Advanced Methods for Detection of Bacillus cereus and Its Pathogenic Factors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pathogenicity of Bacillus cereus
2.1. Bacillus cereus Group
2.2. B. cereus Gastro-Intestinal Infections
2.3. B. cereus Non Gastro-Intestinal Infections
3. Detection of B. cereus
3.1. Traditional Methods
3.2. Molecular Methods
3.3. Biosensors
4. Detection of B. cereus Toxins
4.1. Detection of Cereulide and the Emetic B. cereus Strains
4.2. Detection of Diarrheal Toxins
4.3. Detection of Other B. cereus Pathogenic Factors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bacillus Cereus Factsheet 2016 FINAL ACCESSIBLE. Available online: https://www.fsai.ie/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=10919 (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Risks for public health related to the presence of Bacillus cereus and other Bacillus spp. including Bacillus thuringiensis in foodstuffs. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04524. [Google Scholar]
- Tewari, A.; Abdullah, S. Bacillus cereus food poisoning: International and Indian perspective. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 2500–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glasset, B.; Herbin, S.; Guillier, L.; Cadel-Six, S.; Vignaud, M.-L.; Grout, J.; Pairaud, S.; Michel, V.; Hennekinne, J.-A.; Ramarao, N. Bacillus cereus-induced food-borne outbreaks in France, 2007 to 2014: Epidemiology and genetic characterisation. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasset, B.; Herbin, S.; Granier, S.A.; Cavalié, L.; Lafeuille, E.; Guérin, C.; Ruimy, R.; Casagrande-Magne, F.; Levast, M.; Chautemps, N. Bacillus cereus, a serious cause of nosocomial infections: Epidemiologic and genetic survey. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidic, J.; Chaix, C.; Manzano, M.; Heyndrickx, M. Food Sensing: Detection of Bacillus cereus Spores in Dairy Products. Biosensors 2020, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bottone, E.J. Bacillus cereus, a volatile human pathogen. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 382–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Lai, Q.; Zeng, R.; Ye, D.; Xu, J.; Shao, Z. Proposal of nine novel species of the Bacillus cereus group. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2499–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, Q.; Göker, M.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Shao, Z. Genomic insights into the taxonomic status of the Bacillus cereus group. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okinaka, R.T.; Keim, P. The phylogeny of Bacillus cereus sensu lato. In The Bacterial Spore: From Molecules to Systems; ASM: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 237–251. [Google Scholar]
- Guinebretière, M.H.; Thompson, F.L.; Sorokin, A.; Normand, P.; Dawyndt, P.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Svensson, B.; Sanchis, V.; Nguyen-The, C.; Heyndrickx, M. Ecological diversification in the Bacillus cereus group. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinebretičre, M.-H.; Velge, P.; Couvert, O.; Carlin, F.; Debuyser, M.-L. Ability of Bacillus cereus group strains to cause food poisoning varies according to phylogenetic affiliation (groups I to VII) rather than species affiliation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3388–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altayar, M.; Sutherland, A. Bacillus cereus is common in the environment but emetic toxin producing isolates are rare. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Lereclus, D.; Koehler, T.M. The Bacillus cereus group: Bacillus species with pathogenic potential. In Gram-Positive Pathogens; ASM: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 875–902. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, G.; Hansen, B.; Eilenberg, J.; Mahillon, J. The hidden lifestyles of Bacillus cereus and relatives. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceuppens, S.; Boon, N.; Uyttendaele, M. Diversity of Bacillus cereus group strains is reflected in their broad range of pathogenicity and diverse ecological lifestyles. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 84, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stenfors Arnesen, L.P.; Fagerlund, A.; Granum, P.E. From soil to gut: Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 579–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koletzko, B.; Baker, S.; Cleghorn, G.; Neto, U.F.; Gopalan, S.; Hernell, O.; Hock, Q.S.; Jirapinyo, P.; Lonnerdal, B.; Pencharz, P. Global standard for the composition of infant formula: Recommendations of an ESPGHAN coordinated international expert group. J. Pediatr. Gastr. Nutr. 2005, 41, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Six, S.; De Buyser, M.; Vignaud, M.; Dao, T.; Messio, S.; Pairaud, S.; Hennekinne, J.; Pihier, N. Bacillus cereus food poisoning outbreaks: Strain characterization results, 2006–2010. BEH—Bulletin Épidémiologique Hebdomadaire 2012, 2012, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Riol, C.D.