Epibiotic Communities of Common Crab Species in the Coastal Barents Sea: Biodiversity and Infestation Patterns
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Infestation Patterns
2.1. Hyas araneus
2.2. Lithodes maja
2.3. Paralithodes camtschaticus
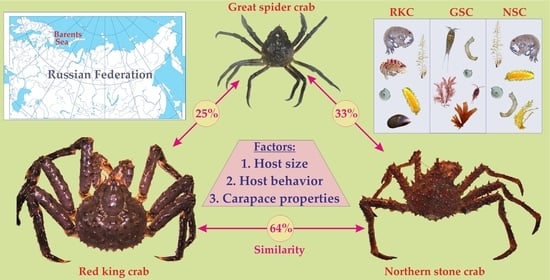
3. Comparison of Epibiotic Communities
3.1. General Patterns
3.2. Factors: Ecology and Behavior of Hosts
3.3. Factors: Ecology and Behavior of Epibionts
3.4. Factors: Host Size and Carapace Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuznetsov, V.V. The Biology of Abundant and the Most Common Species of Crustaceans in the Barents and White Seas; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1964. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) fisheries in Russian waters: Historical review and present status. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2018, 28, 331–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Bichkaeva, F.A.; Baranova, N.F.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fatty acid composition of the Barents Sea red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) leg meat. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 98, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomareva, T.; Timchenko, M.; Filippov, M.; Lapaev, S.; Sogorin, E. Prospects of red king crab hepatopancreas processing: Fundamental and applied biochemistry. Recycling 2021, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epifauna associated with the northern stone crab Lithodes maia in the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2008, 31, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Limb autotomy patterns in Paralithodes camtschaticus (Tilesius, 1815), an invasive crab, in the coastal Barents Sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 377, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Population dynamics of the invasive lithodid crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, in a typical bay of the Barents Sea. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Leborans, G. Epibiosis in Crustacea: An overview. Crustaceana 2010, 83, 549–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Rivera, B.S.; Castro-Mondragon, H.; Kuk-Dzul, J.G.; Flores-Rodríguez, P.; Flores-Garza, R. Diversity of epibionts associated with Lepidochelys olivacea (Eschscholtz 1829) sea turtles nesting in the Mexican South Pacific. Animals 2021, 11, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frahm, J.L.; Brooks, W.R. The use of chemical cues by sargassum shrimps Latreutes fucorum and Leander tenuicornis in establishing and maintaining a symbiosis with the host sargassum algae. Diversity 2021, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.D.; McDermott, J.J. Hermit crab biocoenoses; A worldwide review of the diversity and natural history of hermit crab associates. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 305, 1–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, R.N.; Valentich-Scott, P.; Hilgers, M.; Singh, R. New host record for the California mussel Mytilus californianus (Bivalvia, Mytilidae), epibiotic on the pacific sand crab Emerita analoga (Decapoda, Hippidae) from Monterey Bay, California (U.S.A.). Crustaceana 2017, 90, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gier, W.; Becker, C.A. Review of the ecomorphology of pinnotherine pea crabs (Brachyura: Pinnotheridae), with an updated list of symbiont-host associations. Diversity 2020, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovrich, G.A.; Calcagno, J.A.; Smith, B.D. The barnacle Notobalanus flosculus as an indicator of the intermolt period of the male lithodid crab Paralomis granulosa. Mar. Biol. 2003, 143, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gannon, A.T.; Wheatly, M.G. Physiological effects of an ectocommensal gill barnacle, Octolasmis muelleri, on gas exchange in the blue crab Callinectes sapidus. J. Crustac. Biol. 1992, 12, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Distribution of amphipods Ischyrocerus on the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus: Possible interactions with the host in the Barents Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 82, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. The amphipod Ischyrocerus commensalis on the eggs of the red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus: Egg predator or scavenger? Aquaculture 2010, 298, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. New echinoderm-crab epibiotic associations from the coastal Barents Sea. Animals 2021, 11, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.P.; Jones, C.G. The concept of organisms as ecosystem engineers ten years on: Progress, limitations, and challenges. BioScience 2006, 56, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berke, S.K. Functional groups of ecosystem engineers: A proposed classification with comments on current issues. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2010, 50, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pickering, T.R.; Poirier, L.A.; Barrett, T.J.; McKenna, S.; Davidson, J.; Quijón, P.A. Non-indigenous predators threaten ecosystem engineers: Interactive effects of green crab and oyster size on American oyster mortality. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 127, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Tipisova, E.V.; Elfimova, A.E.; Alikina, V.A.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Sex hormones in hemolymph of red king crabs from the Barents Sea. Animals 2021, 11, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Cucumaria in Russian waters of the Barents Sea: Biological aspects and aquaculture potential. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 613453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Renewal of the recreational red king crab fishery in Russian waters of the Barents Sea: Potential benefits and costs. Mar. Policy 2022, 136, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmin, S.A.; Gudimova, E.N. Introduction of the Kamchatka (Red King) Crab in the Barents Sea: Peculiarities of Biology, Perspectives of Fishery; KSC RAS Press: Apatity, Russia, 2002. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Sokolov, V.I. Decapod Crustaceans of the Barents Sea. Tr. VNIRO 2003, 142, 25–76. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Commercial fish and shellfish in the Barents Sea: Have introduced crab species affected the population trajectories of commercial fish? Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2015, 25, 297–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Size at maturity of female red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, from the costal zone of Kola Peninsula (southern Barents Sea). Cah. Biol. Mar. 2015, 56, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Inter-annual dynamics of the Barents Sea red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) stock indices in relation to environmental factors. Polar Sci. 2016, 10, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Ecology of Red King Crab in the Coastal Barents Sea; SSC RAS Publishers: Rostov-on-Don, Russia, 2018. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Effects of environmental factors on the abundance, biomass, and individual weight of juvenile red king crabs in the Barents Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deart, Y.V.; Antokhina, T.I.; Spiridonov, V.A.; Britayev, T.A. Seasonal distribution of red king crab in Zelenaya Inlet (Murmansk coast, Barents Sea). Tr. VNIRO 2018, 172, 149–159. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Fouling community of the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus (Tilesius 1815), in a subarctic fjord of the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Some aspects of the biology of the amphipods Ischyrocerus anguipes associated with the red king crab, Paralithodes camtschaticus, in the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Copepods associated with the red king crab Paralithodes camtschaticus (Tilesius, 1815) in the Barents Sea. Zool. Stud. 2013, 52, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epibionts and commensals of the troll crab (Lithodes maja, Decapoda, Lithodidae) in the Barents Sea. Zool. Zhurnal 2019, 98, 365–370. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epifauna associated with an introduced crab in the Barents Sea: A 5-year study. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dvoretsky, A.G. Epibionts of the great spider crab, Hyas araneus (Linnaeus, 1758), in the Barents Sea. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Structure of symbiotic assemblages on red king crabs in the coastal Barents Sea in 2012. Tr. VNIRO 2018, 172, 160–171, (In Russian with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Symbionts and sessile microbiota of red king crab from eastern Murman (Dalnezelenetskaya Bay, Barents Sea) in July 2014. Bull. Kamchatka State Tech. Univ. 2020, 51, 66–72. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G. Red king crab in the coastal Barents Sea: A review of MMBI studies. Trans. Kola Sci. Centre 2020, 11, 134–149. