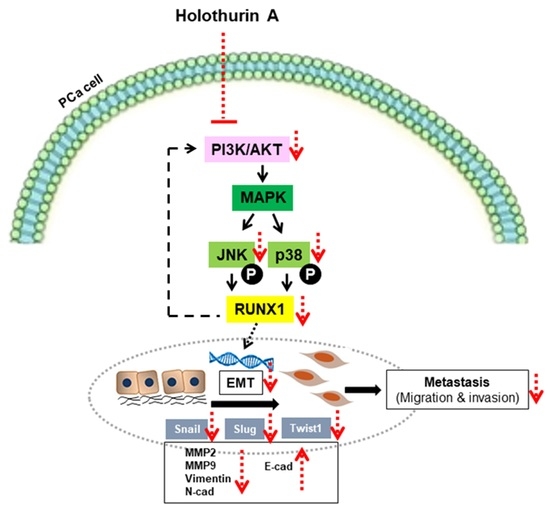
Holothurin A Inhibits RUNX1-Enhanced EMT in Metastasis Prostate Cancer via the Akt/JNK and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HA Promotes Cytotoxicity in Human PCa Cell Lines
2.2. RUNX1 Promotes EMT Process Driving for Metastasis in PCa Cell Line
2.3. HA Suppresses mRNA and Protein Expressions of EMT-Related Transcription Factors
2.4. HA Treatment Suppresses Migration and Invasion of PCa Cell Lines as Well as RUNX1 Overexpression
2.5. HA Diminishes the Gelatinolytic Activities of MMPs in Pca Cell Lines as Well as RUNX1 Overexpression
2.6. HA Inhibits EMT-Mediated Metastasis via Inhibiting Akt, JNK, and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures and Reagents
4.2. MTT Assay
4.3. Observation of Cell Morphology
4.4. Expression Plasmids and Host Selection
4.5. Plasmid Extraction
4.6. Cell Transfection
4.7. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative RT-PCR
4.8. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Gelatin Zymography
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pernar, C.H.; Ebot, E.M.; Wilson, K.M.; Mucci, L.A. The Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a030361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Body, J.J.; Casimiro, S.; Costa, L. Targeting bone metastases in prostate cancer: Improving clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2015, 12, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Initiation by cues from chronic inflammatory tumor microenvironment and termination by anti-inflammatory compounds and specialized pro-resolving lipids. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 158, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, U.G.; Lee, C.F.; Lee, M.S.; Hsieh, J.T. The Role and Mechanism of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Prostate Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, Y.S.; Liu, X.W.; Chirco, R.; Warner, R.B.; Fridman, R.; Kim, H.R. TIMP-1 induces an EMT-like phenotypic conversion in MDCK cells independent of its MMP-inhibitory domain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blyth, K.; Cameron, E.R.; Neil, J.C. The RUNX genes: Gain or loss of function in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangpairoj, K.; Vivithanaporn, P.; Apisawetakan, S.; Chongthammakun, S.; Sobhon, P.; Chaithirayanon, K. RUNX1 Regulates Migration, Invasion, and Angiogenesis via p38 MAPK Pathway in Human Glioblastoma. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keita, M.; Bachvarova, M.; Morin, C.; Plante, M.; Gregoire, J.; Renaud, M.C.; Sebastianelli, A.; Trinh, X.B.; Bachvarov, D. The RUNX1 transcription factor is expressed in serous epithelial ovarian carcinoma and contributes to cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 972–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Lai, Q.; He, C.; Fang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gu, C.; Wang, Y.; Ye, L.; et al. RUNX1 promotes tumour metastasis by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and EMT in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Yang, Z.; Yu, D.; Lin, J.; Cai, W. RUNX1 regulates TGF-β induced migration and EMT in colorectal cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ge, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, W. miR-141 inhibits prostatic cancer cell proliferation and migration, and induces cell apoptosis via targeting of RUNX1. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Messier, T.L.; Tye, C.E.; Dobson, J.R.; Fritz, A.J.; Sikora, K.R.; Browne, G.; Stein, J.L.; Lian, J.B.; Stein, G.S. Runx1 stabilizes the mammary epithelial cell phenotype and prevents epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17610–17627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fowler, M.; Borazanci, E.; McGhee, L.; Pylant, S.W.; Williams, B.J.; Glass, J.; Davis, J.N.; Meyers, S. RUNX1 (AML-1) and RUNX2 (AML-3) cooperate with prostate-derived Ets factor to activate transcription from the PSA upstream regulatory region. J. Cell Biochem. 2006, 97, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratheeshkumar, P.; Sreekala, C.; Zhang, Z.; Budhraja, A.; Ding, S.; Son, Y.O.; Wang, X.; Hitron, A.; Hyun-Jung, K.; Wang, L.; et al. Cancer prevention with promising natural products: Mechanisms of action and molecular targets. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1159–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanley, J.D.; Mezzetti, T.; Sobotka, H. The holothurinogenins. Tetrahedron 1966, 22, 1857–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, I.; Nishino, T.; Kyogoku, Y. Structure of holothurin A a biologically active triterpene-oligoglycoside from the sea cucumber holothuria leucospilota brandt. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wargasetia, T.L.; Permana, S.; Widodo. The Role of Sea Cucumber Active Compound and Its Derivative as an Anti-Cancer Agent. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 4, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wargasetia, T.L.; Widodo. Mechanisms of cancer cell killing by sea cucumber-derived compounds. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pranweerapaiboon, K.; Garon, A.; Seidel, T.; Janta, S.; Plubrukarn, A.; Chaithirayanon, K.; Langer, T. In vitro and in silico studies of holothurin A on androgen receptor in prostate cancer. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 12674–12682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.X.; Massagué, J. Genetic determinants of cancer metastasis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xu, E.; Liu, H.; Wan, L.; Lai, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer metastasis: A system review. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2015, 211, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, M. Involvement of partial EMT in cancer progression. J. Biochem. 2018, 164, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, H.; He, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Fang, L. RUNX Proteins as Epigenetic Modulators in Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Luo, M.; Cai, W.; Zhou, S.; Feng, D.; Xu, C.; Wang, H. Runt-Related Transcription Factor 1 (RUNX1) Promotes TGF-β-Induced Renal Tubular Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and Renal Fibrosis through the PI3K Subunit p110δ. EBioMedicine 2018, 31, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, W.; Yang, Z.; Lu, N. A new role for the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2015, 9, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Julien, S.; Puig, I.; Caretti, E.; Bonaventure, J.; Nelles, L.; van Roy, F.; Dargemont, C.; de Herreros, A.G.; Bellacosa, A.; Larue, L. Activation of NF-kappaB by Akt upregulates Snail expression and induces epithelium mesenchyme transition. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7445–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglin, I.; Passaniti, A. Runx protein signaling in human cancers. Cancer Treat. Res. 2004, 119, 189–215. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Song, S.J.; Hong, H.K.; Lee, Y.; Oh, B.Y.; Lee, W.Y.; Cho, Y.B. Crosstalk between CCL7 and CCR3 promotes metastasis of colon cancer cells via ERK-JNK signaling pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36842–36853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.L.; Lin, C.W.; Yang, J.S.; Hsieh, M.J.; Yang, S.F.; Lu, K.H. Zoledronate blocks geranylgeranylation not farnesylation to suppress human osteosarcoma U2OS cells metastasis by EMT via Rho A activation and FAK-inhibited JNK and p38 pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9742–9758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, T.W.; Tsai, J.P.; Lin, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Chang, H.R. Pentraxin 3 Activates JNK Signaling and Regulates the Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, D.; Gao, P.; Liu, P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Lu, Y.; Shi, T.; Zhang, X. AC3-33, a novel secretory protein, inhibits Elk1 transcriptional activity via ERK pathway. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, P.; Karin, M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1072, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeal, T.; Hibi, M.; Karin, M. Altering the specificity of signal transduction cascades: Positive regulation of c-Jun transcriptional activity by protein kinase A. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 6006–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Mulder, K.M. Requirement of Ras/MAPK pathway activation by transforming growth factor beta for transforming growth factor beta 1 production in a Smad-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 30765–30773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akech, J.; Wixted, J.J.; Bedard, K.; van der Deen, M.; Hussain, S.; Guise, T.A.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, J.L.; Languino, L.R.; Altieri, D.C.; et al. Runx2 association with progression of prostate cancer in patients: Mechanisms mediating bone osteolysis and osteoblastic metastatic lesions. Oncogene 2010, 29, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pratap, J.; Javed, A.; Languino, L.R.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, J.L.; Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B. The Runx2 osteogenic transcription factor regulates matrix metalloproteinase 9 in bone metastatic cancer cells and controls cell invasion. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 8581–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Senbanjo, L.T.; AlJohani, H.; Majumdar, S.; Chellaiah, M.A. Characterization of CD44 intracellular domain interaction with RUNX2 in PC3 human prostate cancer cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Matrix metalloproteinases and metastasis. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1999, 43, S42–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.C.Q.; Yoshimura, K.; Kumazawa, S.; Tawata, S.; Maruta, H. Frondoside A from sea cucumber and nymphaeols from Okinawa propolis: Natural anti-cancer agents that selectively inhibit PAK1 in vitro. Drug Discov. Ther. 2017, 11, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Han, H.; Chen, X.; Yi, Y.; Sun, H. Cytotoxic and apoptosis-inducing activity of triterpene glycosides from Holothuria scabra and Cucumaria frondosa against HepG2 cells. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4274–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Ye, X.; Huang, H.; Peng, R.; Su, Z.; Lian, X.Y.; Zhang, Z. Bioactive sulfated saponins from sea cucumber Holothuria moebii. Planta Med. 2015, 81, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lou, L.; Ye, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Jin, L.; He, J.; Tao, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Deng, A.; et al. Ardipusilloside inhibits survival, invasion and metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Cha, S.W.; Lee, S.G. Anti-metastatic effects of ginsenoside Rd via inactivation of MAPK signaling and induction of focal adhesion formation. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Choi, W.I.; Jeon, B.N.; Choi, K.C.; Kim, K.; Kim, T.J.; Ham, J.; Jang, H.J.; Kang, K.S.; Ko, H. Stereospecific effects of ginsenoside 20-Rg3 inhibits TGF-β1-induced.d epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses lung cancer migration, invasion and anoikis resistance. Toxicology 2014, 322, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.J. Frondoside A has an anti-invasive effect by inhibiting TPA-induced MMP-9 activation via NF-κB and AP-1 signaling in human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janta, S.; Pranweerapaiboon, K.; Vivithanaporn, P.; Plubrukarn, A.; Chairoungdua, A.; Prasertsuksri, P.; Apisawetakan, S.; Chaithirayanon, K. Holothurin A Inhibits RUNX1-Enhanced EMT in Metastasis Prostate Cancer via the Akt/JNK and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060345
Janta S, Pranweerapaiboon K, Vivithanaporn P, Plubrukarn A, Chairoungdua A, Prasertsuksri P, Apisawetakan S, Chaithirayanon K. Holothurin A Inhibits RUNX1-Enhanced EMT in Metastasis Prostate Cancer via the Akt/JNK and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(6):345. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060345
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanta, Sirorat, Kanta Pranweerapaiboon, Pornpun Vivithanaporn, Anuchit Plubrukarn, Arthit Chairoungdua, Prachayaporn Prasertsuksri, Somjai Apisawetakan, and Kulathida Chaithirayanon. 2023. "Holothurin A Inhibits RUNX1-Enhanced EMT in Metastasis Prostate Cancer via the Akt/JNK and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway" Marine Drugs 21, no. 6: 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060345
APA StyleJanta, S., Pranweerapaiboon, K., Vivithanaporn, P., Plubrukarn, A., Chairoungdua, A., Prasertsuksri, P., Apisawetakan, S., & Chaithirayanon, K. (2023). Holothurin A Inhibits RUNX1-Enhanced EMT in Metastasis Prostate Cancer via the Akt/JNK and P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs, 21(6), 345. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21060345