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E.; Jessberger, N. Consumed foodstuffs have a crucial impact on the toxic activity of enteropathogenic Bacillus cereus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeßberger, N.; Krey, V.M.; Rademacher, C.; Böhm, M.-E.; Mohr, A.-K.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Scherer, S.; Märtlbauer, E. From genome to toxicity: A combinatory approach highlights the complexity of enterotoxin production in Bacillus cereus. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 560. [Google Scholar]
- Marxen, S.; Stark, T.D.; Frenzel, E.; Rütschle, A.; Lücking, G.; Pürstinger, G.; Pohl, E.E.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Hofmann, T. Chemodiversity of cereulide, the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 2439–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Kim, J.M.; Cho, S.H.; Oh, H.S.; Choi, N.J.; Oh, D.H. Toxin genes profiles and toxin production ability of Bacillus cereus isolated from clinical and food samples. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, T25–T29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold-Pluta, A.; Pluta, A.; Garbowska, M. The effect of selected factors on the survival of Bacillus cereus in the human gastrointestinal tract. Microb. Pathog. 2015, 82, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, T.; De Buyser, M.L.; Granum, P.E. A new cytotoxin from Bacillus cereus that may cause necrotic enteritis. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agata, N.; Mori, M.; Ohta, M.; Suwan, S.; Ohtani, I.; Isobe, M. A novel dodecadepsipeptide, cereulide, isolated from Bacillus cereus causes vacuole formation in HEp-2 cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1994, 121, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahler, H.; Pasi, A.; Kramer, J.M.; Schulte, P.; Scoging, A.C.; Bär, W.; Krähenbühl, S. Fulminant liver failure in association with the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierick, K.; Van Coillie, E.; Swiecicka, I.; Meyfroidt, G.; Devlieger, H.; Meulemans, A.; Hoedemaekers, G.; Fourie, L.; Heyndrickx, M.; Mahillon, J. Fatal family outbreak of Bacillus cereus-associated food poisoning. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4277–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naranjo, M.; Denayer, S.; Botteldoorn, N.; Delbrassinne, L.; Veys, J.; Waegenaere, J.; Sirtaine, N.; Driesen, R.B.; Sipido, K.R.; Mahillon, J. Sudden death of a young adult associated with Bacillus cereus food poisoning. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 4379–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tschiedel, E.; Rath, P.M.; Steinmann, J.; Becker, H.; Dietrich, R.; Paul, A.; Felderhoff-Müser, U.; Dohna-Schwake, C. Lifesaving liver transplantation for multi-organ failure caused by Bacillus cereus food poisoning. Pediatr. Trans. 2015, 19, E11–E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmaster, A.R.; Hill, K.K.; Gee, J.E.; Marston, C.K.; De, B.K.; Popovic, T.; Sue, D.; Wilkins, P.P.; Avashia, S.B.; Drumgoole, R. Characterization of Bacillus cereus isolates associated with fatal pneumonias: Strains are closely related to Bacillus anthracis and harbor B. anthracis virulence genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3352–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramarao, N.; Belotti, L.; Deboscker, S.; Ennahar-Vuillemin, M.; De Launay, J.; Lavigne, T.; Koebel, C.; Escande, B.; Guinebretiere, M.H. Two unrelated episodes of Bacillus cereus bacteremia in a neonatal intensive care unit. Am. J. Infect. Control 2014, 42, 694–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decousser, J.; Ramarao, N.; Duport, C.; Dorval, M.; Bourgeois-Nicolaos, N.; Guinebretiere, M.H.; Razafimahefa, H.; Doucet-Populaire, F. Bacillus cereus and severe intestinal infections in preterm neonates: Putative role of the pooled breast milk. Am. J. Infect. Control 2013, 41, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotte, R.; Herisse, A.L.; Berrouane, Y.; Lotte, L.; Casagrande, F.; Landraud, L.; Herbin, S.; Ramarao, N.; Boyer, L.; Ruimy, R. Virulence Analysis of Bacillus cereus Isolated after Death of Preterm Neonates, Nice, France, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bacteriological Analytical Manual; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; Volume 1.
