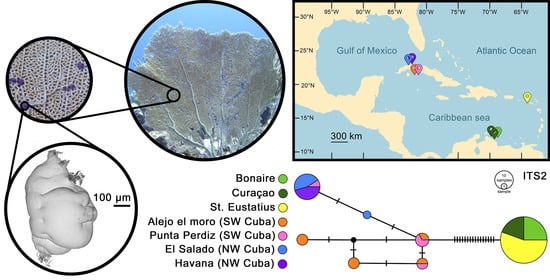
Tracing Geographic and Molecular Footprints of Copepod Crustaceans Causing Multifocal Purple Spots Syndrome in the Caribbean Sea Fan Gorgonia ventalina
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection
2.2. Morphological Examinations
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. DNA Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. DNA Phylogeny and AGBD Analyses
2.6. Host Relationships and Geographical Isolation
2.7. Molecular Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Observation of the Purple Galls on Gorgonia ventalina
3.2. Morphological Features of Sphaerippe spp. from the Purple Galls
3.3. Interspecies Molecular Diversity
3.4. Intraspecific Molecular Diversity
3.5. Phylogeny Reconstruction
4. Discussion
4.1. Morphological Examination of Copepod Specimens
4.2. Molecular Phylogenetic Divergence
4.3. Geographical Heterogeneity of Parasite and Host Populations
4.4. Coral Diseases and the Multifocal Purple Spot Syndrome (MFPS)
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Gene | Primers | Primer Sequences (5’ to 3’) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ITS2 (coral) | 5.8S-436 | AGC ATG TCT GTC TGA GTG TTG G | [29] |
| ITS2 (coral) | 28S-663 | GGG TAA TCT TGC CTG ATC TGA G | [29] |
| msh1 | ND42599 | GCC ATT ATG GTT AAC TAT TAC | [30] |
| msh1 | Mut-3458R | TSG AGC AAA AGC CAC TCC | [30] |
| ITS2 (copepod) | 58dir-cop | CAG TGG ATC AYT TGG CTC GGG GG | [25] |
| ITS2 (copepod) | 28r1-cop | CAT TCG CCA TTA CTA AGG GRA TCA C | [25] |
| COI | LCO1490cop3 | TCI TGI AAY CAY AAA GAY ATY GGI AC | [25] |
| COI | jgHCO2198 | TAI ACY TCI GGR TGI CCR AAR AAY CA | [27] |
| 18S | 18d1 | TGA AAC YGC GAA TGG CTC | A.V. Aleshin, unpublished |
| 18S | 18r3 | CAA CTA CGA GCT TTT TAA C | A.V. Aleshin, unpublished |
| 18S | Q39 | GAA TGA TCC WTC YGC AGG TTC ACC TAC | [28] |
| Primers | Amplification Regime, Min | Amplified Fragments Lengths, bp |
|---|---|---|
| 5.8S-436—28S-663 (coral) |
| 215–240 |
| ND42599—Mut-3458R |
| 822–857 |
| 58dir-cop—28r1 (copepod) |
| 441–576 |
| 28d1—28r3 |
| 657–667 |
| LCO1490cop3—jgH2198 |
| 617–687 |
| 18d1—Q39 |
| 1537–1658 |
| Taxon | Specimen | Sample | ITS2 | msh1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gorgonia ventalina (Linnaeus 1758) | 15-99 | Statia15-99 | OR977951 | OR987860 |
| 15-134 | Statia15-134 | OR977945 | OR987862 | |
| 15-135 | Statia15-135 | OR977959 | OR987863 | |
| 15-141 | Statia15-141 | OR977958 | OR987864 | |
| 15-142 | Statia15-142 | OR977943 | OR987865 | |
| 15-146 | Statia15-146 | OR977957 | ||
| 15-163 | Statia15-163 | OR977950 | OR987872 | |
| 15-174 | Statia15-174 | OR977949 | OR987858 | |
| 17-39 | CUR17-39 | OR977940 | OR987859 | |
| 17-81 | CUR17-81 | OR977944 | ||
| 17-88 | CUR17-88 | OR977946 | OR987873 | |
| 17-96 | CUR17-96 | OR977955 | OR987866 | |
| 19-1 | Cuba19-1 | OR977956 | ||
| 19-3 | Cuba19-3 | OR977954 | OR987867 | |
| 19-5 | Cuba19-5 | OR977942 | OR987868 | |
| 19-22 | Cuba19-22 | OR977948 | OR987861 | |
| 19-23 | Cuba19-23 | OR977941 | OR987869 | |
| 19-25 | Cuba19-25 | OR977953 | OR987870 | |
| 19-27 | Cuba19-27 | OR977952 | OR987871 | |
| 19-28 | Cuba19-28 | OR977947 | OR987857 | |
| 19-32 | Cuba19-32 | OR987874 | ||
| B28-4 | Bonaire19-28 | OR987876 | ||
| B31-4 | Bonaire19-31 | OR987877 | ||
| B47-4 | Bonaire19-47 | OR987875 | ||
| B91-4 | Bonaire19-91 | OR977951 | OR987860 |
| Taxon | Specimen | Sample | 18S | COI | ITS2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lamippidae | SLAVA122 | AU-VI_1898 | PP338814 | PP330795 | PP338815 |
| SLAVA123 | AU-VI_1898 | PP330796 | PP338816 | ||
| Sphaerippe spp. | K1 | Statia15-170 | PP330815 | PP338838 | |
| K2 | Statia15-170 | PP330816 | PP338839 | ||
| K3 | Statia15-170 | PP330817 | PP338840 | ||
| K4 | Statia15-99 | ||||
| K5 | Statia15-99 | PP330818 | PP338841 | ||
| K6 | Statia15-99 | PP338813 | PP330819 | PP338842 | |
| O-1 | CUR17-39 | PP330828 | PP338852 | ||
| O-2 | CUR17-39 | PP330834 | PP338858 | ||
| O-3 | CUR17-39 | PP330835 | PP338859 | ||
| O-4 | CUR17-39 | PP330836 | PP338860 | ||
| O-5 | CUR17-39 | PP330837 | PP338861 | ||
| O-6 | CUR17-39 | PP330838 | PP338862 | ||
| O-7 | CUR17-39 | PP330839 | PP338863 | ||
| O-8 | Statia15-172 | PP330840 | |||
| O-9 | Statia15-173 | PP330841 | PP338864 | ||
| O-10 | Statia15-173 | PP330820 | PP338843 | ||
| O-11 | Statia15-170 | PP330821 | PP338844 | ||
| O-12 | Statia15-170 | PP338845 | |||
| O-13 | Statia15-170 | PP338846 | |||
| O-14 | Statia15-99 | PP330822 | PP338847 | ||
| O-15 | Statia15-99 | PP330823 | PP338848 | ||
| O-16 | Statia15-99 | PP330824 | PP338849 | ||
| O-17 | Statia15-99 | PP330825 | PP338850 | ||
| O-18 | Statia15-141 | PP330826 | |||
| O-19 | Statia15-141 | PP330827 | PP338851 | ||
| O-20 | Statia15-141 | PP330829 | PP338853 | ||
| O-21 | Statia15-142 | PP330830 | PP338854 | ||
