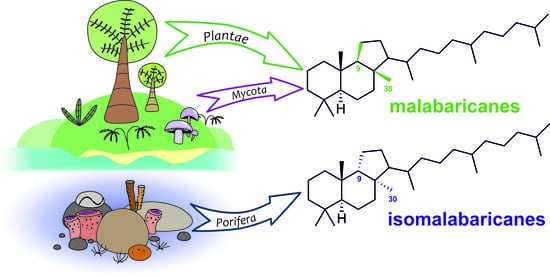
Malabaricane and Isomalabaricane Triterpenoids, Including Their Glycoconjugated Forms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Malabaricanes: Structures, Distribution, Biological Activities, and Biogenesis
2.1. Isolation and Structures
2.2. Biogenesis of Malabaricane Triterpenoids and Their Biological Activities
3. Isomalabaricane Triterpenoids. Structures, Properties, Distribution, and Synthesis
3.1. Isolation and Structures
3.1.1. Stellettins
| N | Name | Structure | Collection | Source | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 57 | Stellettin A |  | Hainan Island | S. tenuis, | [32] |
| Cape Wilberforce (Australia) | Stelletta sp. | [33] | |||
| Mindanao (Philippines) | Rhabdastrella globostellata | [34] | |||
| Hainan Island | R. aff. distincta | [39] | |||
| Xisha Island (South China Sea) | Geodia japonica | [43] | |||
| 43 | Stellettin B |  | Fiji | Jaspis stellifera | [28] |
| Great Barrier Reef | J. stellifera | [29] | |||
| Somalian waters | Stelletta sp. | [30] | |||
| Hainan Island | S. tenuis | [32] | |||
| Cape Wilberforce (Australia) | Stelletta sp. | [33] | |||
| Mindanao (Philippines) | R. globostellata | [34] | |||
| Hainan Island | R. aff. distincta | [39] | |||
| Xisha Island (South China Sea) | Geodia japonica | [43] | |||
| 58 | Stellettin C |  | Cape Wilberforce (Australia) | Stelletta sp. | [33] |
| Mindanao (Philippines) | R. globostellata | [34] | |||
| Hainan Island | R. aff. distincta | [39] | |||
| Hainan Island | S. tenuis | [40] | |||
| Hainan Island | R. globostellata | [44] | |||
| 59 | Stellettin D |  | Cape Wilberforce (Australia) | Stelletta sp. | [33] |
| Mindanao (Philippines) | R. globostellata | [34] | |||
| Hainan Island | Stelletta sp. | [37] | |||
| Hainan Island | S. tenuis | [40] | |||
| Hainan Island | R. globostellata | [44] | |||
| 60 | Stellettin E |  | Cape Wilberforce (Australia) | Stelletta sp. | [33] |
| Mindanao (Philippines) | R. globostellata | [34] | |||
| Hainan Island | R. aff. distincta | [39] | |||
| Hainan Island | R. globostellata | [44] | |||
| 61 | Stellettin F |  | Cape Wilberforce (Australia) | Stelletta sp. | [33] |
| 41 | Stellettin G |  | Fiji | J. stellifera | [28] |
| Cape Wilberforce (Australia) | Stelletta sp. | [33] | |||
| Hainan Island | Stelletta sp. | [37] | |||
| 62 | Stellettin H |  | Mindanao (Philippines) | R. globostellata | [34] |
| Hainan Island | Stelletta sp. | [37] | |||
| 63 | Stellettin I |  | Mindanao (Philippines) | R. globostellata | [34] |
| 64 | Stellettin J |  | Fiji | R. globostellata | [35] |
| 65 | Stellettin K |  | Fiji | R. globostellata | [35] |
| 66 | Stellettin L |  | Hainan Island | S. tenuis | [36] |
| Hainan Island | R. aff. distincta | [45] | |||
| 67 | Stellettin M |  | Hainan Island | S. tenuis | [36] |
| Hainan Island | R. aff. distincta | [45] | |||
| 68 | Stellettin N |  | Hainan Island | Stelletta sp. | [37] |
| 69 | 22,23-Dihydrostellettin D |  | Hainan Island | Stelletta sp. | [37] |
| South China Sea, | Jaspis sp. | [38] | |||
| South China Sea | J. stellifera | [46] | |||
| 70 | 22,23-Dihydrostellettin B |  | Hainan Island | Rhabdastrella aff. distincta | [39] |
| 71 | Stellettin N |  | Hainan Island | S. tenuis | [40] |
| 72 | Stellettin O |  | Hainan Island | S. tenuis | [40] |
| 73 | Stellettin P |  | Hainan Island | S. tenuis | [40] |
| 74 | Stellettin Q |  | Cham Island (Vietnam) | Stelletta sp. | [42] |
| 75 | Stellettin R |  | Cham Island (Vietnam) | Stelletta sp. | [42] |
| 76 | Stellettin S |  | Cham Island (Vietnam) | Stelletta sp. | [42] |
| 77 | Stellettin T |  | Cham Island (Vietnam) | Stelletta sp. | [42] |
| 78 | Stellettin U |  | Cham Island (Vietnam) | Stelletta sp. | [42] |
| 79 | Stellettin V |  | Cham Island (Vietnam) | Stelletta sp. | [42] |
3.1.2. Stelliferins
| N | Name | Structure | Collection | Source | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | Stelliferin A |  | Isigaki Island (Japan) | Jaspis stellifera | [47] |
| Mage-jima Island (Japan) | Stelletta globostellata | [49] | |||
| 81 | Stelliferin B |  | Isigaki Island (Japan) | J. stellifera | [47] |
| 82 | Stelliferin C |  | Isigaki Island (Japan) | J. stellifera | [47] |
| 83 | Stelliferin D |  | Isigaki Island (Japan) | J. stellifera | [47] |
| Mage-jima Island (Japan) | S. globostellata | [49] | |||
| 84 | Stelliferin E |  | Isigaki Island (Japan) | J. stellifera | [47] |
| 85 | Stelliferin F |  | Isigaki Island (Japan) | J. stellifera | [47] |
| 86 | Stelliferin G |  | Tonga (South Pacific) | Jaspis sp. | [48] |
