Leaf Senescence of the Seagrass Cymodocea nodosa in Cádiz Bay, Southern Spain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sampling Locations and Biological Material
2.2. Leaf Morphology
2.3. Leaf Internal Composition
2.4. Leaf Biomechanical Measurements
2.5. Predicting Failure Velocity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological and Internal Composition
3.2. Biomechanical Properties
3.3. Generalized Linear Model Analyses
3.4. Estimated Failure Velocities
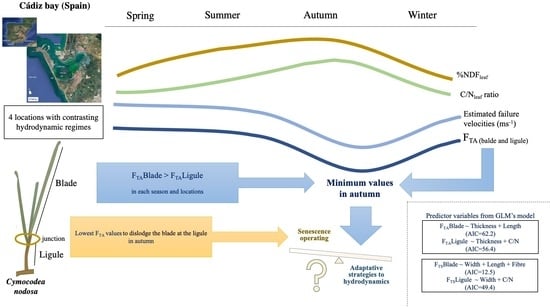
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Den Hartog, C. The Sea-Grasses of the World; North-Holland Publishing Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1970; 275p. [Google Scholar]
- Arber, A. Waterplants: A Study of Aquatic Angiosperms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1920; p. 436. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, J.L.; Rouzé, P.; Verhelst, B.; Lin, Y.C.; Bayer, T.; Collen, J.; Michel, G. The genome of the seagrass Zostera marina reveals angiosperm adaptation to the sea. Nature 2016, 530, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hemminga, M.A.; Duarte, C.M. Seagrass Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; 289p. [Google Scholar]
- Schanz, A.; Asmus, H. Impact of hydrodynamics on development and morphology of intertidal seagrasses in the Wadden Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 261, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.; Stokes, A. Plant biomechanics in an ecological context. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 1546–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villazán, B.; Brun, F.G.; González-Ortiz, V.; Moreno-Marín, F.; Bouma, T.J.; Vergara, J.J. Flow velocity and light level drive non-linear response of seagrass Zostera noltei to ammonium enrichment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 545, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, G.; Brun, F.G.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L.; Bouma, T.J. Direct effects of current velocity on the growth, morphometry and architecture of seagrasses: A case study on Zostera noltii. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 327, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touchette, B.W. Seagrass-salinity interactions: Physiological mechanisms used by submersed marine angiosperms for a life at sea. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 194–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De los Santos, C.B.; Onoda, Y.; Vergara, J.J.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L.; Bouma, T.J.; La Nafie, Y.; Cambridge, M.L.; Brun, F.G. A comprehensive analysis of mechanical and morphological traits in temperate and tropical seagrass species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 551, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouma, T.J.; De Vries, M.B.; Low, E.; Peralta, G.; Tánczos, I.V.; van de Koppel, J.; Herman, P.M.J. Trade-offs related to ecosystem engineering: A case study on stiffness of emerging macrophytes. Ecology 2005, 86, 2187–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, E.W.; Ackerman, J.D.; Verduin, J.; van Keulen, M. Fluid dynamics in seagrass ecology: From molecules to ecosystems. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 193–225. [Google Scholar]
- Chaffey, N. Physiological anatomy and function of the membranous grass ligule. New Phytol. 2000, 146, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirino, B.F.; Noh, Y.S.; Himelblau, E.; Amasino, R.M. Molecular aspects of leaf senescence. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H. Senescence, ageing and death of the whole plant. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 696–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, H.R.; Kim, H.J.; Lim, P.O.; Nam, H.G. Leaf senescence: Systems and dynamics aspects. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, H.; Ougham, H.; Canter, P.; Donnison, I. What stay-green mutants tell us about nitrogen remobilization in leaf senescence. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila-Ospina, L.; Moison, M.; Yoshimoto, K.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Autophagy, plant senescence, and nutrient recycling. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3799–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Mendoza, M.; Velasco-Arroyo, B.; Santamaria, M.E.; González-Melendi, P.; Martinez, M.; Diaz, I. Plant senescence and proteolysis: Two processes with one destiny. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2016, 39, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayta, M.L.; Hajirezaei, M.R.; Carrillo, N.; Lodeyro, A.F. Leaf Senescence: The chloroplast connection comes of age. Plants 2019, 8, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasool, S.; Mir, B.A.; Rehman, M.U.; Amin, I.; Mir, M.U.R.; Ahmad, S.B. Abiotic stress and plant senescence. In Senescence Signalling and Control in Plants; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 15–17. [Google Scholar]
