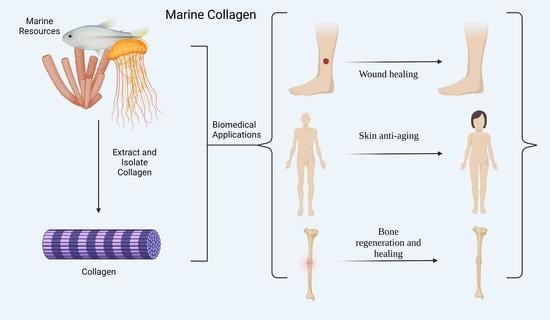
Marine Collagen: A Promising Biomaterial for Wound Healing, Skin Anti-Aging, and Bone Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Collagen Application in Wound Healing and Anti-Aging
3. The Potential Role of Collagen in Bone and Cartilage Regeneration
4. Advantages and Limitations Associated with Marine Collagen Use
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, M.A. Collagen of Extracellular Matrix from Marine Invertebrates and Its Medical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Pascual, F.; Slatter, D.A. Collagen Cross-Linking: Insights on the Evolution of Metazoan Extracellular Matrix. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frantz, C.; Stewart, K.M.; Weaver, V.M. The Extracellular Matrix at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 4195–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Y.; Bharadwaj, S.; Hammam, N.; Carnagey, K.; Myers, R.; Atala, A.; Van Dyke, M. Tissue-Specific Extracellular Matrix Coatings for the Promotion of Cell Proliferation and Maintenance of Cell Phenotype. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4021–4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, C.; Goldbeter, A. The Balance between Cell Cycle Arrest and Cell Proliferation: Control by the Extracellular Matrix and by Contact Inhibition. Interface Focus 2014, 4, 20130075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Townsend, S.E.; Gannon, M. Extracellular Matrix–Associated Factors Play Critical Roles in Regulating Pancreatic β-Cell Proliferation and Survival. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahn, M.S.; Kobler, J.B.; Zeitels, S.M.; Langer, R. Quantitative and Comparative Studies of the Vocal Fold Extracellular Matrix II: Collagen. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2006, 115, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, H.L. Extracellular Matrix and Ageing. In Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Ageing: Part I Biomedical Science; Harris, J.R., Korolchuk, V.I., Eds.; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 90, pp. 169–190. ISBN 9789811328343. [Google Scholar]
- Gelse, K. Collagens—Structure, Function, and Biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorushanova, A.; Delgado, L.M.; Wu, Z.; Shologu, N.; Kshirsagar, A.; Raghunath, R.; Mullen, A.M.; Bayon, Y.; Pandit, A.; Raghunath, M.; et al. The Collagen Suprafamily: From Biosynthesis to Advanced Biomaterial Development. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1801651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whelan, A.; Duffy, J.; Gaul, R.T.; O’Reilly, D.; Nolan, D.R.; Gunning, P.; Lally, C.; Murphy, B.P. Collagen Fibre Orientation and Dispersion Govern Ultimate Tensile Strength, Stiffness and the Fatigue Performance of Bovine Pericardium. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 90, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguez, P.A.; Pereira, P.N.R.; Atsawasuwan, P.; Yamauchi, M. Collagen Cross-Linking and Ultimate Tensile Strength in Dentin. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 807–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raz, P.; Brosh, T.; Ronen, G.; Tal, H. Tensile Properties of Three Selected Collagen Membranes. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5163603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, K.L.; Sebastianelli, W.; Flechsenhar, K.R.; Aukermann, D.F.; Meza, F.; Millard, R.L.; Deitch, J.R.; Sherbondy, P.S.; Albert, A. 24-Week Study on the Use of Collagen Hydrolysate as a Dietary Supplement in Athletes with Activity-Related Joint Pain. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2008, 24, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdzieblik, D.; Oesser, S.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. Improvement of Activity-Related Knee Joint Discomfort Following Supplementation of Specific Collagen Peptides. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, D.F.; Lu, Y.; Starborg, T.; Kadler, K.E. Collagen Fibril Assembly and Function. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 130, pp. 107–142. ISBN 978-0-12-809802-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wess, T.J. Collagen Fibril Form and Function. In Advances in Protein Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 70, pp. 341–374. ISBN 978-0-12-034270-9. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Mh Busra, M.F.; Lokanathan, Y.; Ng, M.H.; Law, J.X.; Cletus, U.C.; Binti Haji Idrus, R. Collagen Type I: A Versatile Biomaterial. In Novel Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine; Chun, H.J., Park, K., Kim, C.-H., Khang, G., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 1077, pp. 389–414. ISBN 9789811309465. [Google Scholar]