- Li, F.; Li, F.; Yang, G.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Lai, W.; Xu, H. Asymmetric polymerase chain assay combined with propidium monoazide treatment and unmodified gold nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of viable emetic Bacillus cereus in milk. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 255, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, C.T.; Whitney, A.M.; Mayer, L.W.; Morey, R.; Steigerwalt, A.; Boras, A.; Weyant, R.S.; Popovic, T. Sequencing of 16S rRNA gene: A rapid tool for identification of Bacillus anthracis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.; Griffiths, H.; Saltmarsh, M.; Peters, A.; Fielding, L. Profiling Bacillus cereus populations in a traditional style, hot-drinks vending machine and vended hot chocolate drink using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) techniques. Food Control 2012, 27, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-No, I.; Guarddon, M.; Böhme, K.; Cepeda, A.; Calo-Mata, P.; Barros-Velázquez, J. Detection and quantification of spoilage and pathogenic Bacillus cereus, Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis by real-time PCR. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Shou, Y.; Yoshida, T.M.; Marrone, B.L. Differentiation of Bacillus anthracis, B. cereus, and B. thuringiensis by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3446–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manzano, M.; Giusto, C.; Iacumin, L.; Cantoni, C.; Comi, G. Molecular methods to evaluate biodiversity in Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis strains from different origins. Food Microbiol. 2009, 26, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbeva, P.; Van Veen, J.; Van Elsas, J. Predominant Bacillus spp. in agricultural soil under different management regimes detected via PCR-DGGE. Microbial Ecol. 2003, 45, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinebretiere, M.-H.; Nguyen-The, C. Sources of Bacillus cereus contamination in a pasteurized zucchini puree processing line, differentiated by two PCR-based methods. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 43, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, P.A.; Ibarra, J.E. Detection of new cry genes of Bacillus thuringiensis by use of a novel PCR primer system. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6150–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antolinos, V.; Fernández, P.S.; Ros-Chumillas, M.; Periago, P.M.; Weiss, J. Development of a high-resolution melting–based approach for efficient differentiation among Bacillus cereus group isolates. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Qu, Q.; Li, L.; Ran, X.; Gui, J.; Wang, Q.; Cui, X.; Jiang, C. Electrochemical DNA Biosensor Based on Magnetite/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes/Chitosan Nanocomposite for Bacillus cereus Detection of Potential Marker for Gold Prospecting. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Pang, G.; Chen, Q.; Liang, X. Fabrication of Bacillus cereus electrochemical immunosensor based on double-layer gold nanoparticles and chitosan. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2013, 177, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassi, A.; Guillon, F.-X.; Amar, A.; Hainque, B.; Amriche, S.; Maugé, D.; Markova, E.; Tsé, C.; Bigey, P.; Lazerges, M. Electrochemical DNA-biosensors based on long-range electron transfer: Optimization of the amperometric detection in the femtomolar range using two-electrode setup and ultramicroelectrode. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 209, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Ma, W.; Zheng, W. PCR microfluidic devices for DNA amplification. Biotechnol. Adv. 2006, 24, 243–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Corstjens, P.L.; Mauk, M.G.; Bau, H.H. A disposable microfluidic cassette for DNA amplification and detection. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, X.; Mauk, M.G.; Chen, D.; Liu, C.; Bau, H.H. A large volume, portable, real-time PCR reactor. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3170–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidic, J.; Manzano, M.; Chang, C.-M.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Advanced biosensors for detection of pathogens related to livestock and poultry. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vidic, J.; Vizzini, P.; Manzano, M.; Kavanaugh, D.; Ramarao, N.; Zivkovic, M.; Radonic, V.; Knezevic, N.; Giouroudi, I.; Gadjanski, I. Point-of-need DNA testing for detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Sensors 2019, 19, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yan, S.; Yin, F.; Feng, X.; Liu, B.-F. Identifying multiple bacterial pathogens by loop-mediated isothermal amplification on a rotate & react slipchip. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2016, 228, 491–499. [Google Scholar]