| O-22 | Statia15-142 | PP330831 | PP338855 | ||
| O-23 | Statia15-142 | PP330832 | PP338856 | ||
| O-24 | Statia15-142 | PP330833 | PP338857 | ||
| C-1 | Cuba19-1 | PP338827 | |||
| C-2 | Cuba19-1 | ||||
| C-3 | Cuba19-1 | PP330797 | PP338832 | ||
| C-4 | Cuba19-2 | PP338833 | |||
| C-5 | Cuba19-3 | PP330806 | PP338834 | ||
| C-6 | Cuba19-3 | PP330807 | PP338835 | ||
| C-7 | Cuba19-3 | PP330808 | |||
| C-8 | Cuba19-5 | PP330813 | PP338836 | ||
| C-9 | Cuba19-5 | PP330814 | PP338837 | ||
| C-10 | Cuba19-5 | PP338817 | |||
| C-11 | Cuba19-21 | PP330798 | PP338818 | ||
| C-12 | Cuba19-5 | PP338819 | |||
| C-13 | Cuba19-23 | PP330799 | PP338820 | ||
| C-14 | Cuba19-25 | PP330800 | PP338821 | ||
| C-15 | Cuba19-25 | PP338822 | |||
| C-16 | Cuba19-25 | PP330801 | PP338823 | ||
| C-17 | Cuba19-28 | PP330803 | PP338824 | ||
| C-18 | Cuba19-28 | PP330804 | PP338825 | ||
| C-19 | Cuba19-30 | PP330809 | PP338826 | ||
| C-20 | Cuba19-33 | PP330811 | PP338828 | ||
| C-21 | Cuba19-32 | PP330810 | PP338829 | ||
| C-22 | Cuba19-27 | PP330802 | PP338830 | ||
| C-23 | Cuba19-3 | PP330805 | PP338831 | ||
| C-24 | Cuba19-5 | PP330812 | |||
| B28-1 | Bonaire19-28 | PP338867 | |||
| B28-2 | Bonaire19-28 | PP330794 | PP338872 | ||
| B28-3 | Bonaire19-28 | PP330790 | PP338871 | ||
| B31-1 | Bonaire19-31 | PP330786 | PP338866 | ||
| B31-2 | Bonaire19-31 | PP330793 | PP338865 | ||
| B31-3 | Bonaire19-31 | PP330791 | PP338873 | ||
| B47-1 | Bonaire19-47 | PP330787 | PP338868 | ||
| B47-2 | Bonaire19-47 | PP330789 | |||
| B47-3 | Bonaire19-47 | ||||
| B91-1 | Bonaire19-91 | PP330788 | PP338869 | ||
| B91-2 | Bonaire19-91 | PP338870 | |||
| B91-3 | Bonaire19-91 | PP330792 |
| Scientific Name | ITS2 | msh1 |
|---|---|---|
| Gorgonia flabellum Bayer, 1961 | AY587521 | AY126427 |
| Gorgonia mariae Bayer, 1961 | AY587523 | AY126426 |
| Gorgonia ventalina (Linnaeus 1758) | AY587522 | AY126425 |
| Antillogorgia bipinnata (Verrill, 1864) (=Pseudopterogorgia bipinnata (Verrill, 1864)) | AY126365 | AY587524 |
| Order | Family | Scientific Name | 18S |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclopoida | Pachospunctatum | GU969182 | |
| Pachos sp. | AY627014 | ||
| Anchimolgidae | Anchimolgidae sp. | AY627000 | |
| Anchimolgus sp. | AY627001 | ||
| Anthessiidae | Anthessius sp. | AY627002 | |
| Archinotodelphyidae | Archinotodelphys sp. | JF781538 | |
| Botryllophilidae | Haplostoma kimi | KR048722 | |
| Cyclopettidae | Paracyclopina nana | FJ214952 | |
| Cyclopidae | Acanthocyclops viridis | AY626999 | |
| Apocyclops borneoensis | KR048733 | ||
| Apocyclops royi | AY626997 | ||
| Ectocyclops affinis | KR048732 | ||
| Ectocyclops polyspinosus | AJ746336 | ||
| Eucyclops serrulatus | AJ746328 | ||
| Eucyclops speratus | KR048717 | ||
| Euryte sp. | AY626996 | ||
| Cyclopidae sp. | AY210814 | ||
| Cyclops insignis | EF532821 | ||
| Cyclops kolensis | EF532820 | ||
| Cyclops sp. | AY626998 | ||
| Macrocyclops albidus | DQ538505 | ||
| Macrocyclops fuscus | KR048720 | ||
| Megacyclops viridis | KR048727 | ||
| Mesocyclops dissimilis | KR048719 | ||
| Mesocyclops pehpeiensis | KR048728 | ||
| Microcyclops varicans | KR048721 | ||
| Tropocyclops ishidai | KR048729 | ||
| Cyclopinidae | Cyclopina gracilis | JF781537 | |
| Lernaeidae | Lamproglena orientalis | DQ107549 | |
| Lernaea cyprinacea | DQ107554 | ||
| Mytilicolidae | Mytilicola intestinalis | AY627005 | |
| Pectenophilus ornatus | AY627032 | ||
| Trochicola entericus | AY627006 | ||
| Notodelphyidae | Bonnierilla curvicaudata | KR048724 | |
| Doropygus elegans | KR048723 | ||
| Doropygus rigidus | KR048730 | ||
| Notodelphys prasina | JF781536 | ||
| Pachypygus curvatus | KR048731 | ||
| Oithonidae | Dioithona oculata | KR048726 | |
| Oithona similis | KR048725 | ||
| Oithona sp. 1 | JF781539 | ||
| Oithona sp. 2 | JF781540 | ||
| Rhynchomolgidae | Doridicola agilis | JF781541 | |
| Critomolgus nudus | KR048760 | ||
| Critomolgus sp. 1 | AY627008 | ||
| Critomolgus sp. 2 | AY627009 | ||
| Critomolgus vicinus | KR048766 | ||
| Zamolgus cavernularius | KR048761 | ||
| Sabelliphilidae | Sabelliphilidae sp. | KR048767 | |
| Sabelliphilus elongatus | AY627010 | ||
| Scambicornus sp. | AY627011 | ||
| Vahiniidae | Vahinius sp. | AY627012 | |
| Xarifiidae | Xarifia sp. | AY627013 | |
| Misophrioida | Misophriidae | Misophria sp. | JF781533 |
| Misophriopsis okinawensis | JF781532 | ||
| Misophriopsis sp. | JF781534 | ||
| Poecilostomatoida | Bomolochidae | Holobomolochus sp. | JF781551 |
| Nothobomolochus thambus | KR048747 | ||
| Catiniidae | Catinia plana | JF781555 | |
| Catiniidae sp. | JF781554 | ||
| Chondracanthidae | Acanthochondria spirigera | KR048753 | |
| Acanthochondria tchangi | KR048754 | ||
| Brachiochondria pinguis | KR048755 | ||
| Chondracanthus distortus | KR048756 | ||
| Chondracanthus zei | KR048770 | ||