- Christ, B.; Hörtensteiner, S. Mechanism and significance of chlorophyll breakdown. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 33, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, P.O.; Kim, H.J.; Gil Nam, H. Leaf senescence. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Distelfeld, A.; Avni, R.; Fischer, A.M. Senescence, nutrient remobilization, and yield in wheat and barley. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3783–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, O.R.; Scheuerlein, A.; Salguero-Gómez, R.; Camarda, C.G.; Schaible, R.; Casper, B.B.; Quintana-Ascencio, P.F. Diversity of ageing across the tree of life. Nature 2014, 505, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, D.A.; Smith, E.F. Life-history trade-offs and senescence in plants. Funct. Ecol. 2020, 34, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibran, R.; Hunter, D.A.; Dijkwel, P.P. Hormonal regulation of leaf senescence through integration of developmental and stress signals. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sade, N.; del Mar Rubio-Wilhelmi, M.; Umnajkitikorn, K.; Blumwald, E. Stress-induced senescence and plant tolerance to abiotic stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 69, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, S.; Abbas, N.; Ashraf, M.; Ahmad, P. Roles of potential plant hormones and transcription factors in controlling leaf senescence and drought tolerance. Protoplasma 2019, 256, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R. Nutrient resorption from senescing leaves of perennials: Are there general patterns? J. Ecol. 1996, 84, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, J.T. Programmed cell death: A way of life for plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 12094–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larkum, A.W.D.; den Hartog, C. Evolution and biogeography of seagrasses. In Biology of Seagrasses; Larkum, A.W.D., Mc Comb, A., Shepherd, S.A., Eds.; Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 112–156. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.; Huang, L.; Young, M.; Ougham, H. Evolution of plant senescence. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateo, M.A.; Cebrián, J.; Dinton, K.; Mutchler, T. Carbon flux in seagrass ecosystems. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 159–192. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, J.; Lee, K.S.; Pérez, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Alcoverro, T. Nutrient dynamics in seagrass ecosystems. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 227–254. [Google Scholar]
- Cuoplant, G.T.; Duarte, C.M.; Walker, D.I. High metabolic rates in beach cast communities. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Trevathan-Tacket, S.M.; Baldock, J.A.; Kelleway, J. Converting beach-cast seagrass wracks into biochar: A climate-friendly solution to a coastal problema. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2017, 574, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, B.S. Effects of Nitrate Fertilization and Shading on Physiological and Biomechanical Properties of Eelgrass (Zostera Marina). Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Rhode Island, South Kingstown, RI, USA, 1999; 187p.
- Brun, F.G.; Hernández, I.; Vergara, J.J.; Peralta, G.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L. Assessing the toxicity of ammonium pulses to the survival and growth of Zostera noltii. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 225, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egea, L.G.; Jiménez-Ramos, R.; Vergara, J.J.; Hernández, I.; Brun, F.G. Interactive effect of temperature, acidification and ammonium enrichment on the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 134, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egea, L.G.; Jiménez-Ramos, R.; Hernández, I.; Brun, F.G. Differential effects of nutrient enrichment on carbon metabolism and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) fluxes in macrophytic benthic communities. Mar. Environ. Res. 2020, 162, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, O.; Mateo, M.A.; Renom, P. Seasonal response of Posidonia oceanica to light disturbances. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 423, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brun, F.G.; Hernández, I.; Vergara, J.J.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L. Growth, carbon allocation and proteolytic activity in the seagrass Zostera noltii shaded by Ulva canopies. Funct. Plant Biol. 2003, 30, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villazán, B.; Pedersen, M.F.; Brun, F.G.; Vergara, J.J. Elevated ammonium concentrations and low light form a dangerous synergy for eelgrass Zostera marina. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2013, 493, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, M.S.; Koehl, M.A.R. Flow in seagrass canopies: The influence of patch width. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.A.; Harrison, P.G.; Van Lent, F. The balance of nutrient losses and gains in seagrass meadows. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1991, 71, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.F.; Borum, J. An annual nitrogen budget for a seagrass Zostera marina population. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1993, 101, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.A.; Romero, J. Detritus dynamics in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: Elements for an ecosystem carbon and nutrient Budget. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1997, 151, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stapel, J.; Hemminga, M.A. Nutrient resorption from seagrass leaves. Mar. Biol. 1997, 128, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.A. The root rhizome system of seagrasses: An asset and a burden. J. Sea Res. 1998, 39, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.A.; Marbá, N.; Stapel, J. Leaf nutrient resorption, leaf lifespan and the retention of nutrients in seagrass systems. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 65, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepoint, G.; Defawe, O.; Gobert, S.; Dauby, P.; Bouquegneau, J.M. Experimental evidence for N recycling in the leaves of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. J. Sea Res. 2002, 48, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapin, F.S., III; Kedrowski, R.A. Seasonal changes in nitrogen and phosphorus fractions and autumn retranslocation in ever- green and deciduous taiga trees. Ecology 1983, 64, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Chen, H.Y. Global-scale patterns of nutrient resorption associated with latitude, temperature and precipitation. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.C.; Townsend, A.R.; Davidson, E.A.; Cleveland, C.C. Stoichiometric patterns in foliar nutrient resorption across multiple scales. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brant, A.N.; Chen, H.Y. Patterns and mechanisms of nutrient resorption in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng, C.A.; Erftemeijer, P.L.A. Accumulation of seagrass beach cast along the Kenyan coast: A quantitative assessment. Aquat. Bot. 1999, 65, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestri, E.; Vallerini, F.; Lardicci, C. Qualitative and quantitative assessment of the reproductive litter from Posidonia oceanica accumulated on a sand beach following a storm. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2006, 66, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, M.A. Beach-Cast Cymodocea nodosa along the shore of a semienclosed say: Sampling and elements to assess its ecological implications. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeone, S.; De Muro, S.; De Falco, G. Seagrass berm deposition on a Mediterranean embayed beach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 135, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldham, C.; McMahon, K.; Brown, E.; Bosserelle, C.; Lavery, P. A preliminary exploration of the physical properties of seagrass wrack that affect its offshore transport, deposition, and retention on a beach. Limnol. Oceanogr. Fluids Environ. 2014, 4, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.H.K.; Ganguly, D.; Paneerselvam, A.; Ramesh, R.; Purvaja, R. Seagrass litter decomposition: An additional nutrient source to shallow coastal waters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morre, D.J. Cell wall dissolution and enzyme secretion during leaf abscission. Plant Physiol. 1968, 43, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anfuso, G.; Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Cortés-Useche, C.; Iglesias-Castillo, B.; Gracia, F.J. Characterization of storm events along the Gulf of Cadiz (eastern central Atlantic Ocean). Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 3690–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Río, L.; Plomaritis, T.A.; Benavente, J.; Valladares, M.; Ribera, P. Establishing storm thresholds for the Spanish Gulf of Cádiz coast. Geomorphology 2012, 143, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Ramos, R.; Egea, L.G.; Vergara, J.J.; Brun, F.G. Factors modulating herbivory patterns in Cymodocea nodosa meadows. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 2218–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, G.; Godoy, O.; Egea, L.G.; de los Santos, C.B.; Jiménez-Ramos, R.; Lara, M.; Brun, F.G.; Hernández, I.; Olivé, I.; Vergara, J.J.; et al. The morphometric acclimation to depth explains the long-term resilience of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa in a shallow tidal lagoon. J. Environ. Res. 2021, 299, 113452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.P.; Peralta, G.; Van Engeland, T.; Bouma, T.J.; Brun, F.G.; Lara, M.; Lucas Perez-Lloréns, J.L. The role of hydrodynamics in structuring in situ ammonium uptake within a submerged macrophyte community. Limnol. Oceanogr. Fluids Environ. 2013, 3, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kagan, B.A.; Álvarez, O.; Izquierdo, A.; Mañanes, R.; Tejedor, B.; Tejedor, L. Weak wind-wave/tide interaction over a moveable bottom: Results of numerical experiments in Cádiz Bay. Cont. Shelf Res. 2003, 23, 435–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, M.; Peralta, G.; Alonso, J.J.; Morris, E.P.; González-Ortiz, V.; Rueda-Márquez, J.J.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.J. Effects of intertidal seagrass habitat fragmentation on turbulent diffusion and retention time of solutes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivé, I.; Vergara, J.J.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L. Photosynthetic and morphological photoacclimation of the seagrass Cymodocea nodosa to season, depth and leaf position. Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea, L.G.; Barrón, C.; Jiménez-Ramos, R.; Hernández, I.; Vergara, J.J.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L.; Brun, F.G. Coupling carbon metabolism and dissolved organic carbon fluxes in benthic and pelagic coastal communities. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 227, 106336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De los Santos, C.B.; Brun, F.G.; Pérez-lloréns, J.L. New aspect in seagrass acclimation: Leaf mechanical properties vary spatially and seasonally in the temperate species Cymodocea nodosa Ucria (Ascherson). Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, F.G.; Vergara, J.J.; Hernández, I.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L. Evidence for vertical growth in Zostera noltii Hornem. Bot. Mar. 2005, 48, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertos del Estado. Red Costera de Boyas. Informe de datos de la boya de Cádiz. Periodo: Sept. 2015–2016. Available online: https://www.puertos.es/es-es/oceanografia/ (accessed on 15 February 2018).
