Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase by Imidazo [1,5-α]pyridines—Synthesis and Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
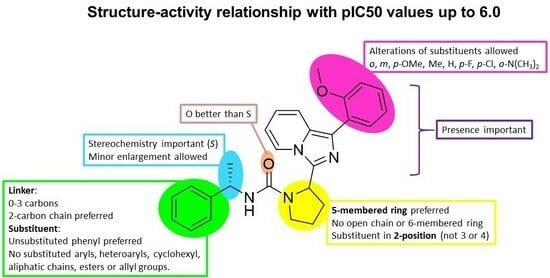
2. Results and Discussions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Procedure Grignard Reaction
3.1.1. (2-Methoxyphenyl)(pyridine-2-yl)methanamine (2a)
3.1.2. (3-Methoxyphenyl)(pyridin-2-yl)methanamine (2b)
3.1.3. (4-Methoxyphenyl)(pyridin-2-yl)methanamine (2c)
3.1.4. 2-(Amino(pyridin-2-yl)methyl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (2d)
3.1.5. Cyclohexyl(pyridin-2-yl)methanamine (2e)
3.2. General Procedure for Peptide Coupling
3.2.1. (2S)-Tert-butyl-2-(((2-methoxyphenyl)(pyridine-2-yl)methyl)carbamoyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (3a)
3.2.2. Tert-butyl-(2-(((2-methoxyphenyl)(pyridin-2-yl)methyl)amino)-2-oxoethyl)(methyl)carbamate (3c)
3.2.3. Tert-butyl-2-(((2-methoxyphenyl)(pyridin-2-yl)methyl)carbamoyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (3d)
3.2.4. Tert-butyl-2-(((3-methoxyphenyl)(pyridin-2-yl)methyl)carbamoyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (3e)
3.2.5. Tert-butyl-2-((cyclohexyl(pyridin-2-yl)methyl)carbamoyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (3h)
3.2.6. (S)-Tert-butyl-2-((pyridin-2-ylmethyl)carbamoyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (3i)
3.3. General Procedure Ring Closure Reaction
3.3.1. Tert-butyl-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (4a)
3.3.2. Tert-butyl-((1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)methyl)(methyl)carbamate (4b)
3.3.3. Tert-butyl-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)piperidine-1-carboxylate (4c)
3.3.4. Tert-butyl-2-(1-(3-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (4d)
3.3.5. Tert-butyl-2-(1-(4-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (4e)
3.3.6. Tert-butyl-2-(1-(2-(dimethylamino)phenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (4f)
3.3.7. Tert-butyl-2-(1-cyclohexylimidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (4g)
3.3.8. Tert-butyl-2-(imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate (4h)
3.4. General Procedure for Boc-Deprotection
3.4.1. 1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(pyrrolidin-2-yl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridine hydrochloride (5a)
3.4.2. 1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(piperidin-2-yl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridine hydrochloride (5c)
3.4.3. 1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(pyrrolidin-2-yl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridine hydrochloride (5d)
3.4.4. 1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(pyrrolidin-2-yl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridine hydrochloride (5e)
3.4.5. N,N-Dimethyl-2-(3-(pyrrolidin-2-yl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-1-yl)aniline hydrochloride (5f)
3.4.6. 1-Cyclohexyl-3-(pyrrolidin-2-yl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridine hydrochloride (5g)
3.4.7. 3-(Pyrrolidin-2-yl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridine hydrochloride (5h)
3.5. General Procedure for Acylation
2-(1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-((S)-1-phenylethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6a) [49]
3.6. Chiral Separation of Compound 6a
3.6.1. 2-(1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-((R)-1-phenylethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6b)
3.6.2. 2-(1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-(2-phenylpropan-2-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6c)
3.6.3. 2-(1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-((S)-1-phenylpropyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6d)
3.6.4. (S)-N-Benzyl-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6e)
3.6.5. 2-(1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-phenethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6f)