| 87 | 29-Hydroxy- stelliferin A |  | Tonga (South Pacific) | Jaspis sp. | [48] |
| 88 | 29-Hydroxy- stelliferin E |  | Tonga (South Pacific) | Jaspis sp. | [48] |
| 89 | 3-Epi-29- Hydroxy- stelliferin A |  | Mage-jima Island (Japan) | S. globostellata | [49] |
| 90 | 3-Epi-29- Hydroxy- stelliferin E |  | Mage-jima Island (Japan) | S. globostellata | [49] |
| Tonga (South Pacific) | Jaspis sp. | [48] | |||
| 91 | 29-Hydroxy- stelliferin D |  | Mage-jima Island (Japan) | S. globostellata | [49] |
| 92 | Stelliferin J |  | Ishigaki (Japan) | Rhabdastrella cf. globostellata | [50] |
| 93 | Stelliferin K |  | Ishigaki (Japan) | R. cf. globostellata | [50] |
| 94 | Stelliferin L |  | Ishigaki (Japan) | R. cf. globostellata | [50] |
| 95 | Stelliferin M |  | Ishigaki (Japan) | R. cf. globostellata | [50] |
| 96 | Stelliferin N |  | Ishigaki (Japan) | R. cf. globostellata | [50] |
| 97 | 29-Hydroxy- stelliferin B |  | Tonga (South Pacific) | Jaspis sp. | [48,51] |
| 98 | 13(E)-29- Hydroxy- stelliferin E |  | Tonga (South Pacific) | Jaspis sp. | [48] |
| 99 | 3-epi-29- Hydroxy- stelliferin E |  | Tonga (South Pacific) | Jaspis sp. | [48] |
| 100 | 13(E)- stelliferin G |  | Tonga (South Pacific) | Jaspis sp. | [48] |
| 101 | Stelliferin riboside |  | Vanua Levu Island (Fiji) | Geodia Globostellifera | [52] |
| Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] | |||
| 102 | 3-O-Deacetyl-13(Z)- stelliferin riboside |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
| 103 | 13(E)- Stelliferin riboside |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
3.1.3. Globostellatic Acids
| N | Name | Structure | Collection | Source | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104 | Globostellatic acid A |  | Mage Island (Japan) | Stelletta globostellata | [54] |
| Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | Rhabdastrella globostellata | [53] | |||
| 105 | Globostellatic acid B |  | Mage Island (Japan) | S. globostellata | [54] |
| Vanuatu Islands | Jaspis sp. | [55] | |||
| 106 | Globostellatic acid C |  | Mage Island (Japan) | S. globostellata | [54] |
| Vanuatu Islands | Jaspis sp. | [55] | |||
| 107 | Globostellatic acid D |  | Mage Island (Japan) | S. globostellata | [54] |
| Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] | |||
| 108 | Globostellatic acid E methyl ester |  | Vanuatu Islands | Jaspis sp. | [55] |
| 109 | Globostellatic acid F |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
| 110 | Globostellatic acid G |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
| 111 | Globostellatic acid H |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
| 112 | Globostellatic acid I |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
| 113 | Globostellatic acid J |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
| 114 | Globostellatic acid K |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
| 115 | Globostellatic acid L |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
| 116 | Globostellatic acid M |  | Kapoposang Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [53] |
| 117 | 13Z,17Z- Globostellatic acid X methyl ester |  | Sulawesi Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [57] |
| 118 | 13Z,17E- Globostellatic acid X methyl ester |  | Sulawesi Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [57] |
| 119 | 13E,17Z- Globostellatic acid X methyl ester |  | Sulawesi Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [57] |
| 120 | 13E,17E- Globostellatic acid X methyl ester |  | Sulawesi Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [57] |
| 121 | Globostellatic acid F methyl ester |  | Sulawesi Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [57] |
| 122 | 13E-Globostellatic acid B methyl ester |  | Sulawesi Island (Indonesia) | R. globostellata | [57] |
3.1.4. Other Isomalabaricane Triterpenoids and Nor-Triterpenoids
3.2. Biogenesis, Taxonomic Distribution, and Biological Activities of Isomalabaricanes
4. Syntheses of Isomalabaricane-Type Compounds