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Population biology of Ischyrocerus commensalis, a crab-associated amphipod, in the southern Barents Sea: A multi-annual summer study. Mar. Ecol. 2011, 32, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, L.V. Red king crab trophic relations and its influence on bottom biocenoses. In Biology and Physiology of the Red King Crab from the Coastal Zone of the Barents Sea; Matishov, G.G., Ed.; KSC RAS Press: Apatity, Russia, 2008; pp. 77–104. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Berke, S.K.; Woodin, S.A. Energetic costs, ontogenetic shifts and sexual dimorphism in spider crab decoration. Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanduo, V.; Virgili, R.; Osca, D.; Crocetta, F. Hiding in fouling communities: A native spider crab decorating with a cryptogenic bryozoan in a Mediterranean marina. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parapar, J.; Fernandez, L.; Gonzalez-Gurriaran, E.; Muino, R. Epibiosis and masking material in the spider crab Maja squinado (Decapoda: Majidae) in the Ria de Arousa (Galicia, NW Spain). Cah. Biol. Mar. 1997, 38, 221–234. [Google Scholar]
- Bedini, R.; Canali, M.G.; Bedini, A. Use of camouflaging materials in some brachyuran crabs of the Mediterranean infralittoral zone. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2003, 44, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Uspenskaya, A.V. Parasitic Fauna of the Benthic Crustaceans in the Barents Sea; AN SSSR Press: Moscow, Russia, 1963. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Interspecific relationships of symbiotic amphipods on the red king crab in the Barents Sea. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2010, 433, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Interspecific competition of symbiotic and fouling species of red king crab in the Barents Sea. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2011, 440, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, Á.; Figueroa, T.; Canete, J.I. Caprella ungulina Mayer, 1903 (Amphipoda: Caprellidae): Epizoan of Paralomis granulosa (Hombron & Jacquinot, 1846) (Decapoda: Lithodidae) in Magellan waters, Chile. Anal. Inst. Patagon. 2017, 45, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Size-at-age of juvenile red king crab (Paralithodes camtschaticus) in the coastal Barents Sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2014, 55, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Savoie, L.; Miron, J.; Biron, M. Fouling community of the snow crab Chionoecetes opilio in Atlantic Canada. J. Crustac. Biol. 2007, 27, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firstater, F.N.; Hidalgo, F.G.; Lomovasky, B.G.; Gallegos, P.; Amero, P.; Iribarne, O.O. Effects of epibiotic Enteromorpha spp. on the mole crab Emerita analoga in the Peruvian central coast. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2009, 89, 363–370. [Google Scholar]
- Di Camillo, C.; Bo, M.; Puce, S.; Tazioli, S.; Froglia, C.; Bavestrello, G. The epibiontic assemblage of Geryon longipes (Crustacea: Decapoda: Geryonidae) from the Southern Adriatic Sea. Ital. J. Zool. 2008, 75, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.K. Epibiont communities of the two spider crabs Schizophrys aspera (H. Milne Edwards, 1834) and Hyastenus hilgendorfi (De Man, 1887) in Great Bitter Lakes, Suez Canal, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2012, 16, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, J.S.; Anil, A.C. Epibiotic community of the horseshoe crab Tachypleus gigas. Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazy, P.; Kuklinski, P. Arctic field experiment shows differences in epifaunal assemblages between natural and artificial substrates of different heterogeneity and origin. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2017, 486, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazy, P.; Kuklinski, P.; Wlodarska-Kowalczuk, M.; Gluchowska, M.; Barnes, D.K.A. Factors affecting biodiversity on hermit crab shells. Hydrobiologia 2016, 773, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gravina, M.F.; Pierri, C.; Mercurio, M.; Nonnis Marzano, C.; Giangrande, A. Polychaete diversity related to different mesophotic bioconstructions along the southeastern Italian coast. Diversity 2021, 13, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uryash, V.F.; Kokurina, N.Y.; Kashtanov, E.A.; Zagorskaya, D.S.; Kovacheva, N.P. Influence of species-specificity of crab families on physicochemical properties of crab shell chitin. Vestn. Lobachevsky Univ. Nizhny Novgorod 2012, 3, 83–86. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Fukuhara, Y.; Mizuta, H.; Yasui, H. Swimming activities of zoospores of Laminaria japonica (Phaeophyceae). Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Taxa | Hyas araneus | Lithodes maja | Paralithodes camtschaticus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pr 95%C.I. | Int | Pr 95%C.I. | Int | Pr 95%C.I. | Int | ||||