| Lernentoma asellina | AY627003 | ||
| Clausidiidae | Conchyliurus dispar | KR048764 | |
| Conchyliurus quintus. | KR048763 | ||
| Hemicyclops ctenidis. | KR048744 | ||
| Hemicyclops sp. | KT030266 | ||
| Hemicyclops tanakai | KR048769 | ||
| Hemicyclops thalassius | JF781552 | ||
| Clausocalanidae | Clausia sp. | KR048749 | |
| Corycaeidae | Corycaeus speciosus | GU969165 | |
| Ergasilidae | Ergasilus tumidus | DQ107569 | |
| Ergasilus wilsoni | KR048765 | ||
| Neoergasilus japonicus | KR048752 | ||
| Sinergasilus undulatus | DQ107562 | ||
| Iveidae | Ive sp. | JF417992 | |
| Lichomolgidae | Astericola clausii | JF781542 | |
| Herrmannella longicaudata | KR048757 | ||
| Lichomolgus marginatus | JF781544 | ||
| Lichomolgus similis | KR048758 | ||
| Stellicola sp. | AY627004 | ||
| Myicolidae | Ostrincola koe | KR048750 | |
| Pseudomyicola spinosus | KR048751 | ||
| Pseudanthessiidae | Mecomerinx heterocentroti | JF781545 | |
| Pseudanthessius sp. | AY627007 | ||
| Sapphirinidae | Copilia mirabilis | GU969205 | |
| Sapphirina scarlata | GU969208 | ||
| Synaptiphilidae | Synaptiphilus longicaudus | KR048745 | |
| Taeniacanthidae | Anchistrotos kojimensis | KT030267 | |
| Clausidium vancouverense | JF781553 | ||
| Clavisodalis abbreviatus | JF781549 | ||
| Irodes sauridi | JF781550 | ||
| Pseudotaeniacanthus congeri | KR048746 | ||
| Taeniacanthus kitamakura | JF781548 | ||
| Taeniacanthus yamagutii | KR048748 | ||
| Taeniacanthus zeugopteri | JF781547 | ||
| Umazuracola elongatus | JF781546 |
| Host | Agent (in Source) | Higher Geography | Site | Geocoordinate | Accuracy (m) | Depth (m) | Month | Year | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gorgonia ventalina | Protozoan (Labyrinthulomycote) | Florida | Florida | 27.588099, −82.739206 | 320000 | 2005 | [9,21] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Protozoan (Labyrinthulomycote) | Mexico | Mexico | 21.773321, −94.070358 | 390000 | 2005 | [9,21] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina and other octocorals | Protozoan (Labyrinthulomycote) | Puerto Rico | Puerto Rico | 17.940083, −66.466573 | 100000 | 3–20 | 2005 | [21,78] | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Aplanochytrium | Puerto Rico | Media Luna | 17.934883, −67.048850 | 3–18 | July, September, October | 2006–2010 | [74] | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Aplanochytrium | Puerto Rico | Buoy | 17.889667, −66.984833 | 18–25 | 2006–2010 | [74] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Aplanochytrium | Florida | Big Pine Ledges | 24.553450, −81.378850 | February | 2010 | [74] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Turrumotico | 17.929050, −66.974783 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Turrumote | 17.934950, −67.018833 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Laurel Patch | 17.942283, −67.067617 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Media Luna | 17.934933, −67.048517 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Pelotas | 17.957433, −67.069717 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Caballo Blanco | 17.963850, −67.049000 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Enrique | 17.954900, −67.043467 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Corral Channel | 17.949317, −66.998967 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Fosfo Bay | 17.959067, −67.013767 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | Mario reef | 17.952833, −67.056450 | June, July | 2013 | [76] | ||
| Gorgonia sp. | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Grand Cayman | Grand Cayman | 19.318796, −81.325228 | 15000 | [1] | |||
| Gorgonia sp. | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Curaçao | Curaçao | 12.218792, −68.971464 | 33000 | [1] | |||
| Gorgonia sp. | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Grenada | Grenada | 12.331716, −61.559601 | 30000 | [1] | |||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Labyrinthulid, Copepod | Puerto Rico | La Parguera | 17.964639, −67.051750 | 12000 | 2003–2012 | [1] | ||
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | St. Eustatius | Anchor Point North | 17.463900, −62.987700 | 15–20 | June | 2015 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | St. Eustatius | Anchor Reef | 17.462433, −62.985483 | 15.6 | June | 2015 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | St. Eustatius | Blund Shoal | 17.464617, −62.977417 | 5.9 | June | 2015 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | St. Eustatius | English Quarter | 17.505067, −62.962867 | 17.3 | June | 2015 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | St. Eustatius | Gallows Bay | 17.475083, −62.986194 | 12 | June | 2015 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | St. Eustatius | Gibraltar | 17.526817, −62.999300 | 5–20 | June | 2015 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia sp. | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | St. Eustatius | The Blocks | 17.464117, −62.985200 | 14.3 | June | 2015 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | St. Eustatius | Twin Sisters | 17.516550, −63.003000 | 13.8 | June | 2015 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia sp. | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | Curaçao | Buoy 1 (north of Piscadera Bay) | 12.123056, −68.970556 | 8.2 | June | 2017 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia sp. | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | Curaçao | Director’s Bay | 12.066389, −68.860556 | 4.1 | June | 2017 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia sp. | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | Curaçao | Tugboat 2 | 12.068056, −68.862222 | 5.2–5.5 | June | 2017 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia sp. | Sphaerippe sp. 1 | Curaçao | Playa Lagun | 12.317222, −69.152500 | 4.9 | June | 2017 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 2 | Cuba | Playa Salado | 23.038981, −82.605153 | 4.5–8.5 | February | 2019 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 2 | Cuba | Alejo el moro | 22.115275, −81.116378 | 4.8–5.0 | February | 2019 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 3 | Cuba | Centro de Investigaciones Marinas de la Universidad de La Habana | 23.127431, −82.422689 | 8.1–11.6 | February | 2019 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Sphaerippe sp. 3 | Cuba | Punta Perdiz | 22.108236, −81.113728 | 8.3–13.8 | February | 2019 | This paper | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Unknown | Virgin Islands | St. Thomas | 18.335765, −64.896335 | 92000 | October | 2010 | [80] | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Unknown | Puerto Rico | Playa Melones Culebra | 18.304499, −65.311489 | 244 | December | 2013 | [80] | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Unknown | Bahamas | Cape Eleuthera | 24.812122, −76.343152 | 244 | May | 2019 | [80] | |
| Gorgonia ventalina | Unknown | St. Nevis | Jones Bay | 17.196492, −62.613952 | April | 2017 | [80] |
References
- Weil, E.; Rogers, C.S.; Croquer, A. Octocoral diseases in a changing ocean. In Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas Saco del Valle, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 1109–1163. [Google Scholar]
- Calderón-Hernández, A.; Urbina-Villalobos, A.; Mora-Barboza, C.; Morales, J.A.; Fernández-García, C.; Cortés, J. Lesions in octocorals of the Costa Rican Caribbean During The 2015–2016 El Niño. Coral Reefs 2021, 40, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.A.M.J.; Freeman, M.A.; Dennis, M.M. A combined diagnostic approach for the investigation of lesions resembling aspergillosis in Caribbean sea fans (Gorgonia spp.). Veter. Pathol. 2023, 60, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowlton, N.; Rohwer, F. Multispecies microbial mutualisms on coral reefs: The host as a habitat. Am. Nat. 2003, 162, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, K.B. Regulation of microbial populations by mucus–associated bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 322, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimes, N.E.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Weil, E.; Zhou, J.; Morris, P.J. Microbial functional structure of Montastraea faveolata, an important Caribbean reef–building coral, differs between healthy and Caribbean yellow–band diseased colonies. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 541–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, C.A.; Mouchka, M.E.; Harvell, C.D.; Roberts, S. Immune response of the Caribbean seafan, Gorgonia ventalina exposed to an Aplanochytrium parasite as revealed by transcriptome sequencing. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.W.; Weil, E. Aspergillosis of gorgonians. In Coral Health and Disease; Rosenberg, E., Loya, Y., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 270–286. [Google Scholar]
- Harvell, C.D.; Markel, S.; Jordan-Dahlgren, E.; Raymundo, L.J.; Rosenberg, E.; Smith, G.W.; Willis, B.L.; Weil, E. Coral disease, environmental drivers and the balance between coral and microbial associates. Oceanography 2007, 20, 36–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Moreno, D.; Willis, B.L.; Page, A.C.; Weil, E.; Croquer, A.; Vargas-Angel, B.; Jordan-Garza, A.G.; Jordán-Dahlgren, E.; Raymundo, L.; Harvell, C.D. Global coral disease prevalence associated with sea temperature anomalies and local factors. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2012, 100, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, F.M. The shallow–water Octocorallia of the West Indian region. Stud. Fauna Curaçao Carib. Isl. 1961, 12, 1–373. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanenko, V.N.; Nikitin, M.A.; Hoeksema, B.W. Multiple purple spots in the Caribbean Sea fan Gorgonia ventalina caused by parasitic copepods at St. Eustatius, Dutch Caribbean. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 79–80. [Google Scholar]