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill, L.A.; Connolly, J.D. Triterpenoids. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 962–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 175–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Dev, S. A new class of triterpenoids from Ailanthus malabarica DC derivatives of malabaricane. Tetrahedron Lett. 1967, 48, 4837–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, W.F.; Paul, I.C.; Bajaj, A.G.; Dev, S. The structure of malabaricol. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 4153–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tamelen, E.E.; Willett, J.; Schwartz, M.; Nadean, R. Non-enzymatic laboratory cyclization of squalene 2,3-oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 5937–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpless, K.B. d,l-Malabaricanediol. The first cyclic natural product derived from squalene in a nonenzymic process. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1970, 92, 6999–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, P.V.; Rao, R.R.; Rao, J.M. Two new tetracyclic triterpenoids from the heartwood of Ailanthus excelsa Roxb. Chem. Biodivers. 2006, 3, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongnest, S.; Boonsombat, J.; Prawat, H.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S. Ailanthusins A-G and nor-lupane triterpenoids from Ailanthus triphysa. Phytochemistry 2017, 134, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, H.L.; Christensen, J.; Olsen, C.E.; Sittie, A.A.; Jaroszewski, J.W. New dammarane and malabaricane triterpenes from Caloncoba echinata. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1764–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, P.S.; Akkinepally, R.R.; Bobbala, R.K.; Achanta, A.R.V.N. Stereochemistry of 2,2,5-trisubstituted tetrahydrofuran ring-containing natural products based on 1H NMR spectroscopy: Some observations. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2016, 54, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, P.S.; Gattu, R.K.; Belvotagi, A.R.V.; Akkinepally, R.R.; Bobbala, R.K.; Achanta, A.R.V.N. New malabaricane triterpenes from the oleoresin of Ailanthus malabarica. Fitoterapia 2015, 100, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.K.; Lv, T.M.; Song, G.S.; Wang, Y.X.; Lin, B.; Huang, X.X. Structure reassignment of two triterpenes with CASE algorithms and DFT chemical shift predictions. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyashberg, M.E.; Blinov, K.A.; Williams, A.J.; Molodtsov, S.G.; Martin, G.E.; Martirosian, E.R. Structure elucidator: A versatile expert system for molecular structure elucidation from 1D and 2D NMR data and molecular fragments. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2004, 44, 771–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elyashberg, M.; Blinov, K.; Molodtsov, S.; Williams, A. Structure revision of asperjinone using computer-assisted structure elucidation methods. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, F.; Curini, M.; Di Sano, C.; Zadra, C.; Gigliarelli, G.; Rascón-Valenzuela, L.A.; Zepeda, R.E.R.; Marcotullio, M.C. Diterpenoids and triterpenoids from the resin of Bursera microphylla and their cytotoxic activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakupovic, J.; Eid, F.; Bohlmann, F.; El-Dahmy, S. Malabaricane derivatives from Pyrethrum santolinoides. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 1536–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marner, F.J.; Freyer, A.; Lex, J. Triterpenoids from gum mastic, the resin of Pistacia lentiscus. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3709–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faini, F.; Castillo, M.; Torres, R.; Delle Monache, G.; Gacs-Baitz, E. Malabaricane triterpene glucosides from Adesmia aconcaguensis. Phytochemistry 1995, 40, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sontag, B.; Fröde, R.; Bross, M.; Steglich, W. Chromogenic triterpenoids from Cortinarius fulvoincarnatus, C. sodagnitus and related toadstools (Agaricales). Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 1, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, K.; Shiojima, K.; Ageta, H. Fern constituents: Two new malabaricatrienes isolated from Lemmaphyllum microphyllum var. obovatum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 1140–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobti, R.R.; Dev, S. A direct correlation of (+)-malabaricol with (+)-ambreinolide. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968, 9, 2215–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageta, H.; Masuda, K.; Inoue, M.; Ishida, T. Fern constituent: Colysanoxide, an onoceroid having a novel carbon skeleton, isolated from Colysis species. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 4349–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, A.; Schaeffer, P.; Bernasconi, S.; Albrecht, P. 17(E)-13α(H)-Malabarica-14(27),17,21-triene, an unexpected tricyclic hydrocarbon in sediments. Org. Geochem. 