An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities
Abstract
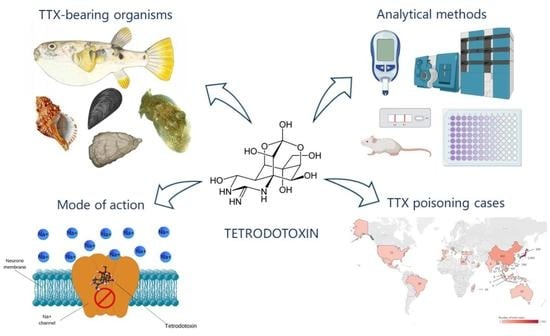
:1. Introduction
2. Origin and Sources of TTX
3. Occurrence and Distribution of TTXs in Potentially Edible Aquatic Organisms
3.1. TTXs in Pufferfish
| Country | Sampling Year | Common Name | Species | Tissue | Maximum TTXs Concentration (µg TTX eq/kg) | Analysis Method Used for Quantification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Croatia | 2014 | Silver stripe blaasop (pufferfish) | Lagocephalus sceleratus | LIV | 30,600 | LC-MS/MS | [23] |
| GON | 48,700 | ||||||
| MUS | 800 | ||||||
| SK | 1500 | ||||||
| Greece | 2007 | Silver stripe blaasop (pufferfish) | Lagocephalus sceleratus | LIV | 87,530 | MBA | [18] |
| GON | 239,320 | ||||||
| GIT | 177,650 | ||||||
| MUS | 10,160 | ||||||
| SK | 6630 | ||||||
| LIV | 1,380,800 | LC-MS/MS | [71] | ||||
| GON | 8,248,510 | ||||||
| GIT | 478,430 | ||||||
| MUS | 58,440 | ||||||
| SK | 33,340 | ||||||
| 2017–2020 | Silver stripe blaasop (pufferfish) | Lagocephalus sceleratus | LIV | 312,950 | LC-MS/MS | [72] | |
| GON | 535,780 | ||||||
| MUS | 41,470 | ||||||
| SK | 35,050 | ||||||
| Spain | 2014 | Silver stripe blaasop (pufferfish) | Lagocephalus sceleratus | LIV | 3080 | LC-MS/MS | [22] |
| GON | 25,950 | ||||||
| MUS | 1010 | ||||||
| SK | 1650 | ||||||
| Portugal (São Miguel Island, Azores) | 2013 | Guinean puffer (pufferfish) | Sphoeroides marmoratus | LIV | 765 | LC-MS/MS | [73] |
| GON | 696,631 | ||||||
| MUS | 15,921 | ||||||
| Turkey | 2012 | Silver stripe blaasop (pufferfish) | Lagocephalus sceleratus | LIV | 46,180 ± 2060 | LC-MS/MS | [74] |
| GON | 52,070 ± 4600 | ||||||
| INT | 7,150 ± 1330 | ||||||
| MUS | 2,830 ± 920 | ||||||
| SK | 3,430 ± 1130 | ||||||
| 2017–2018 | Silver stripe blaasop (pufferfish) | Lagocephalus sceleratus | LIV | 13,480 | ELISA | [75] | |
| GON | 12,870 | ||||||
| INT | 11,740 | ||||||
| MUS | 8320 | ||||||
| SK | 6540 | ||||||
| 2015–2016 | Yellow spotted pufferfish | Torquigener flavimaculosus | LIV | 106,800 ± 5560 | LC-MS/MS | [76] | |
| GON | 100,710 ± 6360 | ||||||
| INT | 86,300 ± 840 | ||||||
| MUS | 86,070 ± 2050 | ||||||
| SK | 139,880 ± 12,210 | ||||||
| 2015–2016 | Suez puffer | Lagocephalus suezensis | LIV | 1440 ± 30 | Q-TOF LC/MS | [51] | |
| GON | 2020 ± 80 | ||||||
| INT | 1910 ± 90 | ||||||
| MUS | 1440 ± 170 | ||||||
| SK | 3090 ± 280 |
3.2. TTXs in Bivalve Mollusks
| Country | Sampling Year | Common Name | Species | Tissue | Maximum TTXs Concentration (µg TTX eq/kg) | Analysis Method Used for Quantification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 2013–2014 | Short-necked clam | Ruditapes philippinarum | WF | 2.22 | LC-MS/MS | [35] |
| Chinese razor clam | Sinonovacula constricta | WF | 16 | ||||
| Mussels | Mytilus edulis | WF | 2.74 | ||||
| Hard-shelled mussel | Mytilus coruscus | WF | 4.39 | ||||
| England | 2013 | Pacific oysters | Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) | WF | 57.4 | LC-MS/MS | [81] |
| 2014 | WF | 137 | |||||
| 2014 | Mussels | Mytilus edulis | WF | 44 | |||
| 2015 | Pacific oysters | Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) | WF | 253 | LC-MS/MS | [55] | |
| Mussels | Mytilus edulis | WF | 73 | ||||
| 2016 | Native oysters | Ostrea edulis | WF | ~80 | |||
| Hard clams | Mercenaria mercenaria | WF | 72 | ||||
| 2019 | Pacific oysters | Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) | WF | 75 | LC-MS/MS | [78] | |
| DG | 242 | ||||||
| 2020 | Clams | Cerastoderma edule | WF | 6.88 | LC-MS/MS | [26] | |
| France | 2018 | Mussels | Mytilus edulis/ galloprovincialis | WF | 11.2 | LC-MS/MS | [30] |
| 2018 | Pacific oysters | Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) | WF | 12.2 | LC-MS/MS | [33] | |
| 2018 | Clams | Ruditapes philippinarum | WF | 8.3 | |||
| 2019 | Pacific oysters | Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) | WF | 32 | |||
| Greece | 2006 | Mussels | Mytilus galloprovincialis | DG | 77.4 | LC-MS/MS | [14] |
| 2008 | DG | 86.2 | |||||
| 2008 | Venus clams | Venus verrucosa | DG | 194.7 | |||
| 2009 | Mussels | Mytilus galloprovincialis | DG | 71.3 | |||
| 2012 | DG | 222.9 | |||||
| 2012 | WF | 193.6 | |||||
| 2014 | WF | 47.0 | |||||
| Italy | 2015 | Mussels | Mytilus galloprovincialis | WF | 3.6 | LC-MS/MS | [34] |
| 2016 | WF | 6.4 | |||||
| 2017 | WF | 5.1 | |||||
| 2017 | Mussels | Mytilus galloprovincialis | WF | 541 | LC-MS/MS | [32] | |
| 2018 | WF | 216 | |||||
| 2018 | Mussels | Mytilus galloprovincialis | WF | ~10 | LC-MS/MS | [31] | |
| 2019 | WF | 76 | |||||
| 2019 | DG | 196 | |||||
| Japan | 1993 | Scallop | Mizuhopecten yessoensis (Patinopecten yessoensis) | DG | ~8000 * | MBA | [77] |
| 2017 | Scallop | Mizuhopecten yessoensis (Patinopecten yessoensis) | WF | 7.3 | LC-MS/MS | [36] | |
| DG | 134.2 | ||||||
| New Zealand | 2011 | NZ rock oyster | Saccostrea glomerata | WF | 140 | LC-MS | [80] |
| 2011 | Pacific oysters | Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) | WF | 80 | |||
| 2011 | Pipi clams | Paphies australis | WF | 160 | |||
| 2012 | WF | 120 | |||||
| 2014 | Pipi clams | Paphies australis | WF | 800 | LC-MS/MS | [79] | |
| 2017 | Pipi clams | Paphies australis | WF | 220 | LC-MS/MS | [64] | |
| 2001–2003 | Shellfish | (unknown) | WF | 19 | LC-MS/MS | [64] | |
| 2007–2009 | Shellfish | (unknown) | WF | 21 | |||
| 2016 | GreenshellTM mussels | Perna canaliculus | WF | 1600 | |||
| 2017 | Pipi clams | Paphies australis | WF | 470 | |||
| 2017 | GreenshellTM mussels | Perna canaliculus | WF | 160 | LC-MS/MS | [82] | |
| Spain | 2017 | Cockles | (unknown) | WF | 2.3 | LC-MS/MS | [29] |
| 2017 | Oysters | (unknown) | WF | 0.9 | |||
| The Netherlands | 2015 | Mussels | Mytilus edulis | WF | 33 | LC-MS/MS | [12] |
| 2015 | Pacific oysters | Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) | WF | 124 | LC-MS/MS | [28] | |
| 2016 | Mussels | Mytilus edulis | WF | 101 | |||
| 2016 | Pacific oysters | Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) | WF | 253 | |||
| 2017 | Mussels | Mytilus edulis | WF | >20 | |||
| 2017 | Pacific oysters | Magallana gigas (Crassostrea gigas) | WF | 51 |
3.3. TTXs in Gastropods and Echinoderms
| Country | Sampling Year | Common Name | Species | Tissue | Maximum TTXs Concentration (µg TTX eq/kg) | Analysis Method Used for Quantification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| France | 2018 | Whelk | Buccinum undatum | DG+GON+ST | 7.4 | LC-MS/MS | [30] |
| Morocco | 2013 | Sea slug | Onchidella celtica | WF | 24 | LC-MS/MS | [73] |
| New Zealand | 2009 | Sea slug | Pleurobranchaea maculata | WF | 850,000 | LC-MS/MS | [87] |
| 2010 | Sand dollar | Arachnoides zelandiae | WF | 250 | LC-MS | [88] | |
| 2010 | Sea slug | Pleurobranchaea maculata | WF | 1,414,000 | LC-MS | [89] | |
| 2011 | WF | 205,600 | |||||
| 2011 | Cat’s eye | Lunella smaragda (Turbo smaragdus) | WF | 110 | LC-MS | [80] | |
| 2011 | Sea slug | Pleurobranchaea maculata | WF | 6 | |||
| 2012 | WF | 5.3 | |||||
| Portugal | 2007 | Trumpet shell | Charonia lampas (Charonia lampas lampas) | DG | 1,319,000 | LC-MS | [25] |
| 2009 | Sea snail | Steromphala umbilicalis (Gibbula umbilicalis) | WF | 63.81 | LC-MS/MS | [7] | |
| 2010 | Sea snail | Phorcus lineatus (Monodonta lineata) | WF | 111.98 | |||
| 2010 | Trumpet shell | Charonia lampas | WF | 6.22 | |||
| 2010 | Trumpet shell | Charonia lampas | MUS | 66.6 | LC-MS/MS | [84] | |
| VIS | 22.4 | ||||||
| 2017 | Trumpet shell | Charonia lampas | Edible MUS | 119.3 | LC-MS/MS | [85] | |
| Non-edible VIS | 98,488.5 |
3.4. TTXs in other Mollusks and Crustaceans
| Country | Sampling Year | Common Name | Species | Tissue | Maximum TTXs Concentration (µg TTX eq/kg) | Analysis Method Used for Quantification | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 2013–2014 | Horseshoe crab | Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda | WF | 162 | LC-MS/MS | [35] |
| Japan | 2015 | Greater blue-ringed octopus | Hapalochlaena lunulata | WS | 13,232 * | MBA | [91] |
| 2016 | 17,907 * | ||||||
| 2017 | 23,491 * | ||||||
| 2019 | Blue-lined octopus | Hapalochlaena fasciata | MUS+SK | 12,900 | LC-MS/MS | [92] | |
| GON | 1980 | ||||||
| PSG | 287,000 | ||||||
| BM | 13,400 | ||||||
| OIO | 24,200 | ||||||
| 2018 | Xanthid crab | Zosimus aeneus | APP | 24,233 | LC-MS/MS | [93] | |
| VIS | 11,238 | ||||||
| 2019 | APP | 28,225 | |||||
| STCON | 881 | ||||||
| New Zealand | 2011 | Seven-armed starfish | Astrostole scabra | WF | 170 | LC-MS | [80] |
| Portugal (São Miguel Island, Azores) | 2013 | Red velvet starfish | Ophidiaster ophidianus | WF | 44,242 | LC-MS/MS | [73] |
| Taiwan | 2010 | Blue-lined octopus | Hapalochlaena fasciata | WS | 38,723 | LC-MS/MS | [90] |
| ARM | 39,208 | ||||||
| ABD | 67,985 | ||||||
| PSG | 819,600 | ||||||
| CEP | 88,127 |
4. Mode of Action of TTX
5. Toxicity of TTX
5.1. Toxicity of TTX (in Human, Experimental Animals, and In Vitro)
| Species | Route | Minimum LD | Median LD50 | LD100 | NOAEL | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | 2 mg (estimation for 50kg BW) | [48] | ||||
| 13.33 μg/kg | [117] | |||||
| Rats | oral | 517.43 μg/kg | [116] | |||
| 10 µg/kg | [118] | |||||
| Rabbit | im | 5.3 µg/kg | 5.8 µg/kg | [115] | ||
| iv | 3.1 µg/kg | 3.8 µg/kg | ||||
| Mice | oral | 232 µg/kg | 75 µg/kg | [119] | ||
| ip | 10.7 µg/kg | [2] | ||||
| sc | 12.5 µg/kg | |||||
| ig | 532 µg/kg | |||||
| ip | 40 µg/kg (for 4-CysTTX) and 860 µg/kg (for 4-GSTTX) | [120] | ||||
| ip | 71 μg/kg (for 11-deoxyTTX) | [121] | ||||
| ip | 10 μg/kg | [122] | ||||
| sc | 16 μg/kg | |||||
| oral | 332 μg/kg | |||||
| oral | 619–700 mg/kg | 1200 μg/kg | [123] | |||
| ip | 10.7 μg/kg | [115] | ||||
| sc | 12.5 μg/kg | |||||
| ig | 532 μg/kg |
5.2. Clinical Symptoms and Findings of Human TTX Intoxications
| Grade | Clinical Symptoms | Onset |
|---|---|---|
| I | Oral numbness and paresthesia, sometimes accompanied by gastrointestinal symptoms (nausea) | 5–45 min |
| II | Numbness of face and other areas, advanced paresthesia, motor paralysis of extremities, incoordination, slurred speech, but still normal reflexes | 10–60 min |
| III | Gross muscular incoordination, aphonia, dysphagia, dyspnea, cyanosis, drop in blood pressure, fixed/dilated pupils, precordial pain, but victims are still conscious | 15 min to several hours |
| IV | Coma, severe respiratory failure and hypoxia, severe hypotension, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmia, heart continues to pulsate for a short period | 15 min to 24 h (death has been recorded 17 min after ingestion) |
5.3. Global Cases of TTX Intoxication in Humans
| Country | Number of Total Cases | Number of Ratal Cases | Source of Intoxication | Case Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 11 | - | Pufferfish | 2001–2002 | [167] |
| 7 | - | Toadfish | [168] | ||
| Bangladesh | 141 | 17 | Pufferfish | 2008 | [185] |
| 37 | 8 | Pufferfish | 2002 | [186] | |
| 53 | Pufferfish | 2001-2006 | [187] | ||
| 36 | 7 | Pufferfish (Takifugu oblongus) | 2002 | [163] | |
| 6 | - | Pufferfish | 2005 | [161] | |
| 8 | 5 | Pufferfish | 1998 | [162] | |
| 11 | - | Pufferfish | 2014 | [109] | |
| Brazil | 11 | - | Pufferfish | - | [170] |
| 27 | 2 | Pufferfish | 1984–2009 | [171] | |
| 1 | 1 | Pufferfish | - | [172] | |
| Cambodia | 57 | 9 | Pufferfish | 2003–2007 | [153] |
| China | 30 | Gastropod, Zeuxis samiplicutus | 2000 (Zheijiang) | [188] | |
| 40 | 8 | Gastropod, Nassarius spp. | 1991–2003 (Lianyungang) | [189] | |
| 309 | 16 | Gastropod, Nassarius spp. | 1977–2001 (Zhoushan) | [190] | |
| 59 | 18 | Gastropod, Nassarius spp. | 1985–2000 (Ningbo) | [191] | |
| 150 | 6 | Gastropod, Nassarius spp. | 2002–2005 (Fujian) | [147] | |
| 22 | Goby fish | 2012 | [146] | ||
| Egypt | 59 | 14 | Pufferfish | 2008–2010 | [176] |
| India | 8 | - | Pufferfish | 2007 (Burla) | [166] |
| Indonesia | 6 | 6 | Pufferfish | 2001 | [164] |
| Israel | 13 | - | Pufferfish | 2005 | [17] |
| 1 | - | Pufferfish | 2012 | [39] | |
| 2 | - | Pufferfish | 2008 | [180] | |
| Italy | 10 | - | Monkfish (Lophius piscatorius) imported from Taiwan | 1977 (Roma) | [183] |
| 3 | Monkfish (Lophius piscatorius) imported from Taiwan | 1978 (Pavia) | [184] | ||
| Japan | 1 | - | Thread-sail filefish | 2008 | [68] |
| 1 | - | Marine snail | 2007 | [68] | |
| 5 | - | Marine snail, Babylonia japonica | 1957 | [192] | |
| 1 | - | Marine snail, C. saulie | 1979 | [193] | |
| 1 | 1 | Pufferfish | - | [194] | |
| 1322 | 265 | Pufferfish | 1965–2002 | [110] | |
| 632 | 19 | Pufferfish | 2003–2020 | [145] | |
| Lebanon | 1 | - | Pufferfish | 2008 | [181] |
| Madagascar | 17 | 5 | Pufferfish | 1993–1998 | [174] |
| Malaysia | 6 | 3 | Horseshoe crab | 2011 | [159] |
| 3 | - | Pufferfish | 2008 | [160] | |
| Mexico | 18 | 2 | Pufferfish | 1970–2000 | [172] |
| Morocco | 3 | 1 | Pufferfish | - | [177] |
| New Caledonia | 1 | - | Diodontidae | 2007 | [169] |
| Oman | 5 | 1 | Pufferfish | 2018 | [173] |
| Reunion Island | 10 | - | Pufferfish | 2013 | [175] |
| Singapore | 1 | - | Pufferfish | - | [165] |
| South Korea | 7 | - | Pufferfish | 2002–2011 | [155] |
| 41 | - | Pufferfish | 2004–2010 (Seul) | [157] | |
| 40 | - | Pufferfish | 1995–1998 | [154] | |
| 111 | 30 | Pufferfish | 1991–2002 (Busan, Gyeongsangnam-do, Jeollanam-do Jeju-do) | [156] | |
| Spain | 1 | - | Trumpet shellfish (Charonia sauliae) | 2007 | [24] |
| Thailand | 55 | - | Pufferfish | - | [149] |
| 8 | - | Pufferfish (Tetraodon fangi) | 1988 | [195] | |
| Taiwan | 2 | Papillosus alectrion and Nassarius gruneri | 2002 | [151] | |
