Twenty Four-Hour Exposure to a 0.12 THz Electromagnetic Field Does Not Affect the Genotoxicity, Morphological Changes, or Expression of Heat Shock Protein in HCE-T Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Exposure Set-Up
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. MN Formation
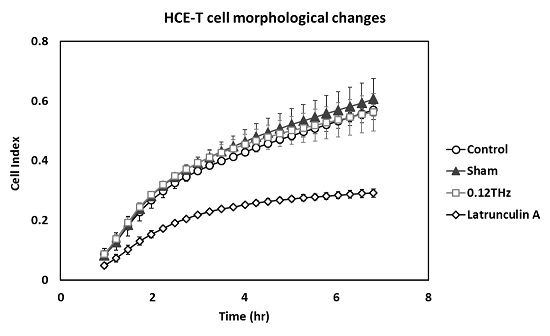
2.4. Morphological Changes
2.5. Hsp Expression
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MN Formation
3.2. Morphological Changes
3.3. Hsp Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| THz | Terahertz |
| HCE-T | Human corneal epithelial |
| MN | Micronucleus |
| Hsp | Heat shock protein |
References
- Hosako, I.; Sekine, N.; Patrashin, M.; Saito, S.; Fukunaga, K.; Kasai, Y.; Baron, P.; Seta, T.; Mendrok, J.; Ochiai, S.; et al. At the dawn of a new era in terahertz technology. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Tonouchi, M. Cutting edge terahertz technology. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumyatsky, P.; Alfani, R.R. Terahertz sources. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Fan, S.; Sun, Y.; Pickwell-Macpherson, E. The potential of terahertz imaging for cancer diagnosis: A review of investigations to date. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2012, 2, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.J.; Kang, J.; Maeng, I.; Suh, J.S.; Huh, Y.M.; Haam, S.; Son, J.H. Nanoparticle-enabled terahertz imaging for cancer diagnosis. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 3469–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, E. THz radiation from free electron lasers and its potential for cell and tissue studies. Phys. Med. Biol. 2002, 47, 3755–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmink, G.J.; Grundt, J.E. Invited review article: Current state of research on biological effects of terahertz radiation. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2011, 32, 1074–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, J.F.; Schulkin, B.; Huang, F.; Gary, D. THz imaging and sensing for security applications-explosives, weapons and drugs. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S266–S280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Zhong, H.; Karpowicz, N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.C. Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging for defense and security applications. Proc. IEEE 2007, 95, 1514–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Jornet, J.M.; Han, C. Terahertz band: Next frontier for wireless communications. Phys. Commun. 2014, 12, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kürner, T; Priebe, S. Towards THz communications—Status in research, standardization and regulation. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatsuma, T.; Horiguchi, S.; Minamikata, Y.; Yoshimizu, Y.; Hisatake, S.; Kuwano, S.; Yoshimoto, N.; Terada, J.; Takahashi, H. Terahertz wireless communications based on photonics technologies. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 23736–23747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, Q.H.; Ur Rehman, M.; Qaraqe, K.; Alomainy, A. Advances in Body-Centric Wireless Communication: Applications and State-of-the-Art; The Institution of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Korenstein-Ilan, A.; Barbul, A.; Hasin, P.; Eliran, A.; Gover, A.; Korenstein, R. Terahertz radiation increases genomic instability in human lymphocytes. Radiat. Res. 2008, 170, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hintzsche, H.; Jastrow, C.; Kleine-Ostmann, T.; Stopper, H.; Schmid, E.; Schrader, T. Terahertz radiation induces spindle disturbances in human-hamster hybrid cells. Radiat. Res. 2011, 175, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, B.S.; Rasmussen, K.Ø.; Bishop, A.R.; Usheva, A.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Chong, S.; Dagon, Y.; Booshehri, L.G.; Mielke, C.H.; Phipps, M.L.; et al. Non-thermal effects of terahertz radiation on gene expression in mouse stem cells. Biomed. Opt. Express 2011, 2, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarfì, M.R.; RomanÒ, M.; di Pietro, R.; Zeni, O.; Doria, A.; Gallerano, G.P.; Giovenale, E.; Messina, G.; Lai, A.; Campurra, G.; et al. THz exposure of whole blood for the study of biological effects on human lymphocytes. J. Biol. Phys. 2003, 29, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, N.; Clothier, R.H.; D’Arienzo, M.; Harrison, P. The effects of terahertz radiation on human keratinocyte primary cultures and neural cell cultures. Altern. Lab. Anim. 2008, 36, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hintzsche, H.; Jastrow, C.; Heinen, B.; Baaske, K.; Kleine-Ostmann, T.; Schwerdtfeger, M.; Shakfa, M.K.; Kärst, U.; Koch, M.; Schrader, T.; et al. Terahertz radiation at 0.380 THz and 2.520 THz does not lead to DNA damage in skin cells in vitro. Radiat. Res. 2013, 179, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiina, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Taki, M. High-efficiency applicator based on printed circuit board in millimeter-wave region. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 3311–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, W. Permittivity of pure water, at standard atmospheric pres-sure, over the frequency range 0–25 THz and the temperature range 0–100 °C. J. Phys. Chem. 2007, 36, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Koyama, S.; Isozumi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Taki, M.; Miyakoshi, J. Effects of 2.45-GHz electromagnetic fields with a wide range of SARs on micronucleus formation in CHO-K1 cells. Sci. World J. 2004, 4, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atienza, J.M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Abassi, Y. Dynamic monitoring of cell adhesion and spreading on microelectronic sensor arrays. J. Biomol. Screen. 2005, 10, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atienzar, F.A.; Tilmant, K.; Gerets, H.H.; Toussaint, G.; Speeckaert, S.; Hanon, E.; Depelchin, O.; Dhalluin, S. The use of real-time cell analyzer technology in drug discovery: Defining optimal cell culture conditions and assay reproducibility with different adherent cellular models. J. Biomol. Screen. 2011, 16, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffman, F.D.; Cohen, S. Impedance measurements in the biomedical sciences. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2012, 35, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, T.; Kiyokawa, T.; Kikuchi, K.; Miyakoshi, J. Intermediate frequency magnetic fields generated by an induction heating (IH) cooktop do not affect genotoxicities and expression of heat shock proteins. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2009, 85, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsonov, A.; Popov, S.V. The effect of a 94 GHz electromagnetic field on neuronal microtubules. Bioelectromagnetics 2013, 34, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmink, G.J.; Rivest, B.D.; Roth, C.C.; Ibey, B.L.; Payne, J.A.; Cundin, L.X.; Grundt, J.E.; Peralta, X.; Mixon, D.G.; Roach, W.P. In vitro investigation of the biological effects associated with human dermal fibroblasts exposed to 2.52 THz radiation. Lasers Surg. Med. 2011, 43, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homenko, A.; Kapilevich, B.; Kornstein, R.; Firer, M.A. Effects of 100 GHz radiation on alkaline phosphatase activity and antigen-antibody interaction. Bioelectromagnetics 2009, 30, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Amicis, A.; Sanctis, S.D.; Cristofaro, S.D.; Franchini, V.; Lista, F.; Regalbuto, E.; Giovenale, E.; Gallerano, G.P.; Nenzi, P.; Bei, R.; et al. Biological effects of in vitro THz radiation exposure in human foetal fibroblasts. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2015, 793, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, J.P. Why most published research findings are false. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fröhlich, H. The extraordinary dielectric properties of biological materials and the action of enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1975, 72, 4211–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koyama, S.; Narita, E.; Shimizu, Y.; Shiina, T.; Taki, M.; Shinohara, N.; Miyakoshi, J. Twenty Four-Hour Exposure to a 0.12 THz Electromagnetic Field Does Not Affect the Genotoxicity, Morphological Changes, or Expression of Heat Shock Protein in HCE-T Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080793
Koyama S, Narita E, Shimizu Y, Shiina T, Taki M, Shinohara N, Miyakoshi J. Twenty Four-Hour Exposure to a 0.12 THz Electromagnetic Field Does Not Affect the Genotoxicity, Morphological Changes, or Expression of Heat Shock Protein in HCE-T Cells. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(8):793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080793
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoyama, Shin, Eijiro Narita, Yoko Shimizu, Takeo Shiina, Masao Taki, Naoki Shinohara, and Junji Miyakoshi. 2016. "Twenty Four-Hour Exposure to a 0.12 THz Electromagnetic Field Does Not Affect the Genotoxicity, Morphological Changes, or Expression of Heat Shock Protein in HCE-T Cells" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 8: 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080793
APA StyleKoyama, S., Narita, E., Shimizu, Y., Shiina, T., Taki, M., Shinohara, N., & Miyakoshi, J. (2016). Twenty Four-Hour Exposure to a 0.12 THz Electromagnetic Field Does Not Affect the Genotoxicity, Morphological Changes, or Expression of Heat Shock Protein in HCE-T Cells. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 13(8), 793. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13080793