A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
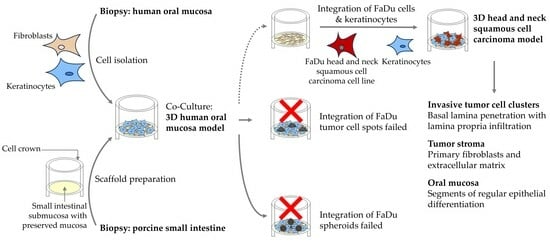
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelucchi, C.; Gallus, S.; Garavello, W.; Bosetti, C.; La Vecchia, C. Cancer risk associated with alcohol and tobacco use: Focus on upper aero-digestive tract and liver. Alcohol. Res. Health 2006, 29, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Chen, T.H.H. Areca Nut and Oral Cancer: Evidence from Studies Conducted in Humans. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, D.; Sartori, S.; Brennan, P.; Curado, M.P.; Wunsch-Filho, V.; Divaris, K.; Olshan, A.F.; Zevallos, J.P.; Winn, D.M.; Franceschi, S.; et al. The role of oral hygiene in head and neck cancer: Results from International Head and Neck Cancer Epidemiology (INHANCE) consortium. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazos, J.P.; Piemonte, E.D.; Lanfranchi, H.E.; Brunotto, M.N. Characterization of Chronic Mechanical Irritation in Oral Cancer. Int. J. Dent. 2017, 2017, 6784526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsetto, D.; Sethi, M.; Polesel, J.; Tomasoni, M.; Deganello, A.; Nicolai, P.; Bossi, P.; Fabbris, C.; Molteni, G.; Marchioni, D.; et al. The risk of recurrence in surgically treated head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: A conditional probability approach. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, F.; Cohen, E.E.W.; Guo, T.W. Evolving treatment paradigms in recurrent and metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: The emergence of immunotherapy. Transl. Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatta, G.; Botta, L.; Sanchez, M.J.; Anderson, L.A.; Pierannunzio, D.; Licitra, L.; Group, E.W. Prognoses and improvement for head and neck cancers diagnosed in Europe in early 2000s: The EUROCARE-5 population-based study. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2130–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapalczynska, M.; Kolenda, T.; Przybyla, W.; Zajaczkowska, M.; Teresiak, A.; Filas, V.; Ibbs, M.; Blizniak, R.; Luczewski, L.; Lamperska, K. 2D and 3D cell cultures—A comparison of different types of cancer cell cultures. Arch. Med. Sci. 2018, 14, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melissaridou, S.; Wiechec, E.; Magan, M.; Jain, M.V.; Chung, M.K.; Farnebo, L.; Roberg, K. The effect of 2D and 3D cell cultures on treatment response, EMT profile and stem cell features in head and neck cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loessner, D.; Stok, K.S.; Lutolf, M.P.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Clements, J.A.; Rizzi, S.C. Bioengineered 3D platform to explore cell-ECM interactions and drug resistance of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8494–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Kuo, J.C.; Wei, M.T.; Wu, M.C.; Yang, M.H.; Chiou, A. Fibroblast Promotes Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Invasion through Mechanical Barriers in 3D Collagen Microenvironments. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 6419–6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickup, M.W.; Mouw, J.K.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, P.; Du, F.; Shang, L.; Li, L. The role of organoids in cancer research. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskin, A.; Scott, E.; Nelson, R.; Gaughan, L.; Robson, C.N.; Heer, R.; Hepburn, A.C. Engineering prostate cancer in vitro: What does it take? Oncogene 2023, 42, 2417–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermod, M.; Hiou-Feige, A.; Bovay, E.; Roh, V.; Sponarova, J.; Bongiovanni, M.; Vermeer, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Petrova, T.V.; Rivals, J.P.; et al. Mouse model of postsurgical primary tumor recurrence and regional lymph node metastasis progression in HPV-related head and neck cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 142, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Tian, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, K. An HNSCC syngeneic mouse model for tumor immunology research and preclinical evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 1501–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, M.; Laban, S.; Theodoraki, M.N.; Doescher, J.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Schuler, P.J.; Brunner, C. Characterization and Differentiation of the Tumor Microenvironment (TME) of Orthotopic and Subcutaneously Grown Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) in Immunocompetent Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, H.; Ranaweera, R.S.; Izumchenko, E.; Makarev, E.