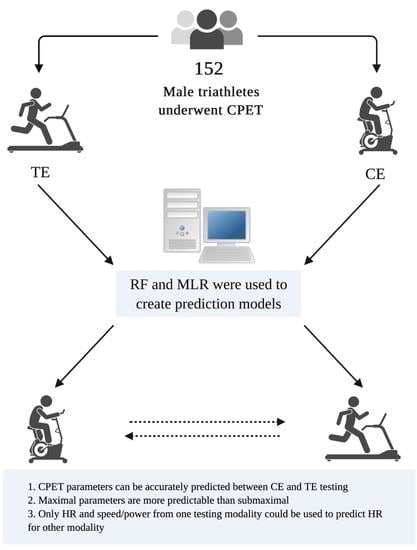
Transferability of Cardiopulmonary Parameters between Treadmill and Cycle Ergometer Testing in Male Triathletes—Prediction Formulae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. General Study Information and Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Conditions and Equipment Used during CPET
2.3. Overview of Testing Protocol
2.4. Blood Lactate Examination
2.5. Final Characteristics of Selected Participants
2.6. Ethical Approval
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mann, T.; Lamberts, R.P.; Lambert, M.I. Methods of Prescribing Relative Exercise Intensity: Physiological and Practical Considerations. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgerud, J.; Høydal, K.; Wang, E.; Karlsen, T.; Berg, P.; Bjerkaas, M.; Simonsen, T.; Helgesen, C.; Hjorth, N.; Bach, R.; et al. Aerobic high-intensity intervals improve VO2max more than moderate training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schabort, E.J.; Killian, S.C.; St Clair Gibson, A.; Hawley, J.A.; Noakes, T.D. Prediction of triathlon race time from laboratory testing in national triathletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, G.; Vleck, V.; Bentley, D. Physiological Differences between Cycling and Running. Sports Med. 2009, 39, 179–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, G.; Vleck, V.; Bentley, D. Physiological requirements in triathlon. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2011, 6, 184–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herdy, A.H.; Ritt, L.E.F.; Stein, R.; Araújo, C.G.S.D.; Milani, M.; Meneghelo, R.S.; Ferraz, A.S.; Hossri, C.; Almeida, A.E.M.D.; Fernandes-Silva, M.M.; et al. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test: Background, Applicability and Interpretation. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2016, 107, 467–481. [Google Scholar]
- Lach, J.; Wiecha, S.; Śliż, D.; Price, S.; Zaborski, M.; Cieśliński, I.; Postuła, M.; Knechtle, B.; Mamcarz, A. HR Max Prediction Based on Age, Body Composition, Fitness Level, Testing Modality and Sex in Physically Active Population. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 695950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northey, J.M.; Rattray, B.; Argus, C.K.; Etxebarria, N.; Driller, M.W. Vascular Occlusion and Sequential Compression for Recovery After Resistance Exercise. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, A.; Ishikura, K.; Nabekura, Y. Exercise Intensity during Olympic-Distance Triathlon in Well-Trained Age-Group Athletes: An Observational Study. Sports 2021, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basset, F.; Boulay, M. Treadmill and Cycle Ergometer Tests are Interchangeable to Monitor Triathletes Annual Training. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2003, 2, 110–116. [Google Scholar]
- Basset, F.; Boulay, M. Specificity of treadmill and cycle ergometer tests in triathletes, runners and cyclists. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 81, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schantz, P.; Salier Eriksson, J.; Rosdahl, H. The heart rate method for estimating oxygen uptake: Analyses of reproducibility using a range of heart rates from cycle commuting. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, D.G.; Tofte, C.; Pliego, G.J.; Raymond, R.L. Transferability of running and cycling training zones in triathletes: Implications for steady-state exercise. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Price, S.; Wiecha, S.; Cieśliński, I.; Śliż, D.; Kasiak, P.S.; Gruba, G.; Lach, J. Differences between treadmill and cycle ergometer cardiopulmonary exercise testing results in amateur triathletes and their association with body composition and body mass index. PREPRINT (Version 1) September 29th 2021. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Rincon, M.; Calbet, J.A.L. Progress Update and Challenges on VO2max Testing and Interpretation. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminsky, L.A.; Arena, R.; Myers, J. Reference standards for cardiorespiratory fitness measured with cardiopulmonary exercise testing data from the fitness registry and the importance of exercise national database. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beaver, W.L.; Wasserman, K.; Whipp, B.J.; Whipp, B.J.A. A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 60, 2020–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Bühlmann, P. Missforest-Non-parametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, H.; Guo, X.; Yu, H. Variable selection using Mean Decrease Accuracy and Mean Decrease Gini based on Random Forest. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), Beijing, China, 26–28 August 2016; pp. 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Pinto, L.N.; Venable, L.R.; Fahrenbach, J.; Churpek, M.M. Comparison of variable selection methods for clinical predictive modeling. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2018, 116, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuer, R.; Poggi, J.-M.; Tuleau-Malot, C. Variable selection using random forests. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decato, T.W.; Bradley, S.M.; Wilson, E.L.; Hegewald, M.J. Repeatability and Meaningful Change of CPET Parameters in Healthy Subjects. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaskólska, A.; Goossens, P.; Veenstra, B.; Jaskólski, A.; Skinner, J.S. Comparison of treadmill and cycle ergometer measurements of force-velocity relationships and power output. Int. J. Sports Med. 1999, 20, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, V. Measurement Error in Maximal Oxygen Uptake Tests; Report No. 04-03; Naval Health Research Center: San Diego, CA, USA, 2003; p. 29.0. [Google Scholar]
- Balady, G.J.; Arena, R.; Sietsema, K.; Myers, J.; Coke, L.; Fletcher, G.F.; Forman, D.; Franklin, B.; Guazzi, M.; Gulati, M.; et al. Clinician’s Guide to cardiopulmonary exercise testing in adults: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 122, 191–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muscat, K.M.; Kotrach, H.G.; Wilkinson-Maitland, C.A.; Schaeffer, M.R.; Mendonca, C.T.; Jensen, D. Physiological and perceptual responses to incremental exercise testing in healthy men: Effect of exercise test modality. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 40, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velicka, D.; Kairiukstiene, Z.; Poderiene, K.; Vainoras, A.; Poderys, J. Interaction between cardiac functional indices during incremental exercise test reveals the peculiarities of adaptation to exercising. Medicina 2019, 55, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, S.; Lemes, B.; Carvalho, P.D.T.C.D.; De Lima, R.N.; Bocalini, D.S.; Junior, J.A.S.; Arsa, G.; Casarin, C.A.; Andrade, E.L.; Serra, A.J. Does Stroke Volume Increase during an Incremental Exercise? A Systematic Review. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2016, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stratton, J.R.; Levy, W.C.; Cerqueira, M.D.; Schwartz, R.S.; Abrass, I.B. Cardiovascular responses to exercise: Effects of aging and exercise training in healthy men. Circulation 1994, 89, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boussana, A.; Matecki, S.; Galy, O.; Hue, O.; Ramonatxo, M.; Le Gallais, D. The effect of exercise modality on respiratory muscle performance in triathletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 2036–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsignore, M.R.; Morici, G.; Abate, P.; Romano, S.; Bonsignore, G. Ventilation and entrainment of breathing during cycling and running in triathletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1998, 30, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, V.; Lira, C.; Vancini, R.; Rayes, A.; Andrade, M. Fat mass is negatively associated with the physiological ability of tissue to consume oxygen. Mot. Rev. Educ. Física 2018, 24, e101808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goran, M.; Fields, D.; Hunter, G.; Herd, S.; Weinsier, R. Total body fat does not influence maximal aerobic capacity. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2000, 24, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sutherland, T.J.T.; McLachlan, C.R.; Sears, M.R.; Poulton, R.; Hancox, R.J. The relationship between body fat and respiratory function in young adults. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Participants Characteristics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Mean | CI | SD | |
| −95% | 95% | |||
| CPET interval (days) | 7.28 | 5.40 | 9.16 | 11.74 |
| Age (years) | 38.20 | 36.68 | 39.73 | 9.53 |
| Height (cm) | 180.64 | 179.55 | 181.72 | 6.77 |
| Weight (kg) | 78.31 | 76.88 | 79.74 | 8.92 |
| BMI (kg·m−2) | 23.97 | 23.64 | 24.31 | 2.10 |
| BF (%) | 15.41 | 14.76 | 16.05 | 4.03 |
| FM (kg) | 12.28 | 11.61 | 12.96 | 4.19 |
| Category | Multiple Regression Equation | MAE | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| VO2AT | 20.83[13.56]SE + 0.56[0.12]SEx RVO2AT − 0.11[0.05]SEx RVEAT − 0.11[0.05]SEx RHRAT + 12.06[9.00]SEx RRERATr + 0.04[0.03]SEx RfRRCP − 23.13[12.59]SEx RRERRCP − 0.36[0.17]SEx RLacmax + 0.30[0.09]SEx RVO2max + 0.05[0.05]SEx RHRmax + 0.05[0.03]SEx RVERCP − 0.13[0.08]SEx BF | 2.17 | 0.71 |
| HRAT | 54.84[30.34]SE + 0.41[0.12]SEx RHRAT − 49.99[27.99]SEx RRERRCP + 0.41[0.12]SEx RHRmax − 0.30[0.19]SEx BF | 6.25 | 0.46 |
| VO2RCP | −2.39[5.83]SE + 0.62[0.17]SEx RVO2AT − 0.01[0.001]SEx RVO2ATA − 0.53[0.17]SEx RLacmax+ 0.32[0.12]SEx RVO2max + 0.34[0.18]SEx RVO2RCP + 0.03[0.03]SEx RVERCP + 0.52[0.24]SEx BMI − 0.32[0.11]SEx BF | 2.44 | 0.78 |
| HRRCP | 53.27[21.96]SE + 0.17[0.11]SEx RHRAT + 0.33[0.20]SEx RHRRCP − 38.36[19.97]SEx RRERRCP + 0.40[0.16]SEx RHRmax − 0.42[0.13]SEx BF | 4.47 | 0.68 |
| VO2max | 11.75[4.59]SE − 0.05[0.03]SEx RVEAT + 0.07[0.03]SEx RfRRCP − 0.35[0.18]SEx RLacmax + 0.44[0.12]SEx RVO2max + 0.50[0.14]SEx RVO2RCP − 0.33[0.09]SEx BF | 2.55 | 0.78 |
| HRmax | 16.51[11.24]SE + 0.26[0.13]SEx RHRRCP + 0.57[0.27]SEx RLacmax + 0.60[0.12]SEx RHRmax + 0.33[0.31]SEx BMI − 0.45[0.15]SEx BF | 3.31 | 0.78 |
| Category | Multiple Regression Equation | MAE | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| VO2AT | −3.59[11.10]SE − 0.09[0.05]SEx CVEAT + 0.10[0.06]SEx CfRAT + 0.002[0.002]SEx CVO2ATA − 0.21[0.16]SEx CLacmax + 0.06[0.03]SEx CHRmax + 0.43[0.05]SEx CVO2RCP + 12.46[7.90]SEx CRERmax − 0.04[0.03]SEx Age | 2.05 | 0.59 |
