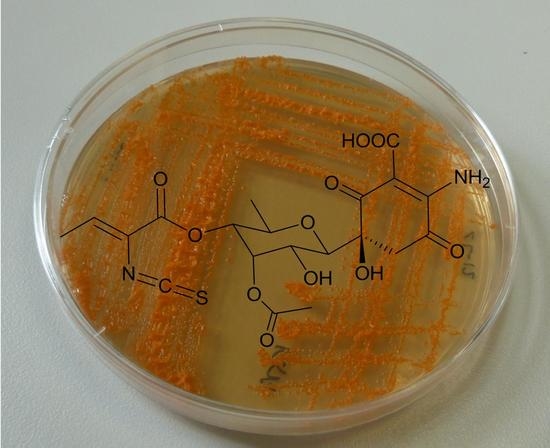
Paulomycin G, a New Natural Product with Cytotoxic Activity against Tumor Cell Lines Produced by Deep-Sea Sediment Derived Micromonospora matsumotoense M-412 from the Avilés Canyon in the Cantabrian Sea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Taxonomy and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Strain
2.2. Structure Determination
2.3. Cytotoxic Activity of Paulomycin G
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity of Paulomycin G
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Microorganism and Fermentation Conditions
3.3. Isolation and Purification of Paulomycin G
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis (Taxonomy) of the Producer Microorganism
3.5. Cytotoxic Activity of Compound 1
3.6. Antimicrobial Activity of Compound 1
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Novak, E. Treating Chlamydia Infections with Paulomycin. Patent PCT/US1987/002420, 21 April 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Argoudelis, A.D.; Brinkley, T.A.; Brodasky, T.F.; Buege, J.A.; Meyer, H.F.; Mizsak, S.A. Paulomycins A and B. Isolation and characterization. J. Antibiot. 1982, 35, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majer, J.; Chater, K. Streptomyces albus G produces an antibiotic complex identical to paulomycins A and B. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1987, 133, 2503–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argoudelis, A.D.; Baczynskyj, L.; Haak, W.J.; Knoll, W.M.; Mizsak, S.A.; Shilliday, F.B. New paulomycins produced by Streptomyces paulus. J. Antibiot. 1988, 41, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braña, A.F.; Rodríguez, M.; Pahari, P.; Rohr, J.; García, L.A.; Blanco, G. Activation and silencing of secondary metabolites in Streptomyces albus and Streptomyces lividans after transformation with cosmids containing the thienamycin gene cluster from Streptomyces cattleya. Arch. Microbiol. 2014, 196, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xie, Z.; Wang, M.; Ai, G.; Chen, Y. Identification and analysis of the paulomycin biosynthetic gene cluster and titer improvement of the paulomycins in Streptomyces paulus NRRL 8115. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Rodríguez, M.; Braña, A.F.; Méndez, C.; Salas, J.A.; Olano, C. New insights into paulomycin biosynthesis pathway in Streptomyces albus J1074 and generation of novel derivatives by combinatorial biosynthesis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.C.; Bora, N. Diversity and biogeography of marine actinobacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameş-Kocabaş, E.E.; Uzel, A. Isolation strategies of marine-derived actinomycetes from sponge and sediment samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 88, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braña, A.F.; Fiedler, H.P.; Nava, H.; González, V.; Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; Molina, A.; Acuña, J.L.; García, L.A.; Blanco, G. Two Streptomyces Species Producing Antibiotic, Antitumor, and Anti Inflammatory Compounds Are Widespread Among Intertidal Macroalgae and Deep Sea Coral Reef Invertebrates from the Central Cantabrian Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 69, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; González, V.; Braña, A.F.; Molina, A.; Acuña, J.L.; García, L.A.; Blanco, G. Myceligenerans cantabricum sp. nov., a barotolerant actinobacterium isolated from a deep cold water coral. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; Braña, A.F.; González, V.; Nava, H.; Molina, A.; Llera, E.; Fiedler, H.P.; Rico, J.M.; García-Flórez, L.; Acuña, J.L.; et al. Atmospheric Dispersal of Bioactive Streptomyces albidoflavus Strains Among Terrestrial and Marine Environments. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; González, V.; Braña, A.F.; Palacios, J.J.; Otero, L.; Fernández, J.; Molina, A.; Kulik, A.; Vázquez, F.; Acuña, J.L.; et al. Pharmacological potential of phylogenetically diverse Actinobacteria isolated from deep-sea coral ecosystems of the submarine Avilés Canyon in the Cantabrian Sea. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 338–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braña, A.F.; Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Otero, L.; Fernández, J.; Palacios, J.J.; Martín, J.; de la Cruz, M.; Díaz, C.; Vicente, F.; et al. Branimycins B and C, Antibiotics Produced by the Abyssal Actinobacterium Pseudonocardia carboxydivorans M-227. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braña, A.F.; Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; Osset, M.