3.6.6. 2-(1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-(3-phenylpropyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6g)
3.6.7. N-(Furan-2-ylmethyl)-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6i)
3.6.8. N-(Cyclohexylmethyl)-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6j)
3.6.9. N-Butyl-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6k)
3.6.10. N-Allyl-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6l)
3.6.11. (S)-1-((1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)methyl)-1-methyl-3-(1-phenylethyl)urea (6m)
3.6.12. 2-(1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-((S)-1-phenylethyl)piperidine-1-carboxamide (6n)
3.6.13. 2-(1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-phenethylpiperidine-1-carboxamide (6o)
3.6.14. 2-(Imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-((S)-1-phenylethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6p)
3.6.15. (S)-N-(1-Phenylethyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6q)
3.6.16. 2-(1-(3-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-phenethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6r)
3.6.17. 2-(1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-phenethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6s)
3.6.18. 2-(1-(2-(Dimethylamino)phenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-phenethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6t)
3.6.19. 2-(1-Cyclohexylimidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-phenethylpyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6u)
3.6.20. N-Benzyl-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carbothioamide (6v)
3.6.21. N-(4-Fluorobenzyl)-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carbothioamide (6w)
3.6.22. 2-(1-(2-Methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)-N-phenethylpyrrolidine-1-carbothioamide (6x)
3.6.23. N-((R)-1-Hydroxy-3-phenylpropan-2-yl)-2-(1-(2-methoxyphenyl)imidazo [1,5-a]pyridin-3-yl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide (6h)
3.7. Biology
3.7.1. Overexpression of Human IRAP and Aminopeptidase N
3.7.2. Membrane Preparations
3.7.3. Concentration-Response Experiments in 96-Well Format
3.8. Mechanism of Action Studies for Compound 6a
3.9. Compound Profiling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braszko, J.; Kupryszewski, G.; Witczuk, B.; Wiśniewski, K. Angiotensin II-(3-8)-Hexapeptide Affects Motor Activity, Performance of Passive Avoidance and a Conditioned Avoidance Response in Rats. Neuroscience 1988, 27, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.W.; Miller-Wing, A.V.; Shaffer, M.J.; Higginson, C.; Wright, D.E.; Hanesworth, J.M.; Harding, J.W. Angiotensin II(3-8) (ANG IV) Hippocampal Binding: Potential Role in the Facilitation of Memory. Brain Res. Bull. 1993, 32, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.W.; Clemens, J.A.; Panetta, J.A.; Smalstig, E.B.; Weatherly, L.A.; Kramár, E.A.; Pederson, E.S.; Mungall, B.H.; Harding, J.W. Effects of LY231617 and Angiotensin IV on Ischemia-Induced Deficits in Circular Water Maze and Passive Avoidance Performance in Rats. Brain Res. 1996, 717, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.W.; Stubley, L.; Pederson, E.S.; Kramar, E.A.; Hanesworth, J.M.; Harding, J.W. Contributions of the Brain Angiotensin IV-AT4 Receptor Subtype System to Spatial Learning. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 3952–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Albiston, A.L.; Allen, A.M.; Mendelsohn, F.A.O.; Ping, S.E.; Barrett, G.L.; Murphy, M.; Morris, M.J.; McDowall, S.G.; Chai, S.Y. Effect of I.C.V. Injection of AT4 Receptor Ligands, NLE1-Angiotensin IV and LVV-Hemorphin 7, on Spatial Learning in Rats. Neuroscience 2004, 124, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braszko, J.J.; Wielgat, P.; Walesiuk, A. Effect of D(3) Dopamine Receptors Blockade on the Cognitive Effects of Angiotensin IV in Rats. Neuropeptides 2008, 42, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bundel, D.; Smolders, I.; Yang, R.; Albiston, A.L.; Michotte, Y.; Chai, S.Y. Angiotensin IV and LVV-Haemorphin 7 Enhance Spatial Working Memory in Rats: Effects on Hippocampal Glucose Levels and Blood Flow. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2009, 92, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiston, A.L.; Fernando, R.; Ye, S.; Peck, G.R.; Chai, S.Y. Alzheimer’s, Angiotensin IV and an Aminopeptidase. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiston, A.L.; McDowall, S.G.; Matsacos, D.; Sim, P.; Clune, E.; Mustafa, T.; Lee, J.; Mendelsohn, F.A.; Simpson, R.J.; Connolly, L.M. Evidence That the Angiotensin IV (AT(4)) Receptor Is the Enzyme Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48623–48626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpakali, A.; Saridakis, E.; Harlos, K.; Zhao, Y.; Kokkala, P.; Georgiadis, D.; Giastas, P.; Papakyriakou, A.; Stratikos, E. Ligand-Induced Conformational Change of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase: Insights on Catalytic Mechanism and Active Site Plasticity. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, J.W.; Cook, V.I.; Miller-Wing, A.V.; Hanesworth, J.M.; Sardinia, M.F.; Hall, K.L.; Stobb, J.W.; Swanson, G.N.; Coleman, J.K.M.; Wright, J.W. Identification of an AII(3–8) [AIV] Binding Site in Guinea Pig Hippocampus. Brain. Brain Res. 1992, 583, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, K.A.; Krebs, L.T.; Kramár, E.A.; Shaffer, M.J.; Harding, J.W.; Wright, J.W. Autoradiographic Identification of Brain Angiotensin IV Binding Sites and Differential C-Fos Expression Following Intracerebroventricular Injection of Angiotensin II and IV in Rats. Brain Res. 1995, 682, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, I.; Chai, S.Y.; Oldfield, B.J.; McKinley, M.J.; Casley, D.; Mendelsohn, F.A. Localization of Angiotensin IV Binding Sites to Motor and Sensory Neurons in the Sheep Spinal Cord and Hindbrain. Brain Res. 1995, 701, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Rogi, T.; Yamashiro, K.; Kodama, S.; Tsuruoka, N.; Hattori, A.; Takio, K.; Mizutani, S. Characterization of a Recombinant Soluble Form of Human Placental Leucine Aminopeptidase/Oxytocinase Expressed in Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Nagasaka, T.; Hattori, A.; Rogi, T.; Tsuruoka, N.; Mizutani, S.; Tsujimoto, M. Expression of Placental Leucine Aminopeptidase/Oxytocinase in Neuronal Cells and Its Action on Neuronal Peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 3259–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alescio-Lautier, B.; Paban, V.; Soumireu-Mourat, B. Neuromodulation of Memory in the Hippocampus by Vasopressin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 405, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallis, M.G.; Lankford, M.F.; Keller, S.R. Vasopressin Is a Physiological Substrate for the Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase IRAP. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderheyden, P.M.L. From Angiotensin IV Binding Site to AT4 Receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 302, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiston, A.L.; Mustafa, T.; McDowall, S.G.; Mendelsohn, F.A.; Lee, J.; Chai, S.Y. AT4 Receptor Is Insulin-Regulated Membrane Aminopeptidase: Potential Mechanisms of Memory Enhancement. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 14, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.Y.; Fernando, R.; Peck, G.; Ye, S.Y.; Mendelsohn, F.A.O.; Jenkins, T.A.; Albiston, A.L. What’s New in the Renin-Angiotensin System? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2728–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.R.; Scott, H.M.; Mastick, C.C.; Aebersold, R.; Lienhard, G.E. Cloning and Characterization of a Novel Insulin-Regulated Membrane Aminopeptidase from Glut4 Vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 23612–23618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragozzino, M.E.; Unick, K.E.; Gold, P.E. Hippocampal Acetylcholine Release during Memory Testing in Rats: Augmentation by Glucose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 4693–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, S.B.; D’Auria, M.; Martin, S.S.; Nguyen, C.; Kozma, L.M.; Luskey, K.L. The Amino Terminus of Insulin-Responsive Aminopeptidase Causes Glut4 Translocation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 23323–23327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiston, A.L.; Cacador, M.; Sinnayah, P.; Burns, P.; Chai, S.Y. Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase Inhibitors Do Not Alter Glucose Handling in Normal and Diabetic Rats. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 58, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Meriin, A.; Huang, G.; Kandror, K.V. Insulin-Responsive Amino Peptidase Follows the Glut4 Pathway but Is Dispensable for the Formation and Translocation of Insulin-Responsive Vesicles. Mol. Biol. Cell 2019, 30, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evnouchidou, I.; Papakyriakou, A.; Stratikos, E. A New Role for Zn(II) Aminopeptidases: Antigenic Peptide Generation and Destruction. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 3656–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zervoudi, E.; Saridakis, E.; Birtley, J.R.; Seregin, S.S.; Reeves, E.; Kokkala, P.; Aldhamen, Y.A.; Amalfitano, A.; Mavridis, I.M.; James, E. Rationally Designed Inhibitor Targeting Antigen-Trimming Aminopeptidases Enhances Antigen Presentation and Cytotoxic T-Cell Responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19890–19895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratikos, E. Regulating Adaptive Immune Responses Using Small Molecule Modulators of Aminopeptidases That Process Antigenic Peptides. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Brown, M.A. Genetic Associations and Functional Characterization of M1 Aminopeptidases and Immune-Mediated Diseases. Genes Immun. 2014, 15, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpakali, A.; Saridakis, E.; Harlos, K.; Zhao, Y.; Papakyriakou, A.; Kokkala, P.; Georgiadis, D.; Stratikos, E. Crystal Structure of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase with Bound Substrate Analogue Provides Insight on Antigenic Epitope Precursor Recognition and Processing. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 2842–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszuk, A.; Demaegdt, H.; Feytens, D.; Vanderheyden, P.; Vauquelin, G.; Tourwé, D. The Replacement of His(4) in Angiotensin IV by Conformationally Constrained Residues Provides Highly Potent and Selective Analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5612–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszuk, A.; Demaegdt, H.; Szemenyei, E.; Tóth, G.; Tymecka, D.; Misicka, A.; Karoyan, P.; Vanderheyden, P.; Vauquelin, G.; Tourwé, D. Beta-Homo-Amino Acid Scan of Angiotensin IV. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, A.; Van den Eynde, I.; Tourwé, D.; Vauquelin, G.; Tóth, G.; Mallareddy, J.R.; Poglitsch, M.; Van Ginderachter, J.A.; Vanderheyden, P.M.L. [3H]IVDE77, a Novel Radioligand with High Affinity and Selectivity for the Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 702, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakyriakou, A.; Zervoudi, E.; Theodorakis, E.A.; Saveanu, L.; Stratikos, E.; Vourloumis, D. Novel Selective Inhibitors of Aminopeptidases That Generate Antigenic Peptides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4832–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakyriakou, A.; Zervoudi, E.; Tsoukalidou, S.; Mauvais, F.-X.; Sfyroera, G.; Mastellos, D.C.; van Endert, P.; Theodorakis, E.A.; Vourloumis, D.; Stratikos, E. 3,4-Diaminobenzoic Acid Derivatives as Inhibitors of the Oxytocinase Subfamily of M1 Aminopeptidases with Immune-Regulating Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1524–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkala, P.; Mpakali, A.; Mauvais, F.