| HRAT | 59.44[16.41]SE − 1.21[0.40]SEx CVO2AT − 0.24[0.09]SEx CVEAT + 0.17[0.13]SEx CHRAT + 0.01[0.04]SEx CVO2ATA + 0.27[0.22]SEx CHRRCP + 0.05[0.03]SEx CPAT − 0.44[0.28]SEx CVO2max + 0.34[0.17]SEx CHRmax + 0.81[0.39]SEx CVO2RCP − 1.36[0.48]SEx BMI + 0.56[0.23]SEx BF | 4.66 | 0.63 |
| VO2RCP | 13.88[2.60]SE + 0.43[0.14]SEx CVO2AT − 0.22[0.07]SEx CVEAT + 0.28[0.11]SEx CfRAT + 0.03[0.02]SEx CVEmax + 0.04[0.01]SEx CPAT − 0.15[0.09]SEx CfRRCP + 0.30[0.10]SEx CVO2max + 0.06[0.04]SEx CVERCP | 2.18 | 0.73 |
| HRRCP | 12.83[2.11]SE + 0.60[0.04]SEx CVO2max + 0.03[0.01]SEx CPAT | 2.28 | 0.71 |
| VO2max | 101.31[26.95]SE − 1.12[0.32]SEx CVO2AT − 0.16[0.09]SEx CHRAT − 0.07[0.02]SEx CVEma + 0.01[0.002]SEx CVO2ATA + 9.70[7.73]SEx CRERAT + 0.30[0.16]SEx CHRRCP − 40.07[25.14]SEx CRERRCP − 0.39[0.20]SEx CVO2max + 0.63[0.13]SEx CHRmax + 0.84[0.28]SEx CVO2RCP − 0.13[0.05]SEx Age − 1.11[0.34]SEx BMI + 0.32[0.17]SEx BF | 3.25 | 0.78 |
| HRmax | 28.49[5.23]SE + 0.39[0.15]SEx CVO2AT − 0.06[0.03]SEx CHRAT − 0.21[0.08]SEx CfRAT − 0.003[0.001]x CVO2ATA − 0.03[0.01]x CPAT − 0.14[0.06]x CfRRCP + 0.49[0.09]SEx CVO2max − 0.07[0.03]SEx Age | 2.38 | 0.74 |
| 112.46[29.03]SE − 0.58[0.26]SEx CVO2AT + 0.07[0.06]SEx CVEAT − 0.06[0.02]SEx CVEmax + 8.49[7.51]SEx CRERAT − 57.77[27.32]SEx CRERRCP + 0.51[0.26]SEx CLacmax + 0.82[0.05]SEx CHRmax + 0.26[0.21]SEx CVO2RCP − 0.14[0.05]SEx Age − 0.77[0.32]SEx BMI + 0.35[0.16]SEx BF | 3.27 | 0.80 |
| Category | Multiple Regression Equation | MAE | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HRAT | 20.64[13.77]SE + 0.71[0.08]SEx RHRAT + 0.83[0.59]SEx RSAT | 6.66 | 0.41 |
| HRRCP | 5.89[11.24]SE + 0.88[0.06]SEx RHRRCP + 0.52[0.41]SEx RSAT | 4.63 | 0.65 |
| HRmax | 16.41[9.27]SE + 0.86[0.05]SEx RHRmax + 0.31[0.33]SEx RSAT | 3.66 | 0.75 |
| Category | Multiple Regression Equation | MAE | Adjusted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HRAT | 73.98[9.05]SE + 0.60[0.07]SEx CHRAT − 0.04[0.02]SEx CPAT | 5.89 | 0.41 |
| HRRCP | 54.69[8.33]SE + 0.76[0.05]SEx CHRRCP − 0.03[0.02]SEx CPAT | 4.28 | 0.66 |
| HRmax | 30.84[8.58]SE + 0.88[0.05]SEx CHRmax − 0.02[0.01]SEx CPAT | 3.71 | 0.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiecha, S.; Price, S.; Cieśliński, I.; Kasiak, P.S.; Tota, Ł.; Ambroży, T.; Śliż, D. Transferability of Cardiopulmonary Parameters between Treadmill and Cycle Ergometer Testing in Male Triathletes—Prediction Formulae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031830
Wiecha S, Price S, Cieśliński I, Kasiak PS, Tota Ł, Ambroży T, Śliż D. Transferability of Cardiopulmonary Parameters between Treadmill and Cycle Ergometer Testing in Male Triathletes—Prediction Formulae. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031830
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiecha, Szczepan, Szymon Price, Igor Cieśliński, Przemysław Seweryn Kasiak, Łukasz Tota, Tadeusz Ambroży, and Daniel Śliż. 2022. "Transferability of Cardiopulmonary Parameters between Treadmill and Cycle Ergometer Testing in Male Triathletes—Prediction Formulae" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031830
APA StyleWiecha, S., Price, S., Cieśliński, I., Kasiak, P. S., Tota, Ł., Ambroży, T., & Śliż, D. (2022). Transferability of Cardiopulmonary Parameters between Treadmill and Cycle Ergometer Testing in Male Triathletes—Prediction Formulae. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031830