Odor Fingerprint Analysis Using Feature Mining Method Based on Olfactory Sensory Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
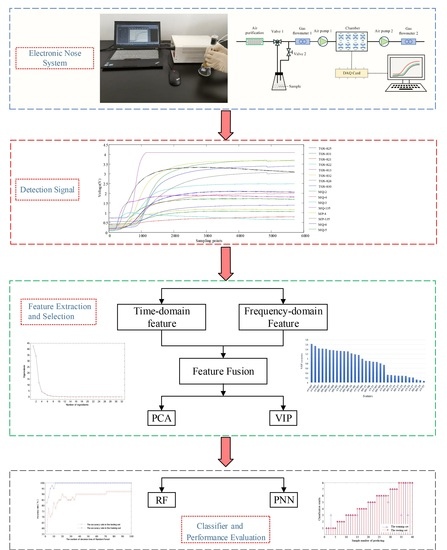
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Liquor Samples
2.2. Intelligent Nose
2.3. Feature Selection
2.3.1. Data Processing of Odor Fingerprint Analysis
2.3.2. Feature Extraction and Filtering
2.3.3. Multivariate Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dimension Reduction by PCA
3.2. Variable Selection by VIP Scores
3.3. Classification Using Random Forest
3.4. Classification Using PNN
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldisserra, D.; Franco, A.; Maio, D.; Maltoni, D. Fake Fingerprint Detection by Odor Analysis International Conference on Advances in Biometrics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics, Hong Kong, China, 5–7 January 2006; pp. 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Kinjo, H.; Oshiro, N.; Duong, S.C. Fruit maturity detection using neural network and an odor sensor: Toward a quick detection. In Proceedings of the 10th Asian Control Conference, Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 31 May–3 June 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.M.; Son, M.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, D.; Hong, S.; Park, T.H.; Chun, H.S.; Choi, S.S. A triangle study of human, instrument and bioelectronic nose for non-destructive sensing of seafood freshness. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covington, J.A.; Wedlake, L.; Andreyev, J.; Ouaret, N.; Thomas, M.G.; Nwokolo, C.U.; Bardhan, K.D.; Arasaradnam, R.P. The detection of patients at risk of gastrointestinal toxicity during pelvic radiotherapy by electronic nose and FAIMS: A pilot study. Sensors 2012, 12, 13002–13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dymerski, T.; Gębicki, J.; Wiśniewska, P.; Śliwińska, M.; Wardencki, W.; Namieśnik, J. Application of the Electronic Nose Technique to Differentiation between Model Mixtures with COPD Markers. Sensors 2013, 13, 5008–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibbs, M.D. Biometrics: Body odor authentication perception and acceptance. ACM SIGCAS Comput. Soc. 2010, 40, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.Q.; Yin, M.M.; Hou, C.J.; Hui, Q.; Zhang, M.M.; Dong, J.L.; Luo, X.G.; Shen, C.H.; Zhang, S.Y. Identification of Different Aromatic Chinese Liquors by Colorimetric Array Sensor Technology. Fenxi Huaxue 2011, 39, 516–520. [Google Scholar]
- Rochaparra, D.; Chirife, J.; Zamora, C.; De Pascual-Teresa, S. Chemical Characterization of an Encapsulated Red Wine Powder and Its Effects on Neuronal Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Fuentes, S.; Torrico, D.; Howell, K.; Dunshea, F.R. Assessment of beer quality based on foamability and chemical composition using computer vision algorithms, near infrared spectroscopy and machine learning algorithms. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chira, K.; Teissedre, P.L. Chemical and sensory evaluation of wine matured in oak barrel: Effect of oak species involved and toasting process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutowska, B.; Wardencki, W. Application of gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O) in analysis and quality assessment of alcoholic beverages—A review. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, S.V.; Avellone, G.; Bongiorno, D.; Cunsolo, V.; Muccilli, V.; Sforza, S.; Dossena, A.; Drahos, L.; Vekey, K. Applications of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for food analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1259, 74–85. [Google Scholar]
- Winquist, F.; Lundström, I.; Wide, P. The combination of an electronic tongue and an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 58, 512–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, K.; Dodd, G. Analysis of discrimination mechanisms in the mammalian olfactory system using a model nose. Nature 1982, 299, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratti, S.; Benedetti, S.; Scampicchio, M.; Pangerod, E.C. Characterization and classification of Italian Barbera wines by using an electronic nose and an amperometric electronic tongue. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 525, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Hosseini, H.G.; Stewart, J.R. Application of ANN with extracted parameters from an electronic nose in cigarette brand identification. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 99, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Seth, S.; Tudu, B.; Tamuly, P.; Jana, A.; Ghosh, D.