Implementing and Monitoring the Use of Artificial Canopy Bridges by Mammals and Birds in an Indonesian Agroforestry Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Artificial Bridge Construction and Monitoring
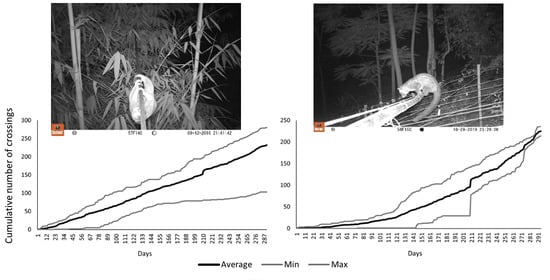
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Busch, J.; Ferretti-Gallon, K. What drives deforestation and what stops it? A meta-analysis. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy. 2017, 11, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dixo, M.; Metzger, J.P.; Morgante, J.S.; Zamudio, K.R. Habitat fragmentation reduces genetic diversity and connectivity among toad populations in the Brazilian Atlantic Coastal Forest. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.C.; Walker, F.M.; Goldingay, R.L.; Ball, T.; Van Der Ree, R. Degree of landscape fragmentation influences genetic isolation among populations of a gliding mammal. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 26651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokochi, K.; Chambers, B.K.; Bencini, R. An artificial waterway and road restrict movements and alter home ranges of endangered arboreal marsupial. J. Mammal. 2015, 96, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cappa, F.M.; Borghi, C.E.; Giannoni, S.M. How roads affect the spatial use of the guanaco in a South American protected area: Human connectivity vs animal welfare. Diversity 2019, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Austin, K.G.; Schwantes, A.; Gu, Y.; Kasibhatla, P.S. What causes deforestation in Indonesia? Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 024007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode-Margono, E.J.; Voskamp, A.; Spaan, D.; Lehtinen, J.K.; Roberts, P.D.; Nijman, V.; Nekaris, K.A.I. Records of small carnivores and of medium-sized nocturnal mammals on Java, Indonesia. Small Carniv. Conserv. 2014, 50, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sunderlin, W.D.; Resosudarmo, I.A.P. The effect of population and migration on forest cover in Indonesia. J. Environ. Dev. 1999, 8, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekaris, K.A.I.; Poindexter, S.; Reinhardt, K.D.; Siguad, M.; Cabana, F.; Wirdateti, W.; Nijman, V. Coexistence between Javan slow lorises (Nycticebus javanicus) and humans in a dynamic agroforestry landscape in West Java, Indonesia. Int. J. Primatol. 2017, 38, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gregory, T.; Carrasco-Rueda, F.; Alonso, A.; Kolowski, J.; Diechmann, J.L. Natural canopy bridges effectively mitigate tropical forest fragmentation for arboreal mammals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birot, H.; Campera, M.; Imron, M.A.; Nekaris, K.A.I. Artificial canopy bridges improve connectivity in fragmented landscapes: The case of Javan slow lorises in an agroforest environment. Am. J. Primat. 2020, 82, 23076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scales, B.R.; Marsden, S.J. Biodiversity in small-scale tropical agroforests: A review of species richness and abundance shifts and the factors influencing them. Environ. Conserv. 2008, 35, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokochi, K.; Bencini, R. A remarkably quick habituation and high use of a rope bridge by an endangered marsupial, the western ringtail possum. Nat. Conserv. 2015, 11, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldingay, R.L.; Taylor, B.D. Can field trials improve the design of road-crossing structures for gliding mammals? Ecol. Res. 2017, 32, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbuena, D.; Alonso, A.; Panta, M.; Garcia, A.; Gregory, T. Mitigating tropical forest fragmentation with natural and semi-artificial canopy bridges. Diversity 2019, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spaan, D.; Williams, M.; Wirdateti, W.; Semiadi, G.; Nekaris, K.A.I. Use of raised plastic water-pipes by common palm civet Paradoxurus hermaphroditus for habitat connectivity in an anthropogenic environment in West Java, Indonesia. Small Carniv. Conserv. 