Integrin Signaling in Glioma Pathogenesis: From Biology to Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Integrin Structure and Signaling
3. Deregulation of Integrin Signaling in Gliomas
4. Roles of Integrins and Their Ligands in Shaping A GBM Permissive Microenvironment
4.1. Cell Migration and Invasion
4.2. Crosstalk with Growth Factor Receptors
4.3. Angiogenesis
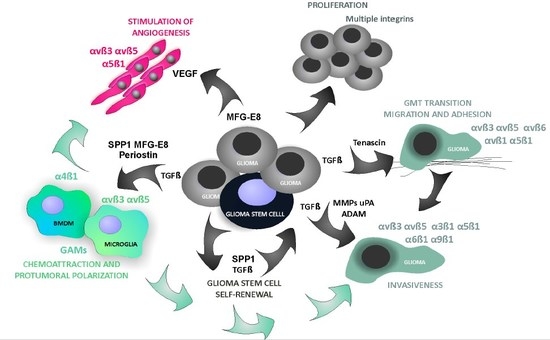
4.4. Glioma-Derived Integrin Ligands Interacting with Stromal Cells in GBM
5. Interfering with Integrin Signaling as a Therapeutic Strategy against Glioblastoma
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brandes, A.A.; Tosoni, A.; Franceschi, E.; Reni, M.; Gatta, G.; Vecht, C. Glioblastoma in adults. Crit. Rev. Oncol. /Hematol. 2008, 67, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.P.; Tirosh, I.; Trombetta, J.J.; Shalek, A.K.; Gillespie, S.M.; Wakimoto, H.; Cahill, D.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Curry, W.T.; Martuza, R.L.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 2014, 344, 1396–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. The Microenvironmental Landscape of Brain Tumors. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weller, M.; van den Bent, M.; Hopkins, K.; Tonn, J.C.; Stupp, R.; Falini, A.; Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal, E.; Frappaz, D.; Henriksson, R.; Balana, C.; et al. EANO guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of anaplastic gliomas and glioblastoma. Lancet. Oncol. 2014, 15, e395–e403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paez-Ribes, M.; Allen, E.; Hudock, J.; Takeda, T.; Okuyama, H.; Vinals, F.; Inoue, M.; Bergers, G.; Hanahan, D.; Casanovas, O. Antiangiogenic therapy elicits malignant progression of tumors to increased local invasion and distant metastasis. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filley, A.C.; Henriquez, M.; Dey, M. Recurrent glioma clinical trial, CheckMate-143: The game is not over yet. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91779–91794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danen, E.H.J. Integrin Signaling as a Cancer Drug Target. ISRN Cell Biol. 2013, 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Reviews. Cancer 2010, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di Giannatale, A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paolillo, M.; Schinelli, S. Integrins and Exosomes, a Dangerous Liaison in Cancer Progression. Cancers 2017, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, P.; Silginer, M.; Goodman, S.L.; Hasenbach, K.; Thies, S.; Maurer, G.; Schraml, P.; Tabatabai, G.; Moch, H.; Tritschler, I.; et al. Integrin control of the transforming growth factor-beta pathway in glioblastoma. Brain 2013, 136, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamkun, J.W.; DeSimone, D.W.; Fonda, D.; Patel, R.S.; Buck, C.; Horwitz, A.F.; Hynes, R.O. Structure of integrin, a glycoprotein involved in the transmembrane linkage between fibronectin and actin. Cell 1986, 46, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, L.R.; Owens, T.W.; Naylor, M.J. Structural and mechanical functions of integrins. Biophys. Rev. 2014, 6, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieberler, M.; Reuning, U.; Reichart, F.; Notni, J.; Wester, H.J.; Schwaiger, M.; Weinmuller, M.; Rader, A.; Steiger, K.; Kessler, H. Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Carman, C.V.; Springer, T.A. Bidirectional transmembrane signaling by cytoplasmic domain separation in integrins. Science 2003, 301, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Playford, M.P.; Schaller, M.D. The interplay between Src and integrins in normal and tumor biology. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7928–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunton, V.G.; Frame, M.C. Src and focal adhesion kinase as therapeutic targets in cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, R.; Antonescu, C.N. Integrins and Cell Metabolism: An Intimate Relationship Impacting Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Autelitano, F.; Loyaux, D.; Roudieres, S.; Deon, C.; Guette, F.; Fabre, P.; Ping, Q.; Wang, S.; Auvergne, R.; Badarinarayana, V.; et al. Identification of novel tumor-associated cell surface sialoglycoproteins in human glioblastoma tumors using quantitative proteomics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schittenhelm, J.; Schwab, E.I.; Sperveslage, J.; Tatagiba, M.; Meyermann, R.; Fend, F.; Goodman, S.L.; Sipos, B. Longitudinal expression analysis of alphav integrins in human gliomas reveals upregulation of integrin alphavbeta3 as a negative prognostic factor. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 72, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malric, L.; Monferran, S.; Gilhodes, J.; Boyrie, S.; Dahan, P.; Skuli, N.; Sesen, J.; Filleron, T.; Kowalski-Chauvel, A.; Cohen-Jonathan Moyal, E.; et al. Interest of integrins targeting in glioblastoma according to tumor heterogeneity and cancer stem cell paradigm: An update. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86947–86968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.S.; Lu, N.; Denessiouk, K.; Heino, J.; Gullberg, D. Integrins during evolution: Evolutionary trees and model organisms. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2009, 1788, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gingras, M.C.; Roussel, E.; Bruner, J.M.; Branch, C.D.; Moser, R.P. Comparison of cell adhesion molecule expression between glioblastoma multiforme and autologous normal brain tissue. J. Neuroimmunol. 1995, 57, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamarre, E.; Taboubi, S.; Mathieu, S.; Berenguer, C.; Rigot, V.; Lissitzky, J.C.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Ouafik, L.; Luis, J. Expression of integrin alpha6beta1 enhances tumorigenesis in glioma cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, T.L.; Sciuto, M.R.; Brunetto, L.; Valvo, C.; Signore, M.; Fiori, M.E.; di Martino, S.; Giannetti, S.; Morgante, L.; Boe, A.; et al. Integrin alpha7 Is a Functional Marker and Potential Therapeutic Target in Glioblastoma. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 35–50.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munksgaard Thoren, M.; Chmielarska Masoumi, K.; Krona, C.; Huang, X.; Kundu, S.; Schmidt, L.; Forsberg-Nilsson, K.; Floyd Keep, M.; Englund, E.; Nelander, S.; et al. Integrin alpha10, a Novel Therapeutic Target in Glioblastoma, Regulates Cell Migration, Proliferation, and Survival. Cancers 2019, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weller, M.; Nabors, L.B.; Gorlia, T.; Leske, H.; Rushing, E.; Bady, P.; Hicking, C.; Perry, J.; Hong, Y.K.; Roth, P.; et al. Cilengitide in newly diagnosed glioblastoma: Biomarker expression and outcome. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15018–15032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, L.; Francolini, M.; Marthyn, P.; Zhang, J.; Carroll, R.S.; Nikas, D.C.; Strasser, J.F.; Villani, R.; Cheresh, D.A.; Black, P.M. Alpha(v)beta3 and alpha(v)beta5 integrin expression in glioma periphery. Neurosurgery 2001, 49, 380–389; discussion 390. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mittelbronn, M.; Warth, A.; Meyermann, R.; Goodman, S.; Weller, M. Expression of integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5 and their ligands in primary and secondary central nervous system neoplasms. Histol. Histopathol. 2013, 28, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooprai, H.K.; Vanmeter, T.; Panou, C.; Schnull, S.; Trillo-Pazos, G.; Davies, D.; Pilkington, G.J. The role of integrin receptors in aspects of glioma invasion in vitro. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. Off. J. Int. Soc. Dev. Neurosci. 1999, 17, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauch, U. Brain matrix: Structure, turnover and necessity. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, V.P.; Moura Neto, V.; Mentlein, R. Glioma infiltration and extracellular matrix: Key players and modulators. Glia 2018, 66, 1542–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, F.; Kienast, Y.; Fuhrmann, M.; Von Baumgarten, L.; Burgold, S.; Mitteregger, G.; Kretzschmar, H.; Herms, J. Imaging glioma cell invasion in vivo reveals mechanisms of dissemination and peritumoral angiogenesis. Glia 2009, 57, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Kurozumi, K.; Date, I. Angiogenesis and invasion in glioma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2011, 28, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candiello, J.; Balasubramani, M.; Schreiber, E.M.; Cole, G.J.; Mayer, U.; Halfter, W.; Lin, H. Biomechanical properties of native basement membranes. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, D.B.; Ames, H.M.; Li, R. Mechanisms of invasion and motility of high-grade gliomas in the brain. Mol. Biol. Cell 2018, 29, 2509–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, J.; Morokoff, A.P.; Luwor, R.B.; Zhu, H.J.; Kaye, A.H.; Stylli, S.S. The emergent role of exosomes in glioma. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2017, 35, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallawaaratchy, D.M.; Hallal, S.; Russell, B.; Ly, L.; Ebrahimkhani, S.; Wei, H.; Christopherson, R.I.; Buckland, M.E.; Kaufman, K.L. Comprehensive proteome profiling of glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles identifies markers for more aggressive disease. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 131, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lane, R.; Simon, T.; Vintu, M.; Solkin, B.; Koch, B.; Stewart, N.; Benstead-Hume, G.; Pearl, F.M.G.; Critchley, G.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Cell-derived extracellular vesicles can be used as a biomarker reservoir for glioblastoma tumor subtyping. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osti, D.; Del Bene, M.; Rappa, G.; Santos, M.; Matafora, V.; Richichi, C.; Faletti, S.; Beznoussenko, G.V.; Mironov, A.; Bachi, A.; et al. Clinical Significance of Extracellular Vesicles in Plasma from Glioblastoma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quail, D.F.; Bowman, R.L.; Akkari, L.; Quick, M.L.; Schuhmacher, A.J.; Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C.; Sutton, J.C.; Joyce, J.A. The tumor microenvironment underlies acquired resistance to CSF-1R inhibition in gliomas. Science 2016, 352, aad3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. The extracellular matrix: A dynamic niche in cancer progression. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Q.; Stewart, J., Jr.; Prince, C.W.; Chang, P.L.; Trikha, M.; Han, X.; Grammer, J.R.; Gladson, C.L. Promotion of malignant astrocytoma cell migration by osteopontin expressed in the normal brain: Differences in integrin signaling during cell adhesion to osteopontin versus vitronectin. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5336–5343. [Google Scholar]
- Serres, E.; Debarbieux, F.; Stanchi, F.; Maggiorella, L.; Grall, D.; Turchi, L.; Burel-Vandenbos, F.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Virolle, T.; Rougon, G.; et al. Fibronectin expression in glioblastomas promotes cell cohesion, collective invasion of basement membrane in vitro and orthotopic tumor growth in mice. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3451–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheev, A.M.; Mikheeva, S.A.; Trister, A.D.; Tokita, M.J.; Emerson, S.N.; Parada, C.A.; Born, D.E.; Carnemolla, B.; Frankel, S.; Kim, D.H.; et al. Periostin is a novel therapeutic target that predicts and regulates glioma malignancy. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mallawaaratchy, D.M.; Buckland, M.E.; McDonald, K.L.; Li, C.C.; Ly, L.; Sykes, E.K.; Christopherson, R.I.; Kaufman, K.L. Membrane proteome analysis of glioblastoma cell invasion. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 425–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maglott, A.; Bartik, P.; Cosgun, S.; Klotz, P.; Ronde, P.; Fuhrmann, G.; Takeda, K.; Martin, S.; Dontenwill, M. The small alpha5beta1 integrin antagonist, SJ749, reduces proliferation and clonogenicity of human astrocytoma cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6002–6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakada, M.; Nambu, E.; Furuyama, N.; Yoshida, Y.; Takino, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Sato, H.; Sai, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Miyamoto, K.I.; et al. Integrin alpha3 is overexpressed in glioma stem-like cells and promotes invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 2516–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawataki, T.; Yamane, T.; Naganuma, H.; Rousselle, P.; Anduren, I.; Tryggvason, K.; Patarroyo, M. Laminin isoforms and their integrin receptors in glioma cell migration and invasiveness: Evidence for a role of alpha5-laminin(s) and alpha3beta1 integrin. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 3819–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahabir, R.; Tanino, M.; Elmansuri, A.; Wang, L.; Kimura, T.; Itoh, T.; Ohba, Y.; Nishihara, H.; Shirato, H.; Tsuda, M.; et al. Sustained elevation of Snail promotes glial-mesenchymal transition after irradiation in malignant glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2014, 16, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matias, D.; Balca-Silva, J.; Dubois, L.G.; Pontes, B.; Ferrer, V.P.; Rosario, L.; do Carmo, A.; Echevarria-Lima, J.; Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B.; Lopes, M.C.; et al. Dual treatment with shikonin and temozolomide reduces glioblastoma tumor growth, migration and glial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell. Oncol. (Dordr.) 