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Bhuyan, M. Monitoring of black tea fermentation process using electronic nose. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Deng, S.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, S. Classification of Rice by Combining Electronic Tongue and Nose. Food Anal. Methods 2015, 8, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lü, E.; Lu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Quality Detection of Litchi Stored in Different Environments Using an Electronic Nose. Sensors 2016, 16, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baietto, M.; Wilson, A.D. Electronic-Nose Applications for Fruit Identification, Ripeness and Quality Grading. Sensors 2015, 15, 899–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brezmes, J.; Llobet, E.; Vilanova, X.; Orts, J.; Saiz, G.; Correig, X. Correlation between electronic nose signals and fruit quality indicators on shelf-life measurements with pinklady apples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 80, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Tan, Y.; Xie, H.; Shen, F. A novel method for diabetes diagnosis based on electronic nose. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1997, 12, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, J.; Romain, A.C.; Ledent, C. The electronic nose as a warning device of the odour emergence in a compost hall. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 116, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Xie, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, A.; Zhu, B.; Wang, L.; Yang, Z. Identification and pattern recognition analysis of Chinese liquors by doped nano ZnO gas sensor array. Sens. Actuators B 2005, 110, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.B.; Yu, T.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Lan, Y.B. Comparison of Algorithms for an Electronic Nose in Identifying Liquors. J. Bionic Eng. 2008, 5, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, M.P.; Busto, O.; Guasch, J. Application of a headspace mass spectrometry system to the differentiation and classification of wines according to their origin, variety and ageing. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1057, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Song, F.; Pu, H. Detection and classification of Chinese spirits with different wine age by z Nose. Shipin Yu Fajiao Gongye 2016, 42, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Luo, G.; Qin, K.; Wang, N.; Niu, W. Online Sensor Drift Compensation for E-Nose Systems Using Domain Adaptation and Extreme Learning Machine. Sensors 2018, 18, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, D. Domain Adaptation Extreme Learning Machines for Drift Compensation in E-Nose Systems. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 1790–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, D. Efficient Solutions for Discreteness, Drift, and Disturbance (3D) in Electronic Olfaction. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2016, 48, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distante, C.; Leo, M.; Siciliano, P.; Persaud, K.C. On the study of feature extraction methods for an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 87, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklöv, T.; Mårtensson, P.; Lundström, I. Enhanced selectivity of MOSFET gas sensors by systematical analysis of transient parameters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 353, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, D.; Durán, A.; Valle, M.D. Use of sequential injection analysis to construct an electronic-tongue: Application to multidetermination employing the transient response of a potentiometric sensor array. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 600, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H. A feature extraction method based on wavelet packet analysis for discrimination of Chinese vinegars using a gas sensors array. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 134, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneş, S.; Dursun, M.; Polat, K.; Yosunkaya, S. Sleep spindles recognition system based on time and frequency domain features. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 2455–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinyomark, A.; Phukpattaranont, P.; Limsakul, C. Feature reduction and selection for EMG signal classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 7420–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, R.