| 192 | 22 | Pufferfish Gastropod (snail) Goby | 1988–2011 | [152] | |
| 2 | - | Blue-lined octopus Hapalochlaena fasciata | 2010 | [90] | |
| Turkey | 7 | 3 | Pufferfish | 2020–2021 | [42,44,182] |
| USA | 2 | - | Pufferfish (imported) | 2014 (Minnesota) | [196] |
| 5 | - | Pufferfish (imported) | 1996, 2006 (California) | [197] | |
| 1 | - | Pufferfish (imported) | 1986 (Hawaii) | [125] | |
| 2 | - | Pufferfish (imported) | 2007 (Chicago) | [197] | |
| 1 | - | Pufferfish (imported) | 2007 (New Jersey) | [197] | |
| Vietnam | 87 | 2 | Blue-lined octopus Hapalochlaena fasciata | 2004 | [130] |
| 7 | 3 | Gastropod, Nassarius spp. | 2006–2007 | [158] |
6. Treatment of TTX Intoxication in Human
7. Therapeutic Use of TTX in Medicine
| Study Direction | Number of Participants | Study Design | Dose and Exposure | Outcome and Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer related pain | 24 | An open-label, multi-dose study | TTX 15 to 90 μg daily, administered intramuscularly in divided doses, over four days | TTX was overall safe. It effectively relieved severe, treatment-resistant cancer pain in the majority of patients and often for prolonged periods after treatment | [232] |
| 77 | A randomized, double blind, parallel design multi-center study | TTX (30 μg, bid) was administered subcutaneously for 4 days | This study suggested TTX may potentially relieve moderate to severe, treatment-resistant cancer pain in a large proportion of patients, and often for prolonged periods following treatment, but further study is warranted using a composite primary endpoint | [229] | |
| 41 | A multi-center open-label longitudinal and efficacy trial | TTX (30 μg) was administered subcutaneously twice daily for 4 days | Long-term treatment with TTX is associated with acceptable toxicity and, in a substantial minority of patients, resulted in a sustained analgesic effect | [230] | |
| 149 | A multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-design trial | TTX (30 μg) was administered subcutaneously twice daily for four consecutive days | TTX may provide clinically meaningful analgesia for patients who have persistent moderate to severe cancer pain despite best analgesic care | [228] | |
| 125 | A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, parallel dose comparison study | TTX (7.5, 15, and 30 μg/kg BID and 30 μg/kg QD) administered as subcutaneous injections for 4 days | This study suggests the TTX 30 µg b.i.d. regimen is well tolerated with promising early efficacy data | [227] | |
| Heroin dependence | 45 | Double blind, placebo-controlled | TTX (5 µg or 10 µg) administered intramuscularly | Low-dose TTX is acutely effective in reducing cue-induced increases in heroin craving and associated anxiety | [234] |
| 216 | A multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled | TTX (5 µg or 10 µg) administered intramuscularly | TTX significantly reduced withdrawal symptoms by day 3 compared with placebo, and there was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse events in study groups | [235] |
| Experimental animals | Model-Technique | Dose and Exposure | Outcome and Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wistar rats Swiss and Webster mice | The formalin test and to partial ligation of the sciatic nerve (Seltzer’s model) | TTX (0.3, 1, 3, or 6 μg/kg) administered subcutaneously 30 min before the formalin test | TTX decreased pain behavior in the formalin test at the highest dose and in the writhing test at 3 and 6 mg/kg. It also reduced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia with an ED50 of 1.08 and 0.62 mg/kg without any adverse effects, respectively | [238] |
| CD-1 mice | Neuropathic pain induced by paclitaxel | TTX (1, 3, or 6 µg/kg) administered subcutaneously | Low doses of TTX can be useful to prevent and treat paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain, and that TTX-sensitive subtypes of sodium channels play a role in the pathogenesis of chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain | [237] |
| Male Sprague–Dawley rats | Chronic unilateral constriction injury to either the sciatic nerve or the infraorbital nerve | TTX (0.3, 1, 3, or 6 μg/kg) administered subcutaneously into the back | TTX alleviates pain-related behaviors in sciatic nerve-lesioned rats through mechanisms that involve complex interactions with endogenous opioid systems | [240] |
| Male Sprague-Dawley rats | Full thickness thermal injury (FTTI) model | TTX (8 μg/kg) administered subcutaneously | TTX reduced thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia | [242] |
| Adult male Sprague–Dawley rats | Carrageenan (k-carrageenan, 1% in NaCl 0.9%) was injected into the belly of the gastrocnemius muscle, | Local injection of TTX (0.03–1 μg) into the gastrocnemius muscle | TTX displays important analgesic effects on rat models of persistent muscle pain, without interfering with the nociceptor function to signal for further potentially harmful stimuli | [240] |
| Adult wild-type Nav1.7 knockout (KO-Nav1.7) mice | Viscero-specific mouse models of chemical stimulation of the colon (intracolonic instillation of capsaicin and mustard oil) and intraperitoneal cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis | TTX (3 and 6 μg/kg) administered subcutaneously | This study suggests that blockade of TTX-sensitive sodium channels, but not Nav1.7 subtype alone, by systemic administration of TTX might be a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of visceral pain | [241] |
| Experimental Animals | Pharmacological Activity | Model- Technique | Dose and Exposure | Outcome and Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats | Local anesthesia | Sciatic Blockade Technique | Co-administration of capsaicin and TTX-loaded liposomes | The combined delivery of capsaicin and TTX using a sustained-release system can achieve prolonged duration local anesthesia without detectable toxicity | [272] |
| Sciatic Blockade Technique | TTX (15.95 mg/L) and bupivacaine (4442 mg/L) or epinephrine (10.08 mg/L) | TTX injected with either bupivacaine or epinephrine, results in prolonged nerve blockade, with myotoxicity that is no worse and perhaps less than that from bupivacaine | [250] | ||
| Sciatic Blockade Technique Modified hotplate test Weight-bearing test | Polymer-TTX conjugates (1–80 μg) | 1.0–80.0 µg of TTX released from these polymers produced a range of durations of nerve block, from several h to 3 days, with minimal systemic or local toxicity | [252] | ||
| Sciatic Blockade Technique | Rats received sciatic nerve blocks with 75 mg of microspheres containing 0.05% TTX, 50% bupivacaine and/or 0.05% dexamethasone | Co-encapsulation of TTX in controlled release devices containing bupivacaine and dexamethasone resulted in very prolonged nerve blocks | [251] | ||
| Sciatic Blockade Technique | TTX [0.3 mL, 10 μM-20 μM (3.19 6.38 mg/L)] with and without epinephrine (10.08 mg/L) or bupivacaine (4442 mg/L) | Bupivacaine increased the local anesthetic potency of tetrodotoxin, reduced its systemic toxicity, and, when co-injected subcutaneously, increased the median lethal dose from 13.95 to 15.23 μg/kg | [249] | ||
| Sciatic Blockade Technique and Neurobehavioral Assessment of Nerve Blockade | TTX [0.3 mL of 3.19 mg/L (0.96 μg dose)] with bupivacaine 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) with or without epinephrine 5 µg/mL | Blocks containing bupivacaine 0.25% with TTX 3.19 mg/L and epinephrine 5 µg/mL were prolonged by roughly 3-fold compared to blocks with bupivacaine 0.25% plain (P < 0.001) or bupivacaine 0.25% with epinephrine 5 µg/mL (P < 0.001) | [253] | ||
| New Zealand White rabbit | Ocular local anesthesia | TTX was applied into the inferior conjunctival cul-de-sac of the right eye | A 40 TTX (32, 319 or 3190 mg/L) or proparacaine 0.5% | TTX is a long-acting topical anesthetic in the rabbit cornea (At a dose of 3190 mg/L, TTX produced an anesthesia up to 8 h) | [254] |
| Adult male Sprague Dawley rats | Attenuation of photophobia | Photophobia by corneal de-epithelialization injury | Topical corneal application of TTX (319 mg/L, 10 μL) in 0.9% saline | TTX markedly attenuated photophobia in rats with corneal injury TTX may be an effective therapeutic option to reduce the symptoms of photophobia that occurs after photorefractive keratectomy and other clinical diseases | [256] |
| Female Sprague-Dawley rats | Ameliorate effect by local blockade on spinal cord injury | A laminectomy was performed | Microinjection of TTX (0.5 μL of 95.7 mg/L–47.8 ng dose) | The results demonstrate that TTX preserves axons from loss after spinal cord injury | [19] |
| A laminectomy at the T8 level exposed a 2.8-mm-diameter circle of dura | TTX (47.85-319 ng/L) 0.5 to 2 μL microinjected into the injury site | The TTX group exhibited a significantly enhanced recovery of coordinated hindlimb functions, more normal hindlimb reflexes, and earlier establishment of a reflex bladder | [260] | ||
| Male Sprague–Dawley rats | Anticonvulsant | Cortical injury in a model of chronic epileptogenesis TTX-impregnated Elvax Neocortical slices Behavioral observations | TTX/Elvax 20 mg/g. The slices incubated with 1.6–15.96 µg and 319 µg/L TTX | The findings indicated that TTX prevents posttraumatic epileptogenesis in rats in a model of chronic epileptogenesis | [263] |
| Adult female Swiss albino mice injected tumor cell line | Anticancer | Ehrlich ascites carcinoma-EAC) | TTX (1/20 of the LD50) administrated intraperitoneally after 10 days into EAC mice | Treatment with TTX caused a significant decrease in the mean tumor weight and an increase in the cumulative mean survival time when compared with EAC group | [265] |
| Adult Swiss female albino mice | Ehrlich Ascite Carcinoma (EAC) | TTX extracted from the fish skin and applied as a dose of 1/10 and the 1/20 of the LD50 | Exposure to TTX caused the rate of cell division to be reduced greatly, especially in the first 6 days post-treatment. The authors suggested that the reduction in cell number is probably due to increased apoptosis | [266] | |
| Male albino mice | Mouse muscle cell line (L929) and leukemia cell line | TTX intraperitoneally administered with 0.25, 0.50, 0.75, and 1.0 mL and dissolved at 5 mg/ml | TTX inhibited the growing of the muscle and leukemia cell lines. It was suggested that TTX can be used to develop anti-tumor compounds | [270] |
| Study Technique | Pharmacological Activity | Model-Technique | Dose and Exposure | Outcome and Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell culture | Anticancer | Human glioma cell lines (HTB-138) | Cell cultures exposed with TTX concentrations of 3.19 and 6.38 mg/L for a period of 24 and 48 h | TTX exert the inhibitory effect on the invasion of metastatic prostate cancer | [274] |
| Metastatic MAT-LyLu Cell Line of Rat Prostate Cancer | TTX at different concentration between 0.32 µg and 319 µg/L | TTX inhibits (IC50: 5.75 μg/L) invasiveness of metastatic prostate cancer | [275] | ||
| MAT-LyLu and AT-2 prostatic carcinoma cell lines | TTX at 319 μg/L | Migration of the MAT-LyLu cell line was reduced significantly by TTX (at 319 μg/L); in contrast, there was no effect on AT-2 cell motility | [267] | ||
| MAT-LyLu and AT-2 prostatic carcinoma cell lines | Incubation of TTX at 1.91 mg/L for 24 h | TTX produced significant changed the morphology of MAT-LyLu cancer cell | [268] | ||
| Cell culture | Neuroprotective effect | Rat cerebellar neurons | TTX 1.6–31.9 µg/L | TTX protected cultured neurons from veratridine-induced toxicity and could be use in treatment of ischemic neuronal injury by preventing excessive neuronal depolarizations. | [258] |
| Male Sprague-Dawley rat hippocampal slices | Anticonvulsant effect | Hippocampal slices blocked stimulus train-evoked electrographic seizures (EGSs) | Localized injection of TTX | Stimulus train-evoked seizures were blocked after localized injection of 15.95 mg/L TTX in rat hippocampal slices. Low concentrations of TTX (1.6, 3.19, or 6.38 µg/L) in the perfusion medium blocked EGSs without decreasing the amplitude of extracellular responses to single stimuli | [262] |
| Ligand-based pharmacophore modeling and Ligand Scout 4.3 software. | Antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2. | Modeling | Structure-based pharmacophore modeling | TTX is a potent active compound against SARS-CoV-2 according to ligand-based approach | [273] |
8. Analytical Methods for the Detection and Quantification of TTXs
8.1. Bioassays
8.2. Cell-Based Assays and Biosensors
8.3. Immunoassays, Immunosensors and Immunostrips
8.4. Aptamer-Based Assays and Aptasensors
8.5. Instrumental Analysis Techniques
8.6. Advantages and Limitations of the Different Analytical Methods
9. Concluding Remarks and Future Orientations
9.1. Origin and Sources
9.2. Occurrence and Distribution of TTXs in Potentially Edible Aquatic Organisms
9.3. Mode of Action and Toxicity of TTX
9.4. Treatment of TTX Intoxications and Therapeutic Use of TTX
9.5. Analytical Methods for the Detection and Quantification of TTXs
