Identification of a Shewanella halifaxensis Strain with Algicidal Effects on Red Tide Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum triestinum in Culture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization and Identification of the 0YLH Strain
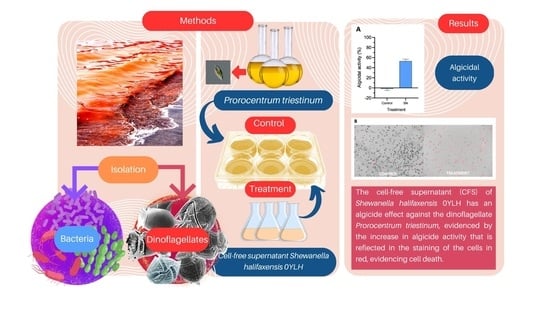
2.2. Algicidal Activity
2.3. Stability of the Bacterial Supernatant of Strain 0YLH
2.4. Specificity of the Bacterial Supernatant of Strain 0YLH against Other Microorganisms
3. Discussion
3.1. Characterization and Identification of 0YLH Strain
3.2. Algicidal Activity
3.3. Stability of the Bacterial Supernatant of Strain 0YLH
3.4. Specificity of the Bacterial Supernatant of Strain 0YLH against Other Microorganisms
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microalgal Strains and Culture Maintenance Conditions
4.2. Bacterial Strain, Experimental Culture Conditions and Characterization
4.2.1. DNA Isolation and Capillary Electrophoresis Sequencing (CES) of the 0YLH Strain
4.2.2. Phylogenetic Analyses of Bacterial Strain 0YLH
4.3. Production of 0YLH CFS for Evaluation of Algicidal Effects
4.4. Algicidal Activity
4.5. Stability of the Bacterial Supernatant
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GEOHAB. Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms. In GEOHAB Core Research Project: HABs in Upwelling Systems; Pitcher, G., Moita, T., Trainer, V., Kudela, R., Figueiras, P., Probyn, T., Eds.; IOC: Baltimore, MD, USA; SCOR: Paris, France, 2005; Volume 3, p. 82. [Google Scholar]
- Reguera, B.; Alonso, R.; Moreira, A.; Méndez, S.; Dechraoui-Bottein, M.Y. Guide for designing and implementing a plan to monitor toxin-producing microalgae—UNESCO Biblioteca Digital. In Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO and International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), 2nd ed.; UNESCO: Paris, France; Viena, Austria, 2016; pp. 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Feki, M.; Brahim, M.B.; Feki-Sahnoun, W.; Mahfoudi, M.; Sammari, C.; Hamza, A. Seasonal and spatial distributions of dinoflagellates in relation to environmental factors along the north and south coasts of Sfax (Tunisia, Eastern Mediterranean Sea). J. Coast. Life Med. 2017, 5, 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ralston, D.K.; Moore, S.K. Modeling harmful algal blooms in a changing climate. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, M.L.; Trainer, V.L.; Smayda, T.J.; Karlson, B.S.O.; Trick, C.G.; Kudela, R.M.; Ishikawa, A.; Bernard, S.; Wulff, A.; Anderson, D.M.; et al. Harmful algal blooms and climate change: Learning from the past and present to forecast the future. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 68–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNESCO. Mareas rojas en el plancton del Pacífico oriental. In Informe del Segundo Taller del Programa de Plancton del Pacífico Oriental, Instituto del Mar: Callao, Perú 19–20 de Noviembre de 1981; UNESCO: Callao, Peru, 1982; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, P.A.; Álvarez, G.; Pizarro, G.; Blanco, J.; Reguera, B. Lipophilic Toxins in Chile: History, Producers and Impacts. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.A.; Álvarez, G.; Varela, D.; Pérez-Santos, I.; Díaz, M.; Molinet, C.; Seguel, M.; Aguilera-Belmonte, A.; Guzmán, L.; Uribe, E.; et al. Impacts of harmful algal blooms on the aquaculture industry: Chile as a case study. Perspect. Phycol. 2019, 6, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávalos, V.; Cameron, H.; Barría, S.; Riquelme, C.; Espinoza, O.; Guzmán, L.; Yarimizu, K.; Okazaki, M.; Nagai, S. Dinoflagellate toxins recorded during an extensive coastal bloom in northern Chile. Harmful Algae News 2019, 62, 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, F.; Qiu, D.; Lin, S. The Synonymy of the Toxic Dinoflagellates Prorocentrum mexicanum and P. rhathymum and the Description of P. steidingerae sp. Nov. (Prorocentrales, Dinophyceae). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muciño Márquez, R.E.; Gárate Lizárraga, I.; López Cortés, D.J. Seasonal Variation of the Genus Prorocentrum (DINOPHYCEAE) in Two Tuna Farms in The Bahía De La Paz, Mexico. Acta Biol. Colomb. 2015, 20, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, N.; Churro, C.; Escalera, L.; Fraga, S.; Hoppenrath, M.; Iwataki, M.; Larsen, J.; Mertens, K.; Moestrup, Ø.; Tillmann, U.; et al. IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae. 2009. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/hab/ (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Anderson, C.R.; Berdalet, E.; Kudela, R.M.; Cusack, C.K.; Silke, J.; O’Rourke, E.; Dugan, D.; McCammon, M.; Newton, J.A.; Moore, S.K.; et al. Scaling Up from Regional Case Studies to a Global Harmful Algal Bloom Observing System. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji-Prasath, B.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.P.; Hamilton, D.P.; Lin, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y. Methods to control harmful algal blooms: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 3133–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Hong, Y.; Xie, X. Inactivation and Removal Technologies for Algal-Bloom Control: Advances and Challenges. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2021, 7, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tao, Y.; Zhan, X.M.; Dao, G.H.; Hu, H.Y. UV-C irradiation for harmful algal blooms control: A literature review on effectiveness, mechanisms, influencing factors and facilities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 137986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Pan, G. A universal method for flocculating harmful algal blooms in marine and fresh waters using modified sand. Environ Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4555–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Sun, P.; Zhang, J.; Esquivel-Elizondo, S.; Wu, Y. Microorganisms-based methods for harmful algal blooms control: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.J.; Huang, L.P.; Su, J.Q.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, T.L. Algicidal effects of a novel marine actinomycete on the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, N.; Bigalke, A.; Kaulfuß, A.; Pohnert, G. Strategies and ecological roles of algicidal bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 880–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ye, Q.; Chen, Q.; Yang, K.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Shao, X.; Fan, Y.; Yao, L.; et al. Algicidal activity of novel marine bacterium Paracoccus sp. strain Y42 against a harmful algal-bloom-causing dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum donghaiense. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 1015–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xiao, Z.; Yue, L.; Wang, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Algae response to engineered nanoparticles: Current understanding, mechanisms and implications. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1026–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ding, G.; Lin, S.; Chen, J. Isolation of an algicidal bacterium and its effects against the harmful-algal- bloom dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Takemura, T.; Pham, A.H.Q.; Tran, H.T.; Vu, K.C.T.; Tu, N.D.; Huong, T.; Cuong, N.T.; Kasuga, I.; Hasebe, I.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of Shewanella xiamenensis strains carrying blaOXA-48-like genes isolated from a water environment in Vietnam. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 1, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zheng, W.; Tian, Y.; Wang, G.; Zheng, T. Optimization of culture conditions and medium composition for the marine algicidal bacterium Alteromonas sp. DH46 by uniform design. J. Ocean Univ. China 2013, 12, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Coyne, K.J. Immobilization of algicidal bacterium Shewanella sp. IRI-160 and its application to control harmful dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2020, 1, 101798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Ma, S.; Chen, T. Algicidal Effects of a High-Efficiency Algicidal Bacterium Shewanella Y1 on the Toxic Bloom-Causing Dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, K.J.; Wang, Y.; Johnson, G. Algicidal Bacteria: A Review of Current Knowledge and Applications to Control Harmful Algal Blooms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 871177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Coyne, K.J. Metabolomic Insights of the Effects of Bacterial Algicide IRI-160AA on Dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum. Metabolites 2022, 12, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.J.; Berges, J.A.; Young, E.B. Rapid effects of diverse toxic water pollutants on chlorophyll a fluorescence: Variable responses among freshwater microalgae. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2615–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Tang, H.; Fu, L.; Tan, J.; Govindjee, G.; Guo, Y. Determination of Fv/Fm from Chlorophyll a Fluorescence without Dark Adaptation by an LSSVM Model. Plant Phenomics 2023, 5, 0034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino-Cruz, A.; Purdie, D.A.; Morris, S. Effect of increasing sea water temperature on the growth and toxin production of the benthic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. Hydrobiologia 2018, 813, 103–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Wang, H.; Abassi, S.; Ki, J.S. The herbicide alachlor severely affects photosystem function and photosynthetic gene expression in the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2020, 55, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Ishizaka, J.; Yang, M.; Ouyang, L.; Yin, Y.; Ma, Z. Changes in community structure and photosynthetic activities of total phytoplankton species during the growth, maintenance, and dissipation phases of a Prorocentrum donghaiense bloom. Harmful Algae 2019, 82, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.G.; Sane, P.V.; Hurry, V.; Öquist, G.; Huner, N.P.A. Photosystem II reaction centre quenching: Mechanisms and physiological role. Photosynth. Res. 2008, 98, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Yang, X.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, T. Comprehensive insights into the response of Alexandrium tamarense to algicidal component secreted by a marine bacterium. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Tan, J.; Pan, J.; Yang, H. A freshwater bacterial strain, Shewanella sp. Lzh-2, isolated from Lake Taihu and its two algicidal active substances, hexahydropyrrolo [1,2-a]pyrazine-1,4-dione and 2, 3-indolinedione]. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4737–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokrzywinski, K.L.; Tilney, C.L.; Modla, S.; Caplan, J.L.; Ross, J.; Warner, M.E.; Coyne, K.J. Effects of the bacterial algicide IRI-160AA on cellular morphology of harmful dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2017, 62, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, W.; Liu, L.; Xie, Y.; Ma, R.; Chen, J. A Novel Algicidal Bacterium and Its Effects against the Toxic Dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi (Dinophyceae). Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00429-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilney, C.L.; Hubbard, K.A. Expression of nuclear-encoded, haptophyte-derived ftsH genes support extremely rapid PSII repair and high-light photoacclimation in Karenia brevis (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2022, 118, 102295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.R.; Le, V.V.; Srivastava, A.; Kang, M.; Oh, H.M.; Ahn, C.Y. Algicidal activity of a novel bacterium, Qipengyuania sp. 3-20A1M, against harmful Margalefidinium polykrikoides: Effects of its active compound. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matantseva, O.; Berdieva, M.; Kalinina, V.; Pozdnyakov, I.; Pechkovskaya, S.; Skarlato, S. Stressor-induced ecdysis and thecate cyst formation in the armoured dinoflagellates Prorocentrum cordatum. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarlato, S.; Filatova, N.; Knyazev, N.; Berdieva, M.; Telesh, I. Salinity stress response of the invasive dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2018, 211, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankiewicz-Boczek, J.; Morón-López, J.; Serwecińska, L.; Font-Nájera, A.; Gałęzowska, G.; Jurczak, T.; Kokociński, M.; Wolska, L. Algicidal activity of Morganella morganii against axenic and environmental strains of Microcystis aeruginosa: Compound combination effects. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Guo, X.; Cai, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, T. Novel algicidal evidence of a bacterium Bacillus sp. LP-10 killing Phaeocystis globosa, a harmful algal bloom causing species. Biol. Control 2014, 76, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrzywinski, K.L.; Place, A.R.; Warner, M.E.; Coyne, K.J. Investigation of the algicidal exudate produced by Shewanella sp. IRI-160 and its effect on dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S.; Bai, X.; Ma, X.; Xie, Z.; Xu, H. Effect and mechanism of the algicidal bacterium Sulfitobacter porphyrae ZFX1 on the mitigation of harmful algal blooms caused by Prorocentrum donghaiense. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yu, C.; Zheng, T. Novel insights into the algicidal bacterium DH77-1 killing the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, L.; Yin, P. Algicidal metabolites produced by Bacillus sp. strain B1 against Phaeocystis globosa. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndhlovu, A.; Dhar, N.; Garg, N.; Xuma, T.; Pitcher, G.C.; Sym, S.D.; Durand, P.M. A red tide forming dinoflagellate Prorocentrum triestinum: Identification, phylogeny and impacts on St Helena Bay, South Africa. Phycologia 2017, 56, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, H.; Laza-Martínez, A.; Miguel, I.; Orive, E. Ostreopsis cf. siamensis and Ostreopsis cf. ovata from the Atlantic Iberian Peninsula: Morphological and phylogenetic characterization. Harmful Algae 2013, 30, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, C.E.; Demir, E.; Coyne, K.J.; Craig Cary, S.; Kirchman, D.L.; Hutchins, D.A. A bacterium that inhibits the growth of Pfiesteria piscicida and other dinoflagellates. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, L.; Hu, X.; Zhao, L.; Yin, P.; Li, Q. Toxic Effect of a Marine Bacterium on Aquatic Organisms and Its Algicidal Substances against Phaeocystis globosa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0114933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloh, A.H.; Abdsharad, A.; Usup, G.; Ahmad, A. Extraction and Characterization of Algicidal Compounds from Algicidal Bacteria Loktanella sp. Gb03 and its Activity Against Toxic Dinoflagellate Cooliamalayensis. Sci. Rev. Chem. Commun. 2016, 6, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Dao, G.H.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, H.S.; Xue, Y.M.; Yu, W.W.; Yong, X.L.; Hu, H.Y. The growth suppression effects of UV-C irradiation on Microcystis aeruginosa and Chlorella vulgaris under solo-culture and co-culture conditions in reclaimed water. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Cao, H.; Zheng, J.; Teng, F.; Wang, X.; Lou, K.; Zhang, X.; Tao, Y. Suppression of water-bloom cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa by algaecide hydrogen peroxide maximized through programmed cell death. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.L.; Yu, X.B.