- Korzhavina, O.A.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Ivanenko, V.N. A review of Caribbean Copepoda associated with reef–dwelling cnidarians, echinoderms, and sponges. Contrib. Zool. 2019, 88, 297–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzhavina, O.A.; Reimer, J.D.; Ehrlich, H.; Ivanenko, V.N. Global diversity and distribution of Lamippidae copepods symbiotic on Octocorallia. Symbiosis 2021, 83, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzhavina, O.A.; Grishina, D.Y.; Chen, X.; Fontaneto, D.; Ivanenko, V.N. Diving into diversity: Copepod crustaceans in octocoral association. Diversity 2023, 15, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humes, A.G. Lamippe concinna sp. n., a copepod parasitic in a West African pennatulid coelenterate. Parasitology 1957, 47, 447–451. [Google Scholar]
- Grygier, M.J. Two new lamippid copepods parasitic on gorgonians from Hawaii and the Bahamas. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1980, 93, 662–673. [Google Scholar]
- Grygier, M.J. An endoparasitic Lamippid Copepod in Acanella from the North Atlantic. Crustaceana 1983, 45, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.D.; Anchaluisa, B.; Boyko, C.B.; McDaniel, N. Description of a new endoparasitic copepod genus and species (Lamippidae) that induces gall formation in leaves of the sea pen Ptilosarcus gurneyi (Octocorallia) from British Columbia. Mar. Biodivers. 2018, 48, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, E. Coral reef diseases in the wider Caribbean. In Coral Health and Disease; Rosenberg, E., Loya, Y., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 35–68. [Google Scholar]
- Weil, E.; Rogers, C.S. Coral reef diseases in the Atlantic–Caribbean. In Coral Reefs: An Ecosystem in Transition; Dubinsky, Z., Stambler, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 465–491. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Rypien, K. Aspergillosis of caribbean sea fan corals, Gorgonia spp. In Diseases of Coral; Woodley, C., Downs, C.A., Bruckner, A., Porter, J., Galloway, S.B., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Hoeksema, B.W.; Reimer, J.D.; Vonk, R. Editorial: Biodiversity of Caribbean coral reefs (with a focus on the Dutch Caribbean). Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanenko, V.N.; Defaye, D. A new and primitive genus and species of deep–sea Tegastidae (Crustacea, Copepoda, Harpacticoida) from the Mid–Atlantic Ridge, 37°N (Azores Triple Junction, Lucky Strike). Cah. Biol. Mar. 2004, 45, 255–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanenko, V.N.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Mudrova, S.V.; Nikitin, M.A.; Martínez, A.; Rimskaya-Korsakova, N.N.; Berumen, M.L.; Fontaneto, D. Lack of host specificity of copepod crustaceans associated with mushroom corals in the Red Sea. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2018, 127, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porco, D.; Rougerie, R.; Deharveng, L.; Hebert, P. Coupling non–destructive DNA extraction and voucher retrieval for small soft–bodied Arthropods in a high–throughput context: The example of Collembola. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, J.; Meyer, C.; Parker, M.; Hawk, H. Redesign of PCR primers for mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I for marine invertebrates and application in all–taxa biotic surveys. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlin, L.; Elwood, H.J.; Stickel, S.; Sogin, M.L. The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S–like rRNA–coding regions. Gene 1988, 71, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, C.; Sánchez, J.A. Phylogenetic hypotheses of gorgoniid octocorals according to ITS2 and their predicted RNA secondary structures. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2007, 43, 774–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.A.; McFadden, C.S.; France, S.C.; Lasker, H.R. Molecular phylogenetic analyses of shallow–water Caribbean octocorals. Mar. Biol. 2003, 142, 975–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones–Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Drummond, A. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuraku, S.; Zmasek, C.M.; Nishimura, O.; Katoh, K. aLeaves facilitates on–demand exploration of metazoan gene family trees on MAFFT sequence alignment server with enhanced interactivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W22–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum–likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfear, R.; Calcott, B.; Ho, S.Y.; Guindon, S. PartitionFinder: Combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trifinopoulos, J.; Nguyen, L.T.