1999, 30, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ourisson, G.; Albrecht, O. Hopanoids. I. Geohopanoids: The most abundant natural products on earth? Acc. Chem. Res. 1992, 25, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.W.; Pearson, A. Hypotheses for the origin and early evolution of triterpenoid cyclases. Geobiology 2007, 5, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pale-Grosdemange, C.; Merkofer, T.; Rohmer, M.; Poralla, K. Production of bicyclic and tricyclic triterpenes by mutated squalene-hopene cyclase. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 6009–6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommakanti, S.S.; Kundeti, L.S.R.; Saddanapu, V. Synthesis and cytotoxicity on human lung cancer cell lines of 2-arylidene and related analogues of malabaricol. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 14069–14077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, B.N.; Wells, R.J.; Croft, K.D. Malabaricane triterpenes from a fijian collection of the sponge Jaspis stellifera. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 1998–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, B.N.; Wells, R.J. Malabaracane triterpenoids from a Great Barrier collection of the sponge Jaspis stellifera. Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, T.; Clardy, J.; Minale, L.; Pizza, C.; Zollo, F.; Riccio, R. A triterpenoid pigment with the isomalabaricane skeleton from the marine sponge Stelletta sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 3307–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeppel, F.; Wiebel, J.M.; Heissler, D. Synthesis of the trans-syn-trans perhydrobenz[e]indene moiety of the stellettins and of the stelliferins. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 6377–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Y.; Meng, Y.H.; Zeng, L.M.; Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J. Stellettin A, a new triterpenoid pigment from the marine sponge Stelletta tenuis. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1450–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.L.; McKee, T.C.; Cardellina, J.H., II; Leid, M.; Boyd, M.R. Cytotoxic triterpenes from a marine sponge, Stelletta sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1047–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, D.; Mangalindan, G.C.; Concepción, G.P.; Verbitsky, S.M.; Rabindran, S.; Miranda, M.; Greenstein, M.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Harper, M.K.; Ireland, C.M. Bioactive isomalabaricane triterpenes from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, J.A.; Li, M.; Hecht, S.M.; Kingston, D.G.I. Bioactive isomalabaricane triterpenoids from Rhabdastrella globostellata that stabilize the binding of DNA polymerase β to DNA. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Shi, N.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Morris-Natschke, S.L.; Lin, A. Stellettins L and M, cytotoxic isomalabaracane-type triterpenes, and sterols from the marine sponge Stelletta tenuis. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1114–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, D.Q.; Mao, S.C.; Yu, X.Q.; Guo, Y.W. Isomalabaricane triterpenes with potent protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibition from the Hainan sponge Stelletta sp. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2013, 49, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.A.; Deng, Z.W.; Li, J.; Fu, H.Z.; Pei, Y.H.; Zhang, S.; Lin, W.H. A new isomalabaricane triterpenoid from sponge Jaspis sp. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2005, 16, 353–355. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, F.; Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Fu, H.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Isomalabaricane-type compounds from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella aff. distincta. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 2033–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Tian, X.; Lin, H.; Wang, M.; Yao, M. Three new cytotoxic isomalabaricane triterpenes from the marine sponge Stelletta tenuis. Fitoterapia 2015, 106, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Nay, B.; Yang, M.; Ni, Y.; Wang, H.; Yao, L.; Li, X. Marine sponges of the genus Stelletta as promising drug sources: Chemical and biological aspects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolesnikova, S.A.; Lyakhova, E.G.; Kozhushnaya, A.B.