- Vizzini, P.; Braidot, M.; Vidic, J.; Manzano, M. Electrochemical and Optical Biosensors for the Detection of Campylobacter and Listeria: An Update Look. Micromachines 2019, 10, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manzano, M.; Viezzi, S.; Mazerat, S.; Marks, R.S.; Vidic, J. Rapid and label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor for detecting hepatitis A virus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubičárová, T.; Fojta, M.; Vidic, J.; Tomschik, M.; Suznjevic, D.; Paleček, E. Voltammetric and chronopotentiometric measurements with nucleic acid-modified mercury film on a glassy carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 2000, 12, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodek, A.; Sauriat-Dorizon, H.; Chevalier, C.; Delmas, B.; Vidic, J.; Korri-Youssoufi, H. Direct electrochemical detection of PB1-F2 protein of influenza A virus in infected cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodek, A.; Vidic, J.; Sauriat-Dorizon, H.; Richard, C.-A.; Le Goffic, R.; Korri-Youssoufi, H.; Chevalier, C. Electrochemical detection of the oligomerization of PB1-F2 influenza A virus protein in infected cells. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9098–9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, Z.; Sheikh-Zeinoddin, M.; Ensafi, A.A.; Soleimanian-Zad, S. Fabrication of an electrochemical DNA-based biosensor for Bacillus cereus detection in milk and infant formula. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 80, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Ying, W.; Alocilja, E.C.; Downes, F.P. Sensitivity and specificity performance of a direct-charge transfer biosensor for detecting Bacillus cereus in selected food matrices. Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 99, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsiri, Z.; Vantarakis, A.; Rizzotto, F.; Kavanaugh, D.; Ramarao, N.; Vidic, J. Sensitive Detection of E. coli in Artificial Seawater by Aptamer-Coated Magnetic Beads and Direct PCR. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Korostynska, O.; Oliwa, K.; Adley, C. Conducting polymer based DNA biosensor for the detection of the Bacillus cereus group species. Proc. SPIE 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skottrup, P.D.; Nicolaisen, M.; Justesen, A.F. Towards on-site pathogen detection using antibody-based sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setterington, E.B.; Alocilja, E.C. Electrochemical biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of magnetically extracted bacterial pathogens. Biosensors 2012, 2, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tawil, N.; Sacher, E.; Mandeville, R.; Meunier, M. Bacteriophages: Biosensing tools for multi-drug resistant pathogens. Analyst 2014, 139, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Sim, J.; Kang, T.; Nguyen, H.H.; Park, H.K.; Chung, B.H.; Ryu, S. A novel and highly specific phage endolysin cell wall binding domain for detection of Bacillus cereus. Eur. Biophys. J. 2015, 44, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Kong, M.; Lee, J.-H.; Ryu, S.; Park, S. Detection of Bacillus Cereus Using Bioluminescence Assay with Cell Wall-Binding Domain Conjugated Magnetic Nanoparticles. BioChip J. 2018, 12, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Shin, J.H.; Heu, S.; Park, J.-K.; Ryu, S. Lateral flow assay-based bacterial detection using engineered cell wall binding domains of a phage endolysin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Alocilja, E.C.; Downes, F.P. Nanowire labeled direct-charge transfer biosensor for detecting Bacillus species. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 22, 2329–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.-T.; Hsieh, M.-F.; Yin, S.-Y.; Wen, H.-W. Development of a rapid and sensitive immunomagnetic-bead based assay for detecting Bacillus cereus in milk. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spieker, E.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecular imprinting studies for developing qcm-sensors for Bacillus cereus. Proc. Eng. 2016, 168, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabutani, M.; Agata, N.; Ohta, M. A new rapid and sensitive detection method for cereulide-producing Bacillus cereus using a cycleave real-time PCR. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 48, 698–704. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, T.; Marxen, S.; Rütschle, A.; Lücking, G.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Hofmann, T. Mass spectrometric profiling of Bacillus cereus strains and quantitation of the emetic toxin cereulide by means of stable isotope dilution analysis and HEp-2 bioassay. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzeau-Szynalski, K.; Stollewerk, K.; Messelhaeusser, U.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Why be serious about emetic Bacillus cereus: Cereulide production and industrial challenges. Food Microbiol. 