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; de Pedro, N.; de la Cruz, M.; Díaz, C.; Vicente, F.; Reyes, F.; et al. Lobophorin K, a New Natural Product with Cytotoxic Activity Produced by Streptomyces sp. M-207 Associated with the Deep-Sea Coral Lophelia pertusa. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; Reyes, F. Combined LC/UV/MS and NMR strategies for the dereplication of marine natural products. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, P.F.; Mizsak, S.A.; Baczynskyj, L.; Argoudelis, A.D.; Duchamp, D.J.; Watt, W. The Structure and Chemistry of Paulomycin. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 2493–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argoudelis, A.D.; Baczynskyj, L.; Mizsak, S.A.; Shilliday, F.B.; Spinelli, P.A.; DeZwaan, J. Paldimycins A and B and antibiotics 273a2α and 273a2β synthesis and characterization. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, E.; Weissbach, U.; Sánchez Reillo, C.; Braña, A.F.; Méndez, C.; Rohr, J.; Salas, J.A. Identification of two genes from Streptomyces argillaceus encoding two glycosyltransferases involved in the transfer of a disaccharide during the biosynthesis of the antitrumor drug mithramycin. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 4929–4937. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.G.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbour-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. Conference limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audoin, C.; Bonhomme, D.; Ivanisevic, J.; de la Cruz, M.; Cautain, B.; Monteiro, M.C.; Reyes, F.; Rios, L.; Perez, T.; Thomas, O.P. Balibalosides, an Original Family of Glucosylated Sesterterpenes Produced by the Mediterranean Sponge Oscarella balibaloi. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Position | δ 13C | δ (1H), (Mult, J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 169.0 | - |
| 2 | 99.1 | - |
| 3 | 159.4 | - |
| 4 | 188.8 | - |
| 5 | 47.7 | 3.22 (d, 16.0), 3.17 (d, 16.0) |
| 6 | 77.5 | - |
| 7 | 197.5 | - |
| 8 | 77.5 | 3.69 (d, 9.9) |
| 9 | 67.0 | 3.61 (br dt, 9.7, 3.3) |
| 10 | 69.8 | 5.29 (dd, 2.6, 2.6) |
| 11 | 73.4 | 4.51 (dd, 9.9, 2.6) |
| 12 | 69.9 | 3.79 (dq, 9.9, 6.2) |
| 13 | 16.3 | 0.88 (d, 6.2) |
| 1′ | 170.1 | - |
| 2′ | 20.8 | 2.10 (s) |
| 1′ | 159.8 | - |
| 2′′ | 122.3 | - |
| 3′′ | 136.9 | 6.71 (quart., 7.1) |
| 4′′ | 14.6 | 1.89 (d, 7.1) |
| 5′′ | 141.6 | - |
| NH2 (3) | - | 9.71 (br s), 9.35 (br s) |
| OH (1) | - | 14.21 (br s) |
| OH (6) | - | 5.43 (s) |
| OH (9) | - | 5.78 (d, 4.4) |
| Cell line | Paulomycin G (IC50 μM) | Paulomycin B (IC50 μM) |
|---|---|---|
| HepG2 | 4.30 ± 0.42 | >36 |
| MCF-7 | 1.58 ± 0.12 | >36 |
| MiaPaca_2 | 2.70 ± 0.25 | >36 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarmiento-Vizcaíno, A.; Braña, A.F.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; De Pedro, N.; Cruz, M.D.l.; Díaz, C.; Vicente, F.; Acuña, J.L.; Reyes, F.; et al. Paulomycin G, a New Natural Product with Cytotoxic Activity against Tumor Cell Lines Produced by Deep-Sea Sediment Derived Micromonospora matsumotoense M-412 from the Avilés Canyon in the Cantabrian Sea. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090271
Sarmiento-Vizcaíno A, Braña AF, Pérez-Victoria I, Martín J, De Pedro N, Cruz MDl, Díaz C, Vicente F, Acuña JL, Reyes F, et al. Paulomycin G, a New Natural Product with Cytotoxic Activity against Tumor Cell Lines Produced by Deep-Sea Sediment Derived Micromonospora matsumotoense M-412 from the Avilés Canyon in the Cantabrian Sea. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(9):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090271
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarmiento-Vizcaíno, Aida, Alfredo F. Braña, Ignacio Pérez-Victoria, Jesús Martín, Nuria De Pedro, Mercedes De la Cruz, Caridad Díaz, Francisca Vicente, José L. Acuña, Fernando Reyes, and et al. 2017. "Paulomycin G, a New Natural Product with Cytotoxic Activity against Tumor Cell Lines Produced by Deep-Sea Sediment Derived Micromonospora matsumotoense M-412 from the Avilés Canyon in the Cantabrian Sea" Marine Drugs 15, no. 9: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090271
APA StyleSarmiento-Vizcaíno, A., Braña, A. F., Pérez-Victoria, I., Martín, J., De Pedro, N., Cruz, M. D. l., Díaz, C., Vicente, F., Acuña, J. L., Reyes, F., García, L. A., & Blanco, G. (2017). Paulomycin G, a New Natural Product with Cytotoxic Activity against Tumor Cell Lines Produced by Deep-Sea Sediment Derived Micromonospora matsumotoense M-412 from the Avilés Canyon in the Cantabrian Sea. Marine Drugs, 15(9), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090271