2014, 51, 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Veron, G.; Patou, M.L.; Tóth, M.; Goonatilake, M.; Jennings, A.P. How many species of Paradoxurus civets are there? New insights from India and Sri Lanka. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2015, 53, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, N.; Goosem, M.; Marsh, H.; Cohen, M.; Wilson, R. Using canopy bridges to link habitat for arboreal mammals: Successful trials in the Wet Tropics of Queensland. Aust. Mammal. 2011, 33, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, A.; Clevenger, A.P.; Huijser, M.; Neale, G. An overview of methods and approaches for evaluating the effectiveness of wildlife crossing structures: Emphasizing the science in applied science. In Proceedings of the 2003 USA International Conference on Ecology and Transportation, New York, NY, USA, 24–29 August 2003; Irwin, C.L., Garrett, P., McDermott, K.P., Eds.; Center for Transportation and the Environment: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2003; pp. 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.N.; Vickers, S.H.; Abu-Bakar, M.S.; Goossens, B. Small carnivores of the Lower Kinabatangan wildlife sanctuary, Sabah, Borneo, including a new locality for the otter civet Cynogale bennetti. Small Carniv. Conserv. 2016, 54, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Meek, P.D.; Ballard, G.; Fleming, P.J.S. The pitfalls of wildlife camera trapping as a survey tool in Australia. Aust. Mammal. 2015, 37, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Bridge | Days of Monitoring | Mean Height (m) | Length (m) | Crossings | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Javan Slow Loris | Javan Palm Civet | Other Mammals | Total | ||||
| Waterline 1 | 312 | 4.0 | 17.4 | 132 | 257 | 64 | 453 |
| Waterline 2 | 294 | 3.8 | 51.3 | 283 | 214 | 60 | 557 |
| Waterline 3 | 209 | 5.0 | 72.3 | 118 | 29 | 3 | 150 |
| Waterline 4 | 271 | 7.0 | 74.5 | 266 | 218 | 56 | 540 |
| Waterline 5 | 290 | 3.0 | 74.0 | 280 | 220 | 62 | 562 |
| Rubber 1 | 276 | 5.5 | 54.9 | 108 | 0 | 9 | 117 |
| Rubber 2 | 87 | 3.5 | 18.4 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 19 |
| Rubber 3 | 266 | 4.0 | 13.7 | 153 | 0 | 1 | 154 |
| Rubber 4 | 113 | 4.5 | 14.3 | 58 | 0 | 0 | 58 |
| Rubber 5 | 88 | 5.5 | 13.9 | 20 | 0 | 5 | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nekaris, K.A.I.; Handby, V.; Campera, M.; Birot, H.; Hedger, K.; Eaton, J.; Imron, M.A. Implementing and Monitoring the Use of Artificial Canopy Bridges by Mammals and Birds in an Indonesian Agroforestry Environment. Diversity 2020, 12, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100399
Nekaris KAI, Handby V, Campera M, Birot H, Hedger K, Eaton J, Imron MA. Implementing and Monitoring the Use of Artificial Canopy Bridges by Mammals and Birds in an Indonesian Agroforestry Environment. Diversity. 2020; 12(10):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100399
Chicago/Turabian StyleNekaris, K. A. I., Victoria Handby, Marco Campera, Hélène Birot, Katherine Hedger, James Eaton, and Muhammad Ali Imron. 2020. "Implementing and Monitoring the Use of Artificial Canopy Bridges by Mammals and Birds in an Indonesian Agroforestry Environment" Diversity 12, no. 10: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100399
APA StyleNekaris, K. A. I., Handby, V., Campera, M., Birot, H., Hedger, K., Eaton, J., & Imron, M. A. (2020). Implementing and Monitoring the Use of Artificial Canopy Bridges by Mammals and Birds in an Indonesian Agroforestry Environment. Diversity, 12(10), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12100399