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W232–W235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Phylogenies and the comparative method. Am. Nat. 1985, 125, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaneto, D.; Flot, J.F.; Tang, C.Q. Guidelines for DNA taxonomy, with a focus on the meiofauna. Mar. Biodivers. 2015, 45, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full–feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanenko, V.N.; Corgosinho, P.H.; Ferrari, F.; Sarradin, P.M.; Sarrazin, J. Microhabitat distribution of Smacigastes micheli (Copepoda: Harpacticoida: Tegastidae) from deepsea hydrothermal vents at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, 37° N (Lucky Strike), with a morphological description of its nauplius. Marine Ecology 2012, 33, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-X. Statistical tests of neutrality against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradi, M.; Bandera, E.; Mudrova, S.V.; Ivanenko, V.N. Five new coexisting species of copepod crustaceans of the genus Spaniomolgus (Poecilostomatoida: Rhynchomolgidae), symbionts of the stony coral Stylophora pistillata (Scleractinia). ZooKeys 2018, 791, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelyakin, P.V.; Garushyants, S.K.; Nikitin, M.A.; Mudrova, S.V.; Berumen, M.; Speksnijder, A.G.C.L.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Fontaneto, D.; Gelfand, M.S.; Ivanenko, V.N. Microbiomes of gall–inducing copepod crustaceans from the corals Stylophora pistillata (Scleractinia) and Gorgonia ventalina (Alcyonacea). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, J.; Appel, E.; Gorb, S.N. Functional diversity of resilin in Arthropoda. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1241–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.S.; Hellberg, M.E. Comparative phylogeography in a genus of coral reef fishes: Biogeographic and genetic concordance in the Caribbean. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, L.A.; Rocha, C.R.; Robertson, D.R.; Bowen, B.W. Comparative phylogeography of Atlantic reef fishes indicates both origin and accumulation of diversity in the Caribbean. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huys, R.; Llewellyn-Hughes, J.; Olson, P.D.; Nagasawa, K. Small subunit rDNA and Bayesian inference reveal Pectenophilus ornatus (Copepoda incertae sedis) as highly transformed Mytilicolidae, and support assignment of Chondracanthidae and Xarifiidae to Lichomolgoidea (Cyclopoida). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2006, 87, 403–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, F.D.; Ivanenko, V.N.; Dahms, H.-U. Body architecture and relationships among basal copepods. J. Crustac. Biol. 2010, 30, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, K.V.; Ivanenko, V.N. Lack of reproducibility of molecular phylogenetic analysis of Cyclopoida. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2019, 139, 106574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailov, K.V.; Ivanenko, V.N. Low support values and lack of reproducibility of molecular phylogenetic analysis of Copepoda orders. Arthropoda Selecta 2021, 30, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.A.; Wirshing, H.H. A field key to the identification of tropical western Atlantic zooxanthellate octocorals (Octocorallia: Cnidaria). Carib. J. Sci. 2005, 41, 508–522. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, C.S.; France, S.C.; Sánchez, J.A.; Alderslade, P. A molecular phylogenetic analysis of the Octocorallia (Cnidaria: Anthozoa) based on mitochondrial protein–coding sequences. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2006, 41, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, C.S.; Sánchez, J.A.; France, S.C. Molecular phylogenetic insights into the evolution of Octocorallia: A review. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2010, 50, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.A.; Aguilar, C.; Dorado, D.; Manrique, N. Phenotypic plasticity and morphological integration in a marine modular invertebrate. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andras, J.P.; Kirk, N.L.; Harvell, C.D. Range–wide population genetic structure of Symbiodinium associated with the Caribbean Sea fan coral, Gorgonia ventalina. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 2525–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andras, J.P.; Rypien, K.L.; Harvell, C.D. Range–wide population genetic structure of the Caribbean sea fan coral, Gorgonia ventalina. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanenko, V.N.; Ferrari, F.D.; Smurov, A.V. Nauplii and copepodids of Scottomyzon gibberum (Copepoda: Siphonostomatoida: Scottomyzotidae, a new family), a symbiont of Asterias rubens (Asteroidea). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 2001, 114, 237–261. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanenko, V.N.; Ferrari, F.D. Redescription of adults and description of copepodid development of Dermatomyzon nigripes (Brady, Robertson, 1876) and of Asterocheres lilljeborgi Boeck, 1859 (Copepoda: Siphonostomatoida: Asterocheridae). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 2003, 116, 661–691. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.R.; Lin, C.Y.; Yu, J.K. Embryonic and post–embryonic development in the parasitic copepod Ive ptychoderae (Copepoda: Iviidae): Insights into its phylogenetic position. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.H., Jr.; Bunkley-Williams, L. Life cycle and life history strategies of parasitic Crustacea. Parasit. Crustac. 2019, 3, 179–266. [Google Scholar]
- Jossart, Q.; De Ridder, C.; Lessios, H.A.; Bauwens, M.; Sébastien, M.; Thierry, R.; Rémi, A.W.; Bruno, D. Highly contrasted population genetic structures in a host–parasite pair in the Caribbean Sea. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 9267–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.W.; Meek, A.H.; Willerberg, P. Veterinary Epidemiology, Principles and Methods; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1987; p. 343. [Google Scholar]
- Work, T.M.; Aeby, G.S. Systematically describing gross lesions in corals. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 70, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.S. Words matter: Recommendations for clarifying coral disease nomenclature and terminology. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2010, 91, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Water, J.A.J.M.; Allemand, D.; Ferrier-Pagès, C. Host–microbe interactions in octocoral holobionts—Recent advances and perspectives. Microbiome 2018, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.; Ben-Haim, Y. Microbial diseases of corals and global warming. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesser, M.P.; Bythell, J.C.; Gates, R.D.; Johnstone, R.W.; Hoegh–Guldberg, O. Are infectious diseases really killing corals? Alternative interpretations of the experimental and ecological data. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 346, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burge, C.A.; Douglas, N.; Conti-Jerpe, I.; Weil, E.; Roberts, S.; Friedman, C.S.; Harvell, C.D. Friend or foe: The association of Labyrinthulomycetes with the Caribbean sea fan Gorgonia ventalina. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2012, 101, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano, S.; Maggioni, D.; Liguori, G.; Arrigoni, R.; Berumen, M.L.; Seveso, D.; Galli, P.; Hoeksema, B.W. Morpho–molecular traits of Indo–Pacific and Caribbean Halofolliculina ciliate infections. Coral Reefs 2020, 39, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, A.M.; Weil, E.; Harvell, C.D. Octocoral co–infection as a balance between host immunity and host environment. Oecologia 2018, 186, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petes, L.E.; Harvell, C.D.; Peters, E.C.; Webb, M.A.H.; Mullen, K.M. Pathogens compromise reproduction and induce melanization in Caribbean Sea fans. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 264, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, E.; Hooten, A.J. Underwater Cards for Assessing Coral Health on Caribbean Reefs; GEF–CRTR Program, Center for Marine Sciences, University of Queensland: Brisbane, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chollett, I.; Müller-Karger, F.E.; Heron, S.F.; Skirving, W.; Mumby, P.J. Seasonal and spatial heterogeneity of recent sea surface temperature trends in the Caribbean Sea and southeast Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- iNaturalist. Available online: https://www.inaturalist.org (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Korein, E.; Vega-Rodriguez, M.; Metz Estrella, T. Developing recommendations for coral disease management in Puerto Rico using key informant interviews and participatory mapping. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 236, 106488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Locality Name | Coordinates | Date of Sampling | Collector(s) | Name of Specimens | Depth, m | Coral | Copepods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gibraltar, St. Eustatius, (Figure 1, point 1) | 17°31′36.5″ N 62°59′57.5″ W | 12 June 2015 | V.N.I. | Statia15-99 | 5–20 | + | + |
| Anchor Point North, St. Eustatius (Figure 1, point 2) | 17°27′50.0″ N 62°59′15.7″ W | 17 June 2015 | V.N.I. | Statia15-134 | 15–20 | + | |
