba, M.; Ciesielski, S. Natural DNA Intercalators as Promising Therapeutics for Cancer and Infectious Diseases. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.; Rasul, A.; Sarfraz, A.; Sarfraz, I.; Hussain, G.; Anwar, H.; Riaz, A.; Liu, S.; Wei, W.; Li, J.; et al. Salvianolic acid A & B: Potential cytotoxic polyphenols in battle against cancer via targeting multiple signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2256–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hajjaji, F.-Z.; Oumeddour, A.; Pommier, A.J.C.; Ouvrier, A.; Viennois, E.; Dufour, J.; Caira, F.; Drevet, J.R.; Volle, D.H.; Baron, S.; et al. Liver X receptors, lipids and their reproductive secrets in the male. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, T.; Fujita, K.; Matsushita, M.; Nonomura, N. Main Inflammatory cells and potentials of anti-inflammatory agents in prostate cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsogiannou, M.; Ziouziou, H.; Karaki, S.; Andrieu, C.; de Villeneuve, M.H.; Rocchi, P. The hallmarks of castration-resistant prostate cancers. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitland, N.J.; Frame, F.M.; Rane, J.K.; Erb, H.H.; Packer, J.R.; Archer, L.K.; Pellacani, D. Resolution of cellular heterogeneity in human prostate cancers: Implications for diagnosis and treatment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1164, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, S.; Gagliano, N.; Procacci, P.; Sartori, P.; Comar, M.; Provenzano, M.; Favi, E.; Ferraresso, M.; Ferrante, P.; Delbue, S. Characterization of an in vitro model to study the possible role of polyomavirus BK in prostate cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 11912–11922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rapisarda, V.; Miozzi, E.; Loreto, C.; Matera, S.; Fenga, C.; Avola, R.; Ledda, C. Cadmium exposure and prostate cancer: Insights, mechanisms and perspectives. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 2018, 23, 1687–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viner, B.; Barberio, A.M.; Haig, T.R.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Brenner, D.R. The individual and combined effects of alcohol consumption and cigarette smoking on site-specific cancer risk in a prospective cohort of 26,607 adults: Results from Alberta’s Tomorrow Project. Cancer Causes Control 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousset, L.; Rambur, A.; Fouache, A.; Bunay, J.; Morel, L.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.A.; Baron, S.; Trousson, A.; de Joussineau, C. New Insights in Prostate Cancer Development and Tumor Therapy: Modulation of Nuclear Receptors and the Specific Role of Liver X Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweeney, C.J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Carducci, M.; Liu, G.; Jarrard, D.F.; Eisenberger, M.; Wong, Y.-N.; Hahn, N.; Kohli, M.; Cooney, M.M.; et al. Chemohormonal Therapy in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornford, P.; Bellmunt, J.; Bolla, M.; Briers, E.; De Santis, M.; Gross, T.; Henry, A.M.; Joniau, S.; Lam, T.B.; Mason, M.D.; et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II: Treatment of relapsing, metastatic, and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuller, L.H. The etiology of breast cancer--from epidemiology to prevention. Public Health Rev. 1995, 23, 157–213. [Google Scholar]
- Dugué, P.-A.; Dowty, J.G.; Joo, J.E.; Wong, E.M.; Makalic, E.; Schmidt, D.F.; English, D.R.; Hopper, J.L.; Pedersen, J.; Severi, G.; et al. Heritable methylation marks associated with breast and prostate cancer risk. Prostate 2018, 78, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, N.L. Genetic factors in the etiology of breast cancer. Cancer 1977, 39, 2709–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, N.W.; Yang, L.; Muti, P.; Meza, J.L.; Pruthi, S.; Ingle, J.N.; Rogan, E.G.; Cavalieri, E.L. The molecular etiology of breast cancer: Evidence from biomarkers of risk. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giovannelli, P.; Di Donato, M.; Galasso, G.; Di Zazzo, E.; Medici, N.; Bilancio, A.; Migliaccio, A.; Castoria, G. Breast cancer stem cells: The role of sex steroid receptors. World J. Stem Cells 2019, 11, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiderlen, M.; Ponti, A.; Tomatis, M.; Boelens, P.G.; Bastiaannet, E.; Wilson, R.