2020, 85, 103279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marxen, S.; Stark, T.D.; Rütschle, A.; Lücking, G.; Frenzel, E.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Hofmann, T. Multiparametric Quantitation of the Bacillus cereus Toxins Cereulide and Isocereulides A–G in Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8307–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbrassinne, L.; Botteldoorn, N.; Andjelkovic, M.; Dierick, K.; Denayer, S. An emetic Bacillus cereus outbreak in a kindergarten: Detection and quantification of critical levels of cereulide toxin. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decleer, M.; Jovanovic, J.; Vakula, A.; Udovicki, B.; Agoua, R.-S.E.; Madder, A.; De Saeger, S.; Rajkovic, A. Oxygen consumption rate analysis of mitochondrial dysfunction caused by Bacillus cereus cereulide in Caco-2 and HepG2 cells. Toxins 2018, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuberovic Muratovic, A.; Tröger, R.; Granelli, K.; Hellenäs, K.-E. Quantitative analysis of cereulide toxin from Bacillus cereus in rice and pasta using synthetic cereulide standard and 13C6-cereulide standard—A short validation study. Toxins 2014, 6, 3326–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.; Bartholomew, B.; Hardy, J.; Kramer, J. Potential application of a HEp-2 cell assay in the investigation of Bacillus cereus emetic-syndrome food poisoning. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1988, 52, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, S.A.; Williams, A. Detection of toxigenic strains of Bacillus cereus and other Bacillus spp. with an improved cytotoxicity assay. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 28, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura-Sato, K.; Hirama, Y.; Agata, N.; Ito, H.; Torii, K.; Takeno, A.; Hasegawa, T.; Shimomura, Y.; Ohta, M. Quantitative analysis of cereulide, an emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus, by using rat liver mitochondria. Microbiol. Immunol. 2005, 49, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.A.; Jääskeläinen, E.L.; Shaheen, R.; Pirhonen, T.; Wijnands, L.M.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M.S. Sperm bioassay for rapid detection of cereulide-producing Bacillus cereus in food and related environments. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesta-Peters, E.G.; Reij, M.W.; Blaauw, R.H.; Rajkovic, A.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Abee, T. Quantification of the emetic toxin cereulide in food products by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry using synthetic cereulide as a standard. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7466–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delbrassinne, L.; Andjelkovic, M.; Dierick, K.; Denayer, S.; Mahillon, J.; Van Loco, J. Prevalence and levels of Bacillus cereus emetic toxin in rice dishes randomly collected from restaurants and comparison with the levels measured in a recent foodborne outbreak. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, S.; Gottschalk, C.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E.; Gareis, M. Identification of cereulide producing Bacillus cereus by MALDI-TOF MS. Food Microbiol. 2019, 82, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducrest, P.J.; Pfammatter, S.; Stephan, D.; Vogel, G.; Thibault, P.; Schnyder, B. Rapid detection of Bacillus ionophore cereulide in food products. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Feng, L.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Shah, N.P.; Wei, H. Detection of viable enterotoxin-producing Bacillus cereus and analysis of toxigenicity from ready-to-eat foods and infant formula milk powder by multiplex PCR. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, B.; Li, F.; Zhao, T.; Li, F.; Zhou, B.; Xu, H. Hybridization chain reaction-based flow cytometric bead sensor for the detection of emetic Bacillus cereus in milk. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2018, 256, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrle, E.; Moravek, M.; Dietrich, R.; Bürk, C.; Didier, A.; Märtlbauer, E. Comparison of multiplex PCR, enzyme immunoassay and cell culture methods for the detection of enterotoxinogenic Bacillus cereus. J. Microbiol. Methods 2009, 78, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrle, E.; Didier, A.; Moravek, M.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E. Detection of Bacillus cereus with enteropathogenic potential by multiplex real-time PCR based on SYBR green I. Mol. Cell. Probes 2010, 24, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, F.; Langaee, T.; Eskandari, M.; Seo, K.-H.; Chung, M.-J.; Oh, D.-H. Rapid detection of viable Bacillus cereus emetic and enterotoxic strains in food by coupling propidium monoazide and multiplex PCR (PMA-mPCR). Food Control 2015, 55, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In’t Veld, P.; Van der Laak, L.; Van Zon, M.; Biesta-Peters, E. Elaboration and validation of the method for the quantification of the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus as described in EN-ISO 18465-Microbiology of the food chain–Quantitative determination of emetic toxin (cereulide) using LC-MS/MS. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 288, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallent, S.M.; Hait, J.M.; Knolhoff, A.M.; Bennett, R.W.; Hammack, T.S.; Croley, T.R. Rapid Testing of Food Matrices for Bacillus cereus Enterotoxins. J. Food Saf. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchoun, R.; Al-Sha’er, A.I.; Khabour, O.F. Molecular characterization of Bacillus cereus toxigenic strains isolated from different food matrices in Jordan. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravek, M.; Dietrich, R.; Buerk, C.; Broussolle, V.; Guinebretière, M.-H.; Granum, P.E.; Nguyen-the, C.; Märtlbauer, E. Determination of the toxic potential of Bacillus cereus isolates by quantitative enterotoxin analyses. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 257, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guinebretière, M.-H.; Broussolle, V. Enterotoxigenic profiles of food-poisoning and food-borne Bacillus cereus strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 3053–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beecher, D.J.; Wong, A. Identification of hemolysin BL-producing Bacillus cereus isolates by a discontinuous hemolytic pattern in blood agar. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 1646–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thompson, N.; Ketterhagen, M.; Bergdoll, M.; Schantz, E. Isolation and some properties of an enterotoxin produced by Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1984, 43, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beecher, D.J.; MacMillan, J.D. A novel bicomponent hemolysin from Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1990, 58, 2220–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beecher, D.J.; Macmillan, J. Characterization of the components of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beecher, D.J.; Wong, A. Improved purification and characterization of hemolysin BL, a hemolytic dermonecrotic vascular permeability factor from Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beecher, D.J.; Schoeni, J.L.; Wong, A. Enterotoxic activity of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 4423–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beecher, D.J.; Wong, A.C. Tripartite haemolysin BL: Isolation and characterization of two distinct homologous sets of components from a single Bacillus cereus isolate. Microbiology 2000, 146, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramarao, N.; Sanchis, V. The pore-forming haemolysins of Bacillus cereus: A review. Toxins 2013, 5, 1119–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otlewska, A.; Oltuszak-Walczak, E.; Walczak, P. Differentiation of strains from the Bacillus cereus group by RFLP-PFGE genomic fingerprinting. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 3023–3028. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabig-Ciminska, M.; Andresen, H.; Albers, J.; Hintsche, R.; Enfors, S.-O. Identification of pathogenic microbial cells and spores by electrochemical detection on a biochip. Microb. Cell Factories 2004, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saleh-Lakha, S.; Leon-Velarde, C.G.; Chen, S.; Lee, S.; Shannon, K.; Fabri, M.; Downing, G.; Keown, B. A study to assess the numbers and prevalence of Bacillus cereus and its toxins in pasteurized fluid milk. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallent, S.; Hait, J.; Bennett, R. Analysis of Bacillus cereus toxicity using PCR, ELISA and a lateral flow device. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinebretiere, M.H.; Auger, S.; Galleron, N.; Contzen, M.; De Sarrau, B.; De Buyser, M.L.; Lamberet, G.; Fagerlund, A.; Granum, P.E.; Lereclus, D. Bacillus cytotoxicus sp. nov. is a new thermotolerant species of the Bacillus cereus group occasionally associated with food poisoning. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceuppens, S.; Rajkovic, A.; Hamelink, S.; Van de Wiele, T.; Boon, N.; Uyttendaele, M. Enterotoxin production by Bacillus cereus under gastrointestinal conditions and their immunological detection by commercially available kits. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2012, 9, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dietrich, R.; Moravek, M.; Bürk, C.; Granum, P.E.; Märtlbauer, E. Production and characterization of antibodies against each of the three subunits of the Bacillus cereus nonhemolytic enterotoxin complex. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8214–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsilia, V.; Devreese, B.; De Baenst, I.; Mesuere, B.; Rajkovic, A.; Uyttendaele, M.; Van de Wiele, T.; Heyndrickx, M. Application of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for the detection of enterotoxins produced by pathogenic strains of the Bacillus cereus group. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 1691–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Blanch, J.; Sánchez, G.; Garay, E.; Aznar, R. Development of a real-time PCR assay for detection and quantification of enterotoxigenic members of Bacillus cereus group in food samples. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemet, E.; Lerééc, A.; Royer, C.; Tran, S.; Barbosa, I.; Sansonetti, P.; Lereclus, D.; Ramarao, N. The bacterial repair protein Mfd confers resistance to the host nitric-oxide response. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charlton, S.; Moir, A.; Baillie, L.; Moir, A. Characterization of the exosporium of Bacillus cereus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 87, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramarao, N.; Lereclus, D. The InhA1 metalloprotease allows spores of the B. cereus group to escape macrophages. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydar, A.; Tran, S.-L.; Guillemet, E.; Darrigo, C.; Perchat, S.; Lereclus, D.; Coquet, L.; Jouenne, T.; Ramarao, N. InhA1-mediated cleavage of the metalloprotease NprA allows Bacillus cereus to escape from macrophages. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guillemet, E.; Cadot, C.; Tran, S.L.; Guinebretiere, M.H.; Lereclus, D.; Ramarao, N. The InhA metalloproteases of Bacillus cereus contribute concomitantly to virulence. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinagawa, K. Analytical methods for Bacillus cereus and other Bacillus species. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1990, 10, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, S.-L.; Guillemet, E.; Gohar, M.; Lereclus, D.; Ramarao, N. CwpFM (EntFM) is a Bacillus cereus potential cell wall peptidase implicated in adhesion, biofilm formation, and virulence. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2638–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, S.L.; Guillemet, E.; Ngo-Camus, M.; Clybouw, C.; Puhar, A.; Moris, A.; Gohar, M.; Lereclus, D.; Ramarao, N. Haemolysin II is a Bacillus cereus virulence factor that induces apoptosis of macrophages. Cell. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, S.-L.; Ramarao, N. Bacillus cereus immune escape: A journey within macrophages. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 347, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chon, J.-W.; Yim, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.; Oh, D.-H.; Kim, S.-K.; Seo, K.-H. Quantitative prevalence and toxin gene profile of Bacillus cereus from ready-to-eat vegetables in South Korea. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerlund, A.; Ween, O.; Lund, T.; Hardy, S.P.; Granum, P.E. Genetic and functional analysis of the cytK family of genes in Bacillus cereus. Microbiology 2004, 150, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cadot, C.; Tran, S.-L.; Vignaud, M.-L.; De Buyser, M.-L.; Kolstø, A.-B.; Brisabois, A.; Lereclus, D.; Guinebretière, M.-H.; Ramarao, N. InhA1, NprA, and HlyII as candidates for markers to differentiate pathogenic from nonpathogenic Bacillus cereus strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hansen, B.M.; Hendriksen, N.B. Detection of Enterotoxic Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis Strains by PCR Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabig-Ciminska, M.; Liu, Y.; Enfors, S.-O. Gene-based identification of bacterial colonies with an electric chip. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 345, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Elsholz, B.; Enfors, S.-O.; Gabig-Ciminska, M. Confirmative electric DNA array-based test for food poisoning Bacillus cereus. J. Microbiol. Methods 2007, 70, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krause, N.; Moravek, M.; Dietrich, R.; Wehrle, E.; Slaghuis, J.; Märtlbauer, E. Performance characteristics of the Duopath® Cereus Enterotoxins assay for rapid detection of enterotoxinogenic Bacillus cereus strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Blanch, J.F.; Sanchez, G.; Garay, E.; Aznar, R. Evaluation of a real-time PCR assay for the detection and quantification of Bacillus cereus group spores in food. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Chen, J.; Fei, P.; Feng, H.; Wang, Y.; Ali, M.A.; Li, S.; Jing, H.; Yang, W. Prevalence, molecular characterization, and antibiotic susceptibility of Bacillus cereus isolated from dairy products in China. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3994–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Bruno, J.G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, T.K. Aptamers in the therapeutics and diagnostics pipelines. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H. Recent developments in cell-SELEX technology for aptamer selection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gener. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2323–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Recognition Element | Biomarker | Method | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Matrice | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyclonal antibodies | Whole-cell | Direct-charge transfer biosensor | 101 to 102 CFU/mL | Pure culture | [70] |