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jal, S.; Khora, S.S. An overview on the origin and production of tetrodotoxin, a potent neurotoxin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, J.; Rodriguez, L.P.; Blanco, L.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Tetrodotoxin, an extremely potent marine neurotoxin: Distribution, toxicity, origin and therapeutical uses. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6384–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bane, V.; Lehane, M.; Dikshit, M.; O’Riordan, A.; Furey, A. Tetrodotoxin: Chemistry, toxicity, source, distribution and detection. Toxins 2014, 6, 693–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saoudi, M.; Rabeh, F.B.; Jammoussi, K.; Abdelmouleh, A.; Belbahri, L.; Feki, A.E. Biochemical and physiological responses in Wistar rat after administration of puffer fish (Lagocephalus lagocephalus) flesh. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2007, 5, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciarelli, G.M.; Lechner, M.; Fontes, A.; Kats, L.B.; Eisthen, H.L.; Shaffer, H.B. From poison to promise: The evolution of tetrodotoxin and its potential as a therapeutic. Toxins 2021, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverté, L.; De La Iglesia, P.; Del Río, V.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.T.; Kawatsu, K.; Katikou, P.; Diogène, J.; Campàs, M. Detection of Tetrodotoxins in Puffer Fish by a Self-Assembled Monolayer-Based Immunoassay and Comparison with Surface Plasmon Resonance, LC-MS/MS, and Mouse Bioassay. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10839–10847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Azevedo, J.; Rodriguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, L.M.; Vasconcelos, V. New gastropod vectors and tetrodotoxin potential expansion in temperate waters of the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biessy, L.; Boundy, M.J.; Smith, K.F.; Harwood, D.T.; Hawes, I.; Wood, S.A. Tetrodotoxin in marine bivalves and edible gastropods: A mini-review. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarlamov, T.Y.; Melnikova, D.I.; Chernyshev, A.V. Tetrodotoxin-producing bacteria: Detection, distribution and migration of the toxin in aquatic systems. Toxins 2017, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xie, L.; Xia, G.; Hu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, R. Toxicity and distribution of tetrodotoxin-producing bacteria in puffer fish Fugu rubripes collected from the Bohai Sea of China. Toxicon 2005, 46, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. TTX accumulation in pufferfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol.-Part D Genom. Proteom. 2006, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, H.K.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; et al. Risks for public health related to the presence of tetrodotoxin (TTX) and TTX analogues in marine bivalves and gastropods. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kodama, M.; Sato, S.; Sakamoto, S.; Ogata, T. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin in Alexandrium tamarense, a causative dinoflagellate of paralytic shellfish poisoning. Toxicon 1996, 34, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlamis, A.; Katikou, P.; Rodriguez, I.; Rey, V.; Alfonso, A.; Papazachariou, A.; Zacharaki, T.; Botana, A.M.; Botana, L.M. First detection of tetrodotoxin in greek shellfish by UPLC-MS/MS potentially linked to the presence of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Toxins 2015, 7, 1779–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez, I.; Alfonso, A.; Alonso, E.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Roel, M.; Vlamis, A.; Katikou, P.; Jackson, S.A.; Menon, M.L.; Dobson, A.; et al. The association of bacterial C9-based TTX-like compounds with Prorocentrum minimum opens new uncertainties about shellfish seafood safety. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyol, O.; Ünal, V.; Ceyhan, T.; Bilecenoglu, M. First confirmed record of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) in the Mediterranean Sea. J. Fish Biol. 2005, 66, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentur, Y.; Ashkar, J.; Lurie, Y.; Levy, Y.; Azzam, Z.S.; Litmanovich, M.; Golik, M.; Gurevych, B.; Golani, D.; Eisenman, A. Lessepsian migration and tetrodotoxin poisoning due to Lagocephalus sceleratus in the eastern Mediterranean. Toxicon 2008, 52, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikou, P.; Georgantelis, D.; Sinouris, N.; Petsi, A.; Fotaras, T. First report on toxicity assessment of the Lessepsian migrant pufferfish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) from European waters (Aegean Sea, Greece). Toxicon 2009, 54, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, L.J.; Wrathall, J.R. Time course studies on the effectiveness of tetrodotoxin in reducing consequences of spinal cord contusion. J. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 66, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michailidis, N. Study on the lessepsian migrant Lagocephalus sceleratus in Cyprus. In Proceedings of the EastMed, 2010. Report of the Sub-Regional Technical Meeting on the Lessepsian Migration and Its Impact on Eastern Mediterranean Fishery, Nicosia, Cyprus, 7−9 December 2010; GCP/INT/041/EC-GRE-ITA/TD-04; FAO: Athens, Greece, 2010; pp. 74–87. Available online: http://www.faoeastmed.org/pdf/publications/EastMed_TD04.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Katikou, P.; Vlamis, A. Tetrodotoxins: Recent advances in analysis methods and prevalence in European waters. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambla-Alegre, M.; Reverté, L.; del Río, V.; de la Iglesia, P.; Palacios, O.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.T.; Izquierdo-Muñoz, A.; et al. Evaluation of tetrodotoxins in puffer fish caught along the Mediterranean coast of Spain. Toxin profile of Lagocephalus sceleratus. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ujević, I.; Roje-Busatto, R.; Dragičević, B.; Dulčić, J. Tetrodotoxin in Invasive Silver-cheeked Toadfish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) in the Adriatic Sea. In The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Joksimović, D., Đurović, M., Zonn, I.S., Kostianoy, A.G., Semenov, A.V., Eds.; The Montenegrin Adriatic Coast; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 110, pp. 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernndez-Ortega, J.F.; Santos, J.M.M.D.L.; Herrera-Gutirrez, M.E.; Fernndez-Snchez, V.; Loureo, P.R.; Rancao, A.A.; Tllez-Andrade, A. Seafood intoxication by tetrodotoxin: First case in europe. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 39, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Vale, C.; Alfonso, C.; Vale, P.; Tellez, A.; Botana, L.M. First toxicity report of tetrodotoxin and 5,6,11-trideoxyTTX in the trumpet shell Charonia lampas lampas in Europe. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 5622–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Dean, K.; Lewis, A.; Jenkins, Z.; Bear, B.; Batista, F.; Ryder, D.; Maskrey, B.; Later, A.; House, C.; et al. ScillyHAB: A Multi-Disciplinary Survey of Harmful Marine Phytoplankton and Shellfish Toxins in the Isles of Scilly, Utilizing Citizen Science in a Remote Offshore U.K. Territory during the COVID-19 Pandemia, 2021. Presentation no. SM-O-15_221 in the 19th International Conference on Harmful Algal Blooms, LaPaz, Mexico, 10–15 October 2021. Available online: https://imsvirtualcenter.com.mx/icha (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Turner, A.D.; Higgins, C.; Higman, W.; Hungerford, J. Potential threats posed by tetrodotoxins in UK waters: Examination of detection methodology used in their control. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 7357–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerssen, A.; Bovee, T.H.F.; Klijnstra, M.D.; Poelman, M.; Portier, L.; Hoogenboom, R.L.A.P. First report on the occurrence of tetrodotoxins in bivalve mollusks in the Netherlands. Toxins 2018, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leão, J.M.; Lozano-Leon, A.; Giráldez, J.; Vilariño, Ó.; Gago-Martínez, A. Preliminary results on the evaluation of the occurrence of tetrodotoxin associated to marine Vibrio spp. in bivalves from the Galician Rias (Northwest of Spain). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hort, V.; Arnich, N.; Guérin, T.; Lavison-Bompard, G.; Nicolas, M. First detection of tetrodotoxin in bivalves and gastropods from the French mainland coasts. Toxins 2020, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchiocchi, S.; Campacci, D.; Siracusa, M.; Dubbini, A.; Leoni, F.; Tavoloni, T.; Accoroni, S.; Gorbi, S.; Giuliani, M.E.; Stramenga, A.; et al. Tetrodotoxins (TTXs) and Vibrio alginolyticus in mussels from central Adriatic Sea (Italy): Are they closely related? Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordin, P.; Dall’Ara, S.; Tartaglione, L.; Antonelli, P.; Calfapietra, A.; Varriale, F.; Guiatti, D.; Milandri, A.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Arcangeli, G.; et al. First occurrence of tetrodotoxins in bivalve mollusks from Northern Adriatic Sea (Italy). Food Control 2021, 120, 107510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réveillon, D.; Savar, V.; Schaefer, E.; Chevé, J.; Halm-Lemeille, M.-P.; Hervio-Heath, D.; Travers, M.-A.; Abadie, E.; Rolland, J.-L.; Hess, P. Tetrodotoxins in French Bivalve Mollusks—Analytical Methodology, Environmental Dynamics and Screening of Bacterial Strain Collections. Toxins 2021, 13, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Aversano, C.; Tartaglione, L.; Polito, G.; Dean, K.; Giacobbe, M.; Casabianca, S.; Capellacci, S.; Penna, A.; Turner, A.D. First detection of tetrodotoxin and high levels of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in shellfish from Sicily (Italy) by three different analytical methods. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Yan, Z.; Gao, X.; Chang, J. Analysis and Evaluation of Tetrodotoxin in Coastal Aquatic Products of Zhejiang Province. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 83, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numano, S.; Kudo, Y.; Cho, Y.; Konoki, K.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Temporal variation of the profile and concentrations of paralytic shellfish toxins and tetrodotoxin in the scallop, Patinopecten yessoensis, cultured in a bay of East Japan. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biessy, L.; Smith, K.F.; Harwood, D.T.; Boundy, M.J.; Hawes, I.; Wood, S.A. Spatial variability and depuration of tetrodotoxin in the bivalve Paphies australis from New Zealand. Toxicon X 2019, 2, 100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessy, L.; Pearman, J.K.; Smith, K.F.; Hawes, I.; Wood, S.A. Seasonal and Spatial Variations in Bacterial Communities From Tetrodotoxin-Bearing and Non-tetrodotoxin-Bearing Clams. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheifets, J.; Rozhavsky, B.; Girsh Solomonovich, Z.; Marianna, R.; Soroksky, A. Severe Tetrodotoxin Poisoning after Consumption of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Pufferfish, Fugu) Fished in Mediterranean Sea, Treated with Cholinesterase Inhibitor. Case Rep. Crit. Care 2012, 2012, 782507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CyprusMail. Mother, Son in Critical Condition after Eating Poisonous Fish (Updated). 2016. Available online: https://cyprus-mail.com/2016/04/14/mother-son-critical-condition-eating-poisonous-fish/ (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Mifsud, R.; Gouder, C.; Deidun, A.; Cachia, M.J.; Montefort, S. The first documented case of neurotoxicity in two patients following octopus flesh ingestion in the Mediterranean: A case study from the Maltese Islands (Central Mediterranean). J. Black Sea/Mediterr. Environ. 2019, 25, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- HaberTürk. This Time It Was Scary! Ate a Pufferfish, Died. 2020. Available online: https://www.haberturk.com/son-dakika-haberi-bu-sefer-korkulan-oldu-balon-baligi-yedi-oldu-2756509 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Bédry, R.; de Haro, L.; Bentur, Y.; Senechal, N.; Galil, B.S. Toxicological risks on the human health of populations living around the Mediterranean Sea linked to the invasion of non-indigenous marine species from the Red Sea: A review. Toxicon 2021, 191, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sputniknews Türkiye. Ship Captain Who Ate Pufferfish Died, 4 Sailors Hospitalized. 2021. Available online: https://tr.sputniknews.com/20210211/balon-baligi-gemi-kaptanini-oldurdu-4-denizci-hastanelik-oldu-1043784529.html (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Guardone, L.; Maneschi, A.; Meucci, V.; Gasperetti, L.; Nucera, D.; Armani, A. A Global Retrospective Study on Human Cases of Tetrodotoxin (TTX) Poisoning after Seafood Consumption. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 36, 645–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Rabou, A.F.N. On the occurrence and health risks of the silver-cheeked Toadfish (Lagocephalus sceleratus Gmelin, 1789) in the marine ecosystem of the Gaza Strip, Palestine. Biodiversitas 2019, 20, 2620–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katikou, P. Public health risks associated with tetrodotoxin and its analogues in European waters: Recent advances after the EFSA scientific opinion. Toxins 2019, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noguchi, T.; Ebesu, J.S.M. Puffer poisoning: Epidemiology and treatment. J. Toxicol.-Toxin Rev. 2001, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Corrigendum to Regulation (EC) no 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2004, 226, 22–82. [Google Scholar]