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Audisio, R.A. eusomaDB Working Group Variations in compliance to quality indicators by age for 41,871 breast cancer patients across Europe: A European Society of Breast Cancer Specialists database analysis. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 1990 2015, 51, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbeck, N.; Gnant, M. Breast cancer. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2017, 389, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.; Costa, A.; Norton, L.; Senkus, E.; Aapro, M.; André, F.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; Biganzoli, L.; Blackwell, K.L.; et al. ESO-ESMO 2nd international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC2). Breast Edinb. Scotl. 2014, 23, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in health and disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Nuclear receptors, RXR, and the big bang. Cell 2014, 157, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, S.; Nishimura, K.-I.; Ochi, M.; Shimmura, H.; Mori, J.-I. Bone and calcium metabolism associated with malignancy. The function of sex hormone receptors in sex hormone-dependent cancers. Clin. Calcium 2018, 28, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, P.S.; Clegg, N.; Arnold, H.; Ferguson, C.; Bonham, M.; White, J.; Hood, L.; Lin, B. The program of androgen-responsive genes in neoplastic prostate epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11890–11895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majumdar, S.; Rinaldi, J.C.; Malhotra, N.R.; Xie, L.; Hu, D.-P.; Gauntner, T.D.; Grewal, H.S.; Hu, W.-Y.; Kim, S.H.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; et al. Differential actions of estrogen receptor α and β via Nongenomic signaling in human prostate stem and progenitor cells. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2692–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prins, G.S.; Hu, W.-Y.; Shi, G.-B.; Hu, D.-P.; Majumdar, S.; Li, G.; Huang, K.; Nelles, J.L.; Ho, S.-M.; Walker, C.L.; et al. Bisphenol A promotes human prostate stem-progenitor cell self-renewal and increases in vivo carcinogenesis in human prostate epithelium. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.G.; Dickler, M.N. Endocrine resistance in hormone-responsive breast cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, R337–R352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brufsky, A.M.; Dickler, M.N. Estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: Exploiting signaling pathways implicated in endocrine resistance. Oncologist 2018, 23, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siersbæk, R.; Kumar, S.; Carroll, J.S. Signaling pathways and steroid receptors modulating estrogen receptor α function in breast cancer. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Proverbs-Singh, T.; Feldman, J.L.; Morris, M.J.; Autio, K.A.; Traina, T.A. Targeting the androgen receptor in prostate and breast cancer: Several new agents in development. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, R87–R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jernberg, E.; Bergh, A.; Wikström, P. Clinical relevance of androgen receptor alterations in prostate cancer. Endocr. Connect. 2017, 6, R146–R161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piccolella, M.; Crippa, V.; Messi, E.; Tetel, M.J.; Poletti, A. Modulators of estrogen receptor inhibit proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 79, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Verma, V.; Jain, A.; Jain, R.K.; Maikhuri, J.P.; Gupta, G. Synergistic chemoprotective mechanisms of dietary phytoestrogens in a select combination against prostate cancer. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culig, Z.; Hoffmann, J.; Erdel, M.; Eder, I.E.; Hobisch, A.; Hittmair, A.; Bartsch, G.; Utermann, G.; Schneider, M.R.; Parczyk, K.; et al. Switch from antagonist to agonist of the androgen receptor bicalutamide is associated with prostate tumour progression in a new model system. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 81, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherbakov, A.M.; Komkov, A.V.; Komendantova, A.S.; Yastrebova, M.A.; Andreeva, O.E.; Shirinian, V.Z.; Hajra, A.; Zavarzin, I.V.; Volkova, Y.A. Steroidal pyrimidines and dihydrotriazines as novel classes of anticancer agents against hormone-dependent breast cancer cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brueggemeier, R.W.; O’Reilly, J.M.; Lovely, C.J.; Ward, P.J.; Quinn, A.L.; Baker, D.; Darby, M.V.; Gu, X.J.; Gilbert, N.E. Biochemistry and pharmacology of 7alpha-substituted androstenediones as aromatase inhibitors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 61, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, A.; Njar, V.; Macedo, L.F.; Vasaitis, T.S.; Sabnis, G. The Coffey Lecture: Steroidogenic enzyme inhibitors and hormone dependent cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2009, 27, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cos, S.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Mediavilla, M.D.; Sánchez-Barceló, E.J. Melatonin modulates aromatase activity in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 38, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan-Sezer, S.; Ince, E.; Akdemir, A.; Ceylan, Ö.Ö.; Suzen, S.; Gurer-Orhan, H. Aromatase inhibition by 2-methyl indole hydrazone derivatives evaluated via molecular docking and in vitro activity studies. Xenobiotica Fate Foreign Compd. Biol. Syst. 2019, 49, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudici, D.; Ornati, G.; Briatico, G.; Buzzetti, F.; Lombardi, P.; di Salle, E. 6-Methylenandrosta-1,4-diene-3,17-dione (FCE 24304): A new irreversible aromatase inhibitor. J. Steroid Biochem. 1988, 30, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, O.; Regan, M.M.; Walley, B.A.; Fleming, G.F.; Colleoni, M.; Láng, I.; Gomez, H.L.; Tondini, C.; Burstein, H.J.; Perez, E.A.; et al. Adjuvant exemestane with ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plourde, P.V.; Dyroff, M.; Dukes, M. Arimidex: A potent and selective fourth-generation aromatase inhibitor. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1994, 30, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Placido, S.; Gallo, C.; De Laurentiis, M.; Bisagni, G.; Arpino, G.; Sarobba, M.G.; Riccardi, F.; Russo, A.; Del Mastro, L.; Cogoni, A.A.; et al. Adjuvant anastrozole versus exemestane versus letrozole, upfront or after 2 years of tamoxifen, in endocrine-sensitive breast cancer (FATA-GIM3): A randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, T.V.; Amaral, C.; Varela, C.L.; Bernardo, F.; da Silva, E.T.; Roleira, F.F.M.; Costa, S.; Teixeira, N.; Correia-da-Silva, G. Effects of new C6-substituted steroidal aromatase inhibitors in hormone-sensitive breast cancer cells: Cell death mechanisms and modulation of estrogen and androgen receptors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 195, 105486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, C.; Varela, C.L.; Maurício, J.; Sobral, A.F.; Costa, S.C.; Roleira, F.M.F.; Tavares-da-Silva, E.J.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Teixeira, N. Anti-tumor efficacy of new 7α-substituted androstanes as aromatase inhibitors in hormone-sensitive and resistant breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 171, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, C.; Varela, C.; Azevedo, M.; da Silva, E.T.; Roleira, F.M.F.; Chen, S.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Teixeira, N. Effects of steroidal aromatase inhibitors on sensitive and resistant breast cancer cells: Aromatase inhibition and autophagy. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 135, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepa, M.; Correia-da-Silva, G.; Tavares da Silva, E.J.; Roleira, F.M.F.; Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Teixeira, N.A. Molecular mechanisms of aromatase inhibition by new A, D-ring modified steroids. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudduth, S.L.; Koronkowski, M.J. Finasteride: The first 5 alpha-reductase inhibitor. Pharmacotherapy 1993, 13, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andriole, G.L.; Bostwick, D.G.; Brawley, O.W.; Gomella, L.G.; Marberger, M.; Montorsi, F.; Pettaway, C.A.; Tammela, T.L.; Teloken, C.; Tindall, D.J.; et al. Effect of dutasteride on the risk of prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azuma, T.; Matayoshi, Y.; Sato, Y.; Nagase, Y. Effect of dutasteride on castration-resistant prostate cancer. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 8, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hirshburg, J.M.; Kelsey, P.A.; Therrien, C.A.; Gavino, A.C.; Reichenberg, J.S. Adverse effects and safety of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (Finasteride, Dutasteride): A systematic review. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2016, 9, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Vihko, P.; Härkönen, P.; Oduwole, O.; Törn, S.; Kurkela, R.; Porvari, K.; Pulkka, A.; Isomaa, V. 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases and cancers. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 83, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, E.; Stål, O.; Jansson, A. Estrogen and androgen-converting enzymes 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and their involvement in cancer: With a special focus on 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, 2, and breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30552–30562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrie, S.E.; Potter, G.A.; Goddard, P.M.; Haynes, B.P.; Dowsett, M.; Jarman, M. Pharmacology of novel steroidal inhibitors of cytochrome P450(17) alpha (17 alpha-hydroxylase/C17-20 lyase). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1994, 50, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, C.J.; Smith, M.R.; de Bono, J.S.; Molina, A.; Logothetis, C.J.; de Souza, P.; Fizazi, K.; Mainwaring, P.; Piulats, J.M.; Ng, S.; et al. Abiraterone in metastatic prostate cancer without previous chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, M.P.; Jones, C.T.; Todd, I.D. A new anti-oestrogenic agent in late breast cancer. An early clinical appraisal of ICI46474. Br. J. Cancer 1971, 25, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-I.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, J.; Heo, J.; Lee, N.-R.; Kim, N.-J.; Inn, K.-S. NJK14013, a novel synthetic estrogen receptor-α agonist, exhibits estrogen receptor-independent, tumor cell-specific cytotoxicity. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ball, S.; Arevalo, M.; Juarez, E.; Payne, J.D.; Jones, C. Breast cancer chemoprevention: An update on current practice and opportunities for primary care physicians. Prev. Med. 2019, 129, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsen, C.; Van den Broeck, T.; Voet, A.; Prekovic, S.; Van Poppel, H.; Joniau, S.; Claessens, F. Androgen receptor antagonists for prostate cancer therapy. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, T105–T118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furr, B.J.; Valcaccia, B.; Curry, B.; Woodburn, J.R.; Chesterson, G.; Tucker, H. ICI 176,334: A novel non-steroidal, peripherally selective antiandrogen. J. Endocrinol. 1987, 113, R7–R9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peets, E.A.; Henson, M.F.; Neri, R. On the mechanism of the anti-androgenic action of flutamide (alpha-alpha-alpha-trifluoro-2-methyl-4′-nitro-m-propionotoluidide) in the rat. Endocrinology 1974, 94, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Séguin, C.; Cusan, L.; Bélanger, A.; Kelly, P.A.; Labrie, F.; Raynaud, J.P. Additive inhibitory effects of treatment with an LHRH agonist and an antiandrogen on androgen-dependent tissues in the rat. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1981, 21, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellhammer, P.; Sharifi, R.; Block, N.; Soloway, M.; Venner, P.; Patterson, A.L.; Sarosdy, M.; Vogelzang, N.; Jones, J.; Kolvenbag, G. Maximal androgen blockade for patients with metastatic prostate cancer: Outcome of a controlled trial of bicalutamide versus flutamide, each in combination with luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogue therapy. Casodex Combination Study Group. Urology 1996, 47, 54–60; discussion 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.; Ouk, S.; Clegg, N.J.; Chen, Y.; Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.; Wongvipat, J.; Smith-Jones, P.M.; Yoo, D.; Kwon, A.; et al. Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science 2009, 324, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rice, M.A.; Malhotra, S.V.; Stoyanova, T. Second-Generation Antiandrogens: From Discovery to Standard of Care in Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fizazi, K.; Massard, C.; Bono, P.; Jones, R.; Kataja, V.; James, N.; Garcia, J.A.; Protheroe, A.; Tammela, T.L.; Elliott, T.; et al. Activity and safety of ODM-201 in patients with progressive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (ARADES): An open-label phase 1 dose-escalation and randomised phase 2 dose expansion trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeling, A.E.; Dukes, M.; Bowler, J. A potent specific pure antiestrogen with clinical potential. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 3867–3873. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Osborne, C.K.; Wakeling, A.; Nicholson, R.I. Fulvestrant: An oestrogen receptor antagonist with a novel mechanism of action. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90 (Suppl. 1), S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardell, S.E.; Yllanes, A.P.; Chao, C.A.; Bae, Y.; Andreano, K.J.; Desautels, T.K.; Heetderks, K.A.; Blitzer, J.T.; Norris, J.D.; McDonnell, D.P. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of fulvestrant in preclinical models of breast cancer to assess the importance of its estrogen receptor-α degrader activity in antitumor efficacy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 179, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahtani, R.L. A role for fulvestrant monotherapy in the first-line treatment of ER+ metastatic breast cancer? Breast J. 2019, 26, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Chen, C.; Pai, P.; Korangath, P.; Sun, S.; Merino, V.F.; Yuan, J.; Li, S.; Nie, G.; Stearns, V.; et al. Intraductal fulvestrant for therapy of ERα-positive ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: A preclinical study. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burki, T.K. Fulvestrant plus anastrozole for metastatic breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Zhao, J.; Gutgesell, L.M.; Wang, Y.; Lee, S.; Karumudi, B.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Y.; Tonetti, D.A.; Thatcher, G.R.J. Novel selective estrogen receptor Downregulators (SERDs) developed against treatment-resistant breast cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1325–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Zhou, P.; Hu, M.; Yang, L.; Yan, G.; Xu, R.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, Y. Discovery and biological evaluation of darolutamide derivatives as inhibitors and down-regulators of wild-type AR and the mutants. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, Z. Screening of aromatase inhibitors in traditional Chinese medicines by electrophoretically mediated microanalysis in a partially filled capillary. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingaew, R.; Mandi, P.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Ruchirawat, S.; Prachayasittikul, V. Synthesis, molecular docking, and QSAR study of sulfonamide-based indoles as aromatase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pailee, P.; Prachyawarakorn, V.; Ruchirawat, S.; Mahidol, C. Bioactive cardinane sesquiterpenes from the stems of Alangium salviifolium. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahiaoui, S.; Fagnere, C.; Pouget, C.; Buxeraud, J.; Chulia, A.-J. New 7,8-benzoflavanones as potent aromatase inhibitors: Synthesis and biological evaluation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balunas, M.J.; Su, B.; Riswan, S.; Fong, H.H.S.; Brueggemeier, R.W.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Kinghorn, A.D. Isolation and Characterization of Aromatase Inhibitors from Brassaiopsis glomerulata (Araliaceae). Phytochem. Lett. 2009, 2, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, L.; Jiao, C.; Shao, R.; Qi, Y.; Fan, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, X. Bakuchiol suppresses oestrogen/testosterone-induced Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia development through up-regulation of epithelial estrogen receptor β and down-regulation of stromal aromatase. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 381, 114637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Jan, N.U.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, B.; Ali, A.; Samrana, S.; Jahan, A.; Ali, H.; Khan, I.A.; Rahim, H.; et al. Steroidal alkaloids efficient aromatase inhibitors with potential for the treatment of post-menopausal breast cancer. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.-S.; Li, P.