-X.; Papakyriakou, A.; Daskalaki, I.; Petropoulou, I.; Kavvalou, S.; Papathanasopoulou, M.; Agrotis, S.; Fonsou, T.M.; et al. Optimization and Structure–Activity Relationships of Phosphinic Pseudotripeptide Inhibitors of Aminopeptidases That Generate Antigenic Peptides. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 9107–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vourloumis, D.; Mavridis, I.; Athanasoulis, A.; Temponeras, I.; Koumantou, D.; Giastas, P.; Mpakali, A.; Magrioti, V.; Leib, J.; van Endert, P.; et al. Discovery of Selective Nanomolar Inhibitors for Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase Based on α-Hydroxy-β-Amino Acid Derivatives of Bestatin. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 10098–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallberg, M. Targeting the Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase/AT4 Receptor for Cognitive Disorders. Drug News Perspect. 2009, 22, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, D.; Ziotopoulou, A.; Kaloumenou, E.; Lelis, A.; Papasava, A. The Discovery of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase (IRAP) Inhibitors: A Literature Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 585838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, M.; Larhed, M. From Angiotensin IV to Small Peptidemimetics Inhibiting Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 590855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwakarla, S.; Nylander, E.; Grönbladh, A.; Vanga, S.R.; Khan, Y.S.; Gutiérrez-De-Terán, H.; Ng, L.; Pham, V.; Sävmarker, J.; Lundbäck, T.; et al. Binding to and Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase by Macrocyclic Disulfides Enhances Spine Density. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, M.B.; Trommald, M.; Andersen, P. An Increase in Dendritic Spine Density on Hippocampal CA1 Pyramidal Cells Following Spatial Learning in Adult Rats Suggests the Formation of New Synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12673–12675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, A.; O’Connell, C.; Regan, C. Ultrastructural Analysis Reveals Avoidance Conditioning to Induce a Transient Increase in Hippocampal Dentate Spine Density in the 6 Hour Post-Training Period of Consolidation. Neuroscience 1998, 87, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, A.; O’Connell, C.; Murphy, K.J.; Regan, C.M. Transient Spine Density Increases in the Mid-Molecular Layer of Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus Accompany Consolidation of a Spatial Learning Task in the Rodent. Neuroscience 2000, 99, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.S.W.; Franke, T.F.; Gan, W.-B. Opposite Effects of Fear Conditioning and Extinction on Dendritic Spine Remodelling. Nature 2012, 483, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Yu, X.; Lu, J.; Zuo, Y. Repetitive Motor Learning Induces Coordinated Formation of Clustered Dendritic Spines in Vivo. Nature 2012, 483, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albiston, A.L.; Morton, C.J.; Ng, H.L.; Pham, V.; Yeatman, H.R.; Ye, S.; Fernando, R.N.; De Bundel, D.; Ascher, D.B.; Mendelsohn, F.A.O. Identification and Characterization of a New Cognitive Enhancer Based on Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 4209–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountford, S.J.; Albiston, A.L.; Charman, W.N.; Ng, L.; Holien, J.K.; Parker, M.W.; Nicolazzo, J.A.; Thompson, P.E.; Chai, S.Y. Synthesis, Structure-Activity Relationships and Brain Uptake of a Novel Series of Benzopyran Inhibitors of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. J. Med. Chem 2014, 57, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, K.; Rosenström, U.; Axelsson, H.; Konda, V.; Dahllund, L.; Otrocka, M.; Sigmundsson, K.; Nikolaou, A.; Vauquelin, G.; Hallberg, M.; et al. Identification of Drug-Like Inhibitors of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase Through Small-Molecule Screening. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2016, 14, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhade, S.R.; Rosenström, U.; Sävmarker, J.; Lundbäck, T.; Jenmalm-Jensen, A.; Sigmundsson, K.; Axelsson, H.; Svensson, F.; Konda, V.; Sköld, C.; et al. Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase (IRAP) by Arylsulfonamides. ChemistryOpen 2014, 3, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diwakarla, S.; Nylander, E.; Grönbladh, A.; Vanga, S.R.; Khan, Y.S.; Gutiérrez-De-Terán, H.; Sävmarker, J.; Ng, L.; Pham, V.; Lundbäck, T.; et al. Aryl Sulfonamide Inhibitors of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase Enhance Spine Density in Primary Hippocampal Neuron Cultures. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engen, K.; Sävmarker, J.; Rosenström, U.; Wannberg, J.; Lundbäck, T.; Jenmalm-Jensen, A.; Larhed, M. Microwave Heated Flow Synthesis of Spiro-Oxindole Dihydroquinazolinone Based IRAP Inhibitors. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2014, 18, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, K.; Vanga, S.R.; Lundbäck, T.; Agalo, F.; Konda, V.; Jensen, A.J.; Åqvist, J.; Gutiérrez-de-Terán, H.; Hallberg, M.; Larhed, M.; et al. Synthesis, Evaluation and Proposed Binding Pose of Substituted Spiro-Oxindole Dihydroquinazolinones as IRAP Inhibitors. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blat, Y. Non-Competitive Inhibition by Active Site Binders. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2010, 75, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temponeras, I.; Chiniadis, L.; Papakyriakou, A.; Stratikos, E. Discovery of Selective Inhibitor Leads by Targeting an Allosteric Site in Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, H.; Larhed, M.; Nilsson, P. Microwave Irradiation as a High-Speed Tool for Activation of Sluggish Aryl Chlorides in Grignard Reactions. Synlett 2005, 2005, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, M.C.; Herrera, R.P. Hydrogen Bonding Networks in Chiral Thiourea Organocatalysts: Evidence on the Importance of the Aminoindanol Moiety. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 5091–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenthall, J.T.; Foster, J.A.; Anderson, K.M.; Probert, M.R.; Howard, J.A.K.; Steed, J.W. Hydrogen Bonding Interactions with the Thiocarbonyl π-System. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 3202–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaegdt, H.; Vanderheyden, P.; De Backer, J.-P.; Mosselmans, S.; Laeremans, H.; Le, M.T.; Kersemans, V.; Michotte, Y.; Vauquelin, G. Endogenous Cystinyl Aminopeptidase in Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells: Characterization by [125I]Ang IV Binding and Catalytic Activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickström, M.; Larsson, R.; Nygren, P.; Gullbo, J. Aminopeptidase N (CD13) as a Target for Cancer Chemotherapy. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurina, S.; Sharifah, H.S.; Mohd, F.M.; Bohari, M.Y.; Ahmad, S.H. A Short and Elegant Synthesis of (±)-Streptopyrrolidine. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2013, 50, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernevik, J.; Bergström, F.; Novén, A.; Hulthe, J.; Fredlund, L.; Addison, D.; Holmgren, J.; Strömstedt, P.-E.; Rehnström, E.; Lundbäck, T. A Fully Integrated Assay Panel for Early Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics Profiling. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2020, 18, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Compound | Structure [a] | IC50 [b] (µM) | pIC50 [c] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1a |  | 2.9 | 5.5 (1) |
| 1b |  | 2.9 | 5.5 ± 0.2 (2) |
| 1c |  | 7.9 | 5.1 ± 0.05 (2) |
| 1d |  | >125 | <3.9 (2) |
| 1e |  | 100 | 4.0 ± 0.3 (2) |
| 1f |  | >125 | <3.9 (2) |
| 1g |  | 100 | 4.0 ± 0.2 (2) |
| 1h |  | 40 | 4.4 ± 0.1 (2) |
| 1i |  | 79 | 4.1 ± 0.1 (2) |
| 1j |  | >125 | <3.9 (1) |