- Kuo, J.; Den Hartog, C. Seagrass morphology, anatomy, and ultrastructure. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 51–87. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and non starch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gere, J.M.; Goodno, B.J. Mechanics of Materials; Cengage Learning: Stamford, CT, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Denny, M.W. Biology and the Mechanics of the Wave-Swept Environment; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1988; 329p. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, S. Life in Moving Fluids: The Physical Biology of Flow; Princeton University Press: London, UK, 1994; 467p. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. Statistician 2017, 56. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 13 September 2019).
- Harrison, X.A.; Donaldson, L.; Correa-Cano, M.E.; Evans, J.; Fisher, D.N.; Goodwin, C.E.D.; Robinson, B.S.; Hodgson, D.J.; Inger, R. A brief introduction to mixed effects modelling and multi-model inference in ecology. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barton, K. Multi-Model Inference. R package 1.43.15 (Issues 1–34). 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: http://www.r-project.org/index.html (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Onoda, Y.; Hikosaka, K.; Hirose, T. Allocation of nitrogen to cell walls decreases photosynthetic nitrogen-use efficiency. Funct. Ecol. 2004, 18, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti-Raverot, B.; Puijalon, S. Nutrient enrichment affects the mechanical resistance of aquatic plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 6115–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brun, F.G.; Vergara, J.J.; Peralta, G.; García-Sánchez, M.P.; Hernández, I.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L. Clonal building, simple growth rules and phylloclimate as key steps to develop functional-structural seagrass models. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 323, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.-S.; Park, S.R.; Kim, Y.K. Effects of irradiance, temperature, and nutrients on growth dynamics of seagrasses: A review. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 144–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, A.J.; Gruber, R.K.; Orr, M.; Scanes, P. Morphological plasticity in Zostera muelleri across light, sediment, and nutrient gradients in Australian temperate coastal lakes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 556, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enríquez, S.; Olivé, I.; Cayabyab, N.; Hedley, J.D. Structural complexity governs seagrass acclimatization to depth with relevant consequences for meadow production, macrophyte diversity and habitat carbon storage capacity. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duarte, C.M. Seagrass depth limits. Aquat. Bot. 1991, 40, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoda, Y.; Westoby, M.; Adler, P.B.; Choong, A.M.F.; Clissold, F.J.; Cornelissen, J.H.; Díaz, S.; Dominy, N.J.; Elgart, A.; Enrico, L.; et al. Global patterns of leaf mechanical properties. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zimmerman, R.C. Light and photosynthesis in seagrass meadows. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 303–321. [Google Scholar]