-P. Shu-Gan-Liang-Xue decoction simultaneously down-regulates expressions of aromatase and steroid Sulfatase in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer Cells. Chin. J. Cancer Res. Chung Kuo Yen Cheng Yen Chiu 2011, 23, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, N.; Han, S.-Y.; Zhou, F.; Li, P. Anti-tumor effect of Shu-Gan-Liang-Xue decoction in breast cancer is related to the inhibition of aromatase and steroid sulfatase expression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chan, F.L.; Chen, S.; Leung, L.K. The plant polyphenol butein inhibits testosterone-induced proliferation in breast cancer cells expressing aromatase. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grube, B.J.; Eng, E.T.; Kao, Y.C.; Kwon, A.; Chen, S. White button mushroom phytochemicals inhibit aromatase activity and breast cancer cell proliferation. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 3288–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Patil, B.S. Obacunone exhibits anti-proliferative and anti-aromatase activity in vitro by inhibiting the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Biochimie 2014, 105, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultan, C.; Terraza, A.; Devillier, C.; Carilla, E.; Briley, M.; Loire, C.; Descomps, B. Inhibition of androgen metabolism and binding by a liposterolic extract of “Serenoa repens B” in human foreskin fibroblasts. J. Steroid Biochem. 1984, 20, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitalone, A.; Bordi, F.; Baldazzi, C.; Mazzanti, G.; Saso, L.; Tita, B. Anti-proliferative effect on a prostatic epithelial cell line (PZ-HPV-7) by Epilobium angustifolium L. Farm. Soc. Chim. Ital. 1989 2001, 56, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiipakka, R.A.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Dai, W.; Dai, Q.; Liao, S. Structure-activity relationships for inhibition of human 5alpha-reductases by polyphenols. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 63, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Heo, J.H.; Hwang, Y.J.; Le, T.T.; Lee, M.W. Inhibitory nst 5α-reductase associated with benign prostatic hypertrophy. Molecules 2016, 21, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, R.; Miao, L.; Yu, X.; Orgah, J.O.; Barnabas, O.; Chang, Y.; Liu, E.; Fan, G.; Gao, X. Cynomorium songaricum Rupr demonstrates phytoestrogenic or phytoandrogenic like activities that attenuates benign prostatic hyperplasia via regulating steroid 5-α-reductase. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivilai, J.; Minale, G.; Scholfield, C.N.; Ingkaninan, K. Discovery of natural steroid 5 alpha-reductase inhibitors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2019, 17, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirota, O.; Takizawa, K.; Sekita, S.; Satake, M.; Hirayama, Y.; Hakamata, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Yanagawa, T. Antiandrogenic natural Diels−alder-type adducts from Brosimum Rubescens. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.T.; Schaldach, C.M.; Firestone, G.L.; Bjeldanes, L.F. Plant-derived 3,3′-Diindolylmethane is a strong androgen antagonist in human prostate cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21136–21145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Du, X.; Yang, R.; Liu, J.; Xu, D.; Shi, J.; Chen, L.; Shao, R.; Fan, G.; Gao, X.; et al. The prevention and treatment effects of tanshinone IIA on oestrogen/androgen-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 145, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabaiou, N.; Fouache, A.; Trousson, A.; Buñay-Noboa, J.; Marceau, G.; Sapin, V.; Zellagui, A.; Baron, S.; Lahouel, M.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.A. Ethanolic extract of Algerian propolis decreases androgen receptor transcriptional activity in cultured LNCaP cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 189, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Zou, J.; Diao, Y.; Xiao, W.; Shan, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. Discovery of natural estrogen receptor modulators with structure-based virtual screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3329–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahlensieck, W.; Fabricius, P.G.; Hell, U. Drug therapy of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Fortschr. Med. 1996, 114, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Wang, D.; Sun, B.; Safoor, A.; Young, C.Y.F.; Lou, H.; Yuan, H. Bisbibenzyls, novel proteasome inhibitors, suppress androgen receptor transcriptional activity and expression accompanied by activation of autophagy in prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zava, D.T.; Blen, M.; Duwe, G. Estrogenic activity of natural and synthetic estrogens in human breast cancer cells in culture. Environ. Health Perspect. 