Sodium Hydrogen Exchanger Regulatory Factor-1 (NHERF1) Regulates Fetal Membrane Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
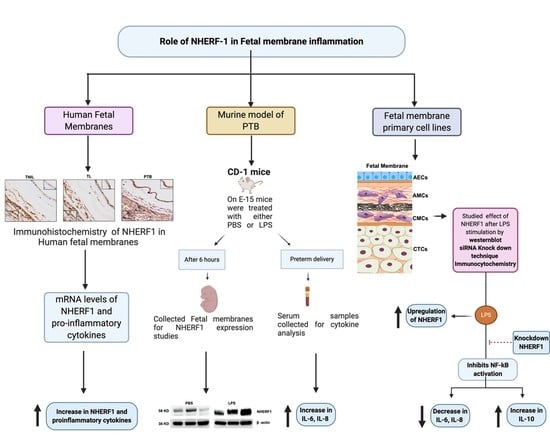
2.1. NHERF1 Levels Are Upregulated in Fetal Membranes of TL and PTB
2.2. NHERF1 Increase Is Associated with Proinflammatory Cytokine Switch in Fetal Membranes
2.3. NHERF1 Levels Were Enhanced in the Fetal Membranes of Mice Subjected to PTB
2.4. NHERF1 Levels Are Enhanced in Different Cell Layers of Fetal Membranes Following LPS Stimulation
2.5. Translocation of NHERF1 in Amnion Epithelial Cells with LPS Stimulation
2.6. Silencing NHERF1 in Primary Cells Results in a Reduction in Phospho-NF-kB Levels and Attenuates IL-6 and IL-8 Production
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Institutional Review Board (IRB) Approval
4.2. Clinical Samples
4.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR for NHERF1 and Cytokines
4.4. Immunohistochemistry for NHERF1
4.5. In Vivo Murine Model for Preterm Birth
4.6. LPS-Induced PTB
4.7. Luminex Assay to Determine Cytokine Concentration in Maternal Plasma
4.8. Isolation and Culture of Human Amnion Epithelial Cells and Human Amnion Mesenchymal Cells
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.10. Cell Culture Treatments
4.11. Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
4.12. siRNA-Mediated Knockdown of NHERF1 in Fetal Membrane Cells
4.13. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEC | amnion epithelial cells |
| AMC | amnion mesenchymal cells |
| cAMP | cyclic amino monophosphate |
| CMC | chorion mesenchymal cells |
| CTC | chorion trophoblast cells |
| ERK | extracellular receptor kinase |
| GPCR | G-protein-coupled receptors |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| IL | interleukin |
| JNK | Janus kinase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MMP | Matrix metallopeptidase |
| NFkB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| NHERF | sodium hydrogen regulatory factor |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| pPROM | preterm premature rupture of membranes |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| PTB | preterm birth |
| RT-PCR | real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| siRNA | small interfering RNA |
| TL | term labor |
| TNF | tissue necrosis factor |
| TNIL | term not in labor |
References
- Racicot, K.; Kwon, J.Y.; Aldo, P.; Silasi, M.; Mor, G. Understanding the complexity of the immune system during pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2014, 72, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G. Inflammation and pregnancy: The role of toll-like receptors in trophoblast-immune interaction. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2008, 1127, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, R.; Dey, S.K.; Fisher, S.J. Preterm labor: One syndrome, many causes. Science 2014, 345, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Herrera, H.; García-López, G.; Díaz, N.F.; Molina-Hernández, A.; Osorio-Caballero, M.; Soriano-Becerril, D.; Zaga-Clavellina, V. An experimental mixed bacterial infection induced differential secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNFα) and proMMP-9 in human fetal membranes. Placenta 2012, 33, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacIntyre, D.A.; Sykes, L.; Teoh, T.G.; Bennett, P.R. Prevention of preterm labour via the modulation of inflammatory pathways. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 25 (Suppl. 1), 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R. Human fetal membranes at term: Dead tissue or signalers of parturition? Placenta 2016, 44, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vora, S.; Abbas, A.; Kim, C.J.; Summerfield, T.L.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Iams, J.D.; Romero, R.; Kniss, D.A.; Ackerman, W.E., 4th. Nuclear factor-kappa B localization and function within intrauterine tissues from term and preterm labor and cultured fetal membranes. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2010, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, R.; Lappas, M. A novel role for GSK3 in the regulation of the processes of human labour. Reproduction 2015, 149, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharp, G.C.; Ma, H.; Saunders, P.T.; Norman, J.E. A computational model of lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear factor kappa B activation: A key signalling pathway in infection-induced preterm labour. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, S.K.; Gayatri, K.; Jammula, S.; Krishna, S.V.; Meher, L.K.; Modi, K.D. Endocrinology of parturition. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 17, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindström, T.M.; Bennett, P.R. The role of nuclear factor kappa B in human labour. Reproduction 2005, 130, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadbent, D.; Ahmadzai, M.M.; Kammala, A.K.; Yang, C.; Occhiuto, C.; Das, R.; Subramanian, H. Roles of NHERF Family of PDZ-Binding Proteins in Regulating GPCR Functions. Adv. Immunol. 2017, 136, 353–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, H.; Gupta, K.; Ali, H. Roles for NHERF1 and NHERF2 on the regulation of C3a receptor signaling in human mast cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leslie, K.L.; Song, G.J.; Barrick, S.; Wehbi, V.L.; Vilardaga, J.P.; Bauer, P.M.; Bisello, A. Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein 50 (EBP50) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB): A feed-forward loop for systemic and vascular inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 36426–36436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pera, T.; Tompkins, E.; Katz, M.; Wang, B.; Deshpande, D.A.; Weinman, E.J.; Penn, R.B. Specificity of NHERF1 regulation of GPCR signaling and function in human airway smooth muscle. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 9008–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; Papaconstantinou, J. p38 Mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK): A new therapeutic target for reducing the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, R.; Richardson, L.S. Preterm prelabor rupture of the membranes: A disease of the fetal membranes. Semin. Perinatol. 2017, 41, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Richardson, L.; Sheller-Miller, S.; Zhong, N.; Menon, R. Oxidative stress induces p38MAPK-dependent senescence in the feto-maternal interface cells. Placenta 2018, 67, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, L.; Dixon, C.L.; Aguilera-Aguirre, L.; Menon, R. Oxidative stress-induced TGF-beta/TAB1-mediated p38MAPK activation in human amnion epithelial cells. Biol. Reprod. 2018, 99, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, L.S.; Taylor, R.N.; Menon, R. Reversible EMT and MET mediate amnion remodeling during pregnancy and labor. Sci. Signal. 2020, 13, eaay1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H. The entry of fetal and amniotic fluid components into the uterine vessel circulation leads to sterile inflammatory processes during parturition. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Li, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Qu, Y.; Wang, H. Cortisol modulates inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells via the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lappas, M.; Permezel, M.; Georgiou, H.M.; Rice, G.E. Nuclear factor kappa B regulation of proinflammatory cytokines in human gestational tissues in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 67, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strauss, J.F. Extracellular matrix dynamics and fetal membrane rupture. Reprod. Sci. 2013, 20, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, S.B.; Sharma, S. Interleukin-10: A pleiotropic regulator in pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2015, 73, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salminen, A.; Paananen, R.; Vuolteenaho, R.; Metsola, J.; Ojaniemi, M.; Autio-Harmainen, H.; Hallman, M. Maternal endotoxin-induced preterm birth in mice: Fetal responses in toll-like receptors, collectins, and cytokines. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 63, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakai, J.; Cammarota, E.; Wright, J.A.; Cicuta, P.; Gottschalk, R.A.; Li, N.; Fraser, I.D.C.; Bryant, C.E. Lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB nuclear translocation is primarily dependent on MyD88, but TNFα expression requires TRIF and MyD88. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, M.M.; Yell, P.; Mobley, B.C.; Shang, P.; Georgescu, T.; Wang, S.H.; Canoll, P.; Hatanpaa, K.J.; White, C.L., III; Raisanen, J.M. NHERF1/EBP50 is an organizer of polarity structures and a diagnostic marker in ependymoma. Acta. Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgescu, M.M.; Olar, A.; Mobley, B.C.; Faust, P.L.; Raisanen, J.M. Epithelial differentiation with microlumen formation in meningioma: Diagnostic utility of NHERF1/EBP50 immunohistochemistry. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 28652–28665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Qiu, T.; Wu, J.; Yang, Y.; Wright, G.D.; Wu, M.; Ge, R. Extracellular anti-angiogenic proteins augment an endosomal protein trafficking pathway to reach mitochondria and execute apoptosis in HUVECs. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1905–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gurney, L.R.I.; Taggart, J.; Tong, W.C.; Jones, A.T.; Robson, S.C.; Taggart, M.J. Inhibition of Inflammatory Changes in Human Myometrial Cells by Cell Penetrating Peptide and Small Molecule Inhibitors of NFκB. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lappas, M. A20, an essential component of the ubiquitin-editing protein complex, is a negative regulator of inflammation in human myometrium and foetal membranes. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 23, 628–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, J.; Capece, D.; Begalli, F.; Verzella, D.; D’Andrea, D.; Tornatore, L.; Franzoso, G. NF-κB in the crosshairs: Rethinking an old riddle. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 95, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinson, L.F.; Ireland, D.J.; Kemp, M.W.; Payne, M.S.; Stock, S.J.; Newnham, J.P.; Keelan, J.A. Effects of cytokine-suppressive anti-inflammatory drugs on inflammatory activation in ex vivo human and ovine fetal membranes. Reproduction 2014, 147, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ireland, D.J.; Kemp, M.W.; Miura, Y.; Saito, M.; Newnham, J.P.; Keelan, J.A. Intra-amniotic pharmacological blockade of inflammatory signalling pathways in an ovine chorioamnionitis model. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2015, 21, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ireland, D.J.; Nathan, E.A.; Li, S.; Charles, A.K.; Stinson, L.F.; Kemp, M.W.; Newnham, J.P.; Keelan, J.A. Preclinical evaluation of drugs to block inflammation-driven preterm birth. Innate Immun. 2017, 23, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundaram, S.; Ashby, C.R.; Pekson, R.; Sampat, V.; Sitapara, R.; Mantell, L.; Chen, C.H.; Yen, H.; Abhichandani, K.; Munnangi, S.; et al. N,N-dimethylacetamide regulates the proinflammatory response associated with endotoxin and prevents preterm birth. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pekson, R.; Poltoratsky, V.; Gorasiya, S.; Sundaram, S.; Ashby, C.R.; Vancurova, I.; Reznik, S.E. N,N-Dimethylacetamide Significantly Attenuates LPS- and TNFα-Induced Proinflammatory Responses Via Inhibition of the Nuclear Factor Kappa B Pathway. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhimschi, I.A.; Buhimschi, C.S.; Weiner, C.P. Protective effect of N-acetylcysteine against fetal death and preterm labor induced by maternal inflammation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 188, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappas, M.; Yee, K.; Permezel, M.; Rice, G.E. Sulfasalazine and BAY 11-7082 interfere with the nuclear factor-kappa B and I kappa B kinase pathway to regulate the release of proinflammatory cytokines from human adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in vitro. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keelan, J.A.; Khan, S.; Yosaatmadja, F.; Mitchell, M.D. Prevention of inflammatory activation of human gestational membranes in an ex vivo model using a pharmacological NF-kappaB inhibitor. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5270–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Yan, Q.; Liu, R.H.; Zhang, L. Preventive and therapeutic effect of N-Acetyl-l-cysteine on infection-associated preterm labor in mice. Asian. Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wall, C.; Lim, R.; Poljak, M.; Lappas, M. Dietary flavonoids as therapeutics for preterm birth: Luteolin and kaempferol suppress inflammation in human gestational tissues in vitro. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 485201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morwood, C.J.; Lappas, M. The citrus flavone nobiletin reduces pro-inflammatory and pro-labour mediators in fetal membranes and myometrium: Implications for preterm birth. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowsky, D.W.; Novy, M.J.; Witkin, S.S.; Gravett, M.G. Dexamethasone or interleukin-10 blocks interleukin-1beta-induced uterine contractions in pregnant rhesus monkeys. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 188, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, S.J.; Menon, R.; Swan, K.F.; Lombardi, S.J. Interleukin-10 inhibition of interleukin-6 in human amniochorionic membrane: Transcriptional regulation. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 175, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S.J.; Menon, R.; Lombardi, S.J. The effect of transforming growth factor and interleukin-10 on interleukin-8 release by human amniochorion may regulate histologic chorioamnionitis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 179, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.J.; Leslie, K.L.; Barrick, S.; Bougoin, S.; Taboas, J.M.; Bisello, A. EBP50 promotes focal adhesion turnover and vascular smooth muscle cells migration. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shibata, T.; Chuma, M.; Kokubu, A.; Sakamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S. EBP50, a beta-catenin-associating protein, enhances Wnt signaling and is over-expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2003, 38, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardone, R.A.; Bellizzi, A.; Busco, G.; Weinman, E.J.; Dell’Aquila, M.E.; Casavola, V.; Azzariti, A.; Mangia, A.; Paradiso, A.; Reshkin, S.J. The NHERF1 PDZ2 domain regulates PKA-RhoA-p38-mediated NHE1 activation and invasion in breast tumor cells. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2007, 18, 1768–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouassier, L.; Rosenberg, P.; Mergey, M.; Saubaméa, B.; Clapéron, A.; Kinnman, N.; Chignard, N.; Jacobsson-Ekman, G.; Strandvik, B.; Rey, C.; et al. Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein (EBP50), an estrogen-inducible scaffold protein, contributes to biliary epithelial cell proliferation. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kislin, K.L.; McDonough, W.S.; Eschbacher, J.M.; Armstrong, B.A.; Berens, M.E. NHERF-1: Modulator of glioblastoma cell migration and invasion. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, G.; Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Hou, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, K. Abnormality of RUNX1 signal transduction in psoriatic CD34+ bone marrow cells. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 164, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.J.; Barrick, S.; Leslie, K.L.; Bauer, P.M.; Alonso, V.; Friedman, P.A.; Fiaschi-Taesch, N.M.; Bisello, A. The scaffolding protein EBP50 promotes vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointima formation by regulating Skp2 and p21(cip1). Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lappas, M. Nuclear factor-κB mediates placental growth factor induced pro-labour mediators in human placenta. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 18, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lappas, M.; Permezel, M.; Rice, G.E. Advanced glycation endproducts mediate pro-inflammatory actions in human gestational tissues via nuclear factor-kappaB and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 193, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, J.; Nguyen Ho-Bouldoires, T.H.; Clapéron, A.; Fouassier, L. Role of the PDZ-scaffold protein NHERF1/EBP50 in cancer biology: From signaling regulation to clinical relevance. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3067–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centonze, M.; Saponaro, C.; Mangia, A. NHERF1 between Promises and Hopes: Overview on Cancer and Prospective Openings. Transl Oncol. 2018, 11, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudalla, H.; Karenberg, K.; Kuon, R.J.; Pöschl, J.; Tschada, R.; Frommhold, D. LPS-induced maternal inflammation promotes fetal leukocyte recruitment and prenatal organ infiltration in mice. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, S.; Rubinstein, L. Changes in generic and degree completion dental hygiene student characteristics. J. Dent. Educ. 1989, 53, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bariani, M.V.; Correa, F.; Leishman, E.; Domínguez Rubio, A.P.; Arias, A.; Stern, A.; Bradshaw, H.B.; Franchi, A.M. Resveratrol protects from lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in the uterus and prevents experimental preterm birth. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 23, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, S.A.; Skinner, R.J.; Care, A.S. Essential role for IL-10 in resistance to lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm labor in mice. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 4888–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowsky, D.W.; Adams, K.M.; Gravett, M.G.; Witkin, S.S.; Novy, M.J. Preterm labor is induced by intraamniotic infusions of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha but not by interleukin-6 or interleukin-8 in a nonhuman primate model. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 195, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, R.; Fortunato, S.J.; Edwards, D.R.; Williams, S.M. Association of genetic variants, ethnicity and preterm birth with amniotic fluid cytokine concentrations. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2010, 74, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caamaño, J.; Hunter, C.A. NF-kappaB family of transcription factors: Central regulators of innate and adaptive immune functions. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bikkavilli, R.K.; Feigin, M.E.; Malbon, C.C. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates canonical Wnt-beta-catenin signaling by inactivation of GSK3beta. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3598–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bikkavilli, R.K.; Malbon, C.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Molecular conversations among signaling pathways. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2009, 2, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.S.; Barrick, S.R.; Grubisha, M.J.; Brufsky, A.M.; Friedman, P.A.; Romero, G. Direct interaction between NHERF1 and Frizzled regulates β-catenin signaling. Oncogene 2011, 30, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neuder, L.E.; Keener, J.M.; Eckert, R.E.; Trujillo, J.C.; Jones, S.L. Role of p38 MAPK in LPS induced pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine gene expression in equine leukocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 129, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Mennone, A.; Soroka, C.J.; Hagey, L.R.; Ouyang, X.; Weinman, E.J.; Boyer, J.L. Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor 1 knockout mice have an attenuated hepatic inflammatory response and are protected from cholestatic liver injury. Hepatology 2015, 62, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Lu, G.; Trescott, L.R.; Hou, Y.; Guan, X.; Wang, S.; Stamenkovich, A.; Brunzelle, J.; Sirinupong, N.; Li, C.; et al. New conformational state of NHERF1-CXCR2 signaling complex captured by crystal lattice trapping. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavu, N.; Richardson, L.; Radnaa, E.; Kechichian, T.; Urrabaz-Garza, R.; Sheller-Miller, S.; Bonney, E.; Menon, R. Oxidative stress-induced downregulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta in fetal membranes promotes cellular senescence. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 101, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmons, B.C.; Reese, J.; Socrate, S.; Ehinger, N.; Paria, B.C.; Milne, G.L.; Akins, M.L.; Auchus, R.J.; McIntire, D.; Houseet, M.; et al. Prostaglandins are essential for cervical ripening in LPS-mediated preterm birth but not term or antiprogestin-driven preterm ripening. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sheller, S.; Papaconstantinou, J.; Urrabaz-Garza, R.; Richardson, L.; Saade, G.; Salomon, C.; Menon, R. Amnion-Epithelial-Cell-Derived Exosomes Demonstrate Physiologic State of Cell under Oxidative Stress. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, B.L.; Collier, E.S.; Vermudez, S.A.; Junker, A.D.; Kendal-Wright, C.E. Human amnion mesenchymal cells are pro-inflammatory when activated by the Toll-like receptor 2/6 ligand, macrophage-activating lipoprotein-2. Placenta 2016, 44, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bailo, M.; Soncini, M.; Vertua, E.; Signoroni, P.B.; Sanzone, S.; Lombardi, G.; Arienti, D.; Calamani, F.; Zatti, D.; Paul, P.; et al. Engraftment potential of human amnion and chorion cells derived from term placenta. Transplantation 2004, 78, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavu, N.; Sheller-Miller, S.; Kechichian, T.; Cayenne, S.; Bonney, E.A.; Menon, R. Changes in mediators of pro-cell growth, senescence, and inflammation during murine gestation. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2020, 83, e13214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kammala, A.K.; Sheller-Miller, S.; Radnaa, E.; Kechichian, T.; Subramanian, H.; Menon, R. Sodium Hydrogen Exchanger Regulatory Factor-1 (NHERF1) Regulates Fetal Membrane Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207747
Kammala AK, Sheller-Miller S, Radnaa E, Kechichian T, Subramanian H, Menon R. Sodium Hydrogen Exchanger Regulatory Factor-1 (NHERF1) Regulates Fetal Membrane Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(20):7747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207747
Chicago/Turabian StyleKammala, Ananth Kumar, Samantha Sheller-Miller, Enkhtuya Radnaa, Talar Kechichian, Hariharan Subramanian, and Ramkumar Menon. 2020. "Sodium Hydrogen Exchanger Regulatory Factor-1 (NHERF1) Regulates Fetal Membrane Inflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 20: 7747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207747
APA StyleKammala, A. K., Sheller-Miller, S., Radnaa, E., Kechichian, T., Subramanian, H., & Menon, R. (2020). Sodium Hydrogen Exchanger Regulatory Factor-1 (NHERF1) Regulates Fetal Membrane Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(20), 7747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21207747