- Alcoverro, T.; Duarte, C.M.; Romero, J. Annual growth dynamics of Posidonia oceanica: Contribution of large-scale versus local factors to seasonality. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 120, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, E.W. Hydrodynamics, diffusion-boundary layers and photosynthesis of the seagrasses Thalassia testudinum and Cymodocea nodosa. Mar. Biol. 1994, 118, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, T.J.; Friedrichs, M.; Klaassen, P.; Van Wesenbeeck, B.K.; Brun, F.G.; Temmerman, S.; Herman, P.M.J. Effects of shoot stiffness, shoot size and current velocity on scouring sediment from around seedlings and propagules. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 388, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, M.S.; Koehl, M.A.R.; Fourqurean, J.W. Effect of seagrass on current speed: Importance of flexibility versus shoot density. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paul, M.; de los Santos, C.B. Variation in flexural, morphological, and biochemical leaf properties of eelgrass (Zostera marina) along the European Atlantic climate regions. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, F.G.; Perez-Pastor, A.; Hernández, I.; Vergara, J.J.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L. Shoot organization in the seagrass Zostera noltii: Implications for space occupation and plant architecture. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2006, 60, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, R.P.W.M. Distribution and aspects of the production and biomass of eelgrass, Zostera marina L., at Roscoff, France. Aquat. Bot. 1979, 7, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De los Santos, C.B.; Vicencio-Rammsy, B.; Lepoint, G.; Remy, F.; Bouma, T.J.; Gobert, S. Ontogenic variation and effect of collection procedure on leaf biomechanical properties of Mediterranean seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Mar. Ecol. 2016, 37, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schönemann, A.M. Estimations of the Net Primary Production of Epiphytes in Seagrass Populations from Cádiz Bay. Master’s Thesis, University of Cádiz, Cádiz, Spain, 2015; 40p. [Google Scholar]
- Hedden, R.L.; Fredericksen, T.S.; Williams, S.A. Modeling the effect of crown shedding and streamlining on the survival of loblolly pine exposed to acute wind. Can. J. For. Res. 1995, 25, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollsinger, S.; Mitchell, S.J.; Byrne, K.E.; Novak, M.D.; Rudnicki, M. Wind tunnel measurements of crown streamlining and drag relationships for several hardwood species. Can. J. For. Res. 2005, 35, 1238–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.J. Wind as a natural disturbance agent in forests: A synthesis. Forestry 2013, 86, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Yoon, T.H.; Lee, J.; Jeon, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.K.; Cho, H.K. A lignin molecular brace controls precision processing of cell walls critical for surface integrity in Arabidopsis. Cell 2018, 173, 1468–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De los Santos, C.B.; Godbold, J.A.; Solan, M. Short-term growth and biomechanical responses of the temperate seagrass Cymodocea nodosa to CO2 enrichment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2017, 572, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patharkar, O.R.; Walker, J.C. Advances in abscission signaling. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Nafie, Y.; de los Santos, C.B.; Brun, F.G.; van Katwijk, M.; Bouma, T.J. Waves and high nutrient loads jointly decrease survival and separately affect morphological and biomechanical properties in the seagrass Zostera noltii. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1667–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molina, R.; Manno, G.; Lo Re, C.; Anfuso, G.; Ciraolo, G. Storm Energy Flux Characterization along the Mediterranean Coast of Andalusia (Spain). Water 2019, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.E.; Hootsmans, M.J.M.; Nienhuis, P.H. Seasonal dynamics and leaf growth of Zostera noltii Hornem., a perennial intertidal seagrass. Aquat. Bot. 1987, 28, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, E.A.; Strother, S. Seasonal changes in standing crop of Zostera muelleri in south-eastern Australia. Aquat. Bot. 1990, 38, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Pergent, G.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Mateo, M.A.; Regnier, C. The detritic compartment in a Posidonia oceanica meadow: Litter features, decomposition rates, and mineral stocks. Mar. Ecol. 1992, 13, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, G.P.; Mazzella, L. Nitrogen acquisition, storage, and use by the Mediterranean seagrasses Cymodocea nodosa and Zostera noltii. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 183, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guidetti, P.; Lorenti, M.; Buia, M.C.; Mazzella, L. Temporal Dynamics and Biomass Partitioning in Three Adriatic Seagrass Species: Posidonia oceanica, Cymodocea nodosa, Zostera marina. Mar. Ecol. 2002, 23, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, R.J.; Moore, K.A.; Marion, S.R.; Wilcox, D.J.; Parrish, D.B. Seed addition facilitates eelgrass recovery in a coastal bay system. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 448, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newell, S.Y.; Fell, J.W.; Statzell-Tallman, A.; Miller, C.; Cefalu, R. Carbon and nitrogen dynamics in decomposing leaves of three coastal marine vascular plants of the subtropics. Aquat. Bot. 1984, 19, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkman, H.; Kendrick, G.A. Ecological significance and commercial harvesting of drifting and beach-cast macro-algae and seagrasses in Australia: A review. J. Appl. Phycol. 1997, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombini, I.; Chelazzi, L.; Gibson, R.N.; Atkinson, R.J.A. Influence of marine allochthonous input on sandy beach communities. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2003, 41, 115–159. [Google Scholar]
- Portillo, E. Relation between the type of wave exposure and seagrass losses (Cymodocea nodosa) in the south of Gran Canaria (Canary Islands—Spain). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2014, 43, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewit, L.; Reid, D.M. Branch abscission in balsam poplar (Populus balsamifera): Characterization of the phenomenon and the influence of wind. Int. J. Plant Sci. 1992, 153, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybczyk, J.M.; Zhang, X.W.; Day, J.W., Jr.; Hesse, I.; Feagley, S. The impact of Hurricane Andrew on tree mortality, litterfall, nutrient flux, and water quality in a Louisiana coastal swamp forest. J. Coast. Res. 1995, 21, 340–353. [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki, Y.; Sakai, A.; Kuramoto, S.; Kodani, E.; Yamada, T.; Kawasaki, T. Inter-annual variations of leaf-fall phenology and leaf-litter nitrogen concentration in a hinoki cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa Endlicher) stand. Ecol. Res. 2008, 23, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, A.E. Visible and invisible effects of hurricanes on forest ecosystems: An international review. Austral Ecol. 2008, 33, 368–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telewski, F.W. Is windswept tree growth negative thigmotropism? Plant Sci. 2012, 184, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| CC | ST | BC | CH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude | 36°52′60′′ N | 36°28′09.08′′ N | 36°31′42.52′′ N | 36°28′38.16′′ N |