| X ± SE | Range | X ± SE | Range | X ± SE | Range | ||||
| Algae | |||||||||
| Acrosiphonia sp. | 17.9 6–30 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Alaria esculenta (Linnaeus) Greville, 1830 | 5.1 1–12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Chordaria flagelliformis (O.F.Müller) C.Agardh, 1817 | 25.6 12–39 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Desmarestia aculeata (Linnaeus) J.V.Lamouroux, 1813 | 12.8 2–23 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Dictyosiphon foeniculaceus (Hudson) Greville, 1830 | 23.1 10–36 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Laminaria digitata (Hudson) J.V.Lamouroux, 1813 | 5.1 1–12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Palmaria palmata (Linnaeus) Weber and Mohr, 1805 | 28.2 14–42 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Ptilota gunneri P.C.Silva, Maggs and M.Irvine, 1993 | 30.8 16–45 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Saccharina latissima (Linnaeus) C.E.Lane, C.Mayes, Druehl and G.W.Saunders, 2006 | 10.3 1–20 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Ulvaria obscura (Kützing) P.Gayral ex C.Bliding, 1969 | 23.1 10–36 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hydrozoa | |||||||||
| Coryne hincksi Bonnevie, 1898 | 2.6 0–8 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Halecium beanii (Johnston, 1838) | 2.6 0–8 | – | – | – | – | – | 2.4 0–7 | – | – |
| Obelia geniculata (Linnaeus, 1758) | 10.3 1–20 | – | – | 48.6 33–65 | – | – | 4.8 1–11 | – | – |
| Obelia longissima (Pallas, 1766) | 17.9 6–30 | – | – | 94.6 87–100 | – | – | 66.7 52–81 | – | – |
| Turbellaria | |||||||||
| Peraclistus oophagus (Friedmann, 1924) | 23.1 10–36 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Nemettini | |||||||||
| Nemertini g. sp. | 10.3 1–20 | 15.8 ± 10.1 | 4–46 | 10.8 1–21 | 4.3 ± 2.6 | 1–12 | 2.4 0–7 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 |
| Polychaeta | |||||||||
| Bushiella (Jugaria) similis (Bush, 1905) | – | – | – | 2.7 0–8 | 2.0 ± 0.0 | 2–2 | – | – | – |
| Circeis armoricana Saint–Joseph, 1894 | 38.5 23–54 | 23.9 ± 6.5 | 3–93 | 59.5 44–75 | 89.4 ± 32.5 | 4–345 | 33.3 19–48 | 5.3 ± 2.3 | 1–33 |
| Eumida sanguinea (Oersted, 1843) | – | – | – | 5.4 0–13 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1–2 | 2.4 0–7 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 |
| Harmothoe imbricata (Linnaeus, 1767) | – | – | – | 70.3 56–85 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1–3 | 33.3 19–48 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 1–3 |
| Lepidonotus squamatus (Linnaeus, 1758) | – | – | – | 2.7 0–8 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 | – | – | – |
| Placostegus tridentatus (Fabricius, 1779) | 43.6 28–59 | – | – | 64.9 49–80 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Protula tubularia (Montagu, 1803) | 7.7 1–16 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 1–2 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Spirobranchus triqueter (Linnaeus, 1758) | 20.5 8–33 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 1–5 | 8.1 1–17 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Hirudinea | |||||||||
| Crangonobdella fabricii (Malm, 1863) | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2.4 0–7 | 2.0 ± 0.0 | 2–2 |
| Johanssonia arctica (Johansson, 1898) | – | – | – | 2.7 0–8 | 3.0 ± 0.0 | 3–3 | 11.9 2–22 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 1–2 |
| Platibdella olriki (Malm, 1863) | 2.6 0–8 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Bivalvia | |||||||||
| Heteranomia squamula (Linnaeus, 1758) | 7.7 1–16 | 3 ± 1.5 | 1–6 | 48.6 33–65 | 13.9 ± 9.4 | 1–79 | 9.5 1–18 | 2 ± 0.7 | 1–4 |
| Hiatella arctica (Linnaeus, 1767) | – | – | – | 13.5 2–25 | 4.4 ± 2.4 | 1–5 | 4.8 1–11 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1–2 |
| Mytilus edulis Linnaeus, 1758 | 10.3 1–20 | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 1–2 | 32.4 17–48 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 1–3 | 26.2 13–39 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 1–8 |
| Gastropoda | |||||||||
| Margarites sp. | 5.1 1–12 | 4.5 ± 3.5 | 1–8 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Copepoda | |||||||||
| Calanus finmarchicus (Gunner, 1765) | 2.6 0–8 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Ectinosoma neglectum Sars G.O., 1904 | 25.6 12–39 | 44.5 ± 25.5 | 1–269 | 2.7 0–8 | 2.0 ± 0.0 | 2–2 | – | – | – |
| Harpacticus uniremis Krøyer, 1842 | 46.2 31–62 | 10.8 ± 5.6 | 1–101 | – | – | – | 2.4 0–7 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 |
