“Candidatus Mystax nordicus” Aggregates with Mitochondria of Its Host, the Ciliate Paramecium nephridiatum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures and Live-Cell Experiments
2.2. Killer-Trait Assessment and Experimental Infection
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.5. Molecular Characterization
2.6. Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH)
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Accession Numbers
3. Results
3.1. Host Identification
3.2. Morphology and Biology of the Endosymbionts
3.3. Fine Structure of the Endosymbionts
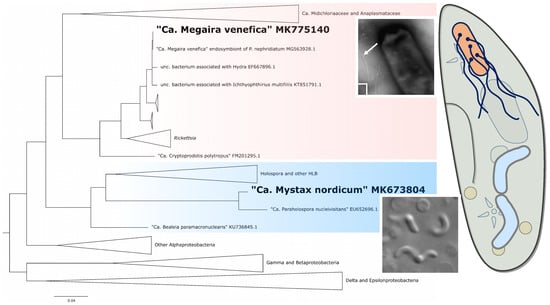
3.4. Molecular Characterization of the Endosymbionts
4. Discussion
4.1. RS- and CS-Bacteria Are Endosymbionts from the Past
4.2. Phylogeny and Taxonomy
4.3. Biological Peculiarities of “Ca. Mystax nordicus”
4.4. Description of "Candidatus Mystax nordicus”
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fenchel, T.; Perry, T.; Thane, A. Anaerobiosis and symbiosis with bacteria in free-living ciliates. J. Protozool. 1977, 24, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görtz, H.-D. Microbial infections in free-living Protozoa. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 30, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokin, S.I. Frequency and biodiversity of symbionts in representatives of the main classes of Ciliophora. Eur. J. Protistol. 2012, 48, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweikert, M.; Gortz, H.-D.; Fujishima, M. Symbiotic associations between Ciliates and prokaryotes. In The Prokaryotes, 4th ed.; Rosenberg, E., DeLong, E.F., Stackebrandt, E., Lory, S., Thompson, F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 427–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, M.; Sabaneyeva, E.; Lanzoni, O.; Lebedeva, N.; Floriano, A.M.; Gaiarsa, S.; Benken, K.; Modeo, L.; Bandi, C.; Potekhin, A.; et al. Deianiraea, an extracellular bacterium associated with the ciliate Paramecium, suggests an alternative scenario for the evolution of Rickettsiales. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2280–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Qing, Y.; Zou, S.; Fu, R.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. Protist-bacteria associations: Gammaproteobacteria and Alphaproteobacteria are prevalent as digestion-resistant bacteria in ciliated protozoa. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fokin, S.; Serra, V. The Hidden Biodiversity of Ciliate-Endosymbionts Systems. JSM Microbiol. 2014, 2, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Lanzoni, O.; Fokin, S.; Lebedeva, N.; Migunova, A.; Petroni, G.; Potekhin, A. Rare freshwater ciliate Paramecium chlorelligerum Kahl, 1935, and its macronuclear symbiotic bacterium “Candidatus Holospora parva”. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, V.; Fokin, S.I.; Castelli, M.; Basuri, C.K.; Nitla, V.M.; Verni, F.; Sandeep, B.V.; Kalavathi, C.; Petroni, G. “Candidatus Gortzia shahrazadis”, a novel endosymbiont of Paramecium multimicronucleatum and revision of the biogeographical distribution of Holospora-like bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senra, M.V.; Dias, R.J.; Castelli, M.; Silva-Neto, I.D.; Verni, F.; Soares, C.A.; Petroni, G. A house for two—Double bacterial infection in Euplotes woodruffi Sq1 (Ciliophora, Euplotia) sampled in Southeastern Brazil. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, C.; Sigona, C.; Hahn, M.; Petroni, G.; Fujishima, M. High degree of specificity in the association between symbiotic betaproteobacteria and the host Euplotes (Ciliophora, Euplotia). Eur. J. Protistol. 2017, 59, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, M.; Serra, V.; Senra, M.V.X.; Basuri, C.K.; Soares, C.A.G.; Fokin, S.I.; Modeo, L.; Petroni, G. The hidden world of Rickettsiales symbionts: “Candidatus Spectririckettsia obscura,” a novel bacterium found in Brazilian and Indian Paramecium caudatum. Microb. Ecol. 2018, 77, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokin, S.; Serra, V.; Ferrantini, F.; Modeo, L.; Petroni, G. “Candidatus Hafkinia simulans” gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel Holospora-like bacterium from the macronucleus of the rare brackish water ciliate Frontonia salmastra (Oligohymenophorea, Ciliophora): Multidisciplinary characterization of the new endosymbiont and its host. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 77, 1092–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusch, J.; Czubatinski, L.; Wegmann, S.; Hubner, M.; Alter, M.; Albrecht, P. Competitive advantages of Caedibacter-infected Paramecia. Protist 2002, 153, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gast, R.; Sanders, R.; Caron, D. Ecological strategies of protists and their symbiotic relationships with prokaryotic microbes. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidelet, T.; Koella, J.C.; Kaltz, O. Effects of shortened host life span on the evolution of parasite life history and virulence in a microbial host-parasite system. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowack, E.; Melkonian, M. Endosymbiotic associations within protists. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2010, 365, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vannini, C.; Boscaro, V.; Ferrantini, F.; Benken, K.A.; Mironov, T.I.; Schweikert, M.; Gortz, H.-D.; Fokin, S.I.; Sabaneyeva, E.; Petroni, G. Flagellar movement in two bacteria of the family Rickettsiaceae: A re-evaluation of motility in an evolutionary perspective. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Gómez, S.A.; Hess, S.; Burger, G.; Lang, B.F.; Susko, E.; Slamovits, C.H.; Roger, A.J. An updated phylogeny of the Alphaproteobacteria reveals that the parasitic Rickettsiales and Holosporales have independent origins. eLife 2019, 8, e42535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassera, D.; Lo, N.; Epis, S.; D’Auria, G.; Montagna, M.; Comandatore, F.; Horner, D.; Peretó, J.; Luciano, A.; Franciosi, F.; et al. Phylogenomic evidence for the presence of a flagellum and cbb3 oxidase in the free-living mitochondrial ancestor. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, B.S.; Shotts, E.B.; Feeley, J.C.; Gorman, G.W.; Martin, W.T. Proliferation of Legionella pneumophila as an intracellular parasite of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena pyriformis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 47, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barker, J.; Brown, M.R. Trojan horses of the microbial world: Protozoa and the survival of bacterial pathogens in the environment. Microbiology 1994, 140, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrantini, F.; Fokin, S.I.; Vannini, C.; Modeo, L.; Verni, F.; Petroni, G. Ciliates as natural hosts of many novel Rickettsia-like bacteria. Protistology 2007, 5, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Fokin, S.I.; Schrallhammer, M.; Chiellini, C.; Verni, F.; Petroni, G. Free-living ciliates as potential reservoirs for eukaryotic parasites: Occurrence of a trypanosomatid in the macronucleus of Euplotes encysticus. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, K.; Nakao, R.; Fujishima, M.; Tachibana, M.; Shimizu, T.; Watarai, M. Ciliate Paramecium is a natural reservoir of Legionella pneumophila. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, S.; Sabaneyeva, E. Euryhaline paramecia (Ciliophora, Peniculina) of the Barents and the White Sea and its endobionts. Ecology, Reproduction and Guards Bioresources of the Seas of Northern Europe. In Proceedings of the III All-Union Conference, Murmansk, USSR, 16–21 July 1990; pp. 139–141. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Smurov, A.; Fokin, S. Resistance of Paramecium caudatum infected with endonuclear bacteria Holospora against salinity impact. Proc. Zool. Inst. RAS 1998, 276, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Fokin, S.I. Bacterial endocytobionts of Ciliophora and their interactions with the host cell. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2004, 236, 181–249. [Google Scholar]
- Görtz, H.-D.; Fokin, S.I. Diversity of endosymbiotic bacteria in Paramecium. In Endosymbionts in Paramecium; Fujishima, M., Ed.; Microbiology Monographs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 12, pp. 131–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscaro, V.; Schrallhammer, M.; Benken, K.A.; Krenek, S.; Szokoli, F.; Berendonk, T.U.; Schweikert, M.; Verni, F.; Sabaneyeva, E.V.; Petroni, G. Rediscovering the genus Lyticum multiflagellated symbionts of the order Rickettsiales. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gelei, J. Uj Paramecium szeged kornyekerol. Paramecium nephridiatum nov. sp. Állat. Közlem. 1925, 22, 121–162, (In Hungarian with German summary). [Google Scholar]