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, D. A Framework for the Multi-Level Fusion of Electronic Nose and Electronic Tongue for Tea Quality Assessment. Sensors 2017, 17, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, H.; Shi, Y.; Fu, S.; Jiao, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, J. Mining Feature of Data Fusion in the Classification of Beer Flavor Information Using E-Tongue and E-Nose. Sensors 2017, 17, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennard, R.W.; Stone, L.A. Computer Aided Design of Experiments. Technometrics 1969, 11, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.K. Random decision forests. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–16 August 1995; pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forest. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Animesh, A.; Bjorn, K.; Visser, R.G.F.; Chris, M. Integration of multi-omics data for prediction of phenotypic traits using random forest. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 180. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.; Baets, B.D.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Samson, R.; Degroeve, S.; Becker, P.D.; Huybrechts, W. Random forests as a tool for ecohydrological distribution modelling. Ecol. Model. 2007, 207, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.L.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Hu, E.J. Random forest based lung nodule classification aided by clustering. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2010, 34, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutler, D.R.; Edwards Jr, E.T.; Beard, K.H.; Cutler, A.; Hess, K.T.; Gibson, J.; Lawler, J.J. Random forests for classification in ecology. Ecology 2007, 88, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, C.; Bromiley, P.A.; Ionita, M.C.; Cootes, T.F. Robust and Accurate Shape Model Matching Using Random Forest Regression-Voting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, T. Decision tree usage for incremental parametric speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal, Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014; pp. 3819–3823. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, C.; Johnson, D.; Xu, R.; Corso, J.J. Random forests for metric learning with implicit pairwise position dependence. J. Mach. Learn. 2012, 57, 958–966. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, D.F. Probabilistic neural networks. Neural Netw. 1990, 3, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.Z.; Tan, K.C.; Ser, W. Probabilistic neural-network structure determination for pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2000, 11, 1009–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, K.L.; Niculescu, S.P. Using probabilistic neural networks to model the toxicity of chemicals to the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas): A study based on 865 compounds. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 3237–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, G.; De La Cruz, J.M. A Probabilistic Neural Network for Attribute Selection in Stereovision Matching. Neural Comput. Appl. 2002, 11, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| No. | Brand | Alcohol Content (%vol) | Flavor Type | Main Raw Material | Place of Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aoxi Erguotou | 56 | Feng-flavor | pure water, Chinese sorghum | Tongzhou district, Peking City |
| 2 | Fangzhuang Beijing Erguotou | 56 | Feng-flavor | pure water, red sorghum | Daxing district, Peking City |
| 3 | Hengshui old white dry | 50 | Laobaigan-flavor | Chinese sorghum, wheat, pure water | Hengshui City, Hebei Province |
| 4 | Huadu Beijing Erguotou | 56 | Feng-flavor | pure water, Chinese sorghum | Changping district, Peking City |
| 5 | Hongxing Erguotou | 56 | Feng-flavor | Chinese sorghum, pure water, corn, barley, pea | Jixian county, Tianjin |
| 6 | Luzhou Laojiao | 45 | Luzhou-flavor | pure water, Chinese sorghum, wheat | Luzhou city, Sichuan Province |
| 7 | Niulanshan Erguotou | 56 | Feng-flavor | pure water, Chinese sorghum, barley, wheat, pea | Shunyi district, Peking City |
| 8 | Zhongde Erguotou | 43 | Feng-flavor | pure water, Chinese sorghum, wheat | Fangshan district, Peking City |
| No. | Sensor Name | Sensitive Gas | Detection Range (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TGS-825 | Hydrogen sulfide | 5–100 |
| 2 | TGS-831 | R-21 and R-22 | 100–3000 |
| 3 | TGS-821 | hydrogen | 30–1000 |
| 4 | TGS-822 | Ethanol | 50–5000 |