| 1k |  | 63 | 4.2 ± 0.2 (2) |
| 1l |  | 50 | 4.3 (1) |
| 1m |  | >125 | <3.9 (2) |
| 1n |  | 63 | 4.2 ± 0.06 (2) |
| 1o |  | >125 | <3.9 (1) |
| 1p |  | >125 | <3.9 (1) |
| 1q |  | >125 | <3.9 (1) |
| 1r |  | >125 | <3.9 (1) |
| 1s |  | >125 | <3.9 (1) |
| 1t |  | Inactive | inactive (1) |
| 1u |  | >125 | <3.9 (1) |
| 1v |  | Inactive | inactive (1) |
| 1w |  | >125 | <3.9 (1) |
| Compounds | Structure | IC50 [a] (µM) | pIC50 [b] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6a |  | 2.0 | 5.7 ± 0.1 (28) |
| 6a_dia1 | Data | 16 | 4.8 ± 0.2 (4) |
| 6a_dia2 | Data | 1.0 | 6.0 ± 0.1 (4) |
| 6b |  | 40 | 4.4 ± 0.1 (8) |
| 6c |  | 32 | 4.5 ± 0.07 (2) |
| 6d |  | 4.0 | 5.4 ± 0.04 (3) |
| 6e |  | 50 | 4.3 ± 0.2 (3) |
| 6f |  | 32 | 4.5 ± 0.1 (3) |
| 6g |  | 63 | 4.2 ± 0.3 (3) |
| 6h |  | 63 | 4.2 ± 0.2 (3) |
| 6i |  | 79 | 4.1 ± 0.03 (2) |
| 6j |  | 16 | 4.8 ± 0.2 (4) |
| 6k |  | 63 | 4.2 ± 0.04 (2) |
| 6l |  | 40 | 4.4 ± 0.4 (4) |
| 6m |  | >125 | <3.9 (3) |
| 6n |  | >125 [c] | <3.9 (3) [c] |
| 6o |  | >125 [c] | <3.9 (3) [c] |
| 6p |  | >125 | <3.9 (3) |
| 6q |  | Inactive | Inactive (3) |
| 6r |  | 8.7 | 5.06 ± 0.07 (3) |
| 6s |  | 40 | 4.4 ± 0.08 (2) |
| 6t |  | 63 | 4.2 ± 0.09 (2) |
| 6u |  | 40 | 4.4 ± 0.5 (3) |
| 6v |  | >125 [c] | <3.9 (3) [c] |
| 6w |  | >125 [c] | <3.9 (3) [c] |
| 6x |  | >125 [c] | <3.9 (3) [c] |
| Compounds | LogD7.4 | Sol. [a] | HLM Clint [b] | HLM t ½ | Rat hep. Clint [c] | Rat hep. t ½ | PPB [d] | Plasma Stab [e] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6a_dia1 | 2.8 ± 0.7 | 40–124 [f] | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 102 ± 5 |
| 6a_dia2 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 76 ± 14 [g] | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 104 ± 3 |
| 6e | 2.7 ± 0.4 | 2.2–11 [f] | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 97 ± 3 |
| 6m | 2.9 ± 0.6 | 55 ± 12 | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 99 ± 5 |
| 6v | 3.3 ± 0.4 | 0.6–2 [f] | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | >300 [h] | <2.3 [h] | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 76 ± 6 |
| Compounds | CHO IRAP [a] IC50 (µM)/pIC50 | hIRAP [b] IC50 (µM)/pIC50 | sIRAP [c] IC50 (µM)/pIC50 | APN [d] IC50 (µM)/pIC50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6a | 2.0/5.7 ± 0.1 (28) | 1.3/5.9 ± 0.05 (2) | 1.0/6.0 (1) | inactive (2) |
| 6a_dia1 | 16/4.8 ± 0.2 (4) | 6.3/5.2 (1) | - | - |
| 6a_dia2 | 1.0/6.0 ± 0.1 (4) | 1.0/6.0 (1) | - | inactive (1) |
| 6b | 40/4.4 ± 0.1 (8) | 50/4.3 ± 0.05 (2) | - | inactive (2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Engen, K.; Lundbäck, T.; Yadav, A.; Puthiyaparambath, S.; Rosenström, U.; Gising, J.; Jenmalm-Jensen, A.; Hallberg, M.; Larhed, M. Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase by Imidazo [1,5-α]pyridines—Synthesis and Evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052516
Engen K, Lundbäck T, Yadav A, Puthiyaparambath S, Rosenström U, Gising J, Jenmalm-Jensen A, Hallberg M, Larhed M. Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase by Imidazo [1,5-α]pyridines—Synthesis and Evaluation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(5):2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052516
Chicago/Turabian StyleEngen, Karin, Thomas Lundbäck, Anubha Yadav, Sharathna Puthiyaparambath, Ulrika Rosenström, Johan Gising, Annika Jenmalm-Jensen, Mathias Hallberg, and Mats Larhed. 2024. "Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase by Imidazo [1,5-α]pyridines—Synthesis and Evaluation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 5: 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052516
APA StyleEngen, K., Lundbäck, T., Yadav, A., Puthiyaparambath, S., Rosenström, U., Gising, J., Jenmalm-Jensen, A., Hallberg, M., & Larhed, M. (2024). Inhibition of Insulin-Regulated Aminopeptidase by Imidazo [1,5-α]pyridines—Synthesis and Evaluation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(5), 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25052516