| Longitude | 6°21′77′’ | 6°15′04.64′′ W | 06°14′32.16” W | 06°15′49.21′′ W |
| Depth (m) | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
| Hydrodynamic exposure | Very low | Low | Medium | High |
| Experimental meadow area (ha) | 0.36 | 0.8 | 0.77 | 0.74 |
| Leaf Traits | Location | Linear Model Effect (df = 1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH | BC | ST-Int | ST-Sub | CC | χ2 | p-value | |
| Leaf Length (cm) | 6.59 ±1.55 | 24.9 ± 2.81 | 19.8 ± 3.71 | 35.4 ± 6.25 | 25.9 ± 4.34 | 6.74 | 0.019 |
| Leaf Width (mm) | 2.66 ± 0.26 | 3.40 ± 0.34 | 3.77 ± 0.43 | 4.40 ± 0.36 | 4.03 ± 0.35 | 5.22 | 0.03 |
| Leaf Thickness (mm) | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | 6.23 | 0.017 |
| Surface area (cm2) | 1.92 ± 0.60 | 8.56 ± 1.18 | 8.04 ± 2.24 | 16.7 ± 4.20 | 10.9 ± 2.41 | 7.23 | 0.007 |
| Cross-sectional area (mm2) | 0.63 ± 0.07 | 1.24 ± 0.13 | 0.98 ± 0.13 | 1.57 ± 0.19 | 1.18 ± 0.15 | 4.23 | 0.009 |
| Fibre content (% DW) | 38.5 ± 1.51 | 38.7 ± 2.41 | 41.0 ± 2.27 | 35.6 ± 2.48 | 36.5 ± 1.95 | 0.06 | 0.43 |
| %C | 31.5 ± 1.26 | 31.1 ± 0.68 | 33.2 ± 0.36 | 33.0 ± 0.29 | 31.6 ± 1.69 | 3.76 | 0.042 |
| %N | 2.63 ± 0.13 | 2.42 ± 0.14 | 2.73 ± 0.15 | 2.70 ± 0.06 | 2.64 ± 0.30 | 2.64 | 0.037 |
| C/N | 14.0 ± 0.20 | 15.2 ± 0.63 | 14.4 ± 0.64 | 14.4 ± 0.24 | 14.4 ± 0.92 | 2.97 | 0.04 |
| FTA Blade (N) | 2.85 ± 0.24 | 5.85 ± 0.78 | 3.33 ± 0.39 | 5.36 ± 0.50 | 3.79 ± 0.34 | 5.12 | 0.022 |
| FTA Ligule (N) | 2.39 ± 0.18 | 3.47 ± 0.60 | 2.72 ± 0.66 | 3.64 ± 0.39 | 2.39 ± 0.05 | 4.82 | 0.013 |
| FTS Blade (N·mm−2) | 4.70 ± 0.32 | 4.97 ± 0.55 | 3.57 ± 0.21 | 3.83 ± 0.67 | 3.44 ± 0.58 | 3.65 | 0.036 |
| FTS Ligule (N·mm−2) | 4.10 ± 0.61 | 2.87 ± 0.43 | 2.83 ± 0.47 | 2.52 ± 0.40 | 2.12 ± 0.24 | 3.12 | 0.041 |
| FTA Blade/FTA Ligule (%) | 133 ± 10.5 | 185 ± 14.5 | 164 ± 35.4 | 164 ± 11.3 | 187 ± 27.8 | 4.23 | 0.02 |
| Leaf Traits | Season | Linear model effect (df = 1) | |||||
| Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | χ2 | p-value | |
| Leaf Length (cm) | 15.6 ± 4.4 | 22.9 ± 3.94 | 26.3 ± 4.42 | 29.5 ± 4.26 | 18.2 ± 5.91 | 2.93 | 0.017 |
| Leaf Width (mm) | 3.04 ± 0.35 | 3.26 ± 0.27 | 4.26 ± 0.27 | 4.56 ± 0.29 | 3.14 ± 0.36 | 1.64 | 0.034 |
| Leaf Thickness (mm) | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.27 ± 0.04 | 0.25 ± 0.03 | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 2.94 | 0.027 |
| Surface area (cm2) | 5.43 ± 1.88 | 8.32 ± 1.81 | 11.6 ± 1.83 | 14.7 ± 1.82 | 6.01 ± 2.79 | 5.19 | 0.012 |
| Cross-sectional area (mm2) | 1.03 ± 0.18 | 0.93 ± 0.18 | 1.09 ± 0.18 | 1.44 ± 0.21 | 1.12 ± 0.21 | 3.84 | 0.03 |
| Fibre content (% DW) | 36.0 ± 1.97 | 34.6 ± 1.39 | 40.6 ± 1.37 | 43.9 ± 0.66 | 35.2 ± 0.47 | 1.64 | 0.041 |
| %C | 33.7 ± 0.38 | 31.3 ± 1.15 | 30.0 ± 1.25 | 31.5 ± 1.21 | 33.9 ± 1.22 | 4.26 | 0.036 |
| %N | 2.97 ± 0.12 | 2.50 ± 0.17 | 2.36 ± 0.2 | 2.34 ± 0.18 | 2.95 ± 0.18 | 7.13 | 0.016 |
| C/N | 13.3 ± 0.39 | 14.7 ± 0.42 | 14.9 ± 0.49 | 15.9 ± 0.47 | 13.5 ± 0.48 | 6.95 | 0.011 |
| FTA Blade (N) | 4.52 ± 0.57 | 3.64 ± 0.68 | 4.04 ± 0.69 | 4.05 ± 0.89 | 4.93 ± 0.81 | 6.42 | 0.015 |
| FTA Ligule (N) | 3.39 ± 0.50 | 2.38 ± 0.58 | 2.90 ± 0.53 | 2.24 ± 0.65 | 3.70 ± 0.39 | 4.26 | 0.01 |
| FTS Blade (N·mm−2) | 4.70 ± 0.38 | 4.40 ± 0.31 | 3.84 ± 0.49 | 3.26 ± 0.42 | 4.31 ± 0.48 | 4.85 | 0.013 |
| FTS Ligule (N·mm−2) | 3.64 ± 0.74 | 2.99 ± 0.60 | 2.86 ± 0.19 | 1.74 ± 0.26 | 3.21 ± 0.44 | 3.85 | 0.02 |
| FTA Blade/FTA Ligule (%) | 149 ± 22.3 | 153 ± 23.2 | 141 ± 12.4 | 203 ± 8.8 | 159 ± 28.6 | 5.24 | 0.036 |
| Coefficient of Variation (CV) | Location | Linear model effect (df = 1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH | BC | ST-Int | ST-Sub | CC | χ2 | p-value | |