| 5 | TGS-813 | Methane, Propane and Butane | 500–10,000 |
| 6 | TGS-832 | R-134a | 100–3000 |
| 7 | TGS-826 | Ammonia | 30–300 |
| 8 | TGS-830 | R-113, hydrogen and Ethanol | 100–3000 |
| 9 | MQ-2 | Ethanol, Propane and hydrogen | 300–10,000 |
| 10 | MQ-4 | Alkanes | 300–10,000 |
| 11 | MQ-3 | Ethanol | 40–4000 |
| 12 | MQ-135 | Hydrogen, R-113 and Ethanol | 10–1000 |
| 13 | MP-4 | Methane | 300–10,000 |
| 14 | MP-135 | hydrogen | 30–1000 |
| 15 | MQ-6 | Isobutane, Propane and LPG | 300–10,000 |
| 16 | MQ-5 | Methylpropane | 300–10,000 |
| Subsets | Features | RF (%) | PNN (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | AVM5 | 35 | 27.5 |
| #2 | AVM5 + AVM4 | 60 | 35 |
| #3 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 | 72.5 | 35 |
| #4 | AVM5 + AVM4+AVM7 + MVM5 | 67.5 | 47.5 |
| #5 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 | 72.5 | 72.5 |
| #6 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 | 77.5 | 60 |
| #7 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 | 70 | 62.5 |
| #8 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 | 85 | 82.5 |
| #9 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 | 85 | 80 |
| #10 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 | 85 | 80 |
| #11 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 | 87.5 | 75 |
| #12 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 | 80 | 67.5 |
| #13 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 | 85 | 60 |
| #14 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 | 85 | 60 |
| #15 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 | 92.5 | 80 |
| #16 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 | 82.5 | 87.5 |
| #17 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 | 85 | 87.5 |
| #18 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 | 87.5 | 87.5 |
| #19 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 | 87.5 | 87.5 |
| #20 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 | 85 | 82.5 |
| #21 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 | 85 | 82.5 |
| #22 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 | 87.5 | 65 |
| #23 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 | 85 | 67.5 |
| #24 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 + AVT3 | 82.5 | 72.5 |
| #25 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 + AVT3 + MVT7 | 82.5 | 77.5 |
| #26 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 + AVT3 + MVT7 + AVT5 | 82.5 | 77.5 |
| #27 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 + AVT3 + MVT7 + AVT5 + MVT4 | 77.5 | 67.5 |
| #28 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 + AVT3 + MVT7 + AVT5 + MVT4 + AVT4 | 77.5 | 67.5 |
| #29 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 + AVT3 + MVT7 + AVT5 + MVT4 + AVT4 + AVT7 | 80 | 67.5 |
| #30 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 + AVT3 + MVT7 + AVT5 + MVT4 + AVT4 + AVT7 + MVT2 | 87.5 | 70 |
| #31 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 + AVT3 + MVT7 + AVT5 + MVT4 + AVT4 + AVT7 + MVT2 + MVT5 | 87.5 | 65 |
| #32 | AVM5 + AVM4 + AVM7 + MVM5 + MVM4 + MVM7 + AVM8 + MVM2 + AVT6 + AVM2 + MVM8 + MVT6 + MVM1 + AVM1 + AVM6 + MVT1 + MVM6 + AVT1 + AVM3 + MVM3 + AVT8 + MVT8 + MVT3 + AVT3 + MVT7 + AVT5 + MVT4 + AVT4 + AVT7 + MVT2 + MVT5 + AVT2 | 87.5 | 75 |
| Method | Classification Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|
| RF | 82.5 |
| PNN | 65 |
| PCA-RF | 82.5 |
| PCA-PNN | 77.5 |
| VIP-RF | 92.5 |
| VIP-PNN | 90 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Men, H.; Jiao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Gong, F.; Chen, Y.; Fang, H.; Liu, J. Odor Fingerprint Analysis Using Feature Mining Method Based on Olfactory Sensory Evaluation. Sensors 2018, 18, 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103387
Men H, Jiao Y, Shi Y, Gong F, Chen Y, Fang H, Liu J. Odor Fingerprint Analysis Using Feature Mining Method Based on Olfactory Sensory Evaluation. Sensors. 2018; 18(10):3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103387
Chicago/Turabian StyleMen, Hong, Yanan Jiao, Yan Shi, Furong Gong, Yizhou Chen, Hairui Fang, and Jingjing Liu. 2018. "Odor Fingerprint Analysis Using Feature Mining Method Based on Olfactory Sensory Evaluation" Sensors 18, no. 10: 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103387
APA StyleMen, H., Jiao, Y., Shi, Y., Gong, F., Chen, Y., Fang, H., & Liu, J. (2018). Odor Fingerprint Analysis Using Feature Mining Method Based on Olfactory Sensory Evaluation. Sensors, 18(10), 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18103387