- Nader, M.; Indary, S.; Boustany, L. FAO EastMed the Puffer Fish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) in the Eastern Mediterranean. GCP/INT/041/EC–GRE –ITA/TD-10. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ap967e/ap967e.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Kosker, A.R.; Özogul, F.; Ayas, D.; Durmus, M.; Ucar, Y.; Regenstein, J.M.; Özogul, Y. Tetrodotoxin levels of three pufferfish species (Lagocephalus sp.) caught in the North-Eastern Mediterranean sea. Chemosphere 2019, 219, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.D.; Fenwick, D.; Powell, A.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Ford, C.; Hatfield, R.G.; Santos, A.; Martinez-Urtaza, J.; Bean, T.P.; Baker-Austin, C.; et al. New invasive Nemertean species (Cephalothrix Simula) in England with high levels of tetrodotoxin and a microbiome linked to toxin metabolism. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chau, R.; Kalaitzis, J.A.; Wood, S.A.; Neilan, B.A. Diversity and biosynthetic potential of culturable microbes associated with toxic marine animals. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2695–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikova, D.I.; Vlasenko, A.E.; Magarlamov, T.Y. Stable tetrodotoxin production by Bacillus sp. Strain 1839. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, A.D.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Coates, L.; Bickerstaff, L.; Milligan, S.; O’Neill, A.; Faulkner, D.; McEneny, H.; Baker-Austin, C.; Lees, D.N.; et al. Detection of Tetrodotoxin Shellfish Poisoning (TSP) toxins and causative factors in bivalve molluscs from the UK. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Taniyama, S.; Tatsuno, R. Toxins of Pufferfish—Distribution, Accumulation Mechanism, and Physiologic Functions. Aqua-BioSci. Monogr. 2017, 10, 41–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durán-Riveroll, L.M.; Cembella, A.D. Guanidinium toxins and their interactions with voltage-gated sodium ion channels. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Tetrodotoxin—Distribution and accumulation in aquatic organisms, and cases of human intoxication. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 220–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoi, S.; Ueda, H.; Yamada, R.; Takei, M.; Sato, T.; Oshikiri, S.; Wajima, Y.; Ogata, R.; Oyama, H.; Shitto, T.; et al. Including planocerid flatworms in the diet effectively toxifies the pufferfish, Takifugu niphobles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, T.; Oyama, H.; Kashitani, M.; Ishimaru, Y.; Suo, R.; Sugita, H.; Itoi, S. Toxic flatworm egg plates serve as a possible source of tetrodotoxin for pufferfish. Toxins 2019, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biessy, L.; Smith, K.F.; Boundy, M.J.; Webb, S.C.; Hawes, I.; Wood, S.A. Distribution of tetrodotoxin in the New Zealand Clam, Paphies australis, established using immunohistochemistry and liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry. Toxins 2018, 10, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Abe, Y.; Kudo, Y.; Ritson-Williams, R.; Paul, V.J.; Konoki, K.; Cho, Y.; Adachi, M.; Imazu, T.; Nishikawa, T.; et al. First identification of 5,11-dideoxytetrodotoxin in marine animals, and characterization of major fragment ions of tetrodotoxin and its analogs by high resolution ESI-MS/MS. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2799–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ueyama, N.; Sugimoto, K.; Kudo, Y.; Onodera, K.I.; Cho, Y.; Konoki, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Spiro Bicyclic Guanidino Compounds from Pufferfish: Possible Biosynthetic Intermediates of Tetrodotoxin in Marine Environments. Chem.-A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 7250–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boundy, M.J.; Biessy, L.; Roughan, B.; Nicolas, J.; Tim Harwood, D. Survey of tetrodotoxin in New Zealand bivalve molluscan shellfish over a 16-month period. Toxins 2020, 12, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y.; Hirata, Y. Studies on the puffer fish toxin. J. Pharm. Soc. Japan (Yakugaku Zasshi) 1909, 328, 587–625. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, Y. Über das Tetrodongift. Biochem. Z. 1911, 30, 255–275. Available online: https://archive.org/details/sim_biochemische-zeitschrift-beitraege-zur-chemischen_1911_30/page/274/mode/2up (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Mosher, H.; Fuhrman, F.A.; Buchwald, H.D.; Fischer, H.G. Tarichatoxin-tetrodotoxin: A potent neurotoxin. Science 1964, 144, 1100–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, O.; Hwang, D.F.; Taniyama, S.; Takayani, T. Toxins of Pufferfish That Cause Human Intoxications. In Coastal Environmental and Ecosystem Issues of the East China Sea; Lie, A., Ishimatsu, H.-J., Eds.; Terrapub and Nagasaki University: Nagasaki, Japan, 2010; pp. 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- Tamele, I.J.; Silva, M.; Vasconcelos, V. The incidence of tetrodotoxin and its analogs in the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/627 of 15 March 2019. Laying down uniform practical arrangements for the performance of official controls on products of animal origin intended for human consumption in accordance with Regulation (EU) 2017/625. Off. J. Eur. Union 2019, 131, 51–100. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, P.; Alfonso, A.; Otero, P.; Katikou, P.; Georgantelis, D.; Botana, L.M. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method to detect Tetrodotoxin and its analogues in the puffer fish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) from European waters. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, G.; Mandalakis, M.; Anastasiou, T.; Tserpes, G.; Peristeraki, P.; Somarakis, S. Keeping Lagocephalus sceleratus off the Table: Sources of Variation in the Quantity of TTX, TTX Analogues, and Risk of Tetrodotoxication. Toxins 2021, 13, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.; Rodríguez, I.; Barreiro, A.; Kaufmann, M.; Neto, A.I.; Hassouani, M.; Sabour, B.; Alfonso, A.; Botana, L.M.; Vasconcelos, V. Tetrodotoxins occurrence in non-traditional vectors of the north Atlantic waters (Portuguese maritime territory, and Morocco coast). Toxins 2019, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosker, A.R.; Özogul, F.; Durmus, M.; Ucar, Y.; Ayas, D.; Regenstein, J.M.; Özogul, Y. Tetrodotoxin levels in pufferfish (Lagocephalus sceleratus) caught in the Northeastern Mediterranean Sea. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbora, H.D.; Kunter, İ.; Erçetin, T.; Elagöz, A.M.; Çiçek, B.A. Determination of tetrodotoxin (TTX) levels in various tissues of the silver cheeked puffer fish (Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789)) in Northern Cyprus Sea (Eastern Mediterranean). Toxicon 2020, 175, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosker, A.R.; Özogul, F.; Durmus, M.; Ucar, Y.; Ayas, D.; Šimat, V.; Özogul, Y. First report on TTX levels of the yellow spotted pufferfish (Torquigener flavimaculosus) in the Mediterranean Sea. Toxicon 2018, 148, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, M.; Sato, S.; Ogata, T. Alexandrium tamarense as a source of tetrodotoxin in the scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. In Toxic Phytoplankton Blooms in the Sea; Smayda, T.J., Shimizu, Y., Eds.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993; Volume 3, pp. 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Turner, A.D.; Baker-Austin, C.; Huggett, J.F.; Ritchie, J.M. Distribution of tetrodotoxin in Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, P.S.; Taylor, D.I.; Ogilvie, S.C.; Wilkinson, L.; Anderson, A.; Hamon, D.; Wood, S.A.; Peake, B.M. First detection of tetrodotoxin in the bivalve Paphies australis by liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry with and without precolumn reaction. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvie, S.; Taylor, D.; McNabb, P.; Hamon, D.; Nathan, P.; Anderson, A. Tetrodotoxin in Kaimoana: Science and Mātauranga Mitigating Health Risks from a Lethal Neurotoxin. Prepared for Ngā Pae O Te Māramatanga (Contract No. 10RF-18); Cawthron Report No. 2219. 22 p. plus appendices; 2012. Available online: http://www.maramatanga.ac.nz/sites/default/files/10RF-18%20Final%20contract%20report.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Turner, A.D.; Powell, A.; Schofield, A.; Lees, D.N.; Baker-Austin, C. Detection of the pufferfish toxin tetrodotoxin in European bivalves, England, 2013 to 2014. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 21009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boundy, M.J.; Harwood, D.T. Review of Literature to Help Identify Risks Associated with Tetrodotoxin in Seafood, Including Bivalve Molluscs; Prepared for MPI; Cawthron Institute Report No. 2986A, 46p; Cawthron Institute: Nelson, New Zealand, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.N.; Lin, J.; Lin, H.L. Identification and quantification of tetrodotoxin in the marine gastropod Nassarius by LC-MS. Toxicon 2008, 51, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzoughet, J.K.; Campbell, K.; Barnes, P.; Cooper, K.M.; Chevallier, O.P.; Elliott, C.T. Comparison of sample preparation methods, validation of an UPLC-MS/MS procedure for the quantification of tetrodotoxin present in marine gastropods and analysis of pufferfish. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.R.; Giráldez, J.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Leão, J.M.; Pinto, E.; Soliño, L.; Gago-Martínez, A. High Levels of Tetrodotoxin (TTX) in Trumpet Shell Charonia lampas from the Portuguese Coast. Toxins 2021, 13, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessy, L. Elucidating the Origin and Transmission of Tetrodotoxin in New Zealand Bivalves; The University of Waikato: Hamilton, New Zealand, 2021; Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/10289/14548 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- McNabb, P.; Selwood, A.I.; Munday, R.; Wood, S.A.; Taylor, D.I.; MacKenzie, L.A.; van Ginkel, R.; Rhodes, L.L.; Cornelisen, C.; Heasman, K.; et al. Detection of tetrodotoxin from the grey side-gilled sea slug—Pleurobranchaea maculata, and associated dog neurotoxicosis on beaches adjacent to the Hauraki Gulf, Auckland, New Zealand. Toxicon 2010, 56, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, S.; Wood, S.A.; Salvitti, L.; Taylor, D.I.; Adamson, J.; McNabb, P.; Cary, S.C. Investigating diet as the source of tetrodotoxin in Pleurobranchaea maculata. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, S.A.; Taylor, D.I.; McNabb, P.; Walker, J.; Adamson, J.; Cary, S.C. Tetrodotoxin concentrations in Pleurobranchaea maculata: Temporal, spatial and individual variability from New Zealand Populations. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.J.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, C.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Jen, H.C.; Jian, S.J.; Hwang, D.F. Toxin and species identification of toxic octopus implicated into food poisoning in Taiwan. Toxicon 2014, 91, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Umezaki, K.; Kaneko, K.; Yu, X.; Gomez-Delan, G.; Tomano, S.; Noguchi, T.; Ohtsuka, S. Toxicity and toxin composition of the greater blue-ringed octopus Hapalochlaena lunulata from Ishigaki Island, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Toxins 2019, 11, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamate, Y.; Takatani, T.; Takegaki, T. Levels and distribution of tetrodotoxin in the blue-lined octopus Hapalochlaena fasciata in Japan, with special reference to within-body allocation. J. Molluscan Stud. 2021, 87, eyaa042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tsutsui, H.; Yamawaki, N.; Morii, Y.; Nishihara, G.N.; Itoi, S.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T. Geographic variations in the toxin profile of the xanthid crab Zosimus aeneus in a single reef on ishigaki island, okinawa, Japan. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvitti, L.; Wood, S.A.; Taylor, D.I.; McNabb, P.; Cary, S.C. First identification of tetrodotoxin (TTX) in the flatworm Stylochoplana sp.; A source of TTX for the sea slug Pleurobranchaea maculata. Toxicon 2015, 95, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.Y. Pharmacology of tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. Fed. Proc. 1972, 31, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, M.; Yasumoto, T. Tetrodotoxin derivatives in puffer fish. Toxicon 1985, 23, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S. Tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 1994, 14, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narahashi, T. Tetrodotoxin—A brief history. Proc. Japan Acad. Ser. B 2008, 84, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Ou, S.-W.; Wang, Y.J. Distribution and function of voltage-gated sodium channels in the nervous system. Channels 2017, 11, 534–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Geffeney, S.L.; Williams, B.L.; Rosenthal, J.J.C.; Birk, M.A.; Felkins, J.; Wisell, C.M.; Curry, E.R.; Hanifin, C.T. Convergent and parallel evolution in a voltage-gated sodium channel underlies TTX-resistance in the Greater Blue-ringed Octopus: Hapalochlaena lunulata. Toxicon 2019, 170, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Q.; Xiao, W.; Wang, S.; Yu, S.; Xiao, M.; Bian, H.; Tang, Y. A membrane-based fluorescence-quenching immunochromatographic sensor for the rapid detection of tetrodotoxin. Food Control 2017, 81, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, T. Effects of tetrodotoxin on the mammalian cardiovascular system. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 741–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- How, C.K.; Chern, C.H.; Huang, Y.C.; Wang, L.M.; Lee, C.H. Tetrodotoxin poisoning. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2003, 21, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narahashi, T. Pharmacology of tetrodotoxin. J. Toxicol.-Toxin Rev. 2001, 20, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courville, D.A.; Halstead, B.W.; Hessel, D.W. Marine Biotoxins: Isolation and Properties. Chem. Rev. 1958, 58, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, G.; Forster, J.R. A Voyage Round the World: In His Britannic Majesty’s Sloop, Resolution, Commanded by Capt. James Cook, during the Years 1772, 3, 4, and 5; B White: London, UK, 1772; Volumes I & II, 607p. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, A.; Tani, A. Records of puffer fish poisonings. Report 3. Nippon Igaku Oyobi Kenko Koken. 1941, 3528, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kaku, N.; Meier, J. Clinical Toxicology of Fugu Poisoning; Handbook of Clinical Toxicology of Animal Venoms and Poisons; CRC Press: Boca Raton FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781351443159. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.R.; Chowdhury, F.R.; Das, S.K.; Rahman, S.M.M.; Amin, M.R. Outbreak of puffer fish poisoning in Dhaka city. J. Med. 2018, 19, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, D.F.; Noguchi, T. Tetrodotoxin Poisoning. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2007, 52, 141–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, F.A. Tetrodotoxin. Sci. Am. 1967, 217, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, B. Poisonous and Venomous Marine Animals of the World; Darwin Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1988; ISBN 978-0878500505. [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi, T.; Anderson, N.C.; Moore, J.W. Comparison of tetrodotoxin and procaine in internally perfused squid giant axons. J. Gen. Physiol. 1967, 50, 1413–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haque, M.A.; Islam, Q.T.; Razzak, M.; Faiz, M.; Bari, M.I. Neurological Manifestations of Puffer Fish Poisoning and It’s Outcome: Study of 83 Cases. TAJ J. Teach. Assoc. 2008, 21, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Huang, K.; Gao, L.; Zhang, H.; Rong, K. Toxicity of tetrodotoxin towards mice and rabbits. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 2003, 32, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, B.; Sun, J.; Zheng, H.; Le, Q.; Wang, C.; Bai, K.; He, J.; He, H.; Dong, Y. Effect of tetrodotoxin pellets in a rat model of postherpetic neuralgia. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasteel, E.E.J.; Westerink, R.H.S. Comparison of the acute inhibitory effects of Tetrodotoxin (TTX) in rat and human neuronal networks for risk assessment purposes. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 270, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.C.P.; Kew, C.K.; Ching, J.W.C. The action of tetrodotoxin on the heart. J. Pathol. 1970, 100, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abal, P.; Louzao, M.C.; Antelo, A.; Alvarez, M.; Cagide, E.; Vilariño, N.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Acute oral toxicity of tetrodotoxin in mice: Determination of Lethal Dose 50 (LD50) and no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL). Toxins 2017, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Goto, A.; Nakagawa, T. Identification of 4-S-cysteinyltetrodotoxin from the liver of the puffer fish, Fugu pardalis, and formation of thiol adducts of tetrodotoxin from 4,9-anhydrotetrodotoxin. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumoto, T.; Yotsu, M.; Murata, M.; Naoki, H. New tetrodotoxin analogues from the newt cynops ensicauda. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 2344–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, C.Y. Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol. Rev. 1966, 18, 997–1049. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cowawintaweewat, S.; Somroop, S.; Khantisitthiporn, O.; Pootong, A. The Study of Anti-tetrodotoxin Effect of Thunbergia laurifolia Linn. crude extract. J. Med. Technol. Assoc. Thail. 2011, 39, 3836–3852. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.C.; Liao, S.C.; Deng, J.F. Tetrodotoxin poisoning in Taiwan: An analysis of poison center data. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1996, 38, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sims, J.K.; Ostman, D.C. Pufferfish poisoning: Emergency diagnosis and management of mild human tetrodotoxication. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1986, 15, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abal, P.; Louzao, M.C.; Vilariño, N.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Acute toxicity assessment: Macroscopic and ultrastructural effects in mice treated with oral tetrodotoxin. Toxins 2019, 11, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanchanapongkul, J. Tetrodotoxin poisoning following ingestion of the toxic eggs of the horseshoe crab Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda, a case series from 1994 through 2006. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2008, 39, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Oda, K.; Araki, K.; Totoki, T.; Shibasaki, H. Nerve conduction study of human tetrodotoxication. Neurology 1989, 39, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.F.; Tominack, R.L.; Chung, H.M.; Tsai, W.J. Hypertension as an unusual feature in an outbreak of tetrodotoxin poisoning. Clin. Toxicol. 1991, 29, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.L.; Caldwell, R.L. Intra-organismal distribution of tetrodotoxin in two species of blue-ringed octopuses (Hapalochlaena fasciata and H. lunulata). Toxicon 2009, 54, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borison, H.L.; McCarthy, L.E.; Clark, W.G.; Radhakrishnan, N. Vomiting, hypothermia, and respiratory paralysis due to tetrodotoxin (puffer fish poison) in the cat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1963, 5, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-K.; Ling, Y.-L.; Wang, J.C. The Failure of Respiration in Death by Tetrodotoxin Poisoning. Q. J. Exp. Physiol. Cogn. Med. Sci. 1968, 53, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flachsenberger, W.A. Respiratory failure and lethal hypotension due to blue-ringed octopus and tetrodotoxin envenomation observed and counteracted in animal models. Clin. Toxicol. 1986, 24, 485–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, M.E. Pharmacologic effects of tetrodotoxin: Cardivascular and antiarrhythmic activities. Toxicon 1969, 7, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.C. Tetrodotoxin. In Critical Care Toxicology: Diagnosis and Management of the Critically Poisoned Patient; Brent, J., Burkhart, K., Dargan, P., Hatten, B., Megarbane, B., Palmer, R., White, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 2085–2099. [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi, T. Mechanism of Tetrodotoxin and Saxitoxin Action. In Handbook of Natural Toxins; Tu, A.T., Ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA; Basel, Switzerland, 1988; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, S.; Strichartz, G.; Moczydlowski, E.; Ravindran, A.; Reichardt, P.B. The saxitoxins: Sources, chemistry and pharmacology. In Marine Toxins. Origin, Structure and Pharmacology; Hall, S., Reichardt, P.B., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; pp. 29–69. [Google Scholar]
- Tsunenari, S.; Uchimura, Y.; Kanda, M. Puffer Poisoning in Japan—A Case Report. J. Forensic Sci. 1980, 25, 10956J. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambyah, P.; Hui, K.P.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Chin, N.K.; Chan, T. Central-nervous-system effects of tetrodotoxin poisoning. Lancet 1994, 343, 538–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibballs, J. Severe tetrodotoxic fish poisoning. Anaesth. Intensive Care 1988, 16, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Wat, J.; So, P. Puffer fish poisoning. Anaesth. Intensive Care 1994, 22, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torda, T.A.; Sinclair, E.; Ulyatt, D.B. Puffer fish (tetrodotoxin) poisoning: Clinical record and suggested management. Med. J. Aust. 1973, 1, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gestal-Otero, J.J. Epidemiology of Marine Toxins. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins. Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection, 3rd ed.; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 123–195. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazawa, K.; Noguchi, T. Distribution and origin of tetrodotoxin. J. Toxicol.-Toxin Rev. 2001, 20, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Risk Profile of Natural Poison: Fish: Puffer Fish Poison. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/topics/syokuchu/poison/animal_det_01.html (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- You, J.; Yue, Y.J.; Xing, F.; Xia, W.; Lai, S.Y.; Zhang, F.L. Tetrodotoxin poisoning caused by goby fish consumption in southeast China: A retrospective case series analysis. Clinics 2015, 70, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, H.X.; Su, J.; Li, L.F.; Ruan, X.Y.; Wang, X.P. Nassariids and their toxicity. Chin Fish. 2007, 376, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.-H. Detection and Biosynthesis of Puffer Fish Toxin from Bacterial Culture for Novel Medical Application. Master’s Thesis, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Joob, B.; Wiwanitkit, V. Puffer fish poisoning: Summary of case reports from Thailand. J. Coast. Life Med. 2015, 3, 416–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laobhripatr, S.; Limpakarnjanarat, K.; Sangwonloy, O.; Sudhasaneya, S.; Anuchatvorakul, B.; Leelasitorn, S.; Saitanu, K. Food poisoning due to consumption of the freshwater puffer Tetraodon fangi in Thailand. Toxicon 1990, 28, 1372–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.M.; Fu, Y.M.; Shih, D.Y.C. Occurrence of tetrodotoxin poisoning in Nassarius papillosus alectrion and Nassarius gruneri niotha. J. Food Drug Anal. 2004, 12, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.F.; Hwang, D.F. Analysis of poisoning cases, monitoring and risk warning for marine toxins (TTX, PSP and CTXs) in Taiwan. J. Food Drug Anal. 2012, 20, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngy, L.; Taniyama, S.; Shibano, K.; Yu, C.F.; Takatani, T.; Arakawa, O. Distribution of tetrodotoxin in pufferfish collected from coastal waters of Sihanouk Ville, Cambodia. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Japan 2008, 49, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahn, S.K.; Lim, Y.S.; Kim, J.K.; Min, S.S.; Ryoo, E.; Yang, H.J.; Park, C.W.; Lee, K. Clinical analysis of puffer fish poisoning. J. Korean Soc. Emerg. Med. 1999, 10, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, D.H. A Series of Cases of Fukuda Classification Grade IV Tetrodotoxin Poisoning due to Ingestion of Tetrodotoxin from Puffer Fish. J. Korean Soc. Emerg. Med. 2012, 23, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-H.; Gong, Q.-L.; Mok, J.-S.; Min, J.-G.; Lee, T.-S.; Park, J.-H. Characteristics of Puffer Fish Poisoning Outbreaks in Korea (1991–2002). Korean Soc. Food Hyg. Saf. 2003, 18, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun, S.-H.; Sohn, C.-H.; Ryoo, S.-M.; Oh, B.-J.; Lim, K.-S. Clinical analysis of puffer fish poisoning cases. J. Korean Soc. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 9, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, D.V.; Sato, S. Toxicity of Some Marine Snails Responsible for Recent Food Poisonings in Vietnam. Vietnam. J. Mar. Sci. Technol.) 2012, 10, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, M.; Muhammad, J.; Jelip, J.; William, T.; Chua, T.H. An outbreak of tetrodotoxin poisoning from consuming horseshoe crabs in Sabah. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2017, 48, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, H.H.; Chew, L.P. Puffer fish poisoning: A family affair. Med. J. Malays. 2009, 64, 181–182. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, F.R.; Ahasan, H.A.M.N.; al Mamun, A.; Rashid, A.K.M.M.; al Mahboob, A. Puffer fish (Tetrodotoxin) poisoning: An analysis and outcome of six cases. Trop. Doct. 2007, 37, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, Y.; Yamamori, K.; Noguchi, T. Occurrence of TTX in a brackish water puffer “midorifugu”, Tetraodon nigroviridis, collected from Thailand. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Japan 1999, 40, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S. Puffer fish tragedy in Bangladesh: An incident of Takifugu oblongus poisoning in Degholia, Khulna. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 28, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kungsuwan, A.; Ittipong, B.; Inthuserdha, P.; Pavitranon, S.; Teeyapan, P.; Yooyen, A.; Loedang, S. Biotoxins Analysis in Dead Fisherman Due to Indesting Marine Puffers; Abstracts of the Seminar on Fisheries 2001; 18–20 September 2001; Department of Fisheries: Bangkok, Thailand, 2001; p. 72.