| Statia15-135 | 15–20 | + | |||||
| Anchor Reef, St. Eustatius (Figure 1, point 3) | 17°27′44.8″ N 62°59′07.7″ W | 18 June 2015 | V.N.I. | Statia15-141 | 15.6 | + | + |
| Statia15-142 | 15.6 | + | + | ||||
| English Quarter, St. Eustatius (Figure 1, point 4) | 17°30′18.2″ N 62°57′46.3″ W | 19 June 2015 | V.N.I. | Statia15-146 | 17.3 | + | |
| Twin Sisters, St. Eustatius (Figure 1, point 5) | 17°30′59.6″ N 63°00′10.8″ W | 22 June 2015 | V.N.I. | Statia15-163 | 13.8 | + | |
| Blund Shoal, St. Eustatius (Figure 1, point 6) | 17°27′52.6″ N 62°58′38.7″ W | 26 June 2015 | V.N.I. | Statia15-170 | 5.9 | + | |
| Gallows Bay, St. Eustatius (Figure 1, point 7) | 17°28′30.3″ N 62°59′10.3″ W | 27 June 2015 | V.N.I. | Statia15-173 | 13.8 | + | |
| Statia15-174 | 2–3 | + | |||||
| Director′s Bay, Curaçao, (Figure 1, point 8) | 12°03′59″ N 68°51′38″ W | 13 June 2017 | V.N.I. | Cur17-39 | 4.1 | + | + |
| Tugboat 2, Curaçao (Figure 1, point 9) | 12°04′05″ N, 68°51′44″ W | 19 June 2017 | V.N.I. | Cur17-81 | 5.2–5.5 | + | |
| Playa Lagun, Curaçao (Figure 1, point 10) | 12°19′02″ N, 69°09′09″ W | 20 June 2017 | V.N.I. | Cur17-88 | 4.9 | + | |
| Buoy 1, Curaçao (Figure 1, point 11) | 12°07′23″ N, 68°58′14″ W | 21 June 2017 | V.N.I. | Cur17-96 | 8.2 | + | |
| Alejo el Moro, Cuba (Figure 1, point 12) | 22°06′54.99″ N 81°06′58.96″ W | 4 February 2019 | V.N.I., O.A.K. | Cuba19-1 | 7.0 | + | + |
| Cuba19-2 | 8.5 | + | + | ||||
| Cuba19-3 | 4.5 | + | + | ||||
| Punta Perdiz, Cuba (Figure 1, point 13) | 22°06′29.65″ N 81°06′49.42″ W | 4 February 2019 | V.N.I., O.A.K. | Cuba19-5 | 4.8–5.0 | + | + |
| Coast near Havana University, Cuba (Figure 1, point 14) | 23°07′38.75″ N 82°25′21.68″ W | 7 February 2019 | V.N.I., O.A.K. | Cuba19-21 | 11.6 | + | |
| Cuba19-22 | 8.5 | + | |||||
| Cuba19-23 | 11 | + | + | ||||
| Cuba19-25 | 8.1–8.2 | + | + | ||||
| El Salado, Cuba (Figure 1, point 15) | 23°02′20.33″ N 82°36′18.55″ W | 8 February 2019 | V.N.I., O.A.K. | Cuba19-27 | 13.8 | + | + |
| Cuba19-28 | 10.0 | + | + | ||||
| Cuba19-30 | 12.6 | + | |||||
| Cuba19-32 | 8.3 | + | + | ||||
| Red Beryl, Bonaire (Figure 1, point 16) | 12°2′49.14″ N 68°16′4.38″ W | 28 October 2019 | V.N.I. | Bonaire19-28 | 5 | + | + |
| Red Slave, Bonaire (Figure 1, point 17) | 12°1′36.3″ N 68°15′4.74″ W | 29 October 2019 | V.N.I. | Bonaire19-31 | 14 | + | + |
| Cai (outside of lagoon), Bonaire (Figure 1, point 18) | 12°6′10.98″ N 68°13′19.98″ W | 31 October 2019 | V.N.I. | Bonaire19-47 | 11 | + | + |
| Klein Bonaire: South Bay, Bonaire (Figure 1, point 19) | 12°9′0.06″ N 68°19′14.04″ W | 8 November 2019 | V.N.I. | Bonaire19-91 | 3 | + | + |
| Species of Sample | Localities | Gene | Number of Sequences | Nucleotide Diversity | Tajima’s D | Fu’s F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sphaerippe spp. | Bonaire, Curaçao, St. Eustatius | COI | 36 | 0.00264 | 0.30709 | −0.850 |
| Sphaerippe spp. | Northwest Cuba | COI | 10 | 0.00250 | −1.49280 | −2.563 |
| Sphaerippe spp. | Southwest Cuba | COI | 8 | 0.00168 | −0.17740 | 0.390 |
| Sphaerippe spp. | Bonaire, Curaçao, St. Eustatius | ITS2 | 36 | All sequences identical | ||
| Sphaerippe spp. | Cuba | ITS2 | 21 | 0.00635 | 1.03432 | −0.378 |
| Gorgonia ventalina (Linnaeus 1758) | Caribbean region | ITS2 | All sequences identical | |||
| Gorgonia ventalina (Linnaeus 1758) | Caribbean region | msh1 | 25 | 0.00538 | −1.92207 * | 2.449 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korzhavina, O.A.; Nikitin, M.A.; Hoeksema, B.W.; Armenteros, M.; Reimer, J.D.; Ivanenko, V.N. Tracing Geographic and Molecular Footprints of Copepod Crustaceans Causing Multifocal Purple Spots Syndrome in the Caribbean Sea Fan Gorgonia ventalina. Diversity 2024, 16, 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050280
Korzhavina OA, Nikitin MA, Hoeksema BW, Armenteros M, Reimer JD, Ivanenko VN. Tracing Geographic and Molecular Footprints of Copepod Crustaceans Causing Multifocal Purple Spots Syndrome in the Caribbean Sea Fan Gorgonia ventalina. Diversity. 2024; 16(5):280. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050280
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorzhavina, Oksana A., Mikhail A. Nikitin, Bert W. Hoeksema, Maickel Armenteros, James D. Reimer, and Viatcheslav N. Ivanenko. 2024. "Tracing Geographic and Molecular Footprints of Copepod Crustaceans Causing Multifocal Purple Spots Syndrome in the Caribbean Sea Fan Gorgonia ventalina" Diversity 16, no. 5: 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050280
APA StyleKorzhavina, O. A., Nikitin, M. A., Hoeksema, B. W., Armenteros, M., Reimer, J. D., & Ivanenko, V. N. (2024). Tracing Geographic and Molecular Footprints of Copepod Crustaceans Causing Multifocal Purple Spots Syndrome in the Caribbean Sea Fan Gorgonia ventalina. Diversity, 16(5), 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/d16050280