Indocyanine Green Loaded Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as an Effective Photothermal Nanoplatform
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization
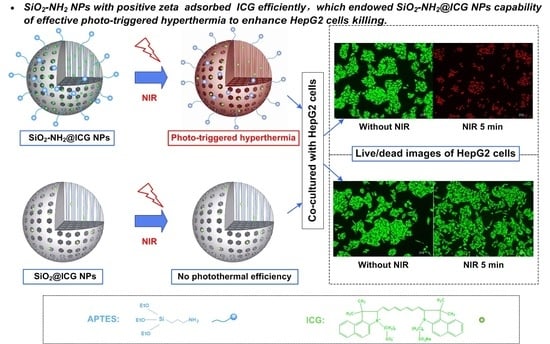
2.2. Loading of ICG Molecules and Photothermal Effect
2.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Phototoxicity Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of the SiO2-NH2 NPs
3.3. Preparation of the ICG-Loaded Nanoparticles
3.4. Characterization
3.5. Measurement of the Photothermal Performance
3.6. Measurement of ICG Stability Performance
3.6.1. Irradiation Stability
3.6.2. Thermal Stability
3.6.3. Long-Term Stability
3.7. Hemolysis Test
3.8. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.9. Cell Apoptosis Assay
3.10. In Vitro Phototoxicity Testing
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seehawer, M.; Heinzmann, F.; D’Artista, L.; Harbig, J.; Roux, P.-F.; Hoenicke, L.; Dang, H.; Klotz, S.; Robinson, L.; Doré, G. Necroptosis microenvironment directs lineage commitment in liver cancer. Nature 2018, 562, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, A.; Sun, H. Power of metabolomics in diagnosis and biomarker discovery of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimori, M.; Takaki, H.; Nakatsuka, A.; Uraki, J.; Yamanaka, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Shiraki, K.; Takei, Y.; Sakuma, H.; Yamakado, K. Survival with up to 10-year follow-up after combination therapy of chemoembolization and radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Single-center experience. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, Y.; Huan, X.; Liang, C.; Chunyang, S.; Jun, W.; Zhuang, L. In vitro and in vivo near-infrared photothermal therapy of cancer using polypyrrole organic nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5586–5592. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Yang, K.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Z. Organic stealth nanoparticles for highly effective in vivo near-infrared photothermal therapy of cancer. Acs Nano 2012, 6, 5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, L.; Liang, C.; Wang, C.; Peng, R.; Liu, Z. Photothermal therapy with immune-adjuvant nanoparticles together with checkpoint blockade for effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Ji, C.; Shi, J.; Pridgen, E.M.; Frieder, J.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. DNA self-assembly of targeted near-infrared-responsive gold nanoparticles for cancer thermo-chemotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11853–11857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rengan, A.K.; Bukhari, A.B.; Pradhan, A.; Malhotra, R.; Banerjee, R.; Srivastava, R.; De, A. In vivo analysis of biodegradable liposome gold nanoparticles as efficient agents for photothermal therapy of cancer. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, M.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, A.; Liu, X.; Liu, J. Multifunctional peg modified dox loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticle@cus nanohybrids as photo-thermal agent and thermal-triggered drug release vehicle for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 025102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, N.A.; Davis, C.; McKernan, P.; Hauser, P.; Hurst, R.E.; Slaton, J.; Silvy, R.P.; Resasco, D.E.; Harrison, R.G. Phosphatidylserine targeted single-walled carbon nanotubes for photothermal ablation of bladder cancer. Nanotechnology 2017, 29, 035101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, K.; Chen, M.; Tian, R.; Ma, Q.; Zhu, L. Hybrid graphene/au activatable theranostic agent for multimodalities imaging guided enhanced photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 79, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Yu, L.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y. Mussel-inspired immobilization of bn nanosheets onto poly (p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) fibers: Multifunctional interface for photothermal self-healing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, F.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y. Fabrication of a graphene/c 60 nanohybrid via γ-cyclodextrin host–guest chemistry for photodynamic and photothermal therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8825–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, H.J.; Mooney, D.J. Microenvironmental regulation of biomacromolecular therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Lu, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yu, L.; Xu, X.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y. Construction of anti-ultraviolet “shielding clothes” on poly (p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) fibers: Metal organic framework-mediated absorption strategy. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 43262–43274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Shao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, D.; Xu, X.; Lin, J.; Liu, H.; Guo, Z. Light triggered interfacial damage self-healing of poly (p-phenylene benzobisoxazole) fiber composites. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 185602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütt, F.; Fischer, J.; Kopitz, J.; Holz, F.G. Indocyanine green angiography in the presence of subretinal or intraretinal haemorrhages: Clinical and experimental investigations. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2002, 30, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fickweiler, S.; Szeimies, R.-M.; Bäumler, W.; Steinbach, P.; Karrer, S.; Goetz, A.E.; Abels, C.; Hofstädter, F. Indocyanine green: Intracellular uptake and phototherapeutic effects in vitro. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1997, 38, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, B.; Choi, K.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kang, K.W.; Chung, D.S. Near infrared dye indocyanine green doped silica nanoparticles for biological imaging. Talanta 2012, 99, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, G.; Loh, S.-W.; Jones, L.; Benson, J. A feasibility study (icg-10) of indocyanine green (icg) fluorescence mapping for sentinel lymph node detection in early breast cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (Ejso) 2012, 38, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, V.; Sadoqi, M.; Shao, J. Degradation kinetics of indocyanine green in aqueous solution. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 92, 2090–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmettre, T.; Devoisselle, J.; Mordon, S. Fluorescence properties and metabolic features of indocyanine green (icg) as related to angiography. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2000, 45, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, M.A.; Yu, J.; Wong, M.S.; Anvari, B. Laser-induced heating of dextran-coated mesocapsules containing indocyanine green. Biotechnol. Prog. 2007, 23, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, C.; Zheng, M.; Gong, P.; Jia, D.; Zhang, P.; Shi, B.; Sheng, Z.; Ma, Y.; Cai, L. Indocyanine green-loaded biodegradable tumor targeting nanoprobes for in vitro and in vivo imaging. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5603–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y. Indocyanine green-loaded hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an activatable theranostic agent. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 185102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, B.-B.; Dong, L.; Lu, Y.; Yu, S.-H. Calcium carbonate-doxorubicin@silica-indocyanine green nanospheres with photo-triggered drug delivery enhance cell killing in drug-resistant breast cancer cells. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 3385–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, A.; Feng, S.; Liu, J. Nir-laser switched icg/dox loaded thermo-responsive polymeric capsule for chemo-photothermal targeted therapy. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 92, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Cheng, S.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, N.T.; Souris, J.; Chen, C.T.; Mou, C.Y.; Yang, C.S.; Lo, L.W. Near-infrared mesoporous silica nanoparticles for optical imaging: Characterization and in vivo biodistribution. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Qiu, W.X.; Hu, J.J.; Cao, P.X.; Zhu, C.H.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.Z. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles with thermal-responsive gatekeeper for nir light-triggered chemo/photothermal-therapy. Small 2016, 12, 4286–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, R.; Wang, D.; Xiao, L.; Chen, G.; Xia, J.; Prasad, P.N. Stable icg-loaded upconversion nanoparticles: Silica core/shell theranostic nanoplatform for dual-modal upconversion and photoacoustic imaging together with photothermal therapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shindo, Y.; Inose, T.; Kubota, Y.; Oikawa, T.; Tokunaga, M.; Kamei, T.; Gonda, K.; Kobayashi, Y. Synthesis on aggregation of colloidal solutions of icg-active silica nanoparticles and their application in in-vivo fluorescence imaging. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 220, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanikumar, L.; Choi, E.S.; Cheon, J.Y.; Joo, S.H.; Ryu, J.H. Noncovalent polymer-gatekeeper in mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a targeted drug delivery platform. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan-Ayisigi, E.; Yesil-Celiktas, O. Silica-based organic-inorganic hybrid nanoparticles and nanoconjugates for improved anticancer drug delivery. Eng. Life Sci. 2018, 18, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S.; Burke, P.A.; Langer, R. Overcoming the challenges in administering biopharmaceuticals: Formulation and delivery strategies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Tse, B.W.-C.; Yang, H.; Thorling, C.A.; Liu, Y.; Touraud, M.; Chouane, J.B.; Liu, X.; Roberts, M.S. Indocyanine green-incorporating nanoparticles for cancer theranostics. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Shi, J. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle based nano drug delivery systems: Synthesis, controlled drug release and delivery, pharmacokinetics and biocompatibility. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 5845–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, J.; González, P.; Liste, S.; Serra, C.; Chiussi, S.; León, B.; Pérez-Amor, M.; Ylänen, H.; Hupa, M. Ftir and xps studies of bioactive silica based glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 332, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wong, C. Study on mono-dispersed nano-size silica by surface modification for underfill applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 292, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigand, R.; Rotermund, F.; Penzkofer, A. Aggregation dependent absorption reduction of indocyanine green. J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 7729–7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Hao, P.; Wang, Z.; Fu, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, J. Pedot nanocomposites mediated dual-modal photodynamic and photothermal targeted sterilization in both nir i and ii window. Biomaterials 2015, 41, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Ke, W.; Ge, Z. A near-infrared photothermal effect-responsive drug delivery system based on indocyanine green and doxorubicin-loaded polymeric micelles mediated by reversible diels–alder reaction. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Z.; Hu, D.; Xue, M.; He, M.; Gong, P.; Cai, L. Indocyanine green nanoparticles for theranostic applications. Nano-Micro Lett. 2013, 5, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Niu, C.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, X. Indocyanine Green Loaded Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as an Effective Photothermal Nanoplatform. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134789
Wang Y, Niu C, Fan S, Li Y, Li X, Dai Y, Shi J, Wang X. Indocyanine Green Loaded Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as an Effective Photothermal Nanoplatform. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(13):4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134789
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yiyu, Chunqing Niu, Sisi Fan, Yuwei Li, Xiang Li, Yujun Dai, Jian Shi, and Xinyu Wang. 2020. "Indocyanine Green Loaded Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as an Effective Photothermal Nanoplatform" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 13: 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134789
APA StyleWang, Y., Niu, C., Fan, S., Li, Y., Li, X., Dai, Y., Shi, J., & Wang, X. (2020). Indocyanine Green Loaded Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as an Effective Photothermal Nanoplatform. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(13), 4789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21134789