| FTA Blade (%) | 37.15 ± 5.34 | 27.29 ± 3.29 | 33.29 ± 3.73 | 34.30 ± 2.52 | 29.30 ± 2.92 | 3.41 | 0.023 |
| FTA Ligule (%) | 25.65 ± 5.99 | 34.69 ± 6.43 | 38.39 ± 9.11 | 36.59 ± 7.93 | 27.25 ± 4.35 | 4.16 | 0.034 |
| FTS Blade (%) | 39.45 ± 7.75 | 29.25 ± 2.65 | 33.87 ± 3.27 | 32.59 ± 1.52 | 29.70 ± 2.73 | 3.72 | 0.01 |
| FTS Ligule (%) | 28.28 ± 5.70 | 30.74 ± 5.98 | 39.82 ± 7.94 | 34.38 ± 6.41 | 28.43 ± 4.55 | 1.06 | 0.38 |
| Coefficient of Variation (CV) | Season | Linear model effect (df = 1) | |||||
| Winter | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | χ2 | p-value | |
| FTA Blade CV (%) | 30.06 ± 2.62 | 33.91 ± 6.07 | 37.60 ± 6.43 | 29.97 ± 5.97 | 29.80 ± 6.09 | 0.23 | 0.42 |
| FTA Ligule CV (%) | 28.54 ± 5.96 | 26.11 ± 5.32 | 26.42 ± 2.38 | 35.10 ± 3.84 | 46.39 ± 3.91 | 3.56 | 0.013 |
| FTS Blade CV (%) | 29.20 ± 1.02 | 39.88 ± 8.18 | 34.86 ± 8.26 | 33.29 ± 8.05 | 27.62 ± 7.83 | 4.53 | 0.037 |
| FTS Ligule CV (%) | 20.72 ± 2.50 | 31.15 ± 4.73 | 28.26 ± 4.85 | 40.01 ± 7.11 | 41.50 ± 6.38 | 3.98 | 0.023 |
| FTALigule~Thickness + C/N (AIC = 56.4) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | t value | Pr(>|t|) |
| (Intercept) | 2.156 | 2.160 | 0.998 | 0.331 |
| Width | −0.032 | 0.331 | −0.097 | 0.924 |
| Thickness | 10.420 | 2.516 | 4.141 | <0.001 *** |
| Length | 0.003 | 0.026 | 0.108 | 0.915 |
| Fibre | −0.009 | 0.041 | −0.232 | 0.819 |
| CN | −0.142 | 0.151 | −0.938 | 0.360 |
| FTABlade~Thickness + Length (AIC = 62.2) | ||||
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | t value | Pr(>|t|) |
| (Intercept) | −0.227 | 2.401 | −0.095 | 0.926 |
| Width | 0.102 | 0.368 | 0.279 | 0.783 |
| Thickness | 16.406 | 2.798 | 5.864 | <0.001 *** |
| Length | 0.017 | 0.029 | 0.567 | 0.578 |
| Fibre | −0.022 | 0.046 | −0.488 | 0.631 |
| CN | −0.032 | 0.168 | −0.188 | 0.853 |
| FTSLigule~Width + C/N (AIC = 49.4) | ||||
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | t value | Pr(>|t|) |
| (Intercept) | 8.541 | 1.804 | 4.734 | <0.001 *** |
| Width | −0.655 | 0.276 | −2.370 | 0.029 * |
| Thickness | −2.163 | 2.102 | −1.029 | 0.316 |
| Length | 0.004 | 0.022 | 0.183 | 0.857 |
| Fibre | 0.010 | 0.034 | 0.302 | 0.766 |
| CN | −0.221 | 0.126 | −1.749 | 0.096 |
| FTSBlade~Width + Length + Fibre (AIC = 12.5) | ||||
| Predictor | Estimate | SE | t value | Pr(>|t|) |
| (Intercept) | 3.242 | 0.850 | 3.814 | 0.001 ** |
| Width | −0.893 | 0.130 | −6.866 | <0.001 *** |
| Thickness | 0.080 | 0.990 | 0.081 | 0.936 |
| Length | 0.023 | 0.010 | 2.222 | 0.039 * |
| Fibre | 0.037 | 0.016 | 2.296 | 0.033 * |
| CN | −0.046 | 0.060 | −0.775 | 0.448 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez-Ramos, R.; Henares, C.; Egea, L.G.; Vergara, J.J.; Brun, F.G. Leaf Senescence of the Seagrass Cymodocea nodosa in Cádiz Bay, Southern Spain. Diversity 2023, 15, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020187
Jiménez-Ramos R, Henares C, Egea LG, Vergara JJ, Brun FG. Leaf Senescence of the Seagrass Cymodocea nodosa in Cádiz Bay, Southern Spain. Diversity. 2023; 15(2):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020187
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez-Ramos, Rocío, Carmen Henares, Luis G. Egea, Juan J. Vergara, and Fernando G. Brun. 2023. "Leaf Senescence of the Seagrass Cymodocea nodosa in Cádiz Bay, Southern Spain" Diversity 15, no. 2: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020187
APA StyleJiménez-Ramos, R., Henares, C., Egea, L. G., Vergara, J. J., & Brun, F. G. (2023). Leaf Senescence of the Seagrass Cymodocea nodosa in Cádiz Bay, Southern Spain. Diversity, 15(2), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15020187