1997, 105 (Suppl. 3), 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adjakly, M.; Ngollo, M.; Dagdemir, A.; Judes, G.; Pajon, A.; Karsli-Ceppioglu, S.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Boiteux, J.-P.; Bignon, Y.-J.; Guy, L.; et al. Prostate cancer: The main risk and protective factors-Epigenetic modifications. Ann. Endocrinol. 2015, 76, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, C.N.; Setzer, W.N. A molecular docking study of phytochemical estrogen mimics from dietary herbal supplements. Silico Pharmacol. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishiguro, T.; Ohata, H.; Sato, A.; Yamawaki, K.; Enomoto, T.; Okamoto, K. Tumor-derived spheroids: Relevance to cancer stem cells and clinical applications. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambur, A.; Lours-Calet, C.; Beaudoin, C.; Buñay, J.; Vialat, M.; Mirouse, V.; Trousson, A.; Renaud, Y.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.; Baron, S.; et al. Sequential Ras/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways recruitment drives basal extrusion in the prostate-like gland of Drosophila. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Pharmacological Targets | Synthetic Compounds | Natural Compounds |
|---|---|---|
| Aromatase | Exemestane [45] Anastrozole [47] 7α-substituted steroids [50]. Δ4-androstenedione derivatives [51]. | Melatonin [44] Naringin, apigenin, berberine, palmatine, bavachin, jatrorrhizine, bavachinin [80] Alangenes [82] Extracts of Brassaiopsis glomerulata [84] Bakuchiol [85] Extracts of Sarcococca saligna [86] Shu-Gan-Liang-Xue decoction [87,88] Aqueous extracts of white button mushrooms [90] Butein [89] Obacunone [91] |
| 5α-reductase | Finasteride [53] Dutasteride [54] | Serenoa repens extracts [92] Ethanolic extracts of Epilobium angustifolium [93] (−)-epigallocatechin gallate, biochanin A, daidzein, genistein, kaempferol [94] caffeic acid, grandifloroside [95] polyphenols from Cynomorium songaricum [96] |
| Androgen receptor (SARM) | Bicalutamide [65] Enzalutamide [69] Darolutamide [71] | Methanolic extract of Brosimum rubescens bark [98] 3,3′-diindolylmethane [99] |
| Androgen receptor (SARD) | Darolutamide derivatives [79] | Tanshinone IIA [100] Ethanolic extracts from propolis [101] |
| Estrogen receptor (SERM) | Tamoxifen [61] Raloxifene [62] | Extracts of Schisandra glaucescens [102] Extracts of Urtica dioica [103] |
| Estrogen receptor (SERD) | Fulvestrant [72] 6-OH benzothiophene [78] | Tanshinone IIA [100] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayala, B.; Zoure, A.A.; Baron, S.; de Joussineau, C.; Simpore, J.; Lobaccaro, J.-M.A. Pharmacological Modulation of Steroid Activity in Hormone-Dependent Breast and Prostate Cancers: Effect of Some Plant Extract Derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103690
Bayala B, Zoure AA, Baron S, de Joussineau C, Simpore J, Lobaccaro J-MA. Pharmacological Modulation of Steroid Activity in Hormone-Dependent Breast and Prostate Cancers: Effect of Some Plant Extract Derivatives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103690
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayala, Bagora, Abdou Azaque Zoure, Silvère Baron, Cyrille de Joussineau, Jacques Simpore, and Jean-Marc A. Lobaccaro. 2020. "Pharmacological Modulation of Steroid Activity in Hormone-Dependent Breast and Prostate Cancers: Effect of Some Plant Extract Derivatives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 10: 3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103690
APA StyleBayala, B., Zoure, A. A., Baron, S., de Joussineau, C., Simpore, J., & Lobaccaro, J. -M. A. (2020). Pharmacological Modulation of Steroid Activity in Hormone-Dependent Breast and Prostate Cancers: Effect of Some Plant Extract Derivatives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10), 3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103690