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Fertig, E.J.; Howard, J.D.; Markovic, A.; Bedi, A.; Ravi, R.; et al. SMAD4 Loss Is Associated with Cetuximab Resistance and Induction of MAPK/JNK Activation in Head and Neck Cancer Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5162–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W.; Qi, B.; Ye, J.; Wu, H.; et al. The histone demethylase LSD1 is a novel oncogene and therapeutic target in oral cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016, 374, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Meng, G.; Chen, F. The role of NLRP3 inflammasome in 5-fluorouracil resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, I.W.; Evaniew, N.; Ghert, M. Lost in translation: Animal models and clinical trials in cancer treatment. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2014, 6, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ben-David, U.; Ha, G.; Tseng, Y.Y.; Greenwald, N.F.; Oh, C.; Shih, J.; McFarland, J.M.; Wong, B.; Boehm, J.S.; Beroukhim, R.; et al. Patient-derived xenografts undergo mouse-specific tumor evolution. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Yoshimura, K.; Sewastjanow-Silva, M.; Song, S.; Ajani, J.A. Challenges and Prospects of Patient-Derived Xenografts for Cancer Research. Cancers 2023, 15, 4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Creighton, C.J.; Zhang, Y.; Sen, B.; Mazumdar, T.; Myers, J.N.; Lai, S.Y.; Woolfson, A.; Lorenzi, M.V.; Bell, D.; et al. Tumor grafts derived from patients with head and neck squamous carcinoma authentically maintain the molecular and histologic characteristics of human cancers. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, S.; O’Driscoll, L. Three-dimensional cell culture: The missing link in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.M.; Van Noort, R.; Scutt, A.M.; Thornhill, M.H. Tissue-engineered oral mucosa: A review of the scientific literature. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckstead, B.L.; Pan, S.; Bhrany, A.D.; Bratt-Leal, A.M.; Ratner, B.D.; Giachelli, C.M. Esophageal epithelial cell interaction with synthetic and natural scaffolds for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6217–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertsching, H.; Walles, T.; Hofmann, M.; Schanz, J.; Knapp, W.H. Engineering of a vascularized scaffold for artificial tissue and organ generation. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6610–6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, A.T.; Fecher, D.; Wangorsch, G.; Gottlich, C.; Walles, T.; Walles, H.; Dandekar, T.; Dandekar, G.; Nietzer, S.L. Establishment of a human 3D lung cancer model based on a biological tissue matrix combined with a Boolean in silico model. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, M.; Gross, R.; Walles, H.; Gangnus, R.; Schutze, K.; Walles, T. An engineered 3D human airway mucosa model based on an SIS scaffold. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7355–7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangan, S.R. A new human cell line (FaDu) from a hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 1972, 29, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecher, D.; Hofmann, E.; Buck, A.; Bundschuh, R.; Nietzer, S.; Dandekar, G.; Walles, T.; Walles, H.; Luckerath, K.; Steinke, M. Human Organotypic Lung Tumor Models: Suitable For Preclinical 18F-FDG PET-Imaging. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivarajan, R.; Kessie, D.K.; Oberwinkler, H.; Pallmann, N.; Walles, T.; Scherzad, A.; Hackenberg, S.; Steinke, M. Susceptibility of Human Airway Tissue Models Derived From Different Anatomical Sites to Bordetella pertussis and Its Virulence Factor Adenylate Cyclase Toxin. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 797491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, P.R.; Kaminagakura, E.; Pires, F.R.; Vargas, P.A.; Almeida, O.P. Cytokeratin expression in initial oral mucositis of head and neck irradiated patients. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhargava, S.; Chapple, C.R.; Bullock, A.J.; Layton, C.; MacNeil, S. Tissue-engineered buccal mucosa for substitution urethroplasty. BJU Int. 2004, 93, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharamzadeh, K.; Brook, I.M.; Van Noort, R.; Scutt, A.M.; Smith, K.G.; Thornhill, M.H. Development, optimization and characterization of a full-thickness tissue engineered human oral mucosal model for biological assessment of dental biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colley, H.E.; Hearnden, V.; Jones, A.V.; Weinreb, P.H.; Violette, S.M.; Macneil, S.; Thornhill, M.H.; Murdoch, C. Development of tissue-engineered models of oral dysplasia and early invasive oral squamous cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, K.; Badylak, S.F. Porcine small intestinal submucosa (SIS): A bioscaffold supporting in vitro primary human epidermal cell differentiation and synthesis of basement membrane proteins. Burns 2001, 27, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulasekara, K.K.; Lukandu, O.M.; Neppelberg, E.; Vintermyr, O.K.; Johannessen, A.C.; Costea, D.E. Cancer progression is associated with increased expression of basement membrane proteins in three-dimensional in vitro models of human oral cancer. Arch. Oral Biol. 2009, 54, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.P.; Xu, K.; Cui, J.; Yuan, D.Y.; Zou, B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.L.; Li, K.Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, B. Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal miR-382-5p promotes the migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bienkowska, K.J.; Hanley, C.J.; Thomas, G.J. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Oral Cancer: A Current Perspective on Function and Potential for Therapeutic Targeting. Front. Oral Health 2021, 2, 686337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaballah, K.; Costea, D.E.; Hills, A.; Gollin, S.M.; Harrison, P.; Partridge, M. Tissue engineering of oral dysplasia. J. Pathol. 2008, 215, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauchle, E.; Johannsen, H.; Nolan, S.; Thude, S.; Schenke-Layland, K. Design and analysis of a squamous cell carcinoma in vitro model system. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7401–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbek, S.; Balasubramanian, P.G.; Chiquet-Ehrismann, R.; Tucker, R.P.; Adams, J.C. The evolution of extracellular matrix. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 4300–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinke, M.; Dally, I.; Friedel, G.; Walles, H.; Walles, T. Host-integration of a tissue-engineered airway patch: Two-year follow-up in a single patient. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freier, K.; Joos, S.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Devens, F.; Benner, A.; Bosch, F.X.; Lichter, P.; Hofele, C. Tissue microarray analysis reveals site-specific prevalence of oncogene amplifications in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1179–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Yu, G.P.; McCormick, S.A.; Mo, J.; Datta, B.; Mahimkar, M.; Lazarus, P.; Schaffer, A.A.; Desper, R.; Schantz, S.P. Genetic differences detected by comparative genomic hybridization in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas from different tumor sites: Construction of oncogenetic trees for tumor progression. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 34, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, S.; Baur, J.; Otto, C.; Burkard, N.; Braspenning, J.; Walles, H.; Nickel, J.; Metzger, M. Evaluation of a Miniaturized Biologically Vascularized Scaffold in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserocchi, G.; Mercatali, L.; Liverani, C.; De Vita, A.; Spadazzi, C.; Pieri, F.; Bongiovanni, A.; Recine, F.; Amadori, D.; Ibrahim, T. Management and potentialities of primary cancer cultures in preclinical and translational studies. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmann, L.; Thierauf, J.; Koerich Laureano, N.; Stark, H.J.; Prigge, E.S.; Horn, D.; Freier, K.; Grabe, N.; Rong, C.; Federspil, P.; et al. Organotypic Co-Cultures as a Novel 3D Model for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Oral Mucosa Model | Tumor Formation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor spots | Regularly formed epithelium | No signs of malignancy or tumor formation | |
| Tumor spheroids | Regularly formed epithelium | Tumor cells located on top of stratum corneum | |
| Single tumor cells | 1:50 | Continuously formed stratum corneum, cells in the basal layers appeared irregular with nuclear pleomorphism and differences in size | Formation of tumor cell clusters; no invasion into lamina propria |
| 1:33 | Disturbed epithelial architecture | Invasive tumor growth | |
| 1:25 | No regular epithelial structure, atypical cornification | Invasive tumor growth | |
| 1:10 | No regular epithelial structure, atypical cornification | Invasive tumor growth |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stöth, M.; Mineif, A.T.; Sauer, F.; Meyer, T.J.; Mueller-Diesing, F.; Haug, L.; Scherzad, A.; Steinke, M.; Rossi, A.; Hackenberg, S. A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 4049-4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050250
Stöth M, Mineif AT, Sauer F, Meyer TJ, Mueller-Diesing F, Haug L, Scherzad A, Steinke M, Rossi A, Hackenberg S. A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Current Issues in Molecular Biology. 2024; 46(5):4049-4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050250
Chicago/Turabian StyleStöth, Manuel, Anna Teresa Mineif, Fabian Sauer, Till Jasper Meyer, Flurin Mueller-Diesing, Lukas Haug, Agmal Scherzad, Maria Steinke, Angela Rossi, and Stephan Hackenberg. 2024. "A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma" Current Issues in Molecular Biology 46, no. 5: 4049-4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050250
APA StyleStöth, M., Mineif, A. T., Sauer, F., Meyer, T. J., Mueller-Diesing, F., Haug, L., Scherzad, A., Steinke, M., Rossi, A., & Hackenberg, S. (2024). A Tissue Engineered 3D Model of Cancer Cell Invasion for Human Head and Neck Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(5), 4049-4062. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46050250