- Yong, Y.S.; Quek, L.S.; Lim, E.K.; Ngo, A. A case report of puffer fish poisoning in Singapore. Case Rep. Med. 2013, 2013, 206971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, A.; Dash, B.K.; Barik, B.K. Rare puffer fish poisoning—A case report. Medico-Legal Updat. 2008, 8, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Isbister, G.K.; Son, J.; Wang, F.; Maclean, C.J.; Lin, C.S.Y.; Ujma, J.; Balit, C.R.; Smith, B.; Milder, D.G.; Kiernan, M.C. Puffer fish poisoning: A potentially life-threatening condition. Med. J. Aust. 2002, 177, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, M.A.; Schneider, J.J.; Isbister, G.K. Use of high performance liquid chromatography to measure tetrodotoxin in serum and urine of poisoned patients. Toxicon 2004, 44, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillaud, C.; Barguil, Y.; Le Coq Saint-Gilles, H.; Mikulski, M.; Guittonneau-Leroy, A.L.; Pérès, H.; Nour, M. Puffer fish poisoning in New Caledonia. Case reports. Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 2016, 28, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Simões, E.M.; Mendes, T.M.A.; Adão, A.; Haddad, V. Poisoning after ingestion of pufferfish in Brazil: Report of 11 cases. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Santana Neto, P.L.; de Aquino, E.C.M.; da Silva, J.A.; Amorim, M.L.P.; de Oliveira Júnior, A.E.; Haddad Júnior, V. Fatal poisoning caused by puffer fish (Tetrodontidae): Report of a case involving a child. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2010, 43, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Sierra-Beltrán, A.P.; Yasumoto, T.; Ochoa, J.L. Toxicities and distribution of tetrodotoxin in the tissues of puffer fish found in the coast of the Baja California Peninsula, Mexico. Toxicon 2000, 38, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhatali, B.; Al Lawatia, S.; Khamis, F.; Kantur, S.; Al-Abri, S.; Kapil, V.; Thomas, J.; Johnson, R.; Hamelin, E.I.; Coleman, R.M.; et al. A cluster of tetrodotoxin poisoning in Oman. Clin. Toxicol. 2021, 59, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaonindrina, N.; Andriamaso, T.H.; Rasolofonirina, N. Puffer fish poisoning in Madagascar: Four case reports. Arch. Inst. Pasteur Madag. 2001, 67, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Puech, B.; Batsalle, B.; Roget, P.; Turquet, J.; Quod, J.P.; Allyn, J.; Idoumbin, J.P.; Chane-Ming, J.; Villefranque, J.; Mougin-Damour, K.; et al. Family tetrodotoxin poisoning in Reunion Island (Southwest Indian Ocean) following the consumption of Lagocephalus sceleratus (Pufferfish). Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 2014, 107, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.M. Tetrodoxin poisoning associated with eating puffer fish in Suez City (Egypt). In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Natural Toxins October 6 University, Cairo, Egypt, 18–19 December 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ababou, A.; Mosadik, A.; Squali, J.; Fikri, K.O.; Lazreq, C.; Sbihi, A. Intoxidation par le poisson coffre. Ann. Fr. Anesth. Reanim. 2000, 19, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köşker, A.R.; Özoğul, F.; Ayas, D.; Durmuş, M.; Uçar, Y. The new toxin of Mediterranean: Tetrodotoxin. Ege J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 32, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streftaris, N.; Zenetos, A. Alien marine species in the Mediterranean—The 100 “worst invasives” and their impact. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2006, 7, 87–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenman, A.; Rusetski, V.; Sharivker, D.; Yona, Z.; Golani, D. An odd pilgrim in the Holy Land. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2008, 26, 383.e3–383.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamandi, S.C.; Kallab, K.; Mattar, H.; Nader, E. Human Poisoning after ingestion of puffer fish caught from Mediterranean sea. Middle East J. Anesthesiol. 2009, 20, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ntv. The “Death” Journey of the Pufferfish from the Mediterranean to Van. 2021. Available online: https://www.ntv.com.tr/galeri/turkiye/balon-baliginin-akdenizden-vana-olum-yolculugu,yjZHfufhVUakIjaaNhLg0Q (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Pocchiari, F. Trade of misbranded frozen fish: Medical and public health implications. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 1977, 13, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berti, M.; Milandri, A. Le biotossine marine. In Igiene Degli Alimenti; Schirone, M., Visciano, P., Eds.; Sistemi Editoriali: Bologna, Italy, 2014; pp. 163–198. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, Q.T.; Razzak, M.A.; Islam, M.A.; Bari, M.I.; Basher, A.; Chowdhury, F.R.; Sayeduzzaman, A.B.M.; Ahasan, H.A.M.N.; Faiz, M.A.; Arakawa, O.; et al. Puffer fish poisoning in Bangladesh: Clinical and toxicological results from large outbreaks in 2008. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 105, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahasan, H.A.M.N.; Mamun, A.A.; Karim, S.R.; Bakar, M.A.; Gazi, E.A.; Bala, C.S. Paralytic Complications of Puffer Fish (Tetrodotoxin) Poisoning. Singap. Med. J. 2004, 45, 73–74. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, F.R.; Nazmul Ahasan, H.A.M.; Mamunur Rashid, A.K.M.; Al Mamun, A.; Khaliduzzaman, S.M. Tetrodotoxin poisoning: A clinical analysis, role of neostigmine and short-term outcome of 53 cases. Singap. Med. J. 2007, 48, 830–833. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, L.M.; Chen, K.; Hwang, P.A.; Hwang, D.F. Identification of tetrodotoxin in marine gastropods implicated in food poisoning. J. Nat. Toxins 2002, 11, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.T.; Zhang, M.S.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.J.; Sun, X.F.; Xing, J.; Pang, Z.Q. Epidemiological study of Nassidae food poisoning in Lianyungang area. Jiangsu Prev. Med. 2005, 16, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shui, L.; Chen, K.; Wang, J.Y.; Mei, H.Z.; Wang, A.Z.; Lu, Y.H.; Hwang, D.F. Tetrodotoxin-associated snail poisoning in Zhoushan: A 25-year retrospective analysis. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.Z.; Yu, M. Research on Nassidae food poisoning in Ningbo City from 1985 to 2000. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2003, 37, 226. [Google Scholar]
- Machida, S. Food poisoning due to ingestion of “ivory shell” Babylonia japonica. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Japan 1965, 6, 87–89. [Google Scholar]
- Narita, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Hida, K.; Noguchi, T.; Maruyama, J.; Ueda, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Occurrence of Tetrodotoxin in a Trumpet Shell, “Boshubora” Charonia sauliae. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1981, 47, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Namera, A.; Giga, H.; Kida, Y.; Ota, K. A Case of Severe Puffer Fish Poisoning: Serum Tetrodotoxin Concentration Measurements for 4 Days after Ingestion. J. Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 5, 2161-0495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saitanu, K.; Laobhripatr, S.; Limpakarnjanarat, K.; Sangwanloy, O.; Sudhasaneya, S.; Anuchatvorakul, B.; Leelasitorn, S. Toxicity of the freshwater puffer fish Tetraodon fangi and T. palembangensis from Thailand. Toxicon 1991, 29, 895–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.B.; Heegaard, W.G.; Deeds, J.R.; McGrath, S.C.; Handy, S.M. Tetrodotoxin poisoning outbreak from imported dried puffer fish--Minneapolis, Minnesota, 2014. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2015, 63, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, N.J.; Deeds, J.R.; Wong, E.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Yancy, H.F.; White, K.D.; Thompson, M.T.; Wahl, M.; Pham, T.U.; Guichard, F.M.; et al. Public Health Response to Puffer Fish (Tetrodotoxin) Poisoning from Mislabeled Product. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoudi, M.; Messarah, M.; Boumendjel, A.; Abdelmouleh, A.; Kammoun, W.; Jamoussi, K.; Feki, A. El Extracted tetrodotoxin from puffer fish Lagocephalus lagocephalus induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity to wistar rats. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 8140–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, R.F.; Williams, S.R.; Nordt, S.P.; Manoguerra, A.S. A review of selected seafood poisonings. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 1999, 26, 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, W.R. Puffer fish poisoning. Am. Fam. Physician 1990, 42, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sims, J.K. A theoretical discourse on the pharmacology of toxic marine ingestions. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1987, 16, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.K.; Chew, L.S.; Wang, K.W.; Mah, P.K.; Tan, B.Y. Anticholinesterase Drugs in the Treatment of Tetrodotoxin Poisoning. Lancet 1984, 324, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.K.; Goh, G.H.; Wang, K.W.; Mah, P.K.; Tan, B.Y. Puffer fish (tetrodotoxin) poisoning: Clinical report and role of anti-cholinesterase drugs in therapy. Singap. Med. J. 1983, 24, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, M.; Yamamoto, S. The effect of tetrodotoxin on the neuromuscular junction and peripheral nerve of the toad. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1954, 4, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Tseng, C.Y.; Lin, C.C. Is neostigmine effective in severe pufferfish-associated tetrodotoxin poisoning? Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, M.Y.; Lai, S.L.; Chen, S.S.; Hwang, D.F. Tetrodotoxin intoxication in a uraemic patient. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 67, 127–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, R.; Nakata, Y.; Kameoka, M.; Hayashi, N.; Watanabe, K.; Yagi, K. Case of tetrodotoxin intoxication in a uremic patient. Jpn. J. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.H. Mechanism of saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin poisoning. Br. Med. Bull. 1969, 25, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K. A monoclonal antibody against tetrodotoxin that reacts to the active group for the toxicity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Environ. Toxicol. 1995, 293, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, V.R.; Poli, M.A.; Bignami, G.S. Prophylaxis and treatment with a monoclonal antibody of tetrodotoxin poisoning in mice. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, R.I.; Armstrong, D.L.; Chanh, T.C. Protection against nerve toxicity by monoclonal antibodies to the sodium channel blocker tetrodotoxin. Am. Soc. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 1821–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaufman, B.; Wright, D.C.; Ballou, W.R.; Monheit, D. Protection against tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin intoxication by a cross-protective rabbit anti-tetrodotoxin antiserum. Toxicon 1991, 29, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, S.; Sato, Y.; Nakaya, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Enomoto, A.; Kaminogawa, S.; Yamauchi, K. Monoclonal antibody raised against tetrodonic acid, a derivative of tetrodotoxin. Toxicon 1989, 27, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukiya, S.; Matsumura, K. Active and passive immunization for tetrodotoxin in mice. Toxicon 1992, 30, 1631–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K. In vivo neutralization of tetrodotoxin by a monoclonal antibody. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1239–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.H.; Wei, C.H.; Huang, K.; Rong, K.T. Toxin-neutralizing effect and activity-quality relationship for mice tetrodotoxin-specific polyclonal antibodies. Toxicology 2005, 206, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qinhui, X.U.; Wei, C.; Huang, K.K. An experimental vaccine against tetrodotoxin with longer term of validity. Chin. J. Immunol. 1985, 12, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill, R.T.; Fenical William, W. Pharmaceuticals from marine natural products: Surge or ebb? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichota, A.; Gwozdzinski, K. Anticancer activity of natural compounds from plant and marine environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Drugs and Drug Candidates from Marine Sources: An Assessment of the Current “State of Play”. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Schwarzenberg, K.; Vollmar, A.M. Targeting apoptosis pathways by natural compounds in cancer: Marine compounds as lead structures and chemical tools for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saoudi, M.; Abdelmouleh, A.; El Feki, A. Tetrodotoxin: A potent marine toxin. Toxin Rev. 2010, 29, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narahashi, T. Mechanism of action of tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin on excitable membranes. Fed. Proc. 1972, 31, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Omana-Zapata, I.; Khabbaz, M.A.; Hunter, J.C.; Clarke, D.E.; Bley, K.R. Tetrodotoxin inhibits neuropathic ectopic activity in neuromas, dorsal root ganglia and dorsal horn neurons. Pain 1997, 72, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moczydlowski, E.G. The molecular mystique of tetrodotoxin. Toxicon 2013, 63, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldlust, S.A.; Kavoosi, M.; Nezzer, J.; Kavoosi, M.; Korz, W.; Deck, K. Tetrodotoxin for Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Dose Finding Trial. Toxins 2021, 13, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, N.A.; Cantin, L.; Constant, J.; Haller, T.; Blaise, G.; Ong-Lam, M.; Du Souich, P.; Korz, W.; Lapointe, B. Tetrodotoxin for Moderate to Severe Cancer-Related Pain: A Multicentre, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Design Trial. Pain Res. Manag. 2017, 2017, 7212713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, N.A.; du Souich, P.; Lapointe, B.; Ong-Lam, M.; Dubuc, B.; Walde, D.; Love, R.; Ngoc, A.H. Tetrodotoxin for Moderate to Severe Cancer Pain: A Randomized, Double Blind, Parallel Design Multicenter Study. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2008, 35, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, N.A.; Lapointe, B.; Ong-Lam, M.; Dubuc, B.; Walde, D.; Gagnon, B.; Love, R.; Goel, R.; Hawley, P.; Ngoc, A.H.; et al. A multicentre open-label safety and efficacy study of tetrodotoxin for cancer pain. Curr. Oncol. 2011, 18, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campos-Ríos, A.; Rueda-Ruzafa, L.; Herrera-Pérez, S.; Rivas-Ramírez, P.; Lamas, J.A. Tetrodotoxin: A new strategy to treat visceral pain? Toxins 2021, 13, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, N.A.; Fisher, K.M.; Lapointe, B.; du Souich, P.; Chary, S.; Moulin, D.; Sellers, E.; Ngoc, A.H. An Open-Label, Multi-Dose Efficacy and Safety Study of Intramuscular Tetrodotoxin in Patients with Severe Cancer-Related Pain. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2007, 34, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, A.; de Henestrosa, A.R.F.; Marín, A.P.; Ho, A.; Borroto, J.I.G.; Carasa, I.; Pritchard, L. Evaluation of the genotoxic potential of the natural neurotoxin Tetrodotoxin (TTX) in a battery of in vitro and in vivo genotoxicity assays. Mutat. Res.-Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2007, 634, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, T.T.; Wang, X.; Epstein, D.H.; Zhao, L.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Lu, L. Tetrodotoxin reduces cue-induced drug craving and anxiety in abstinent heroin addicts. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2009, 92, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; li, J.; Lu, C.L.; Kang, L.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhou, X.B.; Zhong, S. Tetrodotoxin alleviates acute heroin withdrawal syndrome: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011, 38, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Q.; Ren, L.M.; Huang, Z.Q. Effects of tetrodotoxin on naloxone-precipitated withdrawal syndrome in morphine-dependent rats and mice. Chin. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001, 15, 434–440. [Google Scholar]