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Berdyshev, D.V.; Popov, R.S.; Stonik, V.A. New isomalabaricane-derived metabolites from a Stelletta sp. marine sponge. Molecules 2021, 26, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.H.; Che, C.T. Isomalabaricane-type nortriterpenoids and other constituents of the marine sponge Geodia japonica. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, B.; Cui, J.; Deng, Z.; de Voogd, N.J.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Globostelletins A-I, cytotoxic isomalabaricane derivatives from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 4639–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, F.; Xu, M.; Deng, Z.; de Voogd, N.J.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Rhabdastrellins A-F, isomalabaracane triterpenes from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella aff. distincta. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1738–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.G.; Wang, J.; Xing, G.S.; Xu, J.J.; Qiao, W.; Zhao, C.; Tang, S.A. Jaspiferin G, a new isomalabaricane-type triterpenoid from the sponge Jaspis stellifera. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2016, 71, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Ishibashi, M.; Agemi, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Stelliferins A-F, new antineoplastic isomalabaricane triterpenes from the Okinawan marine sponge Jaspis stellifera. Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 2181–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meragelman, K.M.; McKee, T.C.; Boyd, M.R. New cytotoxic isomalabaricane triterpenes from the sponge Jaspis species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oku, N.; Matsunaga, S.; Wada, S.; Watabe, S.; Fusetani, N. New isomalabaracane triterpenes from the marine sponge Stelletta globostellata that induce morphological changes in rat fibroblasts. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Momose, R.; Shibazaki, A.; Gonoi, T.; Fromont, J.; Kobayashi, J. Stelliferins J-N, isomalabaracane-type triterpenoids from Okinawan marine sponge Rhabdastrella cf. globostellata. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 6689–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Himaya, S.W.A.; Kim, S.K. Triterpenoids of marine origin as anti-cancer agents. Molecules 2013, 18, 7886–7909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabudravu, J.N.; Jaspars, M. Stelliferin riboside, a triterpene monosaccharide isolated from the Fijian sponge Geodia globostellifera. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, M.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Müller, W.E.G.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Cytotoxic isomalabaricane triterpenes from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, G.; Matsunaga, S.; Fusetani, N. Globostellatic acids A-D, new cytotoxic isomalabaracane triterpenes from the marine sponge Stelletta globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampella, A.; D’Auria, M.V.; Debitus, C.; Menou, J.L. New isomalabaricane derivatives from a new species of Jaspis sponge collected at the Vanuatu Islands. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, V.; Arteaga, J.F.; del Moral, J.F.Q.; Barrero, A.F. Unusually cyclized triterpenes: Occurrence, biosynthesis and chemical synthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, S.; Sanagawa, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Setiawan, A.; Arai, M.; Kobayashi, M. Novel isomalabarican triterpenes, exhibiting selective anti-proliferative activity against vascular endothelial cells, from marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 4818–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.; Deng, S.; Wu, H.; Jiang, S. Rhabdastrellic acid-A, a novel triterpenoid from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Yuasa, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Sasaki, T.; Tsuda, M. Jaspiferals A-G, new cytotoxic isomalabaracane-type nortriterpenoids from Okinawan marine sponge Jaspis stellifera. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 5745–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Pei, Y.; Fu, H.; Deng, Z.; Li, J.