| Tisbe furcata (Baird, 1837) | 30.8 16–45 | 79.3 ± 18.3 | 7–235 | 8.1 1–17 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 1–3 | 2.4 0–7 | 17.0 ± 0.0 | 17–17 |
| Zaus abbreviatus Sars G.O., 1904 | 2.6 0–8 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Amphipoda | |||||||||
| Ampelisca sp. | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2.4 0–7 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 |
| Gammarellus homari (Fabricius, 1779) | 10.3 1–20 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 | 5.4 0–13 | 2.0 ± 1.0 | 1–3 | 2.4 0–7 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 1–1 |
| Hippomedon propinqvus G.O. Sars, 1890 | 5.1 1–12 | 2.5 ± 1.5 | 1–4 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Ischyrocerus anguipes Krøyer, 1838 | 12.8 2–23 | 5.8 ± 4.1 | 1–22 | 48.6 33–65 | 9.1 ± 1.2 | 1–23 | 52.4 37–67 | 9.4 ± 3.4 | 1–70 |
| Ischyrocerus commensalis Chevreux, 1900 | 5.1 1–12 | 5.5 ± 1.5 | 4–7 | 94.6 87–100 | 26.5 ± 3.5 | 8–109 | 100.0 100–100 | 79.8 ± 11.6 | 5–492 |
| Cirripedia | |||||||||
| Balanus balanus (Linnaeus, 1758) | 2.6 0–8 | 9.0 ± 0.0 | 9–9 | 35.1 20–51 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 1–3 | 4.8 1–11 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1–2 |
| Balanus crenatus Brugiere 1789 | – | – | – | 32.4 17–48 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | 1–8 | 26.2 13–39 | 2.9 ± 0.8 | 1–9 |
| Verruca stroemia (O.F. Muller, 1776) | 2.6 0–8 | 3.0 ± 0.0 | 3–3 | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Bryozoa | |||||||||
| Bugula harmsworth Waters, 1900 | 5.1 1–12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Callopora lineata (Linnaeus, 1767) | 7.7 1–16 | – | – | 29.7 15–44 | – | – | 4.8 1–11 | – | – |
| Crisia denticulata (Lamarck, 1816) | – | – | – | 10.8 1–21 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Disporella hispida (Fleming, 1828) | 7.7 1–16 | – | – | 27.0 13–41 | – | – | 4.8 1–11 | – | – |
| Patinella verrucaria (Linnaeus, 1758) | 15.4 4–27 | – | – | 13.5 2–25 | – | – | 2.4 0–7 | – | – |
| Porella smitti Kluge, 1907 | 2.6 0–8 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Tricellaria arctica Busk, 1855 | 10.3 1–20 | – | – | 18.9 6–32 | – | – | 4.8 1–11 | – | – |
| Taxa | Comparisons | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithodes vs. Hyas | Paralithodes vs. Hyas | Paralithodes vs. Lithodes | |
| Acrosiphonia sp. | 1.94 | 2.42 | – |
| Chordaria flagelliformis | 2.77 | 3.46 | – |
| Desmarestia aculeata | 1.39 | 1.73 | – |
| Dictyosiphon foeniculaceus | 2.49 | 3.11 | – |
| Palmaria palmata | 3.05 | 3.80 | – |
| Ptilota gunneri | 3.33 | 4.15 | – |
| Saccharina latissima | – | 1.38 | – |
| Ulvaria obscura | 2.49 | 3.11 | – |
| Obelia geniculata | 4.15 | – | 10.02 |
| Obelia longissima | 8.29 | 6.57 | 6.37 |
| Peraclistus oophagus | 2.49 | 3.11 | – |
| Nemertini g. sp. | – | 1.06 | 1.92 |
| Circeis armoricana | 2.27 | – | 5.96 |
| Harmothoe imbricata | 7.60 | 4.50 | 8.43 |
| Placostegus tridentatus | 2.30 | 5.88 | 14.81 |
| Protula tubularia | – | 0.84 | – |
| Spirobranchus triqueter | 1.34 | 2.77 | 1.85 |
| Johanssonia arctica | – | 1.61 | 2.10 |
| Heteranomia scuamula | 4.43 | – | 8.93 |
| Hiatella arctica | 1.46 | – | 2.00 |
| Mytilus edulis | 2.40 | 2.15 | 1.42 |
| Ectinosoma neglectum | 2.48 | 3.46 | – |
| Harpacticus uniremis | 4.99 | 5.90 | – |
| Tisbe furcata | 2.45 | 3.83 | – |
| Gamarellus homari | – | 1.06 | – |
| Ischyrocerus anguipes | 3.87 | 5.34 | – |
| Ischyrocerus commensalis | 9.67 | 12.80 | – |
| Balanus balanus | 3.52 | – | 6.93 |
| Balanus crenatus | 3.51 | 3.53 | 1.42 |
| Callopora lineata | 2.38 | – | 5.70 |
| Crisia denticulata | 1.17 | – | 2.47 |
| Lichenopora hispida | – | – | 5.08 |
| Lichenopora verrucaria | 2.09 | 1.75 | 2.54 |
| Scrupocellaria arctica | – | 0.74 | 3.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dvoretsky, A.G.; Dvoretsky, V.G. Epibiotic Communities of Common Crab Species in the Coastal Barents Sea: Biodiversity and Infestation Patterns. Diversity 2022, 14, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14010006
Dvoretsky AG, Dvoretsky VG. Epibiotic Communities of Common Crab Species in the Coastal Barents Sea: Biodiversity and Infestation Patterns. Diversity. 2022; 14(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleDvoretsky, Alexander G., and Vladimir G. Dvoretsky. 2022. "Epibiotic Communities of Common Crab Species in the Coastal Barents Sea: Biodiversity and Infestation Patterns" Diversity 14, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14010006
APA StyleDvoretsky, A. G., & Dvoretsky, V. G. (2022). Epibiotic Communities of Common Crab Species in the Coastal Barents Sea: Biodiversity and Infestation Patterns. Diversity, 14(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14010006