Forward-Looking Infrared Cameras for Micrometeorological Applications within Vineyards
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Site and Instrumentation
2.2. Self-Organizing Maps, SOMs
3. Results
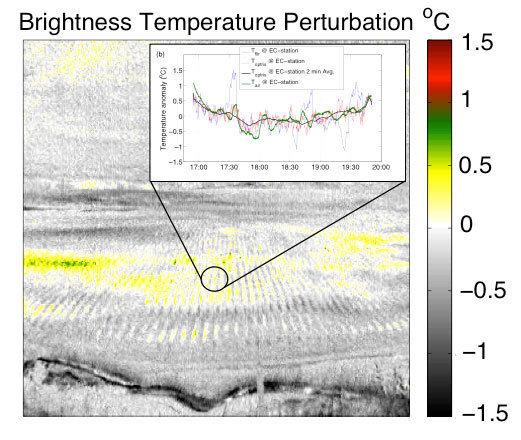
3.1. Micrometeorological Context
3.2. Brightness and Air Temperature Relationship
3.3. Brightness Temperature and Turbulent Heat Flux
3.4. Self-Organizing Maps (SOMs) of Brightness Temperature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, J.M.; Grant, O.M.; Chaves, M.M. Thermography to explore plant–environment interactions. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3937–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araus, J.L.; Cairns, J.E. Field high-throughput phenotyping: The new crop breeding frontier. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katul, G.G.; Schieldge, J.; Hsieh, C.I. Skin temperature perturbations induced by surface layer turbulence above a grass surface. Water Resour. Res. 1998, 34, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Chazdon, R.L. Sunflecks and their importance to forest understorey plants. Adv. Ecol. Res. 1988, 18, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paw, U.K.T.; Brunet, Y.; Collineau, S.; Shaw, R.H.; Maitani, T.; Qiu, J.; Hipps, L. On coherent structures in turbulence above and within agricultural plant canopies. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1992, 61, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyano, A.; Asano, K.; Kanamaru, T. Analysis of the sensible heat flux from the exterior surface of buildings using time sequential thermography. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3941–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voogt, J.A. Assessment of an urban sensor view model for thermal anisotropy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christen, A.; Meier, F.; Scherer, D. High-frequency fluctuations of surface temperatures in an urban environment. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 108, 301–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, A.; Kleissl, J. Interaction between coherent structures and surface temperature and its effect on ground heat flux in an unstably stratified boundary layer. J. Turbul. 2013, 14, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, A.; Kanda, M.; Onomura, S.; Kumemura, H. Thermal Image Velocimetry. Bound.-Layer Meteor. 2013, 149, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SOMPAK. Available online: http://www.cis.hut.fi/research/som-research/nnrc-programs.shtml (accessed on 16 September 2016).
- Katurji, M.; Noonan, B.; Zawar-Reza, P.; Schulmann, T.; Sturman, A. Characteristics of the springtime alpine valley atmospheric boundary layer using self-organizing maps. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2015, 54, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, S.C.; Lee, C.C. The self-organizing map in synoptic climatological research. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2011, 35, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, E.N.; Lynch, A.H.; Cassano, J.J.; Koslow, M.R. Classification of synoptic patterns in the western Arctic associated with extreme events at Barrow, Alaska, USA. Clim. Res. 2006, 30, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, J.J.; Uotila, P.; Lynch, A.H.; Cassano, E.N. Predicted changes in synoptic forcing of net precipitation in large Arctic river basins during the 21st century. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, G04S49. [Google Scholar]
- Cassano, E.N.; Cassano, J.J. Synoptic forcing of precipitation in the Mackenzie and Yukon River basins. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, M.; Cassano, J.J.; Seefeldt, M.W. A weather pattern-based approach to evaluate the Antarctic Mesoscale Prediction System (AMPS) forecasts: Comparison to automatic weather station observations. Weather Forecast. 2011, 26, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.J.; Risien, C.; Shillington, F.A. Using self-organizing maps to identify patterns in satellite imagery. Prog. Oceanogr. 2003, 59, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvocarev, K.; Shapland, T.M.; Snyder, R.L.; Martínez-Cob, A. Surface renewal performance to independently estimate sensible and latent heat fluxes in heterogeneous crop surfaces. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paw, U.K.T.; Qiu, J.; Su, H.B.; Watanabe, T.; Brunet, Y. Surface renewal analysis: A new method to obtain scalar fluxes without velocity data. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1995, 74, 119–137. [Google Scholar]
- Katul, G.; Hsieh, C.; Oren, R.; Ellsworth, D.; Philips, N. Latent and sensible heat flux predictions from a uniform pine forest using surface renewal and flux variance methods. Bound.-Layer Meteor. 1996, 80, 249–282. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, R.L.; Spano, D.; Pawu, K.T. Surface renewal analysis for sensible and latent heat flux density. Bound.-Layer Meteor. 1996, 77, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Instrument | Description | Measured Variable | Range and Accuracy | Sampling Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campbell Scientific CSAT3 | Three-dimensional ultrasonic anemometer | Cartesian components of velocity and sonic temperature (u, v, w, Ts) | ±65 m·s−1 ± 0.08 m·s−1 for u, v ±0.04 m·s−1 for w, and −30 to 50 °C ± 0.01 °C for Ts | 20 Hz |
| LICOR-7500 | Open path infrared H2O analyzer (situated 30 cm below the sonic anemometer) | Specific humidity | 0 to 60 parts per trillion (ppt) ±0.6 ppt | 20 Hz |
| Kipp and Zonen CNR1 | Net radiometer | Incident and reflected long- and short-wave radiation components | ±10% over 24 h | 1 Hz |
| Vaisala HMP45C | Temperature and relative humidity probe | Air temperature, soil surface temperature, and relative humidity | −40 to +60 °C ± 0.3 at 0 °C 0 to 90% ± 2% | 1 Hz |
| HOBO U23 | Radiation shielded temperature sensor | Air temperature at 35 cm above ground level or AGL | −40 to +70 °C ± 0.2 °C | 0.1 Hz |
| FLIR A644sc | Uncooled infrared camera | Brightness temperature on a raster of 640 × 480 pixels | −40 to 150 °C ± 2 °C Spectral range 7.5 to 14 μm Thermal sensitivity 30 mK | 50 Hz |
| Optris Pi 640 | Uncooled infrared camera | Brightness temperature on raster of 640 × 480 pixels | −20 to 900 °C ± 2°C Spectral range 7.5 to 13 μm Thermal sensitivity 75 mK | 0.1 Hz |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katurji, M.; Zawar-Reza, P. Forward-Looking Infrared Cameras for Micrometeorological Applications within Vineyards. Sensors 2016, 16, 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091518
Katurji M, Zawar-Reza P. Forward-Looking Infrared Cameras for Micrometeorological Applications within Vineyards. Sensors. 2016; 16(9):1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091518
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaturji, Marwan, and Peyman Zawar-Reza. 2016. "Forward-Looking Infrared Cameras for Micrometeorological Applications within Vineyards" Sensors 16, no. 9: 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091518
APA StyleKaturji, M., & Zawar-Reza, P. (2016). Forward-Looking Infrared Cameras for Micrometeorological Applications within Vineyards. Sensors, 16(9), 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16091518