| Polyclonal antibodies | Whole-cell | Direct-charge transfer biosensor | 35–88 CFU/mL | Inoculated sprout, strawberries, lettuce, tomatoes, fried rice and corn. | [61] |
| DNA probe | DNA | PCR-TTGE; RAPD-PCR; rep-PCR | Food, patients and pesticides | [41] | |
| DNA probe | motB gene | Electrochemical biosensor | Pure culture | [63] | |
| Antibodies | Whole-cell | IMLN* Magnetic sensor | 10 CFU/mL | Milk | [71] |
| Primer-probe | 16S rRNA | RTi-PCR | 16.5 CFU/mL | Pasteurized food | [39] |
| Primer | gyrB gene | PCR and RAPD PCR | Vended hot chocolate powder and hot-drinks vending machine | [38] | |
| Polyclonal antibodies | Whole-cell | Cyclic voltammetry with IMS* | 40 CFU/mL | Pure culture | [65] |
| Phage endolysin CBD | Whole-cell | Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) | 102 CFU/mL | Pure culture | [67] |
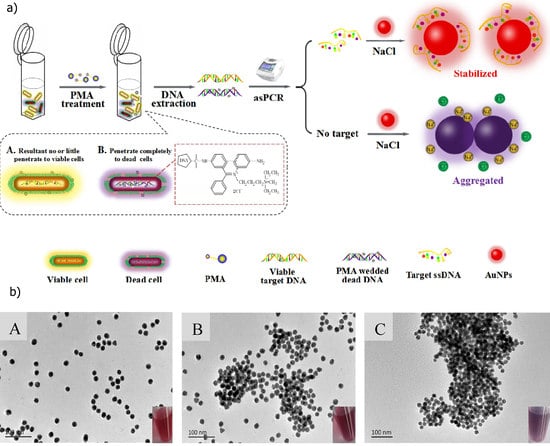
| Primer | Cereulide sinthetase gene (cesB) | PMA-asPCR-AuNPs colorimetric assay | 9.2 × 101 CFU/mL 3.4 × 102 CFU/mL | Pure culture Milk | [36] |
| Antibody or Bacteriophage CBD | Wholecell | ATP bioluminescence assay | 101 CFU /mL | Pure culture | [68] |
| Probe | DNA | Electrochemical DNA biosensor | 2.0 × 10−15 M | Pure culture | [46] |
| Molecularly Imprinted Polymer | Whole-cell | Quartz crystal microbalance | 107 CFU/mL | Water | [72] |
| Recognition Element | Biomarker | Method | Matrice | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primer | ces gene | mPCR | Pure culture | [90] |
| Primer and probe | ces gene | RTi-PCR | Pure culture | [73] |
| Cereulide; valinomycin | m/z 1170.7 m/z 1128.5 | LC-MS | Cooked rice; Chinese noodle dish | [84] |
| Primer | ces gene | mRTi-PCR | Spiked baby food | [91] |
| Cereulide; cereulide-C13 | m/z 1170.7 m/z 1176.7 | UPLC-ESI*-MS/MS | Rice; pasta | [79] |
| Primer | ces gene | PMA*-mPCR | Spiked baby cereal; pasteurized milk rice | [92] |
| Mass/Charge | Cereulide | LC-MS/MS | Spiked rice; cream pastry; mini pancakes; infant formula | [93] |
| Mass/Charge | Cereulide; cereulide variant | *MALDI-TOF/MS | Rice; milk; ready-to-eat meals | [87] |
| Mass/Charge | Cereulide | *MALDI-TOF/MS | Pure culture | [86] |
| Primer and hairpin probe | ces gene | Fluorescence assay combined with PCR, CHA* and GO* | Pure culture Milk | [88] |
| Recognition Element | Biomarker | Method | Matrice | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primer | hblA,hblD,hblC/nheA, nheB,nheC/bceT | PCR | Pure culture | [127] |
| Antibodies | nheA,nheB,nheC | EIAs | Infant formula and dried milk products | [112] |
| Primer and probe | hblC | Electrochemical biosensor | Pure culture | [128] |
| Antibodies, primer | HBL-L2/nheA, nheB,nheC | EIAs, sandwich enzyme immunoassay, cytotoxicity test, PCR | Remnant connected to food-borne outbreak | [96] |
| Primer and probe | hblA,hblD,hblC/nheA, nheB,nheC/cytK/ces | Electric DNA array | Pure culture | [129] |
| DNA probe | Pc-plc gene | RTi-PCR | Artificially contaminated liquid eggs and infant formula | [114] |
| Antibodies, primer | hblA,hblD,hblC/nheA, nheB,nheC/cytK1/ces | Immunoassay, mPCR, cytotoxicity test | Pure culture | [90] |
| Monoclonal antibodies | HBL-L2/nheB | Duopath® kit | Artificially contaminated baby food, rice | [130] |
| Primer | hblA,hblD,hblC/nheA, nheB,nheC/bceT/ cytK1/ces | PCR, BCET-RPLA | Rice, yogurt, pasta, cake | [95] |
| Antibodies | NheA, NheB/Hbl-L2 | BDE VIATM; BCET-RPLA; Duopath® kit | Lasagna, human faeces, potatoes | [111] |
| Mass/charge | Cytk1 and NheA | MALDI-TOF/MS | Pure culture | [113] |
| Primer | hblD/nheA/entFM/cytK/ces | PMA-mPCR | Pure culture | [92] |
| Probe | nheA | Electrochemical DNA-based biosensor | Milk and infant formula | [60] |
| Antibodies, primer | nheA/hblC/entFM/cytK | TECRA, mPCR | Pasteurized milk | [108] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramarao, N.; Tran, S.-L.; Marin, M.; Vidic, J. Advanced Methods for Detection of Bacillus cereus and Its Pathogenic Factors. Sensors 2020, 20, 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092667
Ramarao N, Tran S-L, Marin M, Vidic J. Advanced Methods for Detection of Bacillus cereus and Its Pathogenic Factors. Sensors. 2020; 20(9):2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092667
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamarao, Nalini, Seav-Ly Tran, Marco Marin, and Jasmina Vidic. 2020. "Advanced Methods for Detection of Bacillus cereus and Its Pathogenic Factors" Sensors 20, no. 9: 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092667
APA StyleRamarao, N., Tran, S. -L., Marin, M., & Vidic, J. (2020). Advanced Methods for Detection of Bacillus cereus and Its Pathogenic Factors. Sensors, 20(9), 2667. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20092667