2017, 40, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, G.; Noulet, F.; Mercier, M.C.; Choulier, L.; Etienne-Selloum, N.; Gies, J.P.; Lehmann, M.; Lelong-Rebel, I.; Martin, S.; Dontenwill, M. Expression/activation of alpha5beta1 integrin is linked to the beta-catenin signaling pathway to drive migration in glioma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62194–62207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hattermann, K.; Mentlein, R. An infernal trio: The chemokine CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 in tumor biology. Ann. Anat. Anat. Anz. Off. Organ Anat. Ges. 2013, 195, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaka, N.; Seed, R.I.; Cormier, A.; Bondesson, A.J.; Lou, J.; Elattma, A.; Ito, S.; Yanagisawa, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Ma, R.; et al. Integrin alphavbeta8-expressing tumor cells evade host immunity by regulating TGF-beta activation in immune cells. JCI Insight 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munger, J.S.; Sheppard, D. Cross talk among TGF-beta signaling pathways, integrins, and the extracellular matrix. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munger, J.S.; Huang, X.; Kawakatsu, H.; Griffiths, M.J.; Dalton, S.L.; Wu, J.; Pittet, J.F.; Kaminski, N.; Garat, C.; Matthay, M.A.; et al. The integrin alpha v beta 6 binds and activates latent TGF beta 1: A mechanism for regulating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Cell 1999, 96, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Platten, M.; Wick, W.; Wild-Bode, C.; Aulwurm, S.; Dichgans, J.; Weller, M. Transforming growth factors beta(1) (TGF-beta(1)) and TGF-beta(2) promote glioma cell migration via Up-regulation of alpha(V)beta(3) integrin expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 268, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silginer, M.; Weller, M.; Ziegler, U.; Roth, P. Integrin inhibition promotes atypical anoikis in glioma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wick, W.; Platten, M.; Weller, M. Glioma cell invasion: Regulation of metalloproteinase activity by TGF-beta. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2001, 53, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.V.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Walenkamp, A.; Kruyt, F.A. TGF-beta as a therapeutic target in high grade gliomas - promises and challenges. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iser, I.C.; Pereira, M.B.; Lenz, G.; Wink, M.R. The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition-Like Process in Glioblastoma: An Updated Systematic Review and In Silico Investigation. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 271–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesolowska, A.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Slomnicki, L.; Dembinski, M.; Master, A.; Sliwa, M.; Franciszkiewicz, K.; Chouaib, S.; Kaminska, B. Microglia-derived TGF-beta as an important regulator of glioblastoma invasion--an inhibition of TGF-beta-dependent effects by shRNA against human TGF-beta type II receptor. Oncogene 2008, 27, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papageorgis, P. TGFbeta Signaling in Tumor Initiation, Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition, and Metastasis. J. Oncol. 2015, 2015, 587193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hynes, R.O. A reevaluation of integrins as regulators of angiogenesis. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demircioglu, F.; Hodivala-Dilke, K. alphavbeta3 Integrin and tumour blood vessels-learning from the past to shape the future. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 42, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, S.M.; Cheresh, D.A. alphaV integrins in angiogenesis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garmy-Susini, B.; Jin, H.; Zhu, Y.; Sung, R.J.; Hwang, R.; Varner, J. Integrin alpha4beta1-VCAM-1-mediated adhesion between endothelial and mural cells is required for blood vessel maturation. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murphy, P.A.; Begum, S.; Hynes, R.O. Tumor angiogenesis in the absence of fibronectin or its cognate integrin receptors. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardee, M.E.; Zagzag, D. Mechanisms of glioma-associated neovascularization. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, C.C. Integrin alpha v beta 3 as a therapeutic target for blocking tumor-induced angiogenesis. Curr. Drug Targets 2003, 4, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Bell, K.; Mousa, S.A.; Varner, J.A. Regulation of angiogenesis in vivo by ligation of integrin alpha5beta1 with the central cell-binding domain of fibronectin. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1345–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.Z.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophage diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell 2010, 141, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.; Su, J.; Garmy-Susini, B.; Kleeman, J.; Varner, J. Integrin alpha4beta1 promotes monocyte trafficking and angiogenesis in tumors. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellert-Miklaszewska, A.; Wisniewski, P.; Kijewska, M.; Gajdanowicz, P.; Pszczolkowska, D.; Przanowski, P.; Dabrowski, M.; Maleszewska, M.; Kaminska, B. Tumour-processed osteopontin and lactadherin drive the protumorigenic reprogramming of microglia and glioma progression. Oncogene 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anborgh, P.H.; Mutrie, J.C.; Tuck, A.B.; Chambers, A.F. Role of the metastasis-promoting protein osteopontin in the tumour microenvironment. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 2037–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szulzewsky, F.; Pelz, A.; Feng, X.; Synowitz, M.; Markovic, D.; Langmann, T.; Holtman, I.R.; Wang, X.; Eggen, B.J.; Boddeke, H.W.; et al. Glioma-associated microglia/macrophages display an expression profile different from M1 and M2 polarization and highly express Gpnmb and Spp1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabrusiewicz, K.; Rodriguez, B.; Wei, J.; Hashimoto, Y.; Healy, L.M.; Maiti, S.N.; Thomas, G.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Q.; Elakkad, A.; et al. Glioblastoma-infiltrated innate immune cells resemble M0 macrophage phenotype. JCI Insight 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieryng, A.; Pszczolkowska, D.; Bocian, K.; Dabrowski, M.; Rajan, W.D.; Kloss, M.; Mieczkowski, J.; Kaminska, B. Immune microenvironment of experimental rat C6 gliomas resembles human glioblastomas. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katz, A.M.; Amankulor, N.M.; Pitter, K.; Helmy, K.; Squatrito, M.; Holland, E.C. Astrocyte-specific expression patterns associated with the PDGF-induced glioma microenvironment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Marisetty, A.; Schrand, B.; Gabrusiewicz, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ott, M.; Grami, Z.; Kong, L.Y.; Ling, X.; Caruso, H.; et al. Osteopontin mediates glioblastoma-associated macrophage infiltration and is a potential therapeutic target. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanayama, R.; Tanaka, M.; Miwa, K.; Shinohara, A.; Iwamatsu, A.; Nagata, S. Identification of a factor that links apoptotic cells to phagocytes. Nature 2002, 417, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.; Jacob, A.; Matsuda, A.; Wang, P. Review: Milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 expression, function and plausible signal transduction in resolving inflammation. Apoptosis 2011, 16, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, J.S.; Thery, C.; Hamard, G.; Boddaert, J.; Aguilar, B.; Delcayre, A.; Houbron, C.; Tamarat, R.; Blanc-Brude, O.; Heeneman, S.; et al. Lactadherin promotes VEGF-dependent neovascularization. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, G.; Bernard-Pierrot, I.; Lae, M.; Battail, C.; Allory, Y.; Stransky, N.; Krumeich, S.; Lepage, M.L.; Maille, P.; Donnadieu, M.H.; et al. Milk fat globule--epidermal growth factor--factor VIII (MFGE8)/lactadherin promotes bladder tumor development. Oncogene 2011, 30, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, W.; Ke, S.Q.; Huang, Z.; Flavahan, W.; Fang, X.; Paul, J.; Wu, L.; Sloan, A.E.; McLendon, R.E.; Li, X.; et al. Periostin secreted by glioblastoma stem cells recruits M2 tumour-associated macrophages and promotes malignant growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouanouki, A.; Lamy, S.; Annabi, B. Periostin, a signal transduction intermediate in TGF-beta-induced EMT in U-87MG human glioblastoma cells, and its inhibition by anthocyanidins. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 22023–22037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taverna, D.; Moher, H.; Crowley, D.; Borsig, L.; Varki, A.; Hynes, R.O. Increased primary tumor growth in mice null for beta3- or beta3/beta5-integrins or selectins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brosicke, N.; Faissner, A. Role of tenascins in the ECM of gliomas. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imanaka-Yoshida, K.; Aoki, H. Tenascin-C and mechanotransduction in the development and diseases of cardiovascular system. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orend, G. Potential oncogenic action of tenascin-C in tumorigenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 1066–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, T.R.; da Fonseca, A.C.; Nunes, S.S.; da Silva, A.O.; Dubois, L.G.; Faria, J.; Kahn, S.A.; Viana, N.B.; Marcondes, J.; Legrand, C.; et al. Tenascin-C in the extracellular matrix promotes the selection of highly proliferative and tubulogenesis-defective endothelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 2073–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herold-Mende, C.; Mueller, M.M.; Bonsanto, M.M.; Schmitt, H.P.; Kunze, S.; Steiner, H.H. Clinical impact and functional aspects of tenascin-C expression during glioma progression. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, B.; Degen, M.; Ghaffari, A.; Hegi, M.E.; Hamou, M.F.; Ionescu, M.C.; Zweifel, C.; Tolnay, M.; Wasner, M.; Mergenthaler, S.; et al. Tenascin-C is a novel RBPJkappa-induced target gene for Notch signaling in gliomas. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.Y.; Kim, O.R.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, H.; Park, K.; Lee, C.T.; Kang, K.W.; Jeong, S. Selection and characterization of tenascin C targeting peptide. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, T.; Langlois, B.; Koczorowska, M.M.; Radwanska, A.; Sun, Z.; Hussenet, T.; Lefebvre, O.; Murdamoothoo, D.; Arnold, C.; Klein, A.; et al. Tenascin-C Orchestrates Glioblastoma Angiogenesis by Modulation of Pro- and Anti-angiogenic Signaling. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 2607–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dechantsreiter, M.A.; Planker, E.; Matha, B.; Lohof, E.; Holzemann, G.; Jonczyk, A.; Goodman, S.L.; Kessler, H. N-Methylated cyclic RGD peptides as highly active and selective alpha(V)beta(3) integrin antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 3033–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taga, T.; Suzuki, A.; Gonzalez-Gomez, I.; Gilles, F.H.; Stins, M.; Shimada, H.; Barsky, L.; Weinberg, K.I.; Laug, W.E. alpha v-Integrin antagonist EMD 121974 induces apoptosis in brain tumor cells growing on vitronectin and tenascin. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Bu, X.Y.; Khankaldyyan, V.; Gonzales-Gomez, I.; McComb, J.G.; Laug, W.E. Effect of the angiogenesis inhibitor Cilengitide (EMD 121974) on glioblastoma growth in nude mice. Neurosurgery 2006, 59, 1304–1312; discussion 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, T.J.; Taga, T.; Shimada, H.; Tabrizi, P.; Zlokovic, B.V.; Cheresh, D.A.; Laug, W.E. Preferential susceptibility of brain tumors to the antiangiogenic effects of an alpha(v) integrin antagonist. Neurosurgery 2001, 48, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kurozumi, K.; Ichikawa, T.; Onishi, M.; Fujii, K.; Date, I. Cilengitide treatment for malignant glioma: Current status and future direction. Neurol. Med. -Chir. 2012, 52, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Neyns, B.; Goldbrunner, R.; Schlegel, U.; Clement, P.M.; Grabenbauer, G.G.; Ochsenbein, A.F.; Simon, M.; Dietrich, P.Y.; et al. Phase I/IIa study of cilengitide and temozolomide with concomitant radiotherapy followed by cilengitide and temozolomide maintenance therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2712–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Gorlia, T.; Erridge, S.C.; Perry, J.; Hong, Y.K.; Aldape, K.D.; Lhermitte, B.; Pietsch, T.; Grujicic, D.; et al. Cilengitide combined with standard treatment for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylated MGMT promoter (CENTRIC EORTC 26071-22072 study): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2014, 15, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabors, L.B.; Fink, K.L.; Mikkelsen, T.; Grujicic, D.; Tarnawski, R.; Nam, D.H.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Salacz, M.; Ashby, L.; Zagonel, V.; et al. Two cilengitide regimens in combination with standard treatment for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma and unmethylated MGMT gene promoter: Results of the open-label, controlled, randomized phase II CORE study. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucci, M.; Stucci, S.; Silvestris, F. Does cilengitide deserve another chance? Lancet. Oncol. 2014, 15, e584-585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.R.; Hart, I.R.; Watson, A.R.; Welti, J.C.; Silva, R.G.; Robinson, S.D.; Da Violante, G.; Gourlaouen, M.; Salih, M.; Jones, M.C.; et al. Stimulation of tumor growth and angiogenesis by low concentrations of RGD-mimetic integrin inhibitors. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.Z.; Lin, Q.; Wong, H.L.; Shen, X.T.; Yang, W.; Xu, H.L.; Mao, K.L.; Tian, F.R.; Yang, J.J.; Xu, J.; et al. Glioma-targeted therapy using Cilengitide nanoparticles combined with UTMD enhanced delivery. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2016, 224, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, P.; Arakelian, A.; Chen, G.; Plunkett, M.L.; Beck, I.; Parry, G.C.; Donate, F.; Shaw, D.E.; Mazar, A.P.; Rabbani, S.A. A non-RGD-based integrin binding peptide (ATN-161) blocks breast cancer growth and metastasis in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoeltzing, O.; Liu, W.; Reinmuth, N.; Fan, F.; Parry, G.C.; Parikh, A.A.; McCarty, M.F.; Bucana, C.D.; Mazar, A.P.; Ellis, L.M. Inhibition of integrin alpha5beta1 function with a small peptide (ATN-161) plus continuous 5-FU infusion reduces colorectal liver metastases and improves survival in mice. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 104, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianfrocca, M.E.; Kimmel, K.A.; Gallo, J.; Cardoso, T.; Brown, M.M.; Hudes, G.; Lewis, N.; Weiner, L.; Lam, G.N.; Brown, S.C.; et al. Phase 1 trial of the antiangiogenic peptide ATN-161 (Ac-PHSCN-NH(2)), a beta integrin antagonist, in patients with solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paolillo, M.; Serra, M.; Schinelli, S. Integrins in glioblastoma: Still an attractive target? Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Horst, G.; van den Hoogen, C.; Buijs, J.T.; Cheung, H.; Bloys, H.; Pelger, R.C.; Lorenzon, G.; Heckmann, B.; Feyen, J.; Pujuguet, P.; et al. Targeting of alpha(v)-integrins in stem/progenitor cells and supportive microenvironment impairs bone metastasis in human prostate cancer. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cirkel, G.A.; Kerklaan, B.M.; Vanhoutte, F.; Van der Aa, A.; Lorenzon, G.; Namour, F.; Pujuguet, P.; Darquenne, S.; de Vos, F.Y.; Snijders, T.J.; et al. A dose escalating phase I study of GLPG0187, a broad spectrum integrin receptor antagonist, in adult patients with progressive high-grade glioma and other advanced solid malignancies. Investig. New Drugs 2016, 34, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeravagu, A.; Liu, Z.; Niu, G.; Chen, K.; Jia, B.; Cai, W.; Jin, C.; Hsu, A.R.; Connolly, A.J.; Tse, V.; et al. Integrin alphavbeta3-targeted radioimmunotherapy of glioblastoma multiforme. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7330–7339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugahara, K.N.; Teesalu, T.; Karmali, P.P.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Agemy, L.; Girard, O.M.; Hanahan, D.; Mattrey, R.F.; Ruoslahti, E. Tissue-penetrating delivery of compounds and nanoparticles into tumors. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendes, M.; Sousa, J.J.; Pais, A.; Vitorino, C. Targeted Theranostic Nanoparticles for Brain Tumor Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Kumar, S. CD44-mediated adhesion to hyaluronic acid contributes to mechanosensing and invasive motility. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2014, 12, 1416–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kijewska, M.; Kocyk, M.; Kloss, M.; Stepniak, K.; Korwek, Z.; Polakowska, R.; Dabrowski, M.; Gieryng, A.; Wojtas, B.; Ciechomska, I.A.; et al. The embryonic type of SPP1 transcriptional regulation is re-activated in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 16340–16355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pietras, A.; Katz, A.M.; Ekstrom, E.J.; Wee, B.; Halliday, J.J.; Pitter, K.L.; Werbeck, J.L.; Amankulor, N.M.; Huse, J.T.; Holland, E.C. Osteopontin-CD44 signaling in the glioma perivascular niche enhances cancer stem cell phenotypes and promotes aggressive tumor growth. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ellert-Miklaszewska, A.; Poleszak, K.; Pasierbinska, M.; Kaminska, B. Integrin Signaling in Glioma Pathogenesis: From Biology to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030888
Ellert-Miklaszewska A, Poleszak K, Pasierbinska M, Kaminska B. Integrin Signaling in Glioma Pathogenesis: From Biology to Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030888
Chicago/Turabian StyleEllert-Miklaszewska, Aleksandra, Katarzyna Poleszak, Maria Pasierbinska, and Bozena Kaminska. 2020. "Integrin Signaling in Glioma Pathogenesis: From Biology to Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030888
APA StyleEllert-Miklaszewska, A., Poleszak, K., Pasierbinska, M., & Kaminska, B. (2020). Integrin Signaling in Glioma Pathogenesis: From Biology to Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030888