- Nieto, F.R.; Entrena, J.M.; Cendán, C.M.; Del Pozo, E.; Vela, J.M.; Baeyens, J.M. Tetrodotoxin inhibits the development and expression of neuropathic pain induced by paclitaxel in mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2008, 18, S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcil, J.; Walczak, J.S.; Guindon, J.; Ngoc, A.H.; Lu, S.; Beaulieu, P. Antinociceptive effects of tetrodotoxin (TTX) in rodents. Br. J. Anaesth. 2006, 96, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kayser, V.; Viguier, F.; Ioannidi, M.; Bernard, J.F.; Latrémolière, A.; Michot, B.; Vela, J.M.; Buschmann, H.; Hamon, M.; Bourgoin, S. Differential anti-neuropathic pain effects of tetrodotoxin in sciatic nerve-versus infraorbital nerve-ligated rats—Behavioral, pharmacological and immunohistochemical investigations. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, P.; Levine, J.D. Antihyperalgesic effect of tetrodotoxin in rat models of persistent muscle pain. Neuroscience 2015, 311, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González-Cano, R.; Tejada, M.Á.; Artacho-Cordón, A.; Nieto, F.R.; Entrena, J.M.; Wood, J.N.; Cendán, C.M. Effects of tetrodotoxin in mouse models of visceral pain. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salas, M.M.; McIntyre, M.K.; Petz, L.N.; Korz, W.; Wong, D.; Clifford, J.L. Tetrodotoxin suppresses thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in a rat full thickness thermal injury pain model. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 607, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, H.J.; Blair, M.R.; Takman, B.H. The local anesthetic activity of saxitoxin alone and with vasoconstrictor and local anesthetic agents. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1976, 224, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Chorny, M.; Levy, R.J. Site-specific analgesia with sustained release liposomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6891–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shankarappa, S.A.; Tsui, J.H.; Kim, K.N.; Reznor, G.; Dohlman, J.C.; Langer, R.; Kohane, D.S. Prolonged nerve blockade delays the onset of neuropathic pain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17555–17560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zepeda, R.J.; Candiracci, M.; Lobos, N.; Lux, S.; Miranda, H.F. Chronic Toxicity Study of Neosaxitoxin in Rats. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5055–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-NaVarro, A.J.; Lagos, N.; Lagos, M.; Braghetto, I.; Csendes, A.; Hamilton, J.; Figueroa, C.; Truan, D.; Garcia, C.; Rojas, A. Neosaxitoxin as a local anesthetic: Preliminary observations from a first human trial. Anesthesiology 2007, 106, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manriquez, V.; Castro Caperan, D.; Guzman, R.; Naser, M.; Iglesia, V.; Lagos, N. First evidence of neosaxitoxin as a long-acting pain blocker in bladder pain syndrome. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2015, 26, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohane, D.S.; Yieh, J.; Lu, N.T.; Langer, R.; Strichartz, G.R.; Berde, C.B. A re-examination of tetrodotoxin for prolonged duration local anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1998, 89, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padera, R.F.; Tse, J.Y.; Bellas, E.; Kohane, D.S. Tetrodotoxin for prolonged local anesthesia with minimal myotoxicity. Muscle Nerve 2006, 34, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohane, D.S.; Smith, S.E.; Louis, D.N.; Colombo, G.; Ghoroghchian, P.; Hunfeld, N.G.M.; Berde, C.B.; Langer, R. Prolonged duration local anesthesia from tetrodotoxin-enhanced local anesthetic microspheres. Pain 2003, 104, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, A.; Santamaria, C.M.; Shomorony, A.; Ji, T.; Wei, T.; Gordon, A.; Elofsson, H.; Mehta, M.; Yang, R.; et al. Polymer-tetrodotoxin conjugates to induce prolonged duration local anesthesia with minimal toxicity. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berde, C.B.; Athiraman, U.; Yahalom, B.; Zurakowski, D.; Corfas, G.; Bognet, C. Tetrodotoxin-bupivacaine-epinephrine combinations for prolonged local anesthesia. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2717–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, D.M.; Fields, H.L.; Duncan, K.G.; Duncan, J.L.; Jones, M.R. Experimental study of tetrodotoxin, a long-acting topical anesthetic. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 125, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.M.; Duncan, K.G.; Duncan, J.L. Experimental use of tetrodotoxin for corneal pain after excimer laser keratectomy. Cornea 1998, 17, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.G.; Alvarez, P.; Levine, J.D. Topical Tetrodotoxin Attenuates Photophobia Induced by Corneal Injury in the Rat. J. Pain 2015, 16, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Kogure, K.; Hara, H.; Ban, H.; Akaike, N. The possible involvement of tetrodotoxin-sensitive ion channels in ischemic neuronal damage in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 1991, 121, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysko, P.G.; Webb, C.L.; Yue, T.L.; Gu, J.L.; Feuerstein, G. Neuroprotective effects of tetrodotoxin as a na+ channel modulator and glutamate release inhibitor in cultured rat cerebellar neurons and in gerbil global brain ischemia. Stroke 1994, 25, 2476–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, L.J.; Teng, Y.D.; Wrathall, J.R. Effects of the sodium channel blocker tetrodotoxin on acute white matter pathology after experimental contusive spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 6122–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.D.; Wrathall, J.R. Local blockade of sodium channels by tetrodotoxin ameliorates tissue loss and long-term functional deficits resulting from experimental spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 4359–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsch, R.M.; Farber, S.A.; Growdon, J.H.; Wurtman, R.J. Release of amyloid β-protein precursor derivatives by electrical depolarization of rat hippocampal slices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5191–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burack, M.A.; Stasheff, S.F.; Wilson, W.A. Selective suppression of in vitro electrographic seizures by low-dose tetrodotoxin: A novel anticonvulsant effect. Epilepsy Res. 1995, 22, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, K.D.; Prince, D.A. Tetrodotoxin prevents posttraumatic epileptogenesis in rats. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 46, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, C.; Takahashi, M.; Kondoh, Y.; Tashiro, H.; Tashiro, T. Identification of synaptic activity-dependent genes by exposure of cultured cortical neurons to tetrodotoxin followed by its withdrawal. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 2385–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Dayem, S.M.A.; Fouda, F.M.; Ali, E.H.A.; Motelp, B.A.A. El The antitumor effects of tetrodotoxin and/or doxorubicin on Ehrlich ascites carcinoma-bearing female mice. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 29, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouda, F.M. Anti-tumor activity of tetrodotoxin extracted from the Masked Puffer fish Arothron diadematus. Egypt. J. Biol. 2005, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, S.P.; Salvador, V.; Manning, E.A.; Mizal, J.; Altun, S.; Raza, M.; Berridge, R.J.; Djamgoz, M.B.A. Contribution of functional voltage-gated Na+ channel expression to cell behaviors involved in the metastatic cascade in rat prostate cancer: I. Lateral motility. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 195, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, S.P.; Ding, Y.; Liu, A.; Foster, C.S.; Djamgoz, M.B.A. Tetrodotoxin suppresses morphological enhancement of the metastatic MAT-LyLu rat prostate cancer cell line. Cell Tissue Res. 1999, 295, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavendra Prasad, H.S.; Qi, Z.; Srinivasan, K.N.; Gopalakrishnakone, P. Potential effects of tetrodotoxin exposure to human glial cells postulated using microarray approach. Toxicon 2004, 44, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragadeeswaran, S.; Therasa, D.; Prabhu, K.; Kathiresan, K. Biomedical and pharmacological potential of tetrodotoxin-producing bacteria isolated from marine pufferfish arothron hispidus (Muller, 1841). J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2010, 16, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Bian, Z. Biosynthetic Studies of Tetrodotoxin and Its Anticancer Activities Assessment In Vitro. Master’s Thesis, Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shomorony, A.; Santamaria, C.M.; Zhao, C.; Rwei, A.Y.; Mehta, M.; Zurakowski, D.; Kohane, D.S. Prolonged Duration Local Anesthesia by Combined Delivery of Capsaicin- A nd Tetrodotoxin-Loaded Liposomes. Anesth. Analg. 2019, 129, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Law, W.Y.; Asaruddin, M.R.; Bhawani, S.A.; Mohamad, S. Pharmacophore modelling of vanillin derivatives, favipiravir, chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, monolaurin and tetrodotoxin as MPro inhibitors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dandawate, P.R.; Subramaniam, D.; Anant, S. Targeting Cancer Stem Cells by Functional Foods and Their Constituents. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimes, J.A.; Djamgoz, M.B.A. Electrophysiological characterization of voltage-gated Na+ current expressed in the highly metastatic Mat-LyLu cell line of rat prostate cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 1998, 175, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.S.Y.; Fong, B.M.W.; Tsoi, Y.K. Analytical challenges: Determination of tetrodotoxin in human urine and plasma by LC-MS/MS. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2291–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverté, L.; Soliño, L.; Carnicer, O.; Diogène, J.; Campàs, M. Alternative methods for the detection of emerging marine toxins: Biosensors, biochemical assays and cell-based assays. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5719–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leonardo, S.; Toldrà, A.; Campàs, M. Trends and Prospects on Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of Marine Toxins. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2017, 78, 303–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campàs, M.; Alkassar, M.; Gaiani, G.; Leonardo, S.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Diogène, J. The wide spectrum of methods available to study marine neurotoxins. Mar. Neurotoxins 2021, 6, 275–315. [Google Scholar]
- Kogure, K.; Tamplin, M.L.; Simidu, U.; Colwell, R.R. A tissue culture assay for tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and related toxins. Toxicon 1988, 26, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallacher, S.; Birkbeck, T.H. A tissue culture assay for direct detection of sodium channel blocking toxins in bacterial culture supernates. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 92, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, K.; Kogure, K.; Ohwada, K. A biological method for the quantitative measurement of tetrodotoxin (TTX): Tissue culture bioassay in combination with a water-soluble tetrazolium salt. Toxicon 1996, 34, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, K.; Kogure, K.; Ohwada, K. An Improved Method of Tissue Culture Bioassay for Tetrodotoxin. Fish. Sci. 1996, 62, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiser, T. A novel toxicity-based assay for the identification of modulators of voltage-gated Na+ channels. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 137, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.K.; Molnar, P.; Hickman, J.J. Toxin detection based on action potential shape analysis using a realistic mathematical model of differentiated NG108-15 cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pancrazio, J.J.; Gray, S.A.; Shubin, Y.S.; Kulagina, N.; Cuttino, D.S.; Shaffer, K.M.; Eisemann, K.; Curran, A.; Zim, B.; Gross, G.W.; et al. A portable microelectrode array recording system incorporating cultured neuronal networks for neurotoxin detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 18, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkhkar, H.; Knaack, G.L.; Gnade, B.E.; Keefer, E.W.; Pancrazio, J.J. Development and demonstration of a disposable low-cost microelectrode array for cultured neuronal network recording. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, J.; Hendriksen, P.J.M.; van Kleef, R.G.D.M.; de Groot, A.; Bovee, T.F.H.; Rietjens, I.M.C.M.; Westerink, R.H.S. Detection of marine neurotoxins in food safety testing using a multielectrode array. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 2369–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Su, K.; Hu, L.; Zou, L.; Wang, T.; Zhuang, L.; Hu, N.; Wang, P. A novel and functional assay for pharmacological effects of marine toxins, saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin by cardiomyocyte-based impedance biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raybould, T.J.G.; Bignami, G.S.; Inouye, L.K.; Simpson, S.B.; Byrnes, J.B.; Grothaus, P.G.; Vann, D.C. A monoclonal antibody-based immunoassay for detecting tetrodotoxin in biological samples. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1992, 6, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawatsu, K.; Hamano, Y.; Yoda, T.; Terano, Y.; Shibata, T. Rapid and highly sensitive enzyme immunoassay for quantitative determination of tetrodotoxin. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1997, 50, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.S.; Pan, F.G.; Liu, Z.S.; Wang, Z. Identification of tetrodotoxin antigens and a monoclonal antibody. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Wei, W.J.; Nan, L.; Lei, L.H.; Hui, H.C.; Fen, G.X.; Jun, L.Y.; Jing, Z.; Rong, J. Development of competitive indirect ELISA for the detection of tetrodotoxin and a survey of the distribution of tetrodotoxin in the tissues of wild puffer fish in the waters of south-east China. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2010, 27, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, A.N.; Williams, B.L.; French, S.S. An improved competitive inhibition enzymatic immunoassay method for tetrodotoxin quantification. Biol. Proced. Online 2012, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neagu, D.; Micheli, L.; Palleschi, G. Study of a toxin-alkaline phosphatase conjugate for the development of an immunosensor for tetrodotoxin determination. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambla-Alegre, M.; Leonardo, S.; Barguil, Y.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.T.; Maillaud, C.; Boundy, M.J.; Harwood, D.T.; et al. Rapid screening and multi-toxin profile confirmation of tetrodotoxins and analogues in human body fluids derived from a puffer fish poisoning incident in New Caledonia. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 112, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reverté, L.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Leonardo, S.; Bellés, C.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.T.; Gerssen, A.; Klijnstra, M.D.; Diogène, J.; Campàs, M. Development and validation of a maleimide-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of tetrodotoxin in oysters and mussels. Talanta 2018, 176, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Takaishi, S.; Yasumoto, K.; Watabe, S. Novel polyclonal antibody raised against tetrodotoxin using its haptenic antigen prepared from 4,9-anhydrotetrodotoxin reacted with 1,2-ethaneditiol and further reacted with keyhole limpet hemocyanin. Toxins 2019, 11, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vlasenko, A.E.; Kuznetsov, V.G.; Petrova, I.Y.; Magarlamov, T.Y. Development of a polyclonal antibody-based indirect competitive ELISA for the determination of tetrodotoxins in marine ribbon worms (NEMERTEA) and its comparison with high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2020, 176, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.D.; Ladd, J.; Etheridge, S.; Deeds, J.; Hall, S.; Jiang, S. Quantitative detection of tetrodotoxin (TTX) by a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 130, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.; Barnes, P.; Haughey, S.A.; Higgins, C.; Kawatsu, K.; Vasconcelos, V.; Elliott, C.T. Development and single laboratory validation of an optical biosensor assay for tetrodotoxin detection as a tool to combat emerging risks in European seafood Rapid Detection in Food and Feed. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7753–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.D.; Vaisocherová, H.; Deeds, J.; DeGrasse, S.; Jiang, S. Tetrodotoxin detection by a surface plasmon resonance sensor in pufferfish matrices and urine. J. Sens. 2011, 2011, 601704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaisocherová, H.; Taylor, A.D.; Jiang, S.; Hegnerová, K.; Vala, M.; Homola, J.; Yakes, B.J.; Deeds, J.; Degrasse, S. Surface plasmon resonance biosensor for determination of tetrodotoxin: Prevalidation study. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakes, B.J.; Deeds, J.; White, K.; DeGrasse, S.L. Evaluation of surface plasmon resonance biosensors for detection of tetrodotoxin in food matrices and comparison to analytical methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yakes, B.J.; Kanyuck, K.M.; DeGrasse, S.L. First report of a direct surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for a small molecule seafood toxin. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9251–9255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverté, L.; Campàs, M.; Yakes, B.J.; Deeds, J.R.; Katikou, P.; Kawatsu, K.; Lochhead, M.; Elliott, C.T.; Campbell, K. Tetrodotoxin detection in puffer fish by a sensitive planar waveguide immunosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 253, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kreuzer, M.P.; Pravda, M.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; Guilbault, G.G. Novel electrochemical immunosensors for seafood toxin analysis. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverté, L.; Campbell, K.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Elliott, C.T.; Diogène, J.; Campàs, M. Immunosensor array platforms based on self-assembled dithiols for the electrochemical detection of tetrodotoxins in puffer fish. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 989, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campàs, M.; Reverté, J.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Campbell, K.; Gerssen, A.; Diogène, J. A fast magnetic bead-based colorimetric immunoassay for the detection of tetrodotoxins in shellfish. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 140, 111315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardo, S.; Kiparissis, S.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Almarza, S.; Roque, A.; Andree, K.B.; Christidis, A.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Campbell, K.; et al. Detection of tetrodotoxins in juvenile pufferfish Lagocephalus sceleratus (Gmelin, 1789) from the North Aegean Sea (Greece) by an electrochemical magnetic bead-based immunosensing tool. Food Chem. 2019, 290, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, S.; Ren, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, F.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Gold nanoparticle probe-based immunoassay as a new tool for tetrodotoxin detection in puffer fish tissues. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 146, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thattiyaphong, A.; Unahalekhaka, J.; Mekha, N.; Nispa, W.; Kluengklangdon, P.; Rojanapantip, L. Efficiency of a rapid test for detection of tetrodotoxin in puffer fish. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2014, 35, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Kuang, H.; Xu, L.; Xu, C. A gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of tetrodotoxin. Analyst 2020, 145, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Xu, F.; Xiao, M.; Fu, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, C.; Tang, Y. A new lateral-flow immunochromatographic strip combined with quantum dot nanobeads and gold nanoflowers for rapid detection of tetrodotoxin. Analyst 2017, 142, 4393–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Gao, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, W.; Miao, T.; Peng, J. Screening and Structure Analysis of the Aptamer Against Tetrodotoxin. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Fomo, G.; Waryo, T.T.; Sunday, C.E.; Baleg, A.A.; Baker, P.G.; Iwuoha, E.I. Aptameric recognition-modulated electroactivity of poly(4-styrenesolfonic acid)-doped polyaniline films for single-shot detection of tetrodotoxin. Sensors 2015, 15, 22547–22560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, Y.; Qin, G.; Wei, Y.; Dong, C.; Wang, L. Highly sensitive analysis of tetrodotoxin based on free-label fluorescence aptamer sensing system. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Qin, G.; Wei, Y.; Wang, L.; Dong, C. Exonuclease I-assisted fluorescence aptasensor for tetrodotoxin. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 194, 110417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Duan, N.; Xia, Y.; Hun, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Magnetic Separation-Based Multiple SELEX for Effectively Selecting Aptamers against Saxitoxin, Domoic Acid, and Tetrodotoxin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9801–9809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Wang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, L.; Bai, J.; Peng, Y.; Ning, B.; Gao, Z.; et al. Development of a highly sensitive detection method for TTX based on a magnetic bead-aptamer competition system under triple cycle amplification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1119, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkembi, X.; Skouridou, V.; Svobodova, M.; Leonardo, S.; Bashammakh, A.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; Campàs, M.; O′Sullivan, C.K. Hybrid Antibody–Aptamer Assay for Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Pufferfish. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 14810–14819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Nakamura, M.; Oshima, Y.; Takahata, J. Construction of a Continuous Tetrodotoxin Analyzer. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1982, 48, 1481–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasumoto, T.; Michishita, T. Fluorometric Determination of Tetrodotoxin by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1985, 49, 3077–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu, M.; Endo, A.; Yasumoto, T. An Improved Tetrodotoxin Analyzer. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 893–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Mebs, D.; Yasumoto, T. Tetrodotoxin and its analogues in extracts from the toad Atelopus oxyrhynchus (family: Bufonidae). Toxicon 1992, 30, 1489–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebs, D.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Lötters, S.; Schlüter, A. Further report of the occurrence of tetrodotoxin in Atelopus species (family: Bufonidae). Toxicon 1995, 33, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Mebs, D. Occurrence of 11-oxotetrodotoxin in the red-spotted newt, Notophthalmus viridescens, and further studies on the levels of tetrodotoxin and its analogues in the newt’s efts. Toxicon 2003, 41, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Gilhen, J.; Russell, R.W.; Krysko, K.L.; Melaun, C.; Kurz, A.; Kauferstein, S.; Kordis, D.; Mebs, D. Variability of tetrodotoxin and of its analogues in the red-spotted newt, Notophthalmus viridescens (Amphibia: Urodela: Salamandridae). Toxicon 2012, 59, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, Y.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Miyazawa, T.; Yasumoto, T. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of tetrodotoxin and its analogs: Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry, tandem mass spectrometry, and liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 290, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Shimizu, N.; Nakazawa, H. Determination of tetrodotoxin in puffer-fish by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst 2002, 127, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.W.; Liu, H.X.; Jin, Y.B.; Li, S.F.; Bi, X.; Chung, S.; Zhang, S.S.; Jiang, Y.Y. Separation, identification and quantification of tetrodotoxin and its analogs by LC-MS without calibration of individual analogs. Toxicon 2011, 57, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Jang, J.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of tetrodotoxin and its analogs. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 352, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsu-Yamashita, M.; Jang, J.H.; Cho, Y.; Konoki, K. Optimization of simultaneous analysis of tetrodotoxin, 4-epitetrodotoxin, 4,9-anhydrotetrodotoxin, and 5,6,11-trideoxytetrodotoxin by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Forensic Toxicol. 2011, 29, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Distribution of tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin, and their analogs among tissues of the puffer fish Fugu pardalis. Toxicon 2006, 48, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, M.; Christian, B.; Ahmed, M.S.; Luckas, B. Determination of tetrodotoxin and its analogs in the puffer fish Takifugu oblongus from Bangladesh by hydrophilic interaction chromatography and mass-spectrometric detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 1997–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. LC/MS analysis of tetrodotoxin and its deoxy analogs in the marine puffer fish Fugu niphobles from the southern coast of Korea, and in the brackishwater puffer fishes Tetraodon nigroviridis and Tetraodon biocellatus from Southeast Asia. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.J.; Yu, R.C.; Luo, X.; Zhou, M.J.; Lin, X.T. Toxin-screening and identification of bacteria isolated from highly toxic marine gastropod Nassarius semiplicatus. Toxicon 2008, 52, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jen, H.C.; Anh-Tuyet Nguyen, T.; Wu, Y.J.; Hoang, T.; Arakawa, O.; Lin, W.F.; Hwang, D.F. Tetrodotoxin and paralytic shellfish poisons in gastropod species from Vietnam analyzed by highperformance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bane, V.; Hutchinson, S.; Sheehan, A.; Brosnan, B.; Barnes, P.; Lehane, M.; Furey, A. LC-MS/MS method for the determination of tetrodotoxin (TTX) on a triple quadruple mass spectrometer. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2016, 33, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yu, C.; Tam, S.; Hoi-Fu Yu, P. Rapid screening of tetrodotoxin in urine and plasma of patients with puffer fish poisoning by HPLC with creatinine correction. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2010, 27, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, K.; Yamanouchi, K. A rapid method for tetrodotoxin (TTX) determination by LC-MS/MS from small volumes of human serum, and confirmation of pufferfish poisoning by TTX monitoring. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A Chem. Anal. Control. Expo. Risk Assess. 2015, 32, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Hsieh, C.H.; Hwang, D.F. Development of standardized methodology for identifying toxins in clinical samples and fish species associated with tetrodotoxin-borne poisoning incidents. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boundy, M.J.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T.; McNabb, P.S.; Turner, A.D. Development of a sensitive and selective liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for high throughput analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins using graphitised carbon solid phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1387, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patria, F.P.; Pekar, H.; Zuberovic-Muratovic, A. Multi-toxin quantitative analysis of paralytic shellfish toxins and tetrodotoxins in bivalve mollusks with ultra-performance hydrophilic interaction LC-MS/MS-An in-house validation study. Toxins 2020, 12, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Dhanji-Rapkova, M.; Fong, S.Y.T.; Hungerford, J.; McNabb, P.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Harwood, D.T. Ultrahigh-Performance Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry Method for the Determination of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Tetrodotoxin in Mussels, Oysters, Clams, Cockles, and Scallops: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2020, 103, 533–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, N. Simultaneous determination of ten paralytic shellfish toxins and tetrodotoxin in scallop and short-necked clam by ion-pair solid-phase extraction and hydrophilic interaction chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1651, 462328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boente-Juncal, A.; Vale, C.; Cifuentes, M.; Otero, P.; Camiña, M.; Rodriguez-Vieytes, M.; Botana, L.M. Chronic In Vivo Effects of Repeated Exposure to Low Oral Doses of Tetrodotoxin: Preliminary Evidence of Nephrotoxicity and Cardiotoxicity. Toxins 2019, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boente-Juncal, A.; Otero, P.; Rodríguez, I.; Camiña, M.; Rodriguez-Vieytes, M.; Vale, C.; Botana, L.M. Oral Chronic Toxicity of the Safe Tetrodotoxin Dose Proposed by the European Food Safety Authority and Its Additive Effect with Saxitoxin. Toxins 2020, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katikou, P.; Gokbulut, C.; Kosker, A.R.; Campàs, M.; Ozogul, F. An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20010047
Katikou P, Gokbulut C, Kosker AR, Campàs M, Ozogul F. An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(1):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20010047
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatikou, Panagiota, Cengiz Gokbulut, Ali Rıza Kosker, Mònica Campàs, and Fatih Ozogul. 2022. "An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities" Marine Drugs 20, no. 1: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20010047
APA StyleKatikou, P., Gokbulut, C., Kosker, A. R., Campàs, M., & Ozogul, F. (2022). An Updated Review of Tetrodotoxin and Its Peculiarities. Marine Drugs, 20(1), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20010047