- Fokin, S.I.; Stoeck, T.; Schmidt, H.J. Rediscovery of Paramecium nephridiatum Gelei, 1925 and its characteristics. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1999, 46, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, S.I. Bacterial endobionts of the ciliate Paramecium woodruffi. III. Endobionts of the cytoplasm. Tsitologia 1989, 31, 964–969, (In Russian with English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Skovorodkin, I.N. A device for immobilizing biological objects in the light microscope studies. Tsitologia 1990, 32, 301–302, (In Russian with English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Szokoli, F.; Sabaneyeva, E.; Castelli, M.; Krenek, S.; Schrallhammer, M.; Soares, C.A.G.; Da Silva-Neto, I.D.; Berendonk, T.U.; Petroni, G. “Candidatus Fokinia solitaria”, a novel “stand-alone” symbiotic lineage of Midichloriaceae (Rickettsiales). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0145743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, S.I. Paramecium genus: Biodiversity, some morphological features and the key to the main morphospecies discrimination. Protistology 2010, 6, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Petroni, G.; Dini, F.; Verni, F.; Rosati, G. A molecular approach to the tangled intrageneric relationships underlying phylogeny in Euplotes (Ciliophora, Spirotrichea). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2002, 22, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlin, L.; Elwood, H.J.; Stickel, S.; Sogin, M.L. The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Gene 1988, 7, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosati, G.; Modeo, L.; Melai, M.; Petroni, G.; Verni, F. A multidisciplinary approach to describe protists: A morphological, ultrastructural, and molecular study on Peritromus kahli Villeneuve-Brachon, 1940 (Ciliophora, Heterotrichea). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, C.; Rosati, G.; Verni, F.; Petroni, G. Identification of the bacterial endosymbionts of the marine ciliate Euplotes magnicirratus (Ciliophora, Hypotrichia) and proposal of «Candidatus Devosia euplotis». Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Cardenas, E.; Fish, J.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S.; McGarrell, D.M.; Marsh, T.; Garrity, G.M.; et al. The Ribosomal Database Project: Improved Alignments and New Tools for rRNA Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 40, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manz, W.; Amann, R.; Ludwig, W.; Wagner, M.; Schleifer, K.-H. Phylogenetic oligodeoxynucleotide probes for the major subclasses of proteobacteria: Problems and solutions. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1992, 15, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, R.I.; Binder, B.J.; Olson, R.J.; Chisholm, S.W.; Devereux, R.; Stahl, D.A. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1919–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nawrocki, E.P. Structural RNA Homology Search and Alignment Using Covariance Models. Ph.D. Thesis, Washington University in Saint Louis, School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FigTree. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 8 May 2020).
- Lanzoni, O.; Castelli, M.; Sabaneyeva, E.; Lebedeva, N.; Potekhin, A.; Petroni, G. Diversity and environmental distribution of the cosmopolitan endosymbiont “Candidatus Megaira”. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boscaro, V.; Petroni, G.; Ristori, A.; Verni, F.; Vannini, C. “Candidatus Defluviella procrastinata” and “Candidatus Cyrtobacter zanobii”, two novel ciliate endosymbionts belonging to the “Midichloria clade”. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Görtz, H.-D.; Dieckman, J. Life cycle and infectivity of Holospora elegans, a micronucleus specific symbiont of Paramecium caudatum Ehrenberg. Protistol 1980, 16, 591–603. [Google Scholar]
- Boscaro, V.; Fokin, S.I.; Schrallhammer, M.; Schweikert, M.; Petroni, G. Revised systematics of Holospora-like bacteria and characterization of “Candidatus Gortzia infective”, a novel macronuclear symbiont of Paramecium jenningsi. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potekhin, A.; Schweikert, M.; Nekrasova, I.; Vitali, V.; Schwarzer, S.; Anikina, A.; Kaltz, O.; Petroni, G.; Schrallhammer, M. Complex life cycle, broad host range and adaptation strategy of the intranuclear Paramecium symbiont Preeria caryophila comb. Nov. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschbach, E.; Pfannkuchen, M.; Schweikert, M.; Drutschmann, D.; Brümmer, F.; Fokin, S.; Ludwig, W.; Görtz, H.D. “Candidatus Paraholospora nucleivisitans”, an intracellular bacterium in Paramecium sexaurelia shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus of its host. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 32, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szokoli, F.; Castelli, M.; Sabaneyeva, E.; Schrallhammer, M.; Krenek, S.; Doak, T.G.; Berendonk, T.U.; Petroni, G. Disentangling the taxonomy of Rickettsiales and description of two novel symbionts (“Candidatus Bealeia paramacronuclearis” and “Candidatus Fokinia cryptica”) sharing the cytoplasm of the ciliate protist Paramecium biaurelia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 7236–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumler, J.S.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsiales. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Whitman, W.B., Rainey, F., Kämpfer, P., Trujillo, M., Chun, J., De Vos, P., Hedlund, B., Dedyshed, S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yarza, P.; Yilmaz, P.; Pruesse, E.; Glöckner, F.O.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H.; Whitman, W.B.; Euzéby, J.; Amann, R.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, R.A.; Garrity, G.M.; Scott, J.J.; Amend, J.P.; Nealson, K.H.; Emerson, D. A genus definition for Bacteria and Archaea based on a standard genome relatedness index. mBio 2020, 11, e02475-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Przyboś, E.; Barth, D.; Berendonk, T.U. Paramecium sexaurelia–intra-specific polymorphism and relationships with other Paramecium aurelia spp., revealed by cytochrome b sequence data. Folia Biol. 2009, 58, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osellame, L.D.; Blacker, T.S.; Duchen, M.R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of mitochondrial function. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 26, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garushyants, S.K.; Beliavskaia, A.Y.; Malko, D.B.; Logacheva, M.D.; Rautian, M.S.; Gelfand, M.S. Comparative genomic analysis of Holospora spp., intranuclear symbionts of Paramecia. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokin, S.I.; Schweikert, M.; Görtz, H.-D.; Fujishima, M. Bacterial endocytobionts of Ciliophora. Diversity and some interactions with the host. Eur. J. Protistol. 2003, 39, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassera, D.; Beninati, T.; Bandi, C.; Bouman, E.A.P.; Sacchi, L.; Fabbi, M.; Lo, N. “Candidatus Midichloria mitochondrii”, an endosymbiont of the tick Ixodes ricinus with a unique intramitochondrial lifestyle. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 58, 2535–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashyreva, D.; Prokopchuk, G.; Votýpka, J.; Yabuki, A.; Horák, A.; Lukeš, J. Life cycle, ultrastructure, and phylogeny of new diplonemids and their endosymbiotic bacteria. mBio 2018, 9, e02447-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeshita, K.; Yamada, T.; Kawahara, Y.; Narihiro, T.; Ito, M.; Kamagata, Y.; Shinzato, N. Tripartite Symbiosis of an Anaerobic Scuticociliate with two Hydrogenosome-Associated Endosymbionts, a Holospora-related Alphaproteobacterium and a Methanogenic Archaeon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00854-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Lin, C.C.J.; Hu, G.; Wang, M.C. ‘Inside Out’–a dialogue between mitochondria and bacteria. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ratzka, C.; Gross, R.; Feldhaar, H. Endosymbiont tolerance and control within insect hosts. Insects 2012, 3, 553–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher, R.; Henry, L.; Cornwallis, C.; Kiers, E.T.; West, S.A. The evolution of host-symbiont dependence. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korotaev, A.; Benken, K.; Sabaneyeva, E. “Candidatus Mystax nordicus” Aggregates with Mitochondria of Its Host, the Ciliate Paramecium nephridiatum. Diversity 2020, 12, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12060251
Korotaev A, Benken K, Sabaneyeva E. “Candidatus Mystax nordicus” Aggregates with Mitochondria of Its Host, the Ciliate Paramecium nephridiatum. Diversity. 2020; 12(6):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12060251
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorotaev, Aleksandr, Konstantin Benken, and Elena Sabaneyeva. 2020. "“Candidatus Mystax nordicus” Aggregates with Mitochondria of Its Host, the Ciliate Paramecium nephridiatum" Diversity 12, no. 6: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12060251
APA StyleKorotaev, A., Benken, K., & Sabaneyeva, E. (2020). “Candidatus Mystax nordicus” Aggregates with Mitochondria of Its Host, the Ciliate Paramecium nephridiatum. Diversity, 12(6), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12060251