- Kisling, A.; Lust, R.M.; Katwa, L.C. What Is the Role of Peptide Fragments of Collagen I and IV in Health and Disease? Life Sci. 2019, 228, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, L.; Morar, P.; Wang, Y.; Henriksen, K.; Sun, S.; Karsdal, M.; Smith, R.; Nagamani, S.C.S.; Shapiro, J.; Lee, B.; et al. Alterations in Non-Type I Collagen Biomarkers in Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Bone 2019, 120, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, C.; Rusconi, F.; Pulaj, A.; Macchi, R.; Landini, P.; Paroni, M.; Colombo, G.; Martinello, T.; Melotti, L.; Gomiero, C.; et al. From Food Waste to Innovative Biomaterial: Sea Urchin-Derived Collagen for Applications in Skin Regenerative Medicine. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhan, F.; Ikram, M.; Shehzad, A.; Ghafoor, A. Marine Collagen: An Emerging Player in Biomedical Applications. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4703–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benayahu, D.; Pomeraniec, L.; Shemesh, S.; Heller, S.; Rosenthal, Y.; Rath-Wolfson, L.; Benayahu, Y. Biocompatibility of a Marine Collagen-Based Scaffold In Vitro and In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Yeon Kim, S.; Chun, T.; Byun, H.-J.; Lee, Y.M. Collagen Scaffolds Derived from a Marine Source and Their Biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudko, S.P.; Sasaki, T.; Engel, J.; Lerch, T.F.; Nix, J.; Chapman, M.S.; Bächinger, H.P. Crystal Structure of Human Collagen XVIII Trimerization Domain: A Novel Collagen Trimerization Fold. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 392, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boudko, S.P.; Engel, J.; Bächinger, H.P. The Crucial Role of Trimerization Domains in Collagen Folding. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, H.; Yunoki, S.; Kondo, E.; Ikoma, T.; Tanaka, J.; Yasuda, K. In Vivo Biological Responses and Bioresorption of Tilapia Scale Collagen as a Potential Biomaterial. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2009, 20, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Shao, Z.; Li, C.; Yu, L.; Raja, M.A.; Liu, C. Isolation, Characterization and Evaluation of Collagen from Jellyfish Rhopilema Esculentum Kishinouye for Use in Hemostatic Applications. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widdowson, J.P.; Picton, A.J.; Vince, V.; Wright, C.J.; Mearns-Spragg, A. In Vivo Comparison of Jellyfish and Bovine Collagen Sponges as Prototype Medical Devices: In Vivo comparison of jellyfish and bovine collagen sponges. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coppola, D.; Oliviero, M.; Vitale, G.A.; Lauritano, C.; D’Ambra, I.; Iannace, S.; de Pascale, D. Marine Collagen from Alternative and Sustainable Sources: Extraction, Processing and Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silvipriya, K.; Kumar, K.; Bhat, A.; Kumar, B.; John, A.; Lakshmanan, P. Collagen: Animal Sources and Biomedical Application. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shavandi, A.; Hou, Y.; Carne, A.; McConnell, M.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A. Marine Waste Utilization as a Source of Functional and Health Compounds. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 87, 187–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Shavandi, A.; Carne, A.; Bekhit, A.A.; Ng, T.B.; Cheung, R.C.F.; Bekhit, A.E.A. Marine Shells: Potential Opportunities for Extraction of Functional and Health-Promoting Materials. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 1047–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Gelatin Alternatives for the Food Industry: Recent Developments, Challenges and Prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish Gelatin: Properties, Challenges, and Prospects as an Alternative to Mammalian Gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Ikeda, T.; Yanagiguchi, K.; Hayashi, Y. Potency of Fish Collagen as a Scaffold for Regenerative Medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 302932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, N.; Xue, Y.; Ding, T.; Liu, X.; Mo, X.; Sun, J. Electrospun Tilapia Collagen Nanofibers Accelerating Wound Healing via Inducing Keratinocytes Proliferation and Differentiation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath Kumar, N.S.; Nazeer, R.A.; Jaiganesh, R. Wound Healing Properties of Collagen from the Bone of Two Marine Fishes. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2012, 18, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.; Agwa, M.; Saeed, H.; Khedr, S.M.; Morsy, O.; El-Demellawy, M.A. Fish Scale Collagen Preparation, Characterization and Its Application in Wound Healing. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, X.; Li, F.; Guo, S.; Yang, J. Preparation of Aminated Fish Scale Collagen and Oxidized Sodium Alginate Hybrid Hydrogel for Enhanced Full-Thickness Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, P.; Srivas, P.K.; Dadhich, P.; Das, B.; Maity, P.P.; Moulik, D.; Dhara, S. Accelerating Full Thickness Wound Healing Using Collagen Sponge of Mrigal Fish (Cirrhinus Cirrhosus) Scale Origin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Liang, R.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Oral Administration of Marine Collagen Peptides Prepared from Chum Salmon (Oncorhynchus Keta) Improves Wound Healing Following Cesarean Section in Rats. Food Nutr. Res. 2015, 59, 26411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Dai, X.; Li, Y. Oral Administration of Marine Collagen Peptides from Chum Salmon Skin Enhances Cutaneous Wound Healing and Angiogenesis in Rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2173–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Elango, J.; Bao, B.; Dong, J.; Liu, N.; Wu, W. Fish Collagen Surgical Compress Repairing Characteristics on Wound Healing Process In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, N.; Seki, S.; Ueda, F. Effects of Composite Supplement Containing Collagen Peptide and Ornithine on Skin Conditions and Plasma IGF-1 Levels—A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Luca, C.; Mikhal’chik, E.V.; Suprun, M.V.; Papacharalambous, M.; Truhanov, A.I.; Korkina, L.G. Skin Antiageing and Systemic Redox Effects of Supplementation with Marine Collagen Peptides and Plant-Derived Antioxidants: A Single-Blind Case-Control Clinical Study. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4389410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allouche, M.; Hamdi, I.; Nasri, A.; Harrath, A.H.; Mansour, L.; Beyrem, H.; Boufahja, F. Laboratory Bioassay Exploring the Effects of Anti-Aging Skincare Products on Free-Living Marine Nematodes: A Case Study of Collagen. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11403–11412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.-R.; Kim, Y.-M.; Lee, M.-K.; Kim, I.-H.; Choi, Y.-H.; Nam, T.-J. Pyropia Yezoensis Peptide Promotes Collagen Synthesis by Activating the TGF-β/Smad Signaling Pathway in the Human Dermal Fibroblast Cell Line Hs27. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nomura, Y.; Oohashi, K.; Watanabe, M.; Kasugai, S. Increase in Bone Mineral Density through Oral Administration of Shark Gelatin to Ovariectomized Rats. Nutrition 2005, 21, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sun, J. Potential Application of Hydrolyzed Fish Collagen for Inducing the Multidirectional Differentiation of Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Nagaoka, H.; Terajima, M.; Tsuda, N.; Hayashi, Y.; Yamauchi, M. Effects of Fish Collagen Peptides on Collagen Post-Translational Modifications and Mineralization in an Osteoblastic Cell Culture System. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elango, J.; Robinson, J.; Zhang, J.; Bao, B.; Ma, N.; de Val, J.E.M.S.; Wu, W. Collagen Peptide Upregulates Osteoblastogenesis from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells through MAPK- Runx2. Cells 2019, 8, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capati, M.L.F.; Nakazono, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Sugimoto, K.; Yanagiguchi, K.; Yamada, S.; Hayashi, Y. Fish Collagen Promotes the Expression of Genes Related to Osteoblastic Activity. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 5785819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, H.-H.; Uemura, T.; Yamaguchi, I.; Ikoma, T.; Tanaka, J. Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Fish Scale Collagen. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 122, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, B.; Contentin, R.; Cassé, F.; Maspimby, C.; Oddoux, S.; Noël, A.; Legendre, F.; Gruchy, N.; Galéra, P. Marine Collagen Hydrolysates Downregulate the Synthesis of Pro-Catabolic and Pro-Inflammatory Markers of Osteoarthritis and Favor Collagen Production and Metabolic Activity in Equine Articular Chondrocyte Organoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanpain, C.; Fuchs, E. Epidermal Homeostasis: A Balancing Act of Stem Cells in the Skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elias, P.M. The Skin Barrier as an Innate Immune Element. Semin. Immunopathol. 2007, 29, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, J.; Schröder, J.-M.; Gläser, R. The Skin Surface as Antimicrobial Barrier: Present Concepts and Future Outlooks. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakespeare, P.G. The Role of Skin Substitutes in the Treatment of Burn Injuries. Clin. Dermatol. 2005, 23, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.H.; Mathieu, L.; Maibach, H.I. Acute Chemical Skin Injuries in the United States: A Review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2018, 48, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerutti, C.; Ridley, A.J. Endothelial Cell-Cell Adhesion and Signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 358, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Shuvaev, V.V.; Muzykantov, V.R. Catalase and Superoxide Dismutase Conjugated with Platelet-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule Antibody Distinctly Alleviate Abnormal Endothelial Permeability Caused by Exogenous Reactive Oxygen Species and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Hong, P. Marine Collagen Peptides from the Skin of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus): Characterization and Wound Healing Evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-López, A.; Morales-Peñaloza, A.; Martínez-Juárez, V.M.; Vargas-Torres, A.; Zeugolis, D.I.; Aguirre-Álvarez, G. Hydrolyzed Collagen—Sources and Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, K.; Li, B.; Hou, H. Effects of Oral Administration of Peptides with Low Molecular Weight from Alaska Pollock (Theragra Chalcogramma) on Cutaneous Wound Healing. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzolini, M.; Millo, E.; Oliveri, C.; Mirata, S.; Salis, A.; Damonte, G.; Arkel, M.; Scarfì, S. Elicited ROS Scavenging Activity, Photoprotective, and Wound-Healing Properties of Collagen-Derived Peptides from the Marine Sponge Chondrosia Reniformis. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felician, F.F.; Yu, R.-H.; Li, M.-Z.; Li, C.-J.; Chen, H.-Q.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, T.; Qi, W.-Y.; Xu, H.-M. The Wound Healing Potential of Collagen Peptides Derived from the Jellyfish Rhopilema Esculentum. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2019, 22, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veeruraj, A.; Liu, L.; Zheng, J.; Wu, J.; Arumugam, M. Evaluation of Astaxanthin Incorporated Collagen Film Developed from the Outer Skin Waste of Squid Doryteuthis Singhalensis for Wound Healing and Tissue Regenerative Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 95, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melotti, L.; Martinello, T.; Perazzi, A.; Iacopetti, I.; Ferrario, C.; Sugni, M.; Sacchetto, R.; Patruno, M. A Prototype Skin Substitute, Made of Recycled Marine Collagen, Improves the Skin Regeneration of Sheep. Animals 2021, 11, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Characteristics of the Aging Skin. Adv. Wound Care 2013, 2, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oxlund, H.; Manschot, J.; Viidik, A. The Role of Elastin in the Mechanical Properties of Skin. J. Biomech. 1988, 21, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, J.; Shezali, H.; Radzi, Z.; Yahya, N.A.; Abu Kassim, N.H.; Czernuszka, J.; Rahman, M.T. Molecular Mechanisms of Stress-Responsive Changes in Collagen and Elastin Networks in Skin. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 29, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varani, J.; Dame, M.K.; Rittie, L.; Fligiel, S.E.G.; Kang, S.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. Decreased Collagen Production in Chronologically Aged Skin. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mays, P.; Bishop, J.; Laurent, G. Age-Related Changes in the Proportion of Types I and III Collagen. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1988, 45, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelsma, E.; Hendriks, H.F.; Roza, L. Nutritional Skin Care: Health Effects of Micronutrients and Fatty Acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 73, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pullar, J.; Carr, A.; Vissers, M. The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben-Shabat, S.; Kazdan, Y.; Beit-Yannai, E.; Sintov, A.C. Use of Alpha-Tocopherol Esters for Topical Vitamin E Treatment: Evaluation of Their Skin Permeation and Metabolism. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiserman, A.; Koliada, A.; Zayachkivska, A.; Lushchak, O. Nanodelivery of Natural Antioxidants: An Anti-Aging Perspective. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, X.; Fu, Y. Mineral-Chelating Peptides Derived from Fish Collagen: Preparation, Bioactivity and Bioavailability. LWT 2020, 134, 110209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exposito, J.-Y.; Valcourt, U.; Cluzel, C.; Lethias, C. The Fibrillar Collagen Family. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, A.; Marques, A.; Martins, E.; Silva, T.; Reis, R. Cosmetic Potential of Marine Fish Skin Collagen. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, M.; Lewis, E.D.; Zakaria, N.; Pelipyagina, T.; Guthrie, N. A Randomized, Triple-blind, Placebo-controlled, Parallel Study to Evaluate the Efficacy of a Freshwater Marine Collagen on Skin Wrinkles and Elasticity. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Xu, W.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; He, S.; Ma, H. Improvement of Skin Condition by Oral Administration of Collagen Hydrolysates in Chronologically Aged Mice: Skin Improvement by Collagen Hydrolysates in Chronologically Aged Mice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2721–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Yang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Effects of marine collagen peptide on delaying the skin aging. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi [Chin. J. Prev. Med.] 2008, 42, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, K.J.A.; Quintanilha, A.T.; Brooks, G.A.; Packer, L. Free Radicals and Tissue Damage Produced by Exercise. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1982, 107, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailaja Rao, P.; Kalva, S.; Yerramilli, A.; Mamidi, S. Free Radicals and Tissue Damage: Role of Antioxidants. Free Radic. Antioxid. 2011, 1, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnerthaler, M.; Bischof, J.; Streubel, M.; Trost, A.; Richter, K. Oxidative Stress in Aging Human Skin. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 545–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkatesan, J.; Anil, S.; Kim, S.-K.; Shim, M. Marine Fish Proteins and Peptides for Cosmeceuticals: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.-F.; Hu, F.-Y.; Wang, B.; Ren, X.-J.; Deng, S.-G.; Wu, C.-W. Purification and Characterization of Three Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolyzate of Croceine Croaker (Pseudosciaena Crocea) Muscle. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjiargyrou, M.; Lombardo, F.; Zhao, S.; Ahrens, W.; Joo, J.; Ahn, H.; Jurman, M.; White, D.W.; Rubin, C.T. Transcriptional Profiling of Bone Regeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 30177–30182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armiento, A.R.; Hatt, L.P.; Sanchez Rosenberg, G.; Thompson, K.; Stoddart, M.J. Functional Biomaterials for Bone Regeneration: A Lesson in Complex Biology. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, R.; Jones, E.; McGonagle, D.; Giannoudis, P.V. Bone Regeneration: Current Concepts and Future Directions. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cicciù, M. Real Opportunity for the Present and a Forward Step for the Future of Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Y. Effect of Marine Collagen Peptides on Long Bone Development in Growing Rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Chen, L.; Xia, G.; Shen, X. Effects of Zinc Sulfate and Zinc Lactate on the Properties of Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus) Skin Collagen Peptide Chelate Zinc. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Yoshizawa, Y.; Kawakubo, A.; Ikeda, T.; Yanagiguchi, K.; Hayashi, Y. Early Gene and Protein Expression Associated with Osteoblast Differentiation in Response to Fish Collagen Peptides Powder. Dent. Mater. J. 2013, 32, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diogo, G.; López-Senra, E.; Pirraco, R.; Canadas, R.; Fernandes, E.; Serra, J.; Pérez-Martín, R.; Sotelo, C.; Marques, A.; González, P.; et al. Marine Collagen/Apatite Composite Scaffolds Envisaging Hard Tissue Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flaig, I.; Radenković, M.; Najman, S.; Pröhl, A.; Jung, O.; Barbeck, M. In Vivo Analysis of the Biocompatibility and Immune Response of Jellyfish Collagen Scaffolds and Its Suitability for Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmawati, R.; Hidayat, M.; Permatasari, N.; Widyarti, S. Potential Effect of Jellyfish Aurelia Aurita Collagen Scaffold Induced Alveolar Bone Regeneration in Periodontal Disease. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2021, 12, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Solomon, K.L.; Zhang, X.; Pavlos, N.J.; Abel, T.; Willers, C.; Dai, K.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, M. In Vitro Evaluation of Natural Marine Sponge Collagen as a Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, D.; Howard, D.; Yang, X.; Kelly, M.; Oreffo, R.O.C. Natural Marine Sponge Fiber Skeleton: A Biomimetic Scaffold for Human Osteoprogenitor Cell Attachment, Growth, and Differentiation. Tissue Eng. 2003, 9, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glyn-Jones, S.; Palmer, A.J.R.; Agricola, R.; Price, A.J.; Vincent, T.L.; Weinans, H.; Carr, A.J. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2015, 386, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B.; Otero, M. Inflammation in Osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raabe, O.; Reich, C.; Wenisch, S.; Hild, A.; Burg-Roderfeld, M.; Siebert, H.-C.; Arnhold, S. Hydrolyzed Fish Collagen Induced Chondrogenic Differentiation of Equine Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Cells. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 134, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, A.; Osaki, T.; Matahira, Y.; Tsuka, T.; Imagawa, T.; Okamoto, Y.; Minami, S. Evaluation of the Chondroprotective Effects of Glucosamine and Fish Collagen Peptide on a Rabbit ACLT Model Using Serum Biomarkers. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2013, 75, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, Z.; Powell, L.C.; Matin, N.; Mearns-Spragg, A.; Thornton, C.A.; Khan, I.M.; Francis, L.W. Jellyfish Collagen: A Biocompatible Collagen Source for 3D Scaffold Fabrication and Enhanced Chondrogenicity. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horch, R.E.; Stark, G.B. Comparison of The Effect of A Collagen Dressing and A Polyurethane Dressing on The Healing of Split Thickness Skin Graft (Stsg) Donor Sites. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Hand Surg. 1998, 32, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G.; Floris, R.; Serangeli, C.; Di Paola, L. Fishery Wastes as a Yet Undiscovered Treasure from the Sea: Biomolecules Sources, Extraction Methods and Valorization. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratzl, P.; Misof, K.; Zizak, I.; Rapp, G.; Amenitsch, H.; Bernstorff, S. Fibrillar Structure and Mechanical Properties of Collagen. J. Struct. Biol. 1998, 122, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauza-Włodarczyk, M.; Kubisz, L.; Mielcarek, S.; Włodarczyk, D. Comparison of Thermal Properties of Fish Collagen and Bovine Collagen in the Temperature Range 298–670 K. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 80, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geahchan, S.; Baharlouei, P.; Rahman, A. Marine Collagen: A Promising Biomaterial for Wound Healing, Skin Anti-Aging, and Bone Regeneration. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20010061
Geahchan S, Baharlouei P, Rahman A. Marine Collagen: A Promising Biomaterial for Wound Healing, Skin Anti-Aging, and Bone Regeneration. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20010061
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeahchan, Sarah, Parnian Baharlouei, and Azizur Rahman. 2022. "Marine Collagen: A Promising Biomaterial for Wound Healing, Skin Anti-Aging, and Bone Regeneration" Marine Drugs 20, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20010061
APA StyleGeahchan, S., Baharlouei, P., & Rahman, A. (2022). Marine Collagen: A Promising Biomaterial for Wound Healing, Skin Anti-Aging, and Bone Regeneration. Marine Drugs, 20(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20010061