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Jaspolides A-F, six new isomalabaricane-type terpenoids from the sponge Jaspis sp. Chem. Parm. Bull. 2006, 54, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, S.; Deng, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Jaspolides G and H, unique bisisomalabaricanes from the Chinese marine sponge Jaspis sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5443–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Longeon, A.; Debitus, C.; Guyot, M. New cytotoxic isomalabaracane-type sesterterpenes from the New Caledonian marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 3087–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Xu, R.; Lin, W.; Duan, H. Jaspiferin A and B: Two new secondary metabolites from the South China Sea sponge Jaspis stellifera. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2012, 6, 398–401. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, D.J.; Tang, S.A.; Xing, G.S.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhao, C.; Duan, H.Q.; Lin, W.H. Jaspiferins C-F, four new isomalabaricane-type triterpenoids from the South China Sea sponge Jaspis stellifera. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 16, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Wang, J.; Qiao, W.; Zhao, C.; Tang, S. Jaspiferins H-J, new isomalabaracane-type terpenoids from the South China Sea marine sponge Jaspis stellifera. Chem. Nat. Compds. 2018, 54, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirashima, M.; Tsuda, K.; Hamada, T.; Okamura, H.; Furukawa, T.; Akiyama, S.; Tajitsu, Y.; Ikeda, R.; Komatsu, M.; Doe, M.; et al. Cytotoxic isomalabaricane derivatives and a monocyclic triterpene glycoside from the sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, D.T.; Yen, P.H.; Nhiem, N.X.; Quang, T.H.; Tai, B.H.; Minh, C.V.; Kim, D.C.; Oh, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kiem, P.V. New acetylated terpenoids from sponge Rhabdastrella providentiae inhibit NO production in LPS stimulated BV-2 cells. Nat. Prod. Comm. 2018, 13, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dung, D.T.; Hang, D.T.T.; Nhiem, N.X.; Quang, T.H.; Tai, B.H.; Yen, P.H.; Hoai, N.T.; Thung, D.C.; Minh, C.V.; Kiem, P.V. Rhabdaprovidines D-G, four new 6,6,5-tricyclic terpenoids from the Vietnamese sponge Rhabdastrella providentiae. Nat. Prod. Comm. 2018, 13, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiem, P.V.; Dung, D.T.; Yen, P.H.; Nhiem, N.X.; Quang, T.H.; Tai, B.H.; Minh, C.V. New isomalabaricane analogues from the sponge Rhabdastrella providentiae and their cytotoxic activities. Phytochemisty Lett. 2018, 26, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Ren, J.; Deng, Z.; de Voogd, N.J.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Globostelletins J-S, isomalabaricanes with unusual cyclopentane sidechains from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesnikova, S.A.; Lyakhova, E.G.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Berdyshev, D.V.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Popov, R.S.; Grebnev, B.B.; Makarieva, T.N.; Minh, C.V.; Stonik, V.A. Cyclobutastellettolides A and B, C19-norterpenoids from a Stelletta sp. marine sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3196–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrero, A.F.; Oltra, J.E.; Herrador, M.M.; Cabrera, E.; Sanchez, J.F.; Quílez, J.F.; Rojas, F.J.; Reyes, J.F. Gibepyrones: α-pyrones from Gibberella fujikuroi. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodeiro, S.; Wilson, W.K.; Shan, H.; Matsuda, S.P.T. A putative precursor of isomalabaricane triterpenoids from lanosterol synthase mutants. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, J.A. Resolving the ‘Jaspis stellifera’ complex. Mem. Queensl. Mus. 2000, 45, 453–476. [Google Scholar]
- Ebada, S.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Bioactive sesterterpenes and triterpenes from marine sponges: Occurrence and pharmacological significance. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 313–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.K.; Ho, J.C.K.; Che, C.T. Apoptotic activity of isomalabaricane triterpenes on human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 2005, 230, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.K.; Cheung, F.W.K.; Che, C.T. Stellettin A induces oxidative stress and apoptosis in HL-60 human leukemia and LNCaP prostate cancer cell lines. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.K.; Ling, Y.H.; Cheung, F.W.K.; Che, C.T. Stellettin A induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in murine B16 melanoma cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.A.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, W.Z.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, R.; Jin, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, K.; Yamori, T.; Dan, S.; et al. In vitro antitumor activity of stellettin B, a triterpene from marine sponge Jaspis stellifera, on human glioblastoma cancer SF295 cells. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4200–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, N.F.; Lin, P.Y.; Su, J.H.; Chen, B.H.; Kuo, H.M.; Sung, C.S.; Sung, P.J.; Wen, Z.H.; Chen, W.F. Anti-invasion and antiangiogenic effects of stellettin B through inhibition of the Akt/Girdin signaling pathway and VEGF in glioblastoma cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Gou, Z.; Wen, Y.; Luo, Q.; Huang, Z. Marine compounds targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, X.; Qiu, Y.; Jin, M.; Gong, M.; Kong, D. Stellettin B induces G1 arrest, apoptosis and autophagy in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells via blocking PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Fan, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, R.; Jin, M.; Qiu, Y.; Kong, D. Stellettin B induces apoptosis in human chronic myeloid leukemia cells via targeting PI3K and Stat5. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28906–28921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.F.; Zhou, J.M.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, R.; Liu, J.; Feng, G.K.; Liu, Z.C.; Xiao, D.J.; Deng, S.Z.; Zhu, X.F. Rhabdastrellic acid-A inhibited PI3K/Akt pathway and induced apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, F.W.K.; Li, C.; Che, C.T.; Liu, B.P.L.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.K. Geoditin A induces oxidative stress and apoptosis on human colon HT29 cells. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, F.W.K.; Guo, J.; Ling, Y.H.; Che, C.T.; Liu, W.K. Anti-melanogenic property of geoditin A in murine B16 melanoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, S.Y.; Li, M.; Tang, S.A.; Sun, W.; Xu, B.; Cui, J.R.; Lin, W.H. Induction of apoptosis accompanying with G1 phase arrest and microtubule disassembly in human hepatoma cells by jaspolide B, a new isomalabaricane-type triterpene. Cancer Lett. 2008, 262, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.W.; Chen, N.F.; Wen, Z.H.; Yang, W.Y.; Kuo, H.M.; Sung, P.J.; Su, J.H.; Cheng, S.Y.; Chen, W.F. In vitro and in vivo neuroprotective effects of stellettin B through anti-apoptosis and the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyko, Y.D.; Huck, C.J.; Sarlah, D. Total synthesis of isomalabaricane triterpenoids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 14131–14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



































| Compounds | Biological Source | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kingdom | Class/Clade | Order | Family | Species | |
| 1–5, 8–11 | Plantae | Angiosperms | Sapindales | Simaroubaceae | Ailanthus tryphysa (=malabarica) |
| 6,7 | Plantae | Angiosperms | Malpighiales | Flacourtiaceae | Caloncoba echinata |
| 16,17 | Plantae | Angiosperms | Sapindales | Burseraceae | Bursera microphylla |
| 18,19 | Plantae | Spermatophyta | Asterales | Asteraceae | Pyrethrum santolinoides |
| 18,22 | Plantae | Pistacia | Sapindales | Anacaridiaceae | Pistacia lentiscus |
| 24–26 | Plantae | Magnoliopsida | Fabales | Fabaceae | Adesmia aconcaguensis |
| 27–32 | Mycota | Basidiomycota | Agaricales | Cortinariaceae | Cortinarius arcuatorum, C. sadagnitus, C. fulvoincarnatus |
| 34,35 | Plantae | Tracheophyta | Polypodiales | Adiantaceae | Lemmaphyllum microphyllum var. obovatum |
| 38 | Plantae | Tracheophyta | Polypodiales | Polypodiaceae | Colysis elliptica |
| 35 | Unknown | Bottom sediment, Lake Cadagno (Switzerland) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stonik, V.A.; Kolesnikova, S.A. Malabaricane and Isomalabaricane Triterpenoids, Including Their Glycoconjugated Forms. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060327
Stonik VA, Kolesnikova SA. Malabaricane and Isomalabaricane Triterpenoids, Including Their Glycoconjugated Forms. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(6):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060327
Chicago/Turabian StyleStonik, Valentin A., and Sophia A. Kolesnikova. 2021. "Malabaricane and Isomalabaricane Triterpenoids, Including Their Glycoconjugated Forms" Marine Drugs 19, no. 6: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060327
APA StyleStonik, V. A., & Kolesnikova, S. A. (2021). Malabaricane and Isomalabaricane Triterpenoids, Including Their Glycoconjugated Forms. Marine Drugs, 19(6), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19060327