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.X. Growth inhibition and microcystin degradation effects of Acinetobacter guillouiae A2 on Microcystis aeruginosa. Res. Microbiol. 2015, 166, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manage, P.M.; Kawabata, Z.; Nakano, S. Algicidal effect of the bacterium Alcaligenes denitrificans on Microcystis spp. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2000, 22, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.C.; Zhang, C.L. Identification of a Bacillus thuringiensis Q1 compound with algicidal activity. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Lei, X.; Zhang, H.; Guan, C.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, W.; Xu, H.; Tian, Y.; Yu, Z.; et al. The first evidence of deinoxanthin from Deinococcus sp. Y35 with strong algicidal effect on the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 290, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.X. Optimized culturing conditions for an algicidal bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. SP48 on harmful algal blooms caused by Alexandrium tamarense. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Lin, H.; Balaji-Prasath, B.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, G. A novel algicidal properties of fermentation products from Pseudomonas sp. Ps3 strain on the toxic red tide dinoflagellate species. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1146325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, J.S. Continuous production of algicidal compounds against Akashiwo sanguinea via a Vibrio sp. co-culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredrickson, J.K.; Romine, M.F.; Beliaev, A.S.; Auchtung, J.M.; Driscoll, M.E.; Gardner, T.S.; Nealson, K.H.; Osterman, A.L.; Pinchuk, G.; Reed, J.L.; et al. Towards environmental systems biology of Shewanella. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, O.N.; Méjean, V.; Iobbi-Nivol, C. The Shewanella genus: Ubiquitous organisms sustaining and preserving aquatic ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachanamol, R.S.; Lipton, A.P.; Thankamani, V.; Sarika, A.R.; Selvin, J. Molecular characterization and bioactivity profile of the tropical sponge-associated bacterium Shewanella algae VCDB. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2014, 68, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.D.; Li, H.P.; Shen, L.; Zhang, J.B.; Wu, A.B.; He, W.J.; Yuan, Q.S.; He, J.D.; Liao, Y.C. The Shewanella algae strain YM8 produces volatiles with strong inhibition activity against Aspergillus pathogens and aflatoxins. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 159511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilney, C.L.; Pokrzywinski, K.L.; Coyne, K.J.; Warner, M.E. Growth, death, and photobiology of dinoflagellates (Dinophyceae) under bacterial-algicide control. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Lin, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Su, J.; et al. A marine algicidal actinomycete and its active substance against the harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9207–9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshaw, R.W.; Rosowski, J.R. Methods for microscopic algae. In Handbook of Phycological Methods: Culture Methods and Growth measurements; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973; pp. 53–68. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, R.R.L. Culture of Phytoplankton for Feeding Marine Invertebrates. In Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals, 1st Conference on Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals Greenport; Smith, W.L., Chanley, M.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz-Balladares, V.; Avalos, V.; Vera-Villalobos, H.; Cameron, H.; Gonzalez, L.; Leyton, Y.; Riquelme, C. Identification of a Shewanella halifaxensis Strain with Algicidal Effects on Red Tide Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum triestinum in Culture. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21090501
Cruz-Balladares V, Avalos V, Vera-Villalobos H, Cameron H, Gonzalez L, Leyton Y, Riquelme C. Identification of a Shewanella halifaxensis Strain with Algicidal Effects on Red Tide Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum triestinum in Culture. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(9):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21090501
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz-Balladares, Victoria, Vladimir Avalos, Hernán Vera-Villalobos, Henry Cameron, Leonel Gonzalez, Yanett Leyton, and Carlos Riquelme. 2023. "Identification of a Shewanella halifaxensis Strain with Algicidal Effects on Red Tide Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum triestinum in Culture" Marine Drugs 21, no. 9: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21090501
APA StyleCruz-Balladares, V., Avalos, V., Vera-Villalobos, H., Cameron, H., Gonzalez, L., Leyton, Y., & Riquelme, C. (2023). Identification of a Shewanella halifaxensis Strain with Algicidal Effects on Red Tide Